The cybercriminals in control of Kimwolf — a disruptive botnet that has infected more than 2 million devices — recently shared a screenshot indicating they’d compromised the control panel for Badbox 2.0, a vast China-based botnet powered by malicious software that comes pre-installed on many Android TV streaming boxes. Both the FBI and Google say they are hunting for the people behind Badbox 2.0, and thanks to bragging by the Kimwolf botmasters we may now have a much clearer idea about that.
Our first story of 2026, The Kimwolf Botnet is Stalking Your Local Network, detailed the unique and highly invasive methods Kimwolf uses to spread. The story warned that the vast majority of Kimwolf infected systems were unofficial Android TV boxes that are typically marketed as a way to watch unlimited (pirated) movie and TV streaming services for a one-time fee.
Our January 8 story, Who Benefitted from the Aisuru and Kimwolf Botnets?, cited multiple sources saying the current administrators of Kimwolf went by the nicknames “Dort” and “Snow.” Earlier this month, a close former associate of Dort and Snow shared what they said was a screenshot the Kimwolf botmasters had taken while logged in to the Badbox 2.0 botnet control panel.
That screenshot, a portion of which is shown below, shows seven authorized users of the control panel, including one that doesn’t quite match the others: According to my source, the account “ABCD” (the one that is logged in and listed in the top right of the screenshot) belongs to Dort, who somehow figured out how to add their email address as a valid user of the Badbox 2.0 botnet.
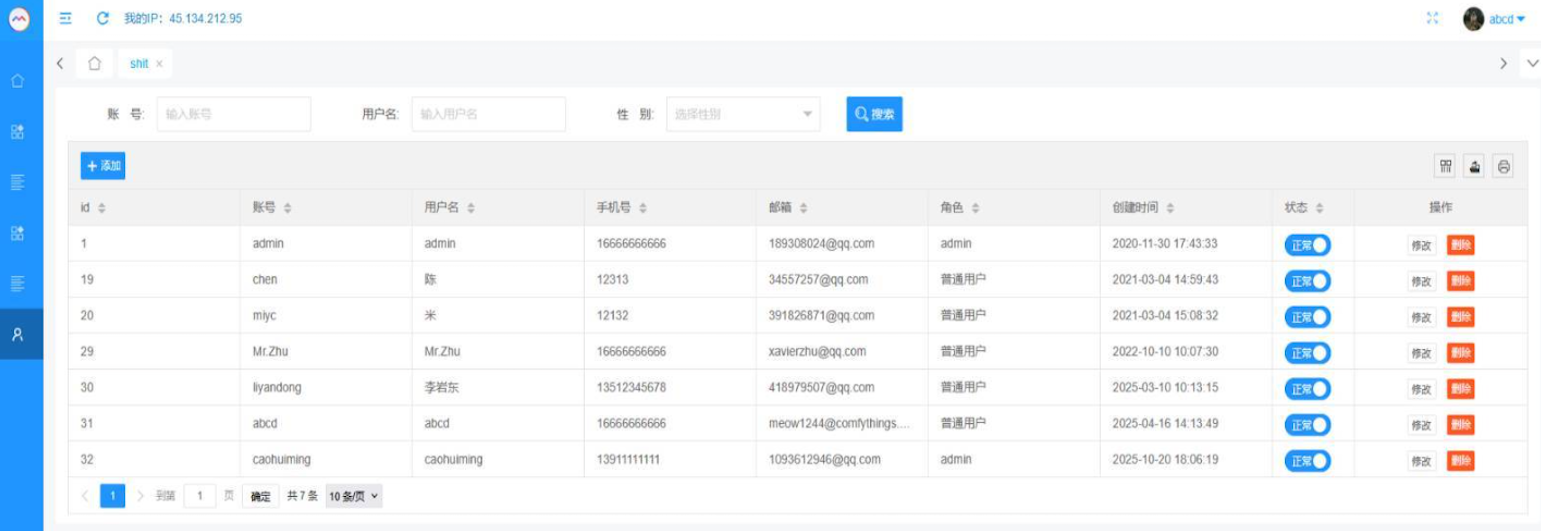
The control panel for the Badbox 2.0 botnet lists seven authorized users and their email addresses. Click to enlarge.
Badbox has a storied history that well predates Kimwolf’s rise in October 2025. In July 2025, Google filed a “John Doe” lawsuit (PDF) against 25 unidentified defendants accused of operating Badbox 2.0, which Google described as a botnet of over ten million unsanctioned Android streaming devices engaged in advertising fraud. Google said Badbox 2.0, in addition to compromising multiple types of devices prior to purchase, also can infect devices by requiring the download of malicious apps from unofficial marketplaces.
Google’s lawsuit came on the heels of a June 2025 advisory from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which warned that cyber criminals were gaining unauthorized access to home networks by either configuring the products with malware prior to the user’s purchase, or infecting the device as it downloads required applications that contain backdoors — usually during the set-up process.
The FBI said Badbox 2.0 was discovered after the original Badbox campaign was disrupted in 2024. The original Badbox was identified in 2023, and primarily consisted of Android operating system devices (TV boxes) that were compromised with backdoor malware prior to purchase.
KrebsOnSecurity was initially skeptical of the claim that the Kimwolf botmasters had hacked the Badbox 2.0 botnet. That is, until we began digging into the history of the qq.com email addresses in the screenshot above.
An online search for the address 34557257@qq.com (pictured in the screenshot above as the user “Chen“) shows it is listed as a point of contact for a number of China-based technology companies, including:
–Beijing Hong Dake Wang Science & Technology Co Ltd.
–Beijing Hengchuang Vision Mobile Media Technology Co. Ltd.
–Moxin Beijing Science and Technology Co. Ltd.
The website for Beijing Hong Dake Wang Science is asmeisvip[.]net, a domain that was flagged in a March 2025 report by HUMAN Security as one of several dozen sites tied to the distribution and management of the Badbox 2.0 botnet. Ditto for moyix[.]com, a domain associated with Beijing Hengchuang Vision Mobile.
A search at the breach tracking service Constella Intelligence finds 34557257@qq.com at one point used the password “cdh76111.” Pivoting on that password in Constella shows it is known to have been used by just two other email accounts: daihaic@gmail.com and cathead@gmail.com.
Constella found cathead@gmail.com registered an account at jd.com (China’s largest online retailer) in 2021 under the name “陈代海,” which translates to “Chen Daihai.” According to DomainTools.com, the name Chen Daihai is present in the original registration records (2008) for moyix[.]com, along with the email address cathead@astrolink[.]cn.
Incidentally, astrolink[.]cn also is among the Badbox 2.0 domains identified in HUMAN Security’s 2025 report. DomainTools finds cathead@astrolink[.]cn was used to register more than a dozen domains, including vmud[.]net, yet another Badbox 2.0 domain tagged by HUMAN Security.
A cached copy of astrolink[.]cn preserved at archive.org shows the website belongs to a mobile app development company whose full name is Beijing Astrolink Wireless Digital Technology Co. Ltd. The archived website reveals a “Contact Us” page that lists a Chen Daihai as part of the company’s technology department. The other person featured on that contact page is Zhu Zhiyu, and their email address is listed as xavier@astrolink[.]cn.
