Krebs on Security
Krebs on Security
The cybercriminals in control of Kimwolf — a disruptive botnet that has infected more than 2 million devices — recently shared a screenshot indicating they’d compromised the control panel for Badbox 2.0, a vast China-based botnet powered by malicious software that comes pre-installed on many Android TV streaming boxes. Both the FBI and Google say they are hunting for the people behind Badbox 2.0, and thanks to bragging by the Kimwolf botmasters we may now have a much clearer idea about that.
Our first story of 2026, The Kimwolf Botnet is Stalking Your Local Network, detailed the unique and highly invasive methods Kimwolf uses to spread. The story warned that the vast majority of Kimwolf infected systems were unofficial Android TV boxes that are typically marketed as a way to watch unlimited (pirated) movie and TV streaming services for a one-time fee.
Our January 8 story, Who Benefitted from the Aisuru and Kimwolf Botnets?, cited multiple sources saying the current administrators of Kimwolf went by the nicknames “Dort” and “Snow.” Earlier this month, a close former associate of Dort and Snow shared what they said was a screenshot the Kimwolf botmasters had taken while logged in to the Badbox 2.0 botnet control panel.
That screenshot, a portion of which is shown below, shows seven authorized users of the control panel, including one that doesn’t quite match the others: According to my source, the account “ABCD” (the one that is logged in and listed in the top right of the screenshot) belongs to Dort, who somehow figured out how to add their email address as a valid user of the Badbox 2.0 botnet.
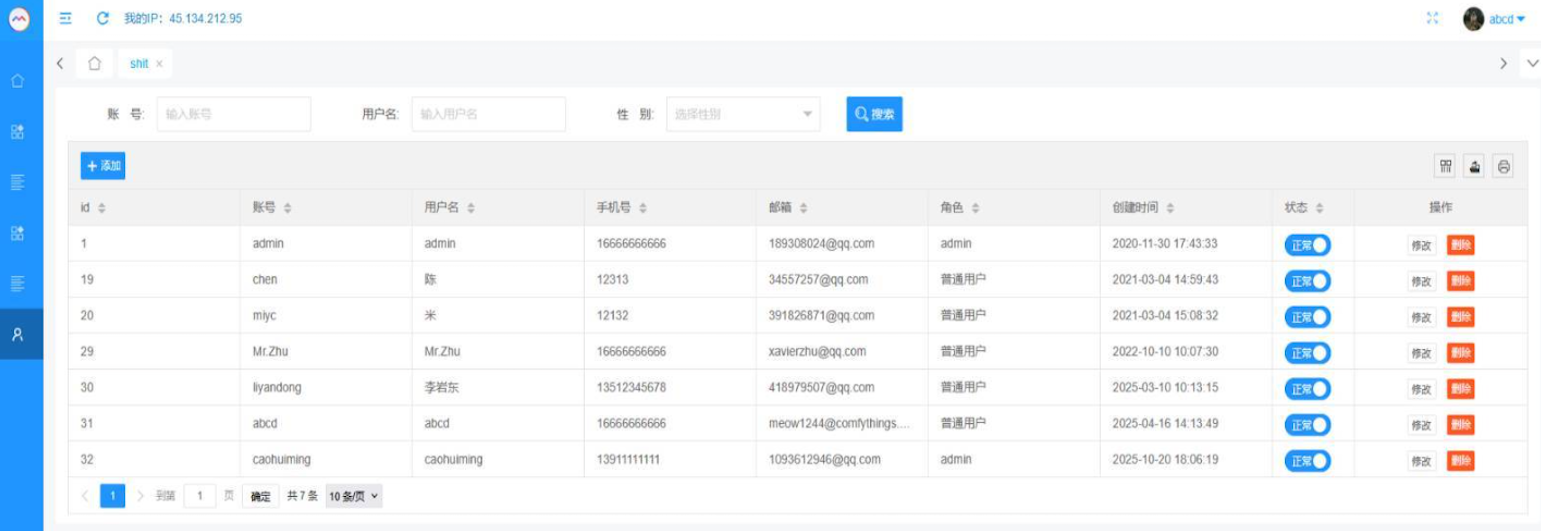
The control panel for the Badbox 2.0 botnet lists seven authorized users and their email addresses. Click to enlarge.
Badbox has a storied history that well predates Kimwolf’s rise in October 2025. In July 2025, Google filed a “John Doe” lawsuit (PDF) against 25 unidentified defendants accused of operating Badbox 2.0, which Google described as a botnet of over ten million unsanctioned Android streaming devices engaged in advertising fraud. Google said Badbox 2.0, in addition to compromising multiple types of devices prior to purchase, also can infect devices by requiring the download of malicious apps from unofficial marketplaces.
