China-based phishing groups blamed for non-stop scam SMS messages about a supposed wayward package or unpaid toll fee are promoting a new offering, just in time for the holiday shopping season: Phishing kits for mass-creating fake but convincing e-commerce websites that convert customer payment card data into mobile wallets from Apple and Google. Experts say these same phishing groups also are now using SMS lures that promise unclaimed tax refunds and mobile rewards points.
Over the past week, thousands of domain names were registered for scam websites that purport to offer T-Mobile customers the opportunity to claim a large number of rewards points. The phishing domains are being promoted by scam messages sent via Apple’s iMessage service or the functionally equivalent RCS messaging service built into Google phones.
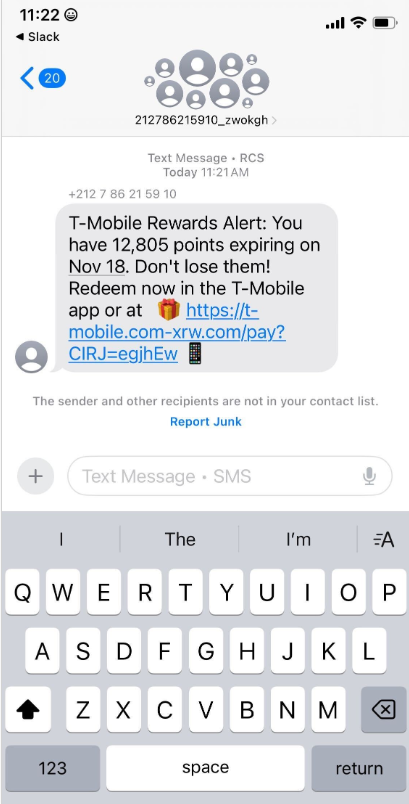
An instant message spoofing T-Mobile says the recipient is eligible to claim thousands of rewards points.
The website scanning service urlscan.io shows thousands of these phishing domains have been deployed in just the past few days alone. The phishing websites will only load if the recipient visits with a mobile device, and they ask for the visitor’s name, address, phone number and payment card data to claim the points.
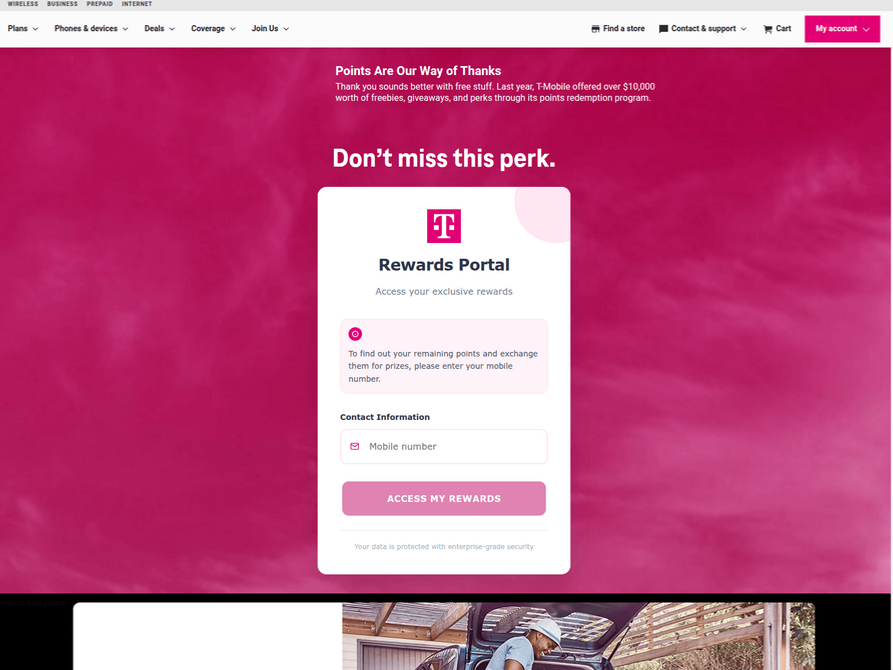
A phishing website registered this week that spoofs T-Mobile.