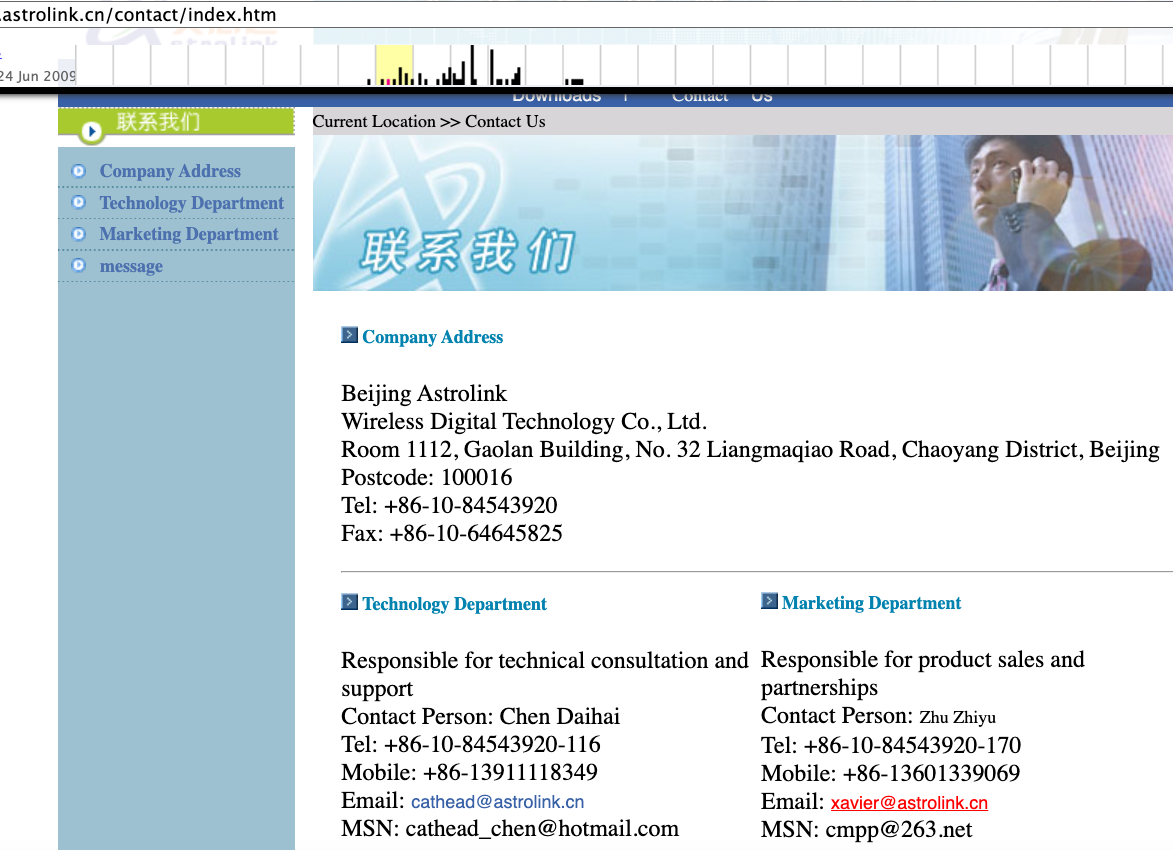
A Google-translated version of Astrolink’s website, circa 2009. Image: archive.org.
Astute readers will notice that the user Mr.Zhu in the Badbox 2.0 panel used the email address xavierzhu@qq.com. Searching this address in Constella reveals a jd.com account registered in the name of Zhu Zhiyu. A rather unique password used by this account matches the password used by the address xavierzhu@gmail.com, which DomainTools finds was the original registrant of astrolink[.]cn.
The very first account listed in the Badbox 2.0 panel — “admin,” registered in November 2020 — used the email address 189308024@qq.com. DomainTools shows this email is found in the 2022 registration records for the domain guilincloud[.]cn, which includes the registrant name “Huang Guilin.”
Constella finds 189308024@qq.com is associated with the China phone number 18681627767. The open-source intelligence platform osint.industries reveals this phone number is connected to a Microsoft profile created in 2014 under the name Guilin Huang (桂林 黄). The cyber intelligence platform Spycloud says that phone number was used in 2017 to create an account at the Chinese social media platform Weibo under the username “h_guilin.”
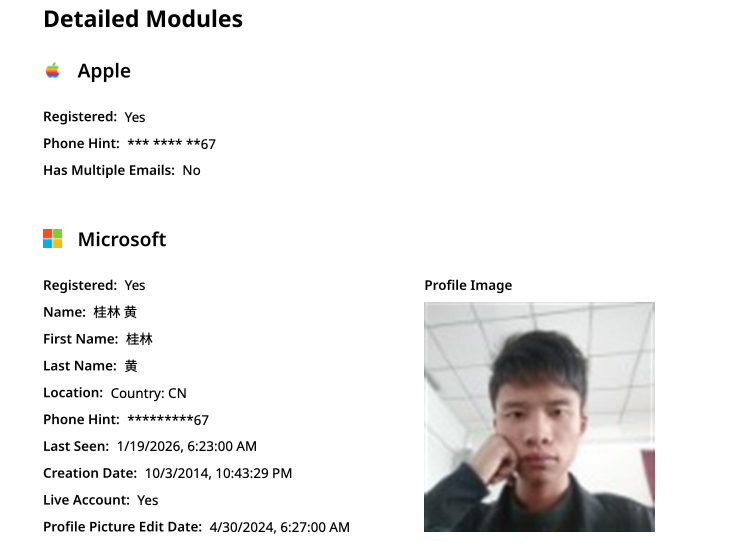
The public information attached to Guilin Huang’s Microsoft account, according to the breach tracking service osintindustries.com.
The remaining three users and corresponding qq.com email addresses were all connected to individuals in China. However, none of them (nor Mr. Huang) had any apparent connection to the entities created and operated by Chen Daihai and Zhu Zhiyu — or to any corporate entities for that matter. Also, none of these individuals responded to requests for comment.
The mind map below includes search pivots on the email addresses, company names and phone numbers that suggest a connection between Chen Daihai, Zhu Zhiyu, and Badbox 2.0.
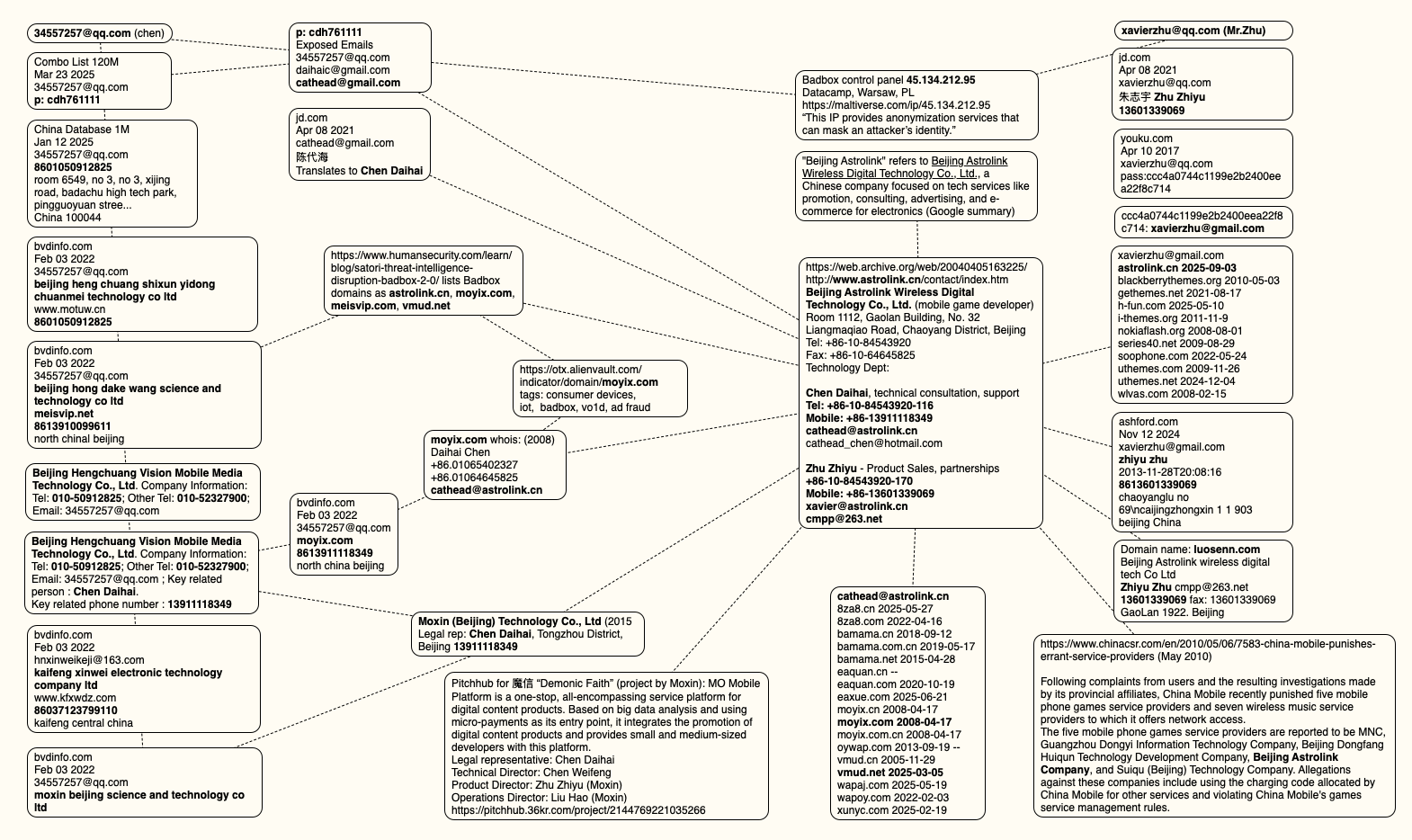
This mind map includes search pivots on the email addresses, company names and phone numbers that appear to connect Chen Daihai and Zhu Zhiyu to Badbox 2.0. Click to enlarge.