Google’s lawsuit came on the heels of a June 2025 advisory from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which warned that cyber criminals were gaining unauthorized access to home networks by either configuring the products with malware prior to the user’s purchase, or infecting the device as it downloads required applications that contain backdoors — usually during the set-up process.
The FBI said Badbox 2.0 was discovered after the original Badbox campaign was disrupted in 2024. The original Badbox was identified in 2023, and primarily consisted of Android operating system devices (TV boxes) that were compromised with backdoor malware prior to purchase.
KrebsOnSecurity was initially skeptical of the claim that the Kimwolf botmasters had hacked the Badbox 2.0 botnet. That is, until we began digging into the history of the qq.com email addresses in the screenshot above.
CATHEAD
An online search for the address 34557257@qq.com (pictured in the screenshot above as the user “Chen“) shows it is listed as a point of contact for a number of China-based technology companies, including:
–Beijing Hong Dake Wang Science & Technology Co Ltd.
–Beijing Hengchuang Vision Mobile Media Technology Co. Ltd.
–Moxin Beijing Science and Technology Co. Ltd.
The website for Beijing Hong Dake Wang Science is asmeisvip[.]net, a domain that was flagged in a March 2025 report by HUMAN Security as one of several dozen sites tied to the distribution and management of the Badbox 2.0 botnet. Ditto for moyix[.]com, a domain associated with Beijing Hengchuang Vision Mobile.
A search at the breach tracking service Constella Intelligence finds 34557257@qq.com at one point used the password “cdh76111.” Pivoting on that password in Constella shows it is known to have been used by just two other email accounts: daihaic@gmail.com and cathead@gmail.com.
Constella found cathead@gmail.com registered an account at jd.com (China’s largest online retailer) in 2021 under the name “陈代海,” which translates to “Chen Daihai.” According to DomainTools.com, the name Chen Daihai is present in the original registration records (2008) for moyix[.]com, along with the email address cathead@astrolink[.]cn.
Incidentally, astrolink[.]cn also is among the Badbox 2.0 domains identified in HUMAN Security’s 2025 report. DomainTools finds cathead@astrolink[.]cn was used to register more than a dozen domains, including vmud[.]net, yet another Badbox 2.0 domain tagged by HUMAN Security.