If card data is submitted, the site will then prompt the user to share a one-time code sent via SMS by their financial institution. In reality, the bank is sending the code because the fraudsters have just attempted to enroll the victim’s phished card details in a mobile wallet from Apple or Google. If the victim also provides that one-time code, the phishers can then link the victim’s card to a mobile device that they physically control.
Pivoting off these T-Mobile phishing domains in urlscan.io reveals a similar scam targeting AT&T customers:
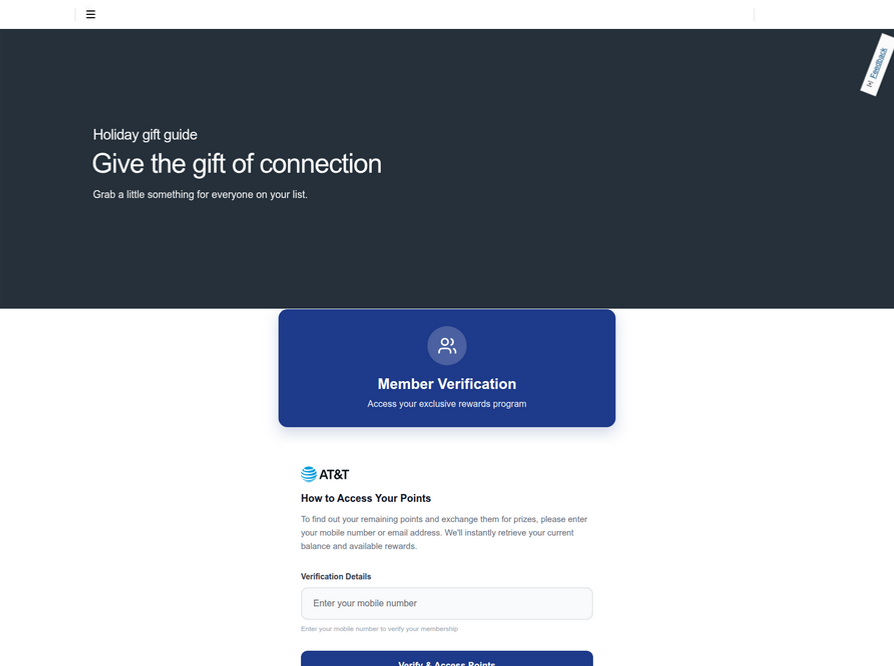
An SMS phishing or “smishing” website targeting AT&T users.
Ford Merrill works in security research at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group company. Merrill said multiple China-based cybercriminal groups that sell phishing-as-a-service platforms have been using the mobile points lure for some time, but the scam has only recently been pointed at consumers in the United States.
“These points redemption schemes have not been very popular in the U.S., but have been in other geographies like EU and Asia for a while now,” Merrill said.
A review of other domains flagged by urlscan.io as tied to this Chinese SMS phishing syndicate shows they are also spoofing U.S. state tax authorities, telling recipients they have an unclaimed tax refund. Again, the goal is to phish the user’s payment card information and one-time code.
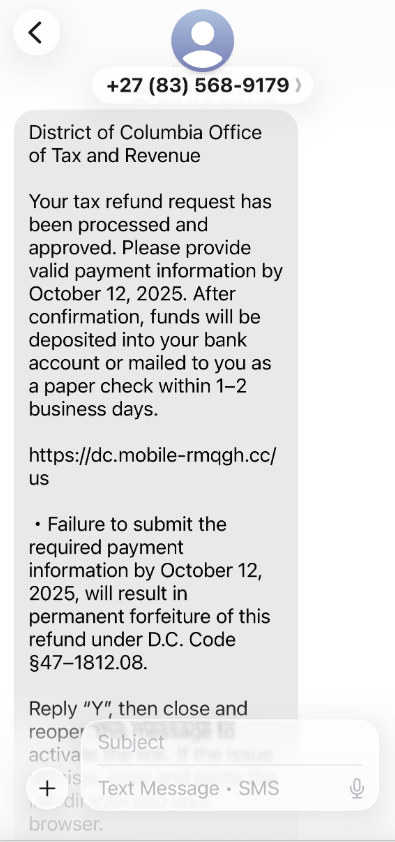
A text message that spoofs the District of Columbia’s Office of Tax and Revenue.