The idea that the Kimwolf botmasters could have direct access to the Badbox 2.0 botnet is a big deal, but explaining exactly why that is requires some background on how Kimwolf spreads to new devices. The botmasters figured out they could trick residential proxy services into relaying malicious commands to vulnerable devices behind the firewall on the unsuspecting user’s local network.
The vulnerable systems sought out by Kimwolf are primarily Internet of Things (IoT) devices like unsanctioned Android TV boxes and digital photo frames that have no discernible security or authentication built-in. Put simply, if you can communicate with these devices, you can compromise them with a single command.
Our January 2 story featured research from the proxy-tracking firm Synthient, which alerted 11 different residential proxy providers that their proxy endpoints were vulnerable to being abused for this kind of local network probing and exploitation.
Most of those vulnerable proxy providers have since taken steps to prevent customers from going upstream into the local networks of residential proxy endpoints, and it appeared that Kimwolf would no longer be able to quickly spread to millions of devices simply by exploiting some residential proxy provider.
However, the source of that Badbox 2.0 screenshot said the Kimwolf botmasters had an ace up their sleeve the whole time: Secret access to the Badbox 2.0 botnet control panel.
“Dort has gotten unauthorized access,” the source said. “So, what happened is normal proxy providers patched this. But Badbox doesn’t sell proxies by itself, so it’s not patched. And as long as Dort has access to Badbox, they would be able to load” the Kimwolf malware directly onto TV boxes associated with Badbox 2.0.
The source said it isn’t clear how Dort gained access to the Badbox botnet panel. But it’s unlikely that Dort’s existing account will persist for much longer: All of our notifications to the qq.com email addresses listed in the control panel screenshot received a copy of that image, as well as questions about the apparently rogue ABCD account.

This week in scams, attackers are leaning hard on familiar brands, everyday tools, and routine behavior to trigger fast, unthinking reactions. From fake Netflix billing alerts to malicious browser extensions and QR code phishing tied to foreign espionage, the common thread is trust being weaponized at exactly the right moment.
Every week, this roundup breaks down the scam and cybersecurity stories making news and explains how they actually work, so readers can better recognize risk and avoid being manipulated.
Let’s get into it.
The big picture: Subscription phishing is resurging, with scammers impersonating Netflix and using fake billing failures to push victims into handing over payment details.
What happened: Multiple Netflix impersonation emails circulated again this month, warning recipients that a payment failed and urging them to “update payment” to avoid service interruption. The messages closely mirror Netflix’s real branding and include polished formatting, official-looking language, and even PDF attachments designed to feel like legitimate billing notices.
What makes these scams effective is timing. Victims often receive them while actively reviewing subscriptions, updating payment methods, or considering canceling services. That context lowers skepticism just enough for a quick click before slowing down to verify.
McAfee’s Scam Detector flagged the messages (which one of our own employees received this week) as phishing, confirming they were designed to steal payment information rather than resolve a real billing issue.

Red flags to watch for:
How this scam works: This is classic brand impersonation phishing. Scammers don’t need to hack Netflix itself. They rely on people recognizing the logo, trusting the message, and reacting emotionally to the idea of losing access. The attachment and clean design help bypass instinctive spam filters in the brain, even when technical filters catch it later.
Netflix has warned customers about these scams and offers advice on its site if you encounter one.
What to do instead: If you get a billing alert, don’t click. Open the Netflix app or manually type the site address to check your account. If there’s no issue there, the email wasn’t real.
The big picture: Attackers are exploiting browser crashes themselves as a social engineering tool, turning technical disruption into a pathway for malware installation.
What happened: Researchers reported a malvertising campaign promoting a fake ad-blocking browser extension called “NexShield,” which falsely claimed to be created by the developer of a well-known, legitimate ad blocker. Once installed, the extension intentionally overwhelmed the browser, causing freezes, crashes, and system instability.
After restart, victims were shown fake security warnings instructing them to “fix” the problem by running commands on their own computer. Following those instructions triggered the download of a remote access tool capable of spying, executing commands, and installing additional malware. The reporting was first detailed by Bleeping Computer, with technical analysis from security researchers.
Red flags to watch for:
How this scam works: This is a variant of ClickFix attacks. Instead of faking a problem, attackers cause a real one, then position themselves as the solution. The crash creates urgency and confusion, making people more likely to follow instructions they’d normally question. It turns frustration into compliance.
The big picture: QR codes are being used as stealth phishing tools, with highly targeted attacks tied to foreign intelligence operations.
What happened: The Federal Bureau of Investigation issued a warning about QR code phishing, or “quishing,” campaigns linked to a North Korean government-backed hacking group. According to reporting by Fox News, attackers sent emails containing QR codes that redirected victims to fake login pages or malware-hosting sites.
In some cases, simply visiting the site allowed attackers to collect device data, location details, and system information, even if no credentials were entered. These campaigns are highly targeted, often aimed at professionals in policy, research, and technology sectors.
Red flags to watch for:
How this scam works: QR codes hide the destination URL, removing the visual cues people rely on to judge safety. Because scanning feels faster and more “passive” than clicking a link, people often skip verification entirely. That moment of trust is what attackers exploit.
Read our ultimate guide to “quishing” and how to spot and avoid QR code scams here.
McAfee will be back next week with another roundup of the scams making headlines and the practical steps you can take to stay safer online.
The post This Week in Scams: Netflix Phishing and QR Code Espionage appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Microsoft users across the U.S. experienced widespread disruptions Thursday after a technical failure prevented people from sending or receiving email through Outlook, a core service within Microsoft 365.
The outage occurred during U.S. business hours and quickly affected schools, government offices, and companies that rely on Outlook for daily operations. Microsoft confirmed the issue publicly and said it was working to restore service. There is no indication the disruption was caused by a cyberattack, according to company statements.
Still, McAfee warns in these situations to be wary of phishing attempts as scammers latch onto these outages to take advantage of innocent users.
“Outages like this create uncertainty, and scammers move fast to take advantage of it,” said Steve Grobman, McAfee’s Chief Technology Officer. “When people can’t get into email or the tools they use every day, it’s easy to assume something is wrong with your account — and that’s exactly the moment attackers look for.”