XAVIER
A cached copy of astrolink[.]cn preserved at archive.org shows the website belongs to a mobile app development company whose full name is Beijing Astrolink Wireless Digital Technology Co. Ltd. The archived website reveals a “Contact Us” page that lists a Chen Daihai as part of the company’s technology department. The other person featured on that contact page is Zhu Zhiyu, and their email address is listed as xavier@astrolink[.]cn.
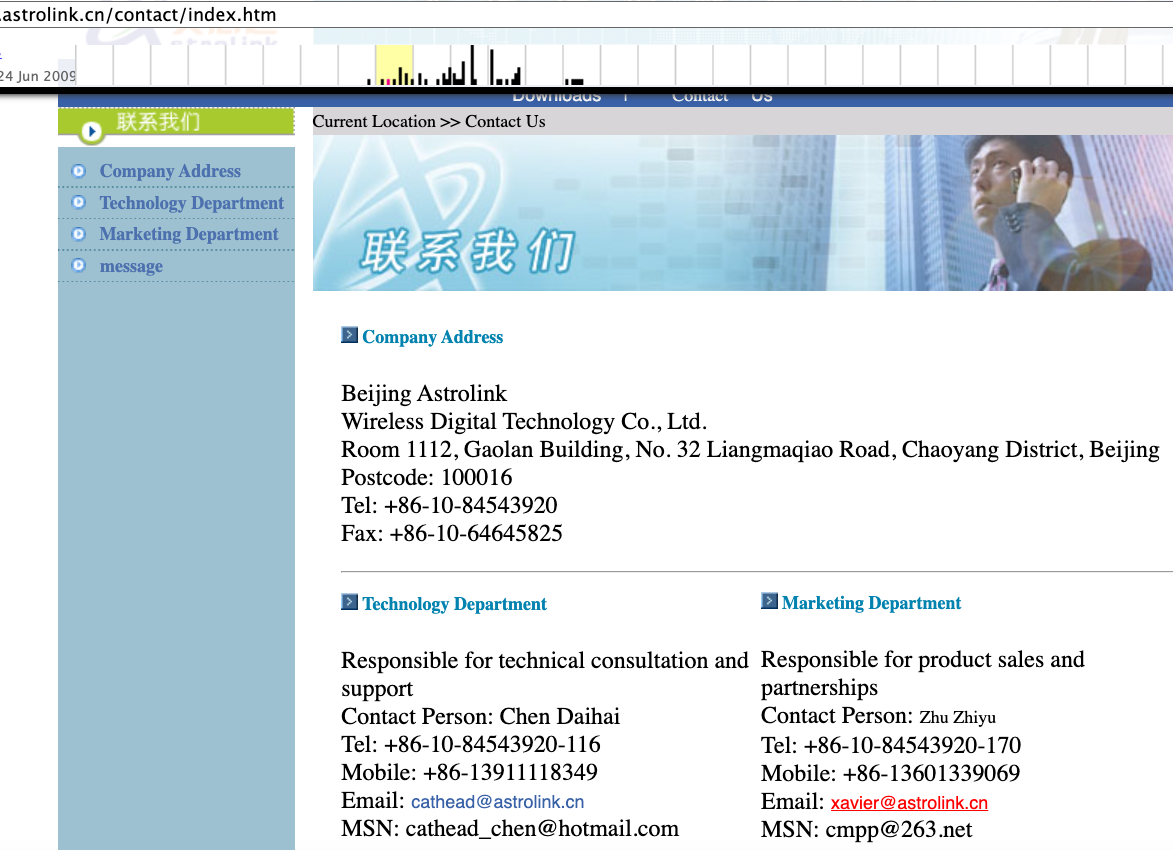
A Google-translated version of Astrolink’s website, circa 2009. Image: archive.org.
Astute readers will notice that the user Mr.Zhu in the Badbox 2.0 panel used the email address xavierzhu@qq.com. Searching this address in Constella reveals a jd.com account registered in the name of Zhu Zhiyu. A rather unique password used by this account matches the password used by the address xavierzhu@gmail.com, which DomainTools finds was the original registrant of astrolink[.]cn.
ADMIN
The very first account listed in the Badbox 2.0 panel — “admin,” registered in November 2020 — used the email address 189308024@qq.com. DomainTools shows this email is found in the 2022 registration records for the domain guilincloud[.]cn, which includes the registrant name “Huang Guilin.”
Constella finds 189308024@qq.com is associated with the China phone number 18681627767. The open-source intelligence platform osint.industries reveals this phone number is connected to a Microsoft profile created in 2014 under the name Guilin Huang (桂林 黄). The cyber intelligence platform Spycloud says that phone number was used in 2017 to create an account at the Chinese social media platform Weibo under the username “h_guilin.”
The public information attached to Guilin Huang’s Microsoft account, according to the breach tracking service osintindustries.com.
The remaining three users and corresponding qq.com email addresses were all connected to individuals in China. However, none of them (nor Mr. Huang) had any apparent connection to the entities created and operated by Chen Daihai and Zhu Zhiyu — or to any corporate entities for that matter. Also, none of these individuals responded to requests for comment.
The mind map below includes search pivots on the email addresses, company names and phone numbers that suggest a connection between Chen Daihai, Zhu Zhiyu, and Badbox 2.0.
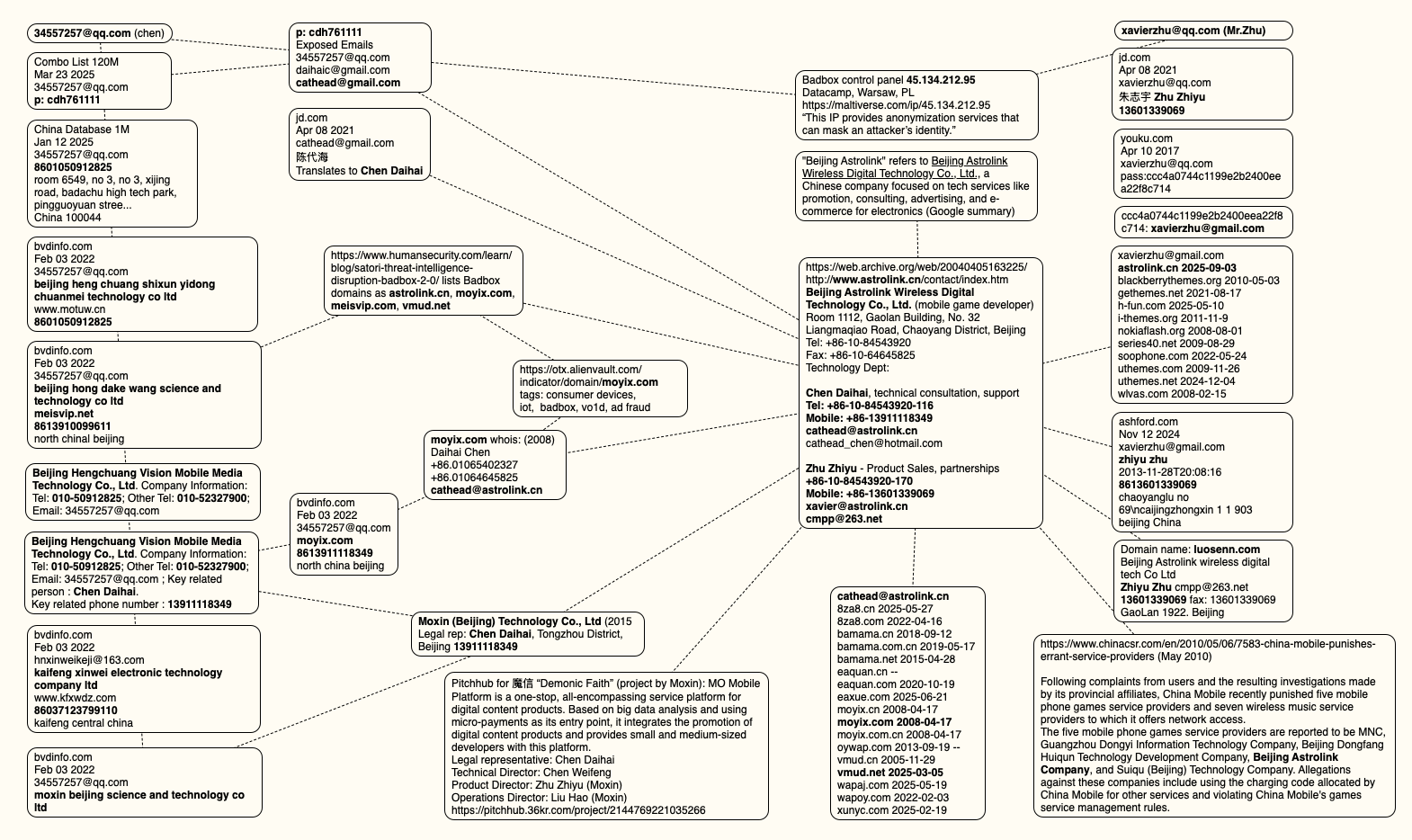