Many SMS phishing or “smishing” domains are quickly flagged by browser makers as malicious. But Merrill said one burgeoning area of growth for these phishing kits — fake e-commerce shops — can be far harder to spot because they do not call attention to themselves by spamming the entire world.
Merrill said the same Chinese phishing kits used to blast out package redelivery message scams are equipped with modules that make it simple to quickly deploy a fleet of fake but convincing e-commerce storefronts. Those phony stores are typically advertised on Google and Facebook, and consumers usually end up at them by searching online for deals on specific products.
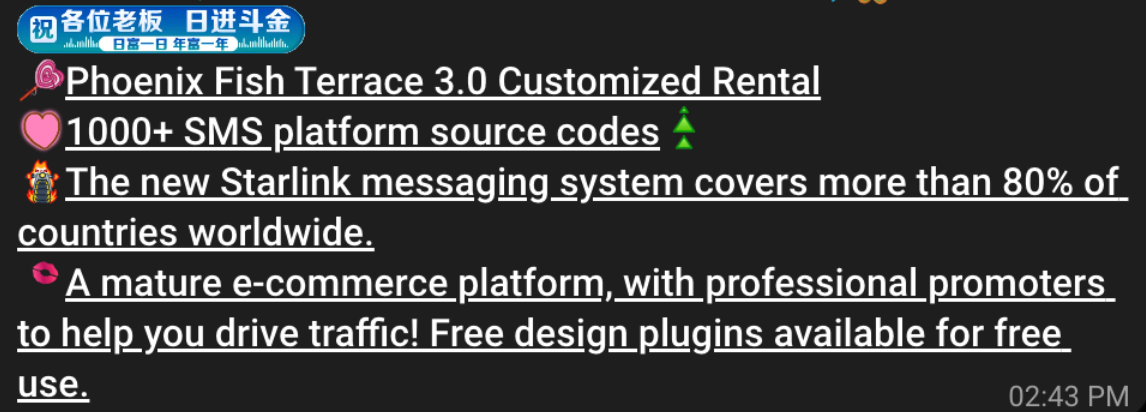
A machine-translated screenshot of an ad from a China-based phishing group promoting their fake e-commerce shop templates.
With these fake e-commerce stores, the customer is supplying their payment card and personal information as part of the normal check-out process, which is then punctuated by a request for a one-time code sent by your financial institution. The fake shopping site claims the code is required by the user’s bank to verify the transaction, but it is sent to the user because the scammers immediately attempt to enroll the supplied card data in a mobile wallet.
According to Merrill, it is only during the check-out process that these fake shops will fetch the malicious code that gives them away as fraudulent, which tends to make it difficult to locate these stores simply by mass-scanning the web. Also, most customers who pay for products through these sites don’t realize they’ve been snookered until weeks later when the purchased item fails to arrive.
“The fake e-commerce sites are tough because a lot of them can fly under the radar,” Merrill said. “They can go months without being shut down, they’re hard to discover, and they generally don’t get flagged by safe browsing tools.”
Happily, reporting these SMS phishing lures and websites is one of the fastest ways to get them properly identified and shut down. Raymond Dijkxhoorn is the CEO and a founding member of SURBL, a widely-used blocklist that flags domains and IP addresses known to be used in unsolicited messages, phishing and malware distribution. SURBL has created a website called smishreport.com that asks users to forward a screenshot of any smishing message(s) received.
“If [a domain is] unlisted, we can find and add the new pattern and kill the rest” of the matching domains, Dijkxhoorn said. “Just make a screenshot and upload. The tool does the rest.”
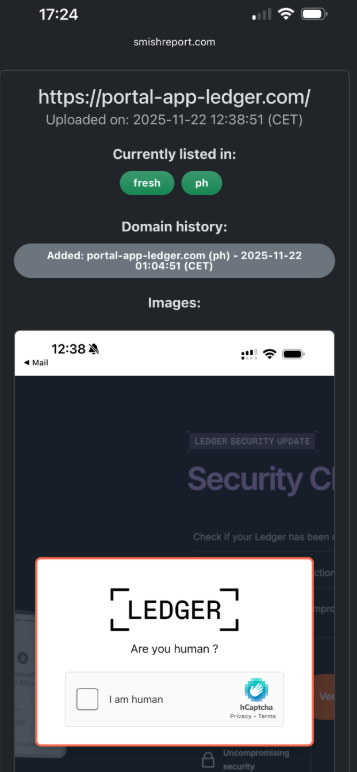
The SMS phishing reporting site smishreport.com.