“Fake alerts start circulating that look like they’re coming from the real company, with logos and urgent language telling you to reset a password or verify your information,” Grobman added. “Some push fake support numbers or messages claiming they can restore access. If you’re impacted, slow down, go straight to the official source for updates, and don’t share passwords, verification codes, or payment details in response to an unexpected message.”
“Tools that can spot suspicious links and fake login pages help reduce risk — especially when people are trying to get back online quickly,” Grobman said.
Here, we break down what happened and why outages are prime time for scammers.
A Microsoft infrastructure failure disrupted email delivery.
Microsoft said the outage was caused by a portion of its North American service infrastructure that was failing to properly handle traffic. Users attempting to send or receive email encountered a “451 4.3.2 temporary server issue” error message.
Microsoft also warned that related services, including OneDrive search and SharePoint Online, could experience slowdowns or intermittent failures during the incident.
The disruption unfolded over several hours on Thursday afternoon (ET).
Based on timelines reported by CNBC and live coverage from Tom’s Guide, the outage progressed as follows:
Around 2:00 p.m. ET: User reports spike across Microsoft services, especially Outlook, according to Down Detector data cited by Tom’s Guide.
2:37 p.m. ET: Microsoft confirms it is investigating an Outlook email issue, per CNBC.
3:17 p.m. ET: Microsoft says it identified misrouted traffic tied to infrastructure problems in North America, CNBC reports.
4:14 p.m. ET: The company announces affected infrastructure has been restored and traffic is being redirected to recover service.
Tom’s Guide reported that while outage reports declined after Microsoft’s fix, some users continued to experience intermittent access issues as systems rebalanced.
No. Microsoft says the outage was caused by technical infrastructure issues.
According to CNBC, Microsoft has not indicated that the outage was the result of hacking, ransomware, or any external attack. Instead, the company attributed the disruption to internal infrastructure handling errors, similar to a previous Outlook outage last July that lasted more than 21 hours.

A message sent by Microsoft about the server issue.
Modern work depends on shared cloud infrastructure.
That sudden loss of access often leaves users unsure whether:
That uncertainty is exactly what scammers look for.
They impersonate the company and trick users into signing in again.
After major outages involving Microsoft, Google, or Amazon Web Services, security researchers, including McAfee, have observed scam campaigns emerge within hours.
These scams typically work by:
Impersonating Microsoft using logos, branding, and language copied from real outage notices
Sending fake “service restoration” emails or texts claiming users must re-authenticate
Linking to realistic login pages designed to steal Microsoft usernames and passwords
Posing as IT support or Microsoft support and directing users to fake phone numbers
Once credentials are stolen, attackers can access email accounts, reset passwords on other services, or launch further phishing attacks from a trusted address.
How to stay safe during a Microsoft outage
Outages are confusing. Scammers rely on urgency and familiarity.
To reduce risk:
If you already clicked or entered information:
Using advanced artificial intelligence, McAfee’s built-in Scam Detector automatically detects scams across text, email, and video, blocks dangerous links, and identifies deepfakes, helping stop harm before it happens.
McAfee’s identity protection tools also monitor for signs your personal information may be exposed and guide you through recovery if scammers gain access.
|
Q: Is Microsoft Outlook still down? A: Microsoft said Thursday afternoon that it had restored affected infrastructure and was redirecting traffic to recover service, according to CNBC. Some users may still experience intermittent issues. |
|
Q: Was the Microsoft outage caused by hackers? A: No. Microsoft has not reported any cyberattack or data breach related to the outage, per CNBC. |
|
Q: Can scammers really use outages to steal accounts? A: Yes. During major outages, scammers often impersonate companies like Microsoft and trick users into signing in again on fake websites. |
|
Q: Should I reset my password after an outage? A: Only if you clicked a suspicious link or entered your credentials somewhere outside Microsoft’s official site. Otherwise, resetting passwords isn’t necessary. |
The post Today’s Microsoft Outage Explained and Why it Triggers a Scam Playbook appeared first on McAfee Blog.

You thought you were scanning a menu.
Or paying for parking. Or checking a package notice taped to your door. A quick scan, a familiar logo, a page that loads instantly on your phone.
Nothing about it felt risky.
That’s exactly why QR code scams are spreading so quickly.
QR codes have become part of everyday life. They’re on restaurant tables, public signs, emails, mailers, and payment screens. We’re taught to treat them as shortcuts—faster than typing a URL, easier than downloading an app, safer than clicking a link.
Scammers know that.
Instead of asking you to click something suspicious, they ask you to scan something ordinary. Once you do, you can be routed to fake login pages, payment requests, or malicious sites designed to steal your information before you realize anything is wrong.
This tactic has a name: quishing.
And as QR codes continue to replace links in the real world, understanding how quishing works is essential to staying safe online.
Quishing is a form of phishing that uses QR codes instead of clickable links to trick people into visiting malicious websites or giving up sensitive information.
The term combines QR and phishing, and it reflects a simple but dangerous shift in scam tactics: instead of asking you to click, scammers ask you to scan.
Once scanned, a fake QR code can lead to:
Because QR codes don’t show a visible URL before you scan, they remove one of the most important scam warning signs people rely on.
While quishing attacks vary, most fall into a few predictable patterns.
Scammers place stickers over legitimate parking meter QR codes. When scanned, victims are taken to fake payment pages that steal card details.
Red flag: A QR code that asks for full payment details without redirecting to a known parking or city service.
Fraudsters replace real menu QR codes with fake ones that redirect to phishing pages or malicious downloads.
Red flag: A menu page that asks you to “sign in,” download an app, or confirm personal details.
Flyers or door tags claim you missed a delivery and instruct you to scan a QR code to reschedule.
Red flag: Vague delivery details and pressure to act quickly.
QR codes claim your bank, streaming service, or email account needs verification.
Red flag: Any QR code that demands immediate action for “security reasons.”
Some QR codes promise discounts, refunds, or rewards but quietly enroll users in recurring charges.
Red flag: Fine print that’s hard to find, or missing entirely.
QR scams succeed not because people are careless, but because they exploit trust and routine.
Unlike traditional phishing emails, quishing:
Once a victim lands on a fake site, the damage can escalate quickly, from stolen credentials to drained accounts to identity theft.
You don’t need to avoid QR codes entirely, but you do need to slow down.
Check the physical context
Is the QR code taped on, scratched, or layered over another code? That’s a common tactic.
Look for branding inconsistencies
Misspellings, generic logos, or mismatched colors are red flags.
Preview the link
Most phone cameras now show the URL before opening it. Take a second to read it.
Be skeptical of urgency
Any QR code that pressures you to act immediately deserves extra scrutiny.
Step 1: Treat QR codes like links
A QR code is a shortcut to a website. Apply the same caution you would to any link.
Step 2: Avoid entering sensitive information
Legitimate services rarely ask for passwords, payment info, or personal details via QR codes.
Step 3: Use mobile security tools
Security software can help detect malicious sites and block risky downloads before damage is done.
Step 4: When in doubt, go direct
Instead of scanning, manually visit the official website or app you trust.
If you think you interacted with a malicious QR code:
Early action can limit long-term fallout.
What is quishing in simple terms?
Quishing is phishing that uses QR codes to trick people into visiting fake or malicious websites.
Are QR codes inherently unsafe?
No, but they can be exploited. The risk comes from where they lead, not the code itself.
Can scanning a QR code install malware?
In some cases, yes, especially if it prompts a download or redirects to a malicious site.
Are QR scams increasing?
Yes. As QR codes become more common, scammers are increasingly using them to bypass traditional defenses.