This mind map includes search pivots on the email addresses, company names and phone numbers that appear to connect Chen Daihai and Zhu Zhiyu to Badbox 2.0. Click to enlarge.
UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS
The idea that the Kimwolf botmasters could have direct access to the Badbox 2.0 botnet is a big deal, but explaining exactly why that is requires some background on how Kimwolf spreads to new devices. The botmasters figured out they could trick residential proxy services into relaying malicious commands to vulnerable devices behind the firewall on the unsuspecting user’s local network.
The vulnerable systems sought out by Kimwolf are primarily Internet of Things (IoT) devices like unsanctioned Android TV boxes and digital photo frames that have no discernible security or authentication built-in. Put simply, if you can communicate with these devices, you can compromise them with a single command.
Our January 2 story featured research from the proxy-tracking firm Synthient, which alerted 11 different residential proxy providers that their proxy endpoints were vulnerable to being abused for this kind of local network probing and exploitation.
Most of those vulnerable proxy providers have since taken steps to prevent customers from going upstream into the local networks of residential proxy endpoints, and it appeared that Kimwolf would no longer be able to quickly spread to millions of devices simply by exploiting some residential proxy provider.
However, the source of that Badbox 2.0 screenshot said the Kimwolf botmasters had an ace up their sleeve the whole time: Secret access to the Badbox 2.0 botnet control panel.
“Dort has gotten unauthorized access,” the source said. “So, what happened is normal proxy providers patched this. But Badbox doesn’t sell proxies by itself, so it’s not patched. And as long as Dort has access to Badbox, they would be able to load” the Kimwolf malware directly onto TV boxes associated with Badbox 2.0.
The source said it isn’t clear how Dort gained access to the Badbox botnet panel. But it’s unlikely that Dort’s existing account will persist for much longer: All of our notifications to the qq.com email addresses listed in the control panel screenshot received a copy of that image, as well as questions about the apparently rogue ABCD account.




 Figure 1. Types of scams reported in our consumer survey.
Figure 1. Types of scams reported in our consumer survey.