Merrill said the last few weeks of the calendar year typically see a big uptick in smishing — particularly package redelivery schemes that spoof the U.S. Postal Service or commercial shipping companies.
“Every holiday season there is an explosion in smishing activity,” he said. “Everyone is in a bigger hurry, frantically shopping online, paying less attention than they should, and they’re just in a better mindset to get phished.”
As we can see, adopting a shopping strategy of simply buying from the online merchant with the lowest advertised prices can be a bit like playing Russian Roulette with your wallet. Even people who shop mainly at big-name online stores can get scammed if they’re not wary of too-good-to-be-true offers (think third-party sellers on these platforms).
If you don’t know much about the online merchant that has the item you wish to buy, take a few minutes to investigate its reputation. If you’re buying from an online store that is brand new, the risk that you will get scammed increases significantly. How do you know the lifespan of a site selling that must-have gadget at the lowest price? One easy way to get a quick idea is to run a basic WHOIS search on the site’s domain name. The more recent the site’s “created” date, the more likely it is a phantom store.
If you receive a message warning about a problem with an order or shipment, visit the e-commerce or shipping site directly, and avoid clicking on links or attachments — particularly missives that warn of some dire consequences unless you act quickly. Phishers and malware purveyors typically seize upon some kind of emergency to create a false alarm that often causes recipients to temporarily let their guard down.
But it’s not just outright scammers who can trip up your holiday shopping: Often times, items that are advertised at steeper discounts than other online stores make up for it by charging way more than normal for shipping and handling.
So be careful what you agree to: Check to make sure you know how long the item will take to be shipped, and that you understand the store’s return policies. Also, keep an eye out for hidden surcharges, and be wary of blithely clicking “ok” during the checkout process.
Most importantly, keep a close eye on your monthly statements. If I were a fraudster, I’d most definitely wait until the holidays to cram through a bunch of unauthorized charges on stolen cards, so that the bogus purchases would get buried amid a flurry of other legitimate transactions. That’s why it’s key to closely review your credit card bill and to quickly dispute any charges you didn’t authorize.
For nearly a dozen years, residents of South Carolina have been kept in the dark by state and federal investigators over who was responsible for hacking into the state’s revenue department in 2012 and stealing tax and bank account information for 3.6 million people. The answer may no longer be a mystery: KrebsOnSecurity found compelling clues suggesting the intrusion was carried out by the same Russian hacking crew that stole of millions of payment card records from big box retailers like Home Depot and Target in the years that followed.
Questions about who stole tax and financial data on roughly three quarters of all South Carolina residents came to the fore last week at the confirmation hearing of Mark Keel, who was appointed in 2011 by Gov. Nikki Haley to head the state’s law enforcement division. If approved, this would be Keel’s third six-year term in that role.
The Associated Press reports that Keel was careful not to release many details about the breach at his hearing, telling lawmakers he knows who did it but that he wasn’t ready to name anyone.
“I think the fact that we didn’t come up with a whole lot of people’s information that got breached is a testament to the work that people have done on this case,” Keel asserted.
A ten-year retrospective published in 2022 by The Post and Courier in Columbia, S.C. said investigators determined the breach began on Aug. 13, 2012, after a state IT contractor clicked a malicious link in an email. State officials said they found out about the hack from federal law enforcement on October 10, 2012.
KrebsOnSecurity examined posts across dozens of cybercrime forums around that time, and found only one instance of someone selling large volumes of tax data in the year surrounding the breach date.
On Oct. 7, 2012 — three days before South Carolina officials say they first learned of the intrusion — a notorious cybercriminal who goes by the handle “Rescator” advertised the sale of “a database of the tax department of one of the states.”