The post What Is Quishing? How QR Code Scams Work and How to Avoid Them appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Because Android uses an open source operating system, it usually gets a bad rap for being vulnerable to data loss and compromised apps as a result of malware, insecure app coding, unprotected cloud storage, outdated software, sideloading from untrusted sources, and even specific website vulnerabilities. Suffice it to say that any of these risks can be destructive and costly.
While Google addresses specific vulnerabilities, cyberthreats continue to evolve as criminals become more scheming or desperate. For these reasons, it is still best to exercise caution to protect the data on your device. In this article, we will share vital tips on how you can secure your device.
Determining if you’re vulnerable isn’t always easy. There are, however, some measures you can take to protect your device.
Your first line of defense against Android vulnerability threats is maintaining current software. Android security patches fix security weaknesses that cybercriminals actively take advantage of to access your personal data, install malware, or take control of your device. When you delay updates, you leave known security gaps open for attackers to exploit.
To enable automatic updates, navigate to Settings > System > System update > Advanced settings, then toggle on “Automatic system updates.” For Google Pixel devices, security updates typically arrive monthly, while other manufacturers may have varying schedules.
On top of this, set your Google Play Store to auto-update apps by opening the Play Store, tapping your profile picture, going to Settings > Network preferences > Auto-update apps, and selecting “Over any network” if you have unlimited data or “Over Wi-Fi only” to preserve your data plan.
One of the most effective Android phone security best practices is restricting app installations to the Google Play Store. Sideloading apps from unknown sources significantly increases your risk of installing malware, spyware, or apps with hidden malicious functionality.
Before installing any app, examine the permissions it requests. Apps asking for excessive permissions should raise your suspicions. Navigate to Settings > Apps > Special app access > Install unknown apps and ensure all toggles are disabled.
In addition, choose apps with consistent positive ratings and active developer responses to user concerns. Google’s Play Console policies provide guidelines for safe app development, but your vigilance remains essential.
Google Play Protect scans over 125 billion apps daily for malware and policy violations. While not perfect, this automated screening catches the majority of malicious apps before they reach your device, and even detects them after installation. In contrast, apps outside this ecosystem lack this protection layer.
Activate Play Protect by opening Google Play Store, tapping your profile picture, selecting “Play Protect,” and ensuring both “Scan apps with Play Protect” and “Improve harmful app detection” are enabled. This service runs automatic security scans and can remove or disable harmful apps even after you’ve installed them.
For comprehensive, real-time protection against phishing sites, malware downloads, and suspicious web content, enable safe browsing Android features in Chrome. Open Chrome, tap the three dots menu, go to Settings > Privacy and security > Safe Browsing, and select “Enhanced protection.” This setting checks URLs against Google’s constantly updated database of dangerous sites.
Modern Android devices offer multiple authentication methods, and using them strategically provides layered security for your most sensitive information. Set up a strong screen lock by going to Settings > Security > Screen lock and choosing either a complex PIN with at least 6 digits, a pattern with at least 6 points, or a password that combines letters, numbers, and symbols.
Enable biometric authentication, whether fingerprint and/or facial recognition, as an additional layer, but always maintain a strong backup PIN or password since biometrics can be circumvented.
For critical applications containing sensitive data such as banking apps, password managers, email clients, and social media, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) where possible for extra security.
Android’s built-in backup and encryption features provide essential protection against data loss from device theft, hardware failure, malware attacks, or accidental deletion, forming a crucial part of your Android incident response strategy.
Enable automatic backups of your app data, call history, and device settings by navigating to Settings > System > Backup, then toggle on “Back up to Google Drive.” You can set the frequency to daily. For photos and videos, enable Google Photos backup with high-quality or original quality settings based on your storage plan.
Device encryption can be activated through Settings > Security > Encryption & credentials > Encrypt phone. Modern Android devices (Android 6.0+) typically have encryption enabled by default, but you will need to verify this setting. Google’s Android backup service documentation provides detailed information on what data is protected and how to manage your backup settings effectively.
Your Google account serves as the master key to most Android functionality, so having an account recovery system can be invaluable to restore access to your device when local authentication methods fail. To ensure your recovery information is current, visit Security settings on your account profile, add a secondary email address that you can access independently, but avoid using another Gmail account as your backup. Include a mobile phone number for SMS verification, and consider adding multiple phone numbers if you frequently travel or change devices.
Google also provides one-time-use back-up codes that can restore account access when other methods fail. Download these codes and store them securely offline. Consider using a password manager like Google’s built-in option or a reputable third-party solution. Never store recovery codes in easily accessible digital formats like unencrypted text files or photos on the same device.
Google’s Find My Device service provides powerful remote management capabilities that can prevent permanent data loss during Android vulnerability situations or lockout scenarios. This service allows you to locate, lock, or completely erase your device remotely.
To enable this feature, navigate to Find My Device through Settings > Security > Find My Device. Ensure that your location services remain active for this feature to function properly.
Take note that when you decide to remotely erase your data from your device, this feature completely wipes all local data but preserves the information you backed up to Google’s cloud services. Only use this option when you’re certain your back-up systems are current.
Android offers multiple backup solutions that transform potential data disasters into minor inconveniences. To store your photos, videos, SMS messages, and call logs, you can go to Settings > System > Backup and choose the frequency that matches your usage patterns, daily backups for heavy users, weekly for lighter usage.
For sensitive information that you would like to access even when offline, you might want to consider periodic local backups by connecting your device to a computer monthly and copying important files manually. Test your systems regularly by attempting to restore a small amount of data to ensure your backups work when needed and identify any gaps in your protection strategy.
A mobile security incident can escalate from a nuisance to real damage in minutes, especially if an attacker can access your accounts, intercept messages, or install persistent apps. Speed matters when you respond, especially when prioritizing the high-impact steps that will stop the bleeding, regain control, and protect your data before you move on to cleanup and recovery. The actions below follow that order, so you can respond calmly and effectively even under stress.
When evaluating mobile security solutions for your Android device, focus on apps that offer comprehensive protection across multiple threat vectors. The most effective solutions combine several key capabilities into a single, user-friendly platform that doesn’t slow down your device or drain your battery.
Your Android device holds your most precious digital memories, important work files, and personal information, making it a prime target for cybercriminals who continue to exploit new vulnerabilities. While threats like remote factory resets and malicious web attacks can disrupt your daily digital routine, you do have the power to protect yourself against them by keeping your OS and security patches current, enabling Google Play Protect and built-in safe browsing features, maintaining regular backups of your essential data, and considering a comprehensive mobile security solution that provides real-time protection. For additional steps to safeguard your Android mobile life, visit McAfee’s security best practices.
The post Guard Your Android Phones Against Loss of Data and Infected Apps appeared first on McAfee Blog.

The practice of locking our possessions is relevant in every aspect of our modern lives. We physically lock our houses, cars, bikes, hotel rooms, computers, and even our luggage when we go to the airport. There are lockers at gyms, schools, amusement parks, and sometimes even at the workplace.
Digitally, we lock our phones with passcodes and protect them from malware with a security solution. Why, then, don’t we lock the individual apps that house some of our most personal and sensitive data?
From photos to emails to credit card numbers, our mobile apps hold invaluable data that is often left unprotected, especially given that some of the most commonly used apps on the Android platform such as Facebook, LinkedIn and Gmail don’t necessarily require a log in each time they’re launched.
Without an added layer of security, those apps are leaving room for nosy family members, jealous significant others, prankster friends, and worst of all thieves to hack into your social media or email accounts at the drop of a hat. In this article, we will discuss what an app lock is, everyday scenarios you may need it, and how to set it up on your smartphone.
Your mobile phone is more than just a gadget. It’s your wallet, camera, diary, and connection to the world. You likely keep photos, messages, social media, payment apps, and even confidential work files on it. To protect these bits of personal information, we use PINs, patterns, or biometrics to lock our devices, but once the phone is open, every app is fair game.
I f someone were able to go beyond your phone’s lock screen and gain access to the information in your phone, how much of your life could they see? A friend could scroll through your photos. Your child could open your shopping app and make purchases. Or a thief could get into your banking and social media accounts in seconds.
One way to avoid this from happening is by applying an app lock, a digital padlock that adds an authentication step such as a password, pattern, or biometric before an application can be launched.
In your home, a locked front door keeps strangers out. But what happens if you unwittingly leave the front door unlocked and someone walks in? Without interior locks, your bedroom, office, and safe are now accessible to anyone.
This same concept applies to your device with unprotected apps. Once unlocked, apps like Gmail, Facebook, or mobile banking don’t always require you to log in every time. It’s convenient, until it’s not.
An app lock serves as an indoor lock, protecting your sensitive data even after an unauthorized person has accessed it, and maintaining privacy boundaries.
When you or another person attempts to open an app on your device, the system first triggers an authentication screen. After verifying your PIN, fingerprint, or face, the app will open, ensuring that your personal information stays off-limits to people who do not know your authentication step. In Android, app locks work seamlessly in the background without slowing performance.
This layered defense mirrors the cybersecurity approach used on enterprise systems, but scaled down for consumers. Each layer handles different threats, so if one fails, the others still protect you:
Leaving apps unprotected can do more than just embarrass you. Here are some examples of how unprotected apps could lead to lasting harm:
Even just one unauthorized session could cascade into identity theft or financial fraud. That’s why security experts recommend app-level protection as part of a layered, reinforced mobile defense strategy.
While many Android phones include some app-locking capabilities, dedicated mobile security apps provide more robust options and better protection. Here’s how to set up app locks effectively:
Use a 6-digit or longer PIN, complex pattern, or biometric such as fingerprint or face unlock. Avoid using the same PIN as your main device.
Choose the priority mobile apps that you want to protect. Start with your most sensitive apps, such as:
Set timeouts based on app sensitivity:
Hide notification content for locked apps. This keeps private messages or bank alerts from showing up on your lock screen.
Most Android manufacturers now offer convenient, built-in app locking features. However, they are limited, often lacking biometric integration, cloud backup, or smart settings.
Dedicated solutions go further, providing:
With an app lock, your mischievous friends will never be able to post embarrassing status updates on your Facebook profile, and your jealous partner won’t be able to snoop through your photos or emails. For parents, you can keep your kids locked out of the apps that would allow them to access inappropriate content without having to watch their every move.
Most importantly, app locks protect you from thieves and strangers in case of a stolen or lost device.
Your phone carries more than just apps. It holds the details of your daily life. From private conversations and family photos to financial information and work data, much of what matters most to you lives behind those app icons. While a device lock is an important first step, it isn’t always enough on its own.
App locks give you greater control over your privacy by protecting individual apps, even when your phone is already unlocked. They help prevent accidental access, discourage snooping, and reduce the risk of serious harm if your device is lost or stolen. Most importantly, they allow you to use and share your phone, without worrying about who might see what they shouldn’t.
By adding app-level protection to your mobile security routine, you’re taking a simple but meaningful step toward safeguarding your personal information.
The post App Locks Can Improve the Security of Your Mobile Phones appeared first on McAfee Blog.

It’s no longer possible to deny that your life in the physical world and your digital life are one and the same. Coming to terms with this reality will help you make better decisions in many aspects of your life.
The same identity you use at work, at home, and with friends also exists in apps, inboxes, accounts, devices, and databases, whether you actively post online or prefer to stay quiet. Every purchase, login, location ping, and message leaves a trail. And that trail shapes what people, companies, and scammers can learn about you, how they can reach you, and what they might try to take.
That’s why digital security isn’t just an IT or a “tech person” problem. It’s a daily life skill. When you understand how your digital life works, what information you’re sharing, where it’s stored, and how it can be misused, you make better decisions. This guide is designed to help you build that awareness and translate it into practical habits: protecting your data, securing your accounts, and staying in control of your privacy in a world that’s always connected.
Being digitally secure doesn’t mean hiding from the internet or using complicated tools you don’t understand. It means having intentional control over your digital life to reduce risks while still being able to live, work, and communicate online safely. A digitally secure person focuses on four interconnected areas:
Your personal data is the foundation of your digital identity. Protecting it includes limiting how much data you share, understanding where it’s stored, and reducing how easily it can be collected, sold, or stolen. At its heart, personal information falls into two critical categories that require different levels of protection:
Account security ensures that only you can access them. Strong, unique passwords, multi-factor authentication, and secure recovery options prevent criminals from hijacking your email, banking, cloud storage, social media, and other online accounts, often the gateway to everything else in your digital life.
Privacy control means setting boundaries and deciding who can see what about you, and under what circumstances. This includes managing social media visibility, app permissions, browser tracking, and third-party access to your data.
Digital security is an ongoing effort as threats evolve, platforms change their policies, and new technologies introduce new risks. Staying digitally secure requires periodic check-ins, learning to recognize scams and manipulation, and adjusting your habits as the digital landscape changes.
Your personal information faces exposure risks through multiple channels during routine digital activities, often without your explicit knowledge.
Implementing comprehensive personal data protection requires a systematic approach that addresses the common exposure points. These practical steps provide layers of security that work together to minimize your exposure to identity theft and fraud.
Start by conducting a thorough audit of your online accounts and subscriptions to identify where you have unnecessarily shared more data than needed. Remove or minimize details that aren’t essential for the service to function. Moving forward, provide only the minimum required information to new accounts and avoid linking them across different platforms unless necessary.
Be particularly cautious with loyalty programs, surveys, and promotional offers that ask for extensive personal information, as they may share it with third parties. Read privacy policies carefully, focusing on sections that describe data sharing, retention periods, and your rights regarding your personal information.
If possible, consider using separate email addresses for different accounts to limit cross-platform tracking and reduce the impact if one account is compromised. Create dedicated email addresses for shopping, social media, newsletters, and important accounts like banking and healthcare.
Privacy protection requires regular attention to your account settings across all platforms and services you use. Social media platforms frequently update their privacy policies and settings, often defaulting to less private configurations that allow them to collect and share your data. For this reason, it is a good idea to review your privacy settings at least quarterly. Limit who can see your posts, contact information, and friend lists. Disable location tracking, facial recognition, and advertising customization features that rely on your personal data. Turn off automatic photo tagging and prevent search engines from indexing your profile.
On Google accounts, visit your Activity Controls and disable Web & App Activity, Location History, and YouTube History to stop this data from being saved. You can even opt out of ad personalization entirely if desired by adjusting Google Ad Settings. If you are more tech savvy, Google Takeout allows you to export and review what data Google has collected about you.
For Apple ID accounts, you can navigate to System Preferences on Mac or Settings on iOS devices to disable location-based Apple ads, limit app tracking, and review which apps have access to your contacts, photos, and other personal data.
Meanwhile, Amazon accounts store extensive purchase history, voice recordings from Alexa devices, and browsing behavior. Review your privacy settings to limit data sharing with third parties, delete voice recordings, and manage your advertising preferences.
Regularly audit the permissions you’ve granted to installed applications. Many apps request far more permissions to your location, contacts, camera, and microphone even though they don’t need them. Cancel these unnecessary permissions, and be particularly cautious about granting access to sensitive data.
Create passwords that actually protect you; they should be long and complex enough that even sophisticated attacks can’t easily break them. Combine uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to make it harder for attackers to crack.
Aside from passwords, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your most critical accounts: banking and financial services, email, cloud storage, social media, work, and healthcare. Use authenticator apps such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy rather than SMS-based authentication when possible, as text messages can be intercepted through SIM swapping attacks. When setting up MFA, ensure you save backup codes in a secure location and register multiple devices when possible to keep you from being locked out of your accounts if your primary authentication device is lost, stolen, or damaged.