“Bank account information, SSN and all other information,” Rescator’s sales thread on the Russian-language crime forum Embargo read. “If you purchase the entire database, I will give you access to it.”
A week later, Rescator posted a similar offer on the exclusive Russian forum Mazafaka, saying he was selling information from a U.S. state tax database, without naming the state. Rescator said the data exposed included Social Security Number (SSN), employer, name, address, phone, taxable income, tax refund amount, and bank account number.
“There is a lot of information, I am ready to sell the entire database, with access to the database, and in parts,” Rescator told Mazafaka members. “There is also information on corporate taxpayers.”
On Oct. 26, 2012, the state announced the breach publicly. State officials said they were working with investigators from the U.S. Secret Service and digital forensics experts from Mandiant, which produced an incident report (PDF) that was later published by South Carolina Dept. of Revenue. KrebsOnSecurity sought comment from the Secret Service, South Carolina prosecutors, and Mr. Keel’s office. This story will be updated if any of them respond. Update: The Secret Service declined to comment.
On Nov. 18, 2012, Rescator told fellow denizens of the forum Verified he was selling a database of 65,000 records with bank account information from several smaller, regional financial institutions. Rescator’s sales thread on Verified listed more than a dozen database fields, including account number, name, address, phone, tax ID, date of birth, employer and occupation.
Asked to provide more context about the database for sale, Rescator told forum members the database included financial records related to tax filings of a U.S. state. Rescator added that there was a second database of around 80,000 corporations that included social security numbers, names and addresses, but no financial information.
The AP says South Carolina paid $12 million to Experian for identity theft protection and credit monitoring for its residents after the breach.
“At the time, it was one of the largest breaches in U.S. history but has since been surpassed greatly by hacks to Equifax, Yahoo, Home Depot, Target and PlayStation,” the AP’s Jeffrey Collins wrote.
As it happens, Rescator’s criminal hacking crew was directly responsible for the 2013 breach at Target and the 2014 hack of Home Depot. The Target intrusion saw Rescator’s cybercrime shops selling roughly 40 million stolen payment cards, and 56 million cards from Home Depot customers.
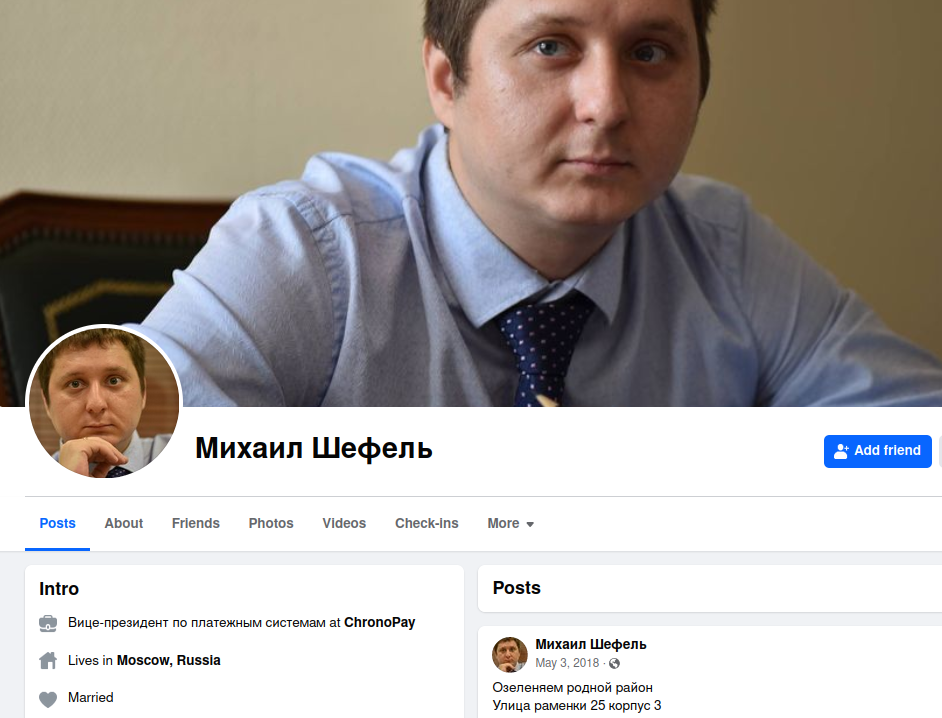
Who is Rescator? On Dec. 14, 2023, KrebsOnSecurity published the results of a 10-year investigation into the identity of Rescator, a.k.a. Mikhail Borisovich Shefel, a 36-year-old who lives in Moscow and who recently changed his last name to Lenin.