Alternatively, many services now offer passkeys which use cryptographic keys stored on your device, providing stronger security than passwords while being more convenient to use. Consider adopting passkeys for accounts that support them, particularly for your most sensitive accounts.
Device encryption protects your personal information if your smartphone, tablet, or laptop is lost, stolen, or accessed without authorization. Modern devices typically offer built-in encryption options that are easy to enable and don’t noticeably impact performance.
You can implement automatic backup systems such as secure cloud storage services, and ensure backup data is protected. iOS users can utilize encrypted iCloud backups, while Android users should enable Google backup with encryption. Regularly test your backup systems to ensure they’re working correctly and that you can successfully restore your data when needed.
Identify major data brokers that likely have your information and look for their privacy policy or opt-out procedures, which often involves submitting a request with your personal information and waiting for confirmation that your data has been removed.
In addition, review your subscriptions and memberships to identify services you no longer use. Request account deletion rather than simply closing accounts, as many companies retain data from closed accounts. When requesting deletion, ask specifically for all personal data to be removed from their systems, including backups and archives.
Keep records of your opt-out and deletion requests, and follow up if you don’t receive confirmation within the stated timeframe. In the United States, key data broker companies include Acxiom, LexisNexis, Experian, Equifax, TransUnion, Whitepages, Spokeo, BeenVerified, and PeopleFinder. Visit each company’s website.
Connect only to trusted, secure networks to reduce the risk of your data being intercepted by attackers lurking behind unsecured or fake Wi-Fi connections. Avoid logging into sensitive accounts on public networks in coffee shops, airports, or hotels, and use encrypted connections such as HTTPS or a virtual private network to hide your IP address and block third parties from monitoring your online activities.
Rather than using a free VPN service that often collects and sells your data to generate revenue, it is better to choose a premium, reputable VPN service that doesn’t log your browsing activities and offers servers in multiple locations.
Cyber threats evolve constantly, privacy policies change, and new services collect different types of personal information, making personal data protection an ongoing process rather than a one-time task. Here are measures to help regularly maintain your personal data protection:
By implementing these systematic approaches and maintaining regular attention to your privacy settings and data sharing practices, you significantly reduce your risk of identity theft and fraud while maintaining greater control over your digital presence and personal information.
You don’t need to dramatically overhaul your entire digital security in one day, but you can start making meaningful improvements right now. Taking action today, even small steps, builds the foundation for stronger personal data protection and peace of mind in your digital life. Choose one critical account, update its password, enable multi-factor authentication, and you’ll already be significantly more secure than you were this morning. Your future self will thank you for taking these proactive steps to protect what matters most to you.
Every step you take toward better privacy protection strengthens your overall digital security and reduces your risk of becoming a victim of scams, identity theft, or unwanted surveillance. You’ve already taken the first step by learning about digital security risks and solutions. Now it’s time to put that knowledge into action with practical steps that fit seamlessly into your digital routine.
The post What Does It Take To Be Digitally Secure? appeared first on McAfee Blog.

The holidays are just around the corner and amid the hustle and bustle, many of us will fire up our devices to go online, order gifts, plan travel, and spread cheer. But while we’re getting festive, the cybercriminals are getting ready to take advantage of the influx of your good cheer to spread scams and malware.
With online shopping expected to grow by 7.9% year-on-year in the U.S. alone in 2025, according to Mastercard, and more people than ever using social media and mobile devices to connect, the cybercriminals have a lot of opportunities to spoil our fun. Using multiple devices provides the bad guys with more ways to access your valuable “digital assets,” such as personal information and files, especially if the devices are under-protected.
In this guide, let’s look into the 12 most common cybercrimes and scams of Christmas, and what you can do to keep your money, information, and holiday spirit safe.
The festive atmosphere, continued increase in online shopping activity, and charitable spirit that define the holidays create perfect conditions for scammers to exploit your generosity and urgency.
Not surprisingly, digital criminals become more active and professional during this period, driven even more by the increasing power of artificial intelligence. A new McAfee holiday shopping report revealed that 86% of consumers surveyed receive a daily average of 11 shopping-related text or email messages that seem suspicious. This includes 3 scam texts, 5 emails, and 3 social media messages. Meanwhile, 22% admit they have been scammed during a holiday season in the past.
Their scams succeed because they exploit the psychological and behavioral patterns that are rife during the holidays. The excitement and time pressure of holiday shopping often prevail over our usual caution, while the emotional aspects of gift-giving and charitable donations can be exploited and move us to be more generous. Meanwhile, scammers understand that you’re more likely to make quick purchasing decisions when the fear of missing out on limited-time offers overtakes your judgment or when you’re rushing to find the perfect gift before it’s too late.
Overall, the frenzied seasonal themes create an environment where criminals can misuse the urgency of their fake offers and cloud our judgment, making fraudulent emails and websites appear more legitimate, while you’re already operating under the stress of holiday deadlines and budget concerns. After all, holiday promotions and charity appeals are expected during this time of year.
Now that you understand the psychology behind the scams, it’s time to become more aware of the common scams that cybercriminals run during the holiday season.
As you head online this holiday season, stay on guard and stay aware of scammers’ attempts to steal your money and your information. Familiarize yourself with the “12 Scams of Christmas” to ensure a safe and happy holiday season:
Many of us use social media sites to connect with family, friends, and co-workers over the holidays, and the cybercriminals know that this is a good place to catch you off guard because we’re all “friends,” right? Here are some ways that criminals will use these channels to obtain shoppers gift money, identity or other personal information:
As the popularity of smartphone apps has grown, so have the chances of you downloading a malicious application that steals your information or sends premium-rate text messages without your knowledge. Apps ask for more permissions than they need, such as access to your contacts or location.
If you unwrap a new smartphone this holiday season, make sure that you only download applications from official app stores and check other users’ reviews, as well as the app’s permission policies, before downloading. Software, such as McAfee Mobile Security, can also help protect you against dangerous apps.
Many of us travel to visit family and friends over the holidays. We begin our journey online by looking for deals on airfare, hotels, and rental cars. Before you book, keep in mind that scammers are looking to hook you with phony travel webpages with too-fantastic deals—beautiful pictures and rock-bottom prices—to deceive you into handing over your financial details and money.
Even when you’re already on the road, you need to be careful. Sometimes, scammers who have gained unauthorized access to hotel Wi-Fi will release a malicious pop-up ad on your device screen, and prompt you to install software before connecting. If you agree to the installation, it downloads malware onto your machine. To thwart such an attempt, it’s important that you perform a security software update before traveling.
You are probably already familiar with email phishing and SMiShing messages containing questionable offers and links. The scammer will mimic a legitimate organization offering cheap Rolex watches and luxury products as the “perfect gift” for that special someone, or send a message posing as your bank with a holiday promo and try to lure you into revealing information or direct you to a fake webpage. Never respond to these scams or click on an included link. Be aware that real banks won’t ask you to divulge personal information via text message. If you have any questions about your accounts, you should contact your bank directly.
QR code phishing, or “quishing,” has emerged as a significant new threat during holiday shopping seasons. In this scam method, cybercriminals place malicious QR codes in holiday advertisements posted on social media or printed flyers, parking meters and payment kiosks at shopping centers, or at restaurant tables during holiday dining. They could also email attachments claiming to offer exclusive holiday deals or fake shipping labels placed over legitimate tracking QR codes.
The kind of excitement and buzz surrounding Apple’s new iPad and iPhone is just what cybercrooks dream of when they plot their scams. They will mention must-have holiday gifts in dangerous links, phony contests, and phishing emails to grab your attention. Once they’ve caught your eye, they will again try to get you to reveal personal information or click on a dangerous link that could download malware onto your machine. Be suspicious of any deal mentioning hot holiday gift items—especially at extremely low prices—and try to verify the offer with the real retailer involved.