Mr. Keel’s assertion that somehow the efforts of South Carolina officials following the breach may have lessened its impact on citizens seems unlikely. The stolen tax and financial data appears to have been sold openly on cybercrime forums by one of the Russian underground’s most aggressive and successful hacking crews.
While there are no indications from reviewing forum posts that Rescator ever sold the data, his sales threads came at a time when the incidence of tax refund fraud was skyrocketing.
Tax-related identity theft occurs when someone uses a stolen identity and SSN to file a tax return in that person’s name claiming a fraudulent refund. Victims usually first learn of the crime after having their returns rejected because scammers beat them to it. Even those who are not required to file a return can be victims of refund fraud, as can those who are not actually owed a refund from the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
According to a 2013 report from the Treasury Inspector General’s office, the IRS issued nearly $4 billion in bogus tax refunds in 2012, and more than $5.8 billion in 2013. The money largely was sent to people who stole SSNs and other information on U.S. citizens, and then filed fraudulent tax returns on those individuals claiming a large refund but at a different address.
It remains unclear why Shefel has never been officially implicated in the breaches at Target, Home Depot, or in South Carolina. It may be that Shefel has been indicted, and that those indictments remain sealed for some reason. Perhaps prosecutors were hoping Shefel would decide to leave Russia, at which point it would be easier to apprehend him if he believed no one was looking for him.
But all signs are that Shefel is deeply rooted in Russia, and has no plans to leave. In January 2024, authorities in Australia, the United States and the U.K. levied financial sanctions against 33-year-old Russian man Aleksandr Ermakov for allegedly stealing data on 10 million customers of the Australian health insurance giant Medibank.
A week after those sanctions were put in place, KrebsOnSecurity published a deep dive on Ermakov, which found that he co-ran a Moscow-based IT security consulting business along with Mikhail Shefel called Shtazi-IT.

A Google-translated version of Shtazi dot ru. Image: Archive.org.

Elder scams cost seniors in the U.S. some $3 billion annually. And tax season adds a healthy sum to that appalling figure.
What makes seniors such a prime target for tax scams? The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) states several factors. For one, elders are typically trusting and polite. Additionally, many own their own home, have some manner of savings, and enjoy the benefits of good credit—all of which make for an ideal victim profile.
Also according to the FBI, elders may be less able or willing to report being scammed because they may not know the exact way in which they were scammed, or they may feel a sense of shame over it, or even some combination of the two. Moreover, being scammed may instill fear that family members will lose confidence in their ability to look after their own affairs.
If there’s one thing that we can do for our elders, it’s help them raise their critical hackles so they can spot these scams and stop them in their tracks, particularly around tax time. With that, let’s see how crooks target elders, what those scams look and feel like, along with the things we can do to keep ourselves and our loved ones from getting stung.
The phone rings, and an assertive voice admonishes an elder for non-payment of taxes. The readout on the caller ID shows “Internal Revenue Service” or “IRS,” the person cites an IRS badge number, and the victim is told to pay now via a wire transfer or prepaid gift card. The caller even knows the last four digits of their Social Security Number (SSN). This is a scam.
The caller, and the claim of non-payment, are 100 percent bogus. Even with those last four digits of the SSN attempting to add credibility, it’s still bogus. (Chances are, those last four digits were compromised elsewhere and ended up in the hands of the thieves by way of the black market or dark web so that they could use them in scams just like these.)
Some IRS imposter scams take it a step further. Fraudsters will threaten victims with arrest, deportation, or other legal action, like a lien on funds or the suspension of a driver’s license. They’ll make repeated calls as well, sometimes with additional imposters posing as law enforcement as a means of intimidating elders into payment.
The IRS will never threaten you or someone you know in such a way.
In fact, the IRS will never call you to demand payment. Nor will the IRS ever ask you to wire funds or pay with a gift card or prepaid debit card. And if the IRS claims you do owe funds, you will be notified of your rights as a taxpayer and be given the opportunity to make an appeal. If there’s any question about making payments to the IRS, the IRS has specific guidelines as to how to make a payment properly and safely on their official website.
It’s also helpful to know what the IRS will do in the event you owe taxes. In fact, they have an entire page that spells out how to know it’s really the IRS calling or knocking at your door. It’s a quick read and a worthwhile one at that.
In all, the IRS will contact you by mail or in person. Should you get one of these calls, hang up. Then, report it. I’ll include a list of ways you can file a report at the end of the article.
Whether it’s a disembodied voice generated by a computer or a scripted message that’s been recorded by a person, robocalls provide scammers with another favorite avenue of attack. The approach is often quite like the phone scam outlined above, albeit less personalized because the attack is a canned robocall. However, robocalls allow crooks to cast a much larger net in the hopes of illegally wresting money away from victims. In effect, they can spam hundreds or thousands of people with one message in the hopes of landing a bite.
While perhaps not as personalized as other imposter scams, they can still create that innate sense of unease of being contacted by the IRS and harangue a victim into dialing a phony call center where they are further pressured into paying by wire or with a prepaid card, just like in other imposter scams. As above, your course of action here is to simply hang up and report it.
Here’s another popular attack. An elder gets an unsolicited email from what appears to be the IRS, yet isn’t. The phony email asks them to update or verify their personal or financial information for a payment or refund. The email may also contain an attachment which they are instructed to click and open. Again, all of these are scams.
Going back to what we talked about earlier, that’s not how the IRS will contact you. These are phishing attacks aimed at grifting prized personal and financial information that scammers can use to commit acts of theft or embezzlement. In the case of the attachment, it very well may contain malware that can do further harm to their device, finances, or personal information.
If you receive one of these emails, don’t open it. And certainly don’t open any attachments—which holds true for any unsolicited email you receive with an attachment.
Beyond simply knowing how to spot a possible attack, you can do several things to prevent one from happening in the first place.
First let’s start with some good, old-fashioned physical security. You may also want to look into purchasing a locking mailbox. Mail and porch theft are still prevalent, and it’s not uncommon for thieves to harvest personal and financial information by simply lifting it from your mailbox.
Another cornerstone of physical security is shredding paper correspondence that contains personal or financial information, such as bills, medical documents, bank statements and so forth. I suggest investing a few dollars on an actual paper shredder, which are typically inexpensive if you look for a home model. If you have sensitive paper documents in bulk, such as old tax records that you no longer need to save, consider calling upon a professional service that can drive up to your home and do that high volume of shredding for you.
Likewise, consider the physical security of your digital devices. Make sure you lock your smartphones, tablets, and computers with a PIN or password. Losing a device is a terrible strain enough, let alone knowing that the personal and financial information on them could end up in the hands of a crook. Also see if tracking is available on your device. That way, enabling device tracking can help you locate a lost or stolen item.
There are plenty of things you can do to protect yourself on the digital front too. Step one is installing comprehensive security software on your devices. This will safeguard you in several ways, such as email filters that will protect you from phishing attacks, features that will warn you of sketchy links and downloads, plus further protection for your identity and privacy—in addition to overall protection from viruses, malware, and other cyberattacks.
Additional features in comprehensive security software that can protect you from tax scams include:
And here’s one item that certainly bears mentioning: dispose of your old technology securely. What’s on that old hard drive of yours? That old computer may contain loads of precious personal and financial info on it. Look into the e-waste disposal options in your community. There are services that will dispose of and recycle old technology while doing it in a secure manner so the data and info on your device doesn’t see the light of day again.
As said earlier, don’t let a bad deed go unreported. The IRS offers the following avenues of communication to report scams.
In all, learning to recognize the scams that crooks aim at elders and putting some strong security measures in place can help prevent these crimes from happening to you or a loved one. Take a moment to act. It’s vital, because your personal information has a hefty price tag associated with it—both at tax time and any time.
The post How to Spot, and Prevent, the Tax Scams That Target Elders appeared first on McAfee Blog.