Cybercriminals exploit employee expectations of year-end communications by creating fake emails that appear to come from your HR department. These messages often claim to contain annual bonus information, updated benefits packages, or mandatory holiday attendance announcements. These scams are particularly effective because they prey on legitimate employee concerns about compensation, benefits, and personal time off during the holiday season. The emails often feature real-looking company logos, proper formatting, and even references to company policies to increase their credibility.
Gift cards are probably the perfect gift for some people on your holiday list. Given their popularity, cybercriminals can’t help but want to get in on the action by offering bogus gift cards online. Be wary of buying gift cards from third parties. It’s best to buy from the official retailer. Just imagine how embarrassing it would be to find out that the gift card you gave your mother-in-law was fraudulent!
No matter what gift you’re looking for, chances are you can find it quickly and easily online, but you still want to be careful in selecting which site to shop. By promoting great deals, phony e-commerce sites will try to convince you to type in your credit card number and other personal details. After obtaining your money and information, you never receive the merchandise, and your personal information is put at risk. To prevent falling victim to bogus e-commerce stores, shop only at trusted and well-known e-commerce sites. If you’re shopping on a site for the first time, check other users’ reviews and verify that the phone number listed on the site is legitimate.
This is one of the biggest scams of every holiday season. As we open our hearts and wallets, the bad guys will send spam emails and pretend to be a real charity in the hope of getting in on the giving. Their emails will sport a stolen logo and copycat text, or come from an entirely invented charity. If you want to give, it’s always safer to visit the charity’s legitimate website, and do a little research about the charity before you donate.
E-cards are a popular way to send a quick “thank you” or holiday greeting. While most e-cards are safe, some are malicious and may contain spyware or viruses that download onto your computer once you click on the link to view the greeting. Before clicking, look for clues that the e-card is legitimate. Make sure it comes from a well-known e-card site by checking the domain name of the included link. Also check to see that the sender is someone you actually know, and that there are no misspellings or other red flags that the card is a fake.
With increased package deliveries during the holiday season, fake shipping notifications have become a common attack. These messages claim to be from legitimate shipping companies such as UPS, FedEx, or DHL, informing you of package delivery attempts or shipping delays. To complete the delivery, these notices will ask you to click on malicious links or attachments that will download malware or direct you to fake websites that will steal personal information. The timing of these attacks coincides with legitimate increased shipping activity, making them harder to distinguish from authentic communications. To track your deliveries, it is best to check the shipping company’s real website or through the trusted platform from which you ordered the product.
Knowing about these common scam tactics is only the first step toward protecting yourself and those you care about. The next step is for you to learn and implement practical, effective strategies to stay safe while still enjoying digital holiday shopping and giving.
The holiday season brings joy and connection, but it’s also a time when scammers work hardest to exploit your festive but rushed and distracted spirit. Effective Christmas scam prevention starts with awareness. By slowing down and taking a moment to verify before you click or buy, and using layered cybersecurity protections, you can worry about one less thing and focus on what matters most this season.
Stay security-conscious without letting fear diminish your holiday enjoyment and pursue your digital holiday activities with the right knowledge and tools. We hope that the specific, actionable protections will help you identify red flags, verify legitimate offers, secure your devices and accounts, and respond effectively to suspicious activity. Stay informed by following trusted sources for the latest cybersecurity tips during the holidays, and make this season about celebrating safely with the people you care about most.
Send the link to this page to your family and friends to increase their awareness and take steps to protect themselves.
The post The Top 12 Scams Of Christmas To Watch Out For appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Thanksgiving—not before Halloween as we see things in stores and online now. It seems like the holiday season and decorations start earlier and earlier every year.
But one thing that hasn’t changed is that Black Friday is still a big shopping day. With the advent of online shopping has emerged Cyber Monday, another big sale day for online shoppers on the first Monday after Thanksgiving.
Although many of us may take advantage of these great deals that the holidays offer, we also need to be aware of the risks. Online shopping is a fun and convenient way to make purchases, locate hard-to-find items, and discover bargains, but we need to take steps to protect ourselves.
This guide looks at the methods and warning signs behind online shopping scams, shows you how to recognize fake shopping apps and websites, and shares tips for staying safe online.
Online shopping has become a cornerstone of American life. CapitalOne Shopping projects American online spending to reach $1.34 trillion in 2024 and exceed $2.5 trillion in 2030.
With such a massive sum at stake, cybercriminals are laser-focused on taking a share of it, posing financial risk to the 288 million Americans who shop online. As e-commerce grows, so does fraud. In 2024, e-commerce fraud was valued at $44.3 billion, a number seen to grow by 141% to $107 billion in 2029.
Be that as it may, there are many smart shopping habits you can apply to dramatically reduce your risk of becoming a victim of online shopping fraud and enjoy the convenience and benefits of online commerce.
Online shopping scams are designed to look normal—at first glance—especially during busy sale seasons when we’re distracted by a million preparations, moving fast, and chasing deals. These are the very circumstances that fraudsters bank on to victimize you into taking the bait. Being aware of the common scam indicators will help you pause and think, recognize trouble early, and protect both your money and your personal information.
Safe online shopping starts with recognizing the hallmarks of legitimate retailers. Before you enter any payment details, take a moment to verify that the website you’re shopping on is genuine. Scam stores can look polished and convincing, but they often leave behind subtle clues. Here are quick ways to check their authenticity:
 trustmark, indicating that the site has been scanned and verified as secure by a trusted third party. This security seal indicates that the site will help protect you from identity theft, credit card fraud, spam, and other malicious threats.
trustmark, indicating that the site has been scanned and verified as secure by a trusted third party. This security seal indicates that the site will help protect you from identity theft, credit card fraud, spam, and other malicious threats.The FTC also recommends these additional tips so you can enjoy all the advantages that online shopping has to offer and prevent risking your personal information.
Online shopping should feel exciting, not a dangerous undertaking you have to brace for, especially during the season of giving. It can be, with a few simple steps—checking the URL, looking for HTTPS, verifying the seller, paying with a credit card or virtual number, and trusting your gut when something feels suspicious. These small habits will keep your money and your identity where they belong: with you.
For increased safety while shopping online, seek out the help of a trusted security solution such as McAfee+ that will alert you of risky links and compromised websites to prevent identity theft or malware infection.
If this guide helps you, pass it along to someone you care about. Scams don’t just target individuals—they cascade into families and friend groups. The more we normalize safe shopping habits and increase our vigilance, the harder it is for fraudsters to win. If you ever feel unsure mid-purchase, take a breath and double-check. A few extra seconds now can save you a lot of stress later. Stay safe, and happy shopping!
The post Helpful Tips for Safe Online Shopping appeared first on McAfee Blog.

This is a critical time for our personal security, particularly in terms of privacy and personal information. A battle is being waged over our data by multiple parties, from criminal hackers to advertisers and data brokers. This article provides essential tips to help you protect the personal details you want to keep private and stay safe online.
Criminal hackers and identity thieves want to use your name to open new accounts, which they can turn into cash. They may try to obtain credit cards, utility services, or mobile phones using your good credit. In other cases, these same thieves take over existing bank or credit card accounts and completely empty them out. Identity theft affects millions of Americans each year, with over 1.4 million reports filed to the FTC in recent years and an estimated 15 million victims annually.
Online, advertisers and marketers use tracking cookies and sophisticated technologies to gather information about you and your web browsing habits. They can then offer you products or services based on the profile they’ve developed. Almost every major website contains cookies, and they are changing the way advertising is created and targeted.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has explored options, such as “Do Not Track” mechanisms, to allow consumers to opt out of data collection; however, these efforts have faced significant challenges. Browser-based solutions have been proposed, but the advertising industry’s partnerships with major media and tech companies have made comprehensive opt-out mechanisms difficult to implement effectively.
Social media companies compete for your attention and your information because user data is valuable to advertisers and marketers. Whatever you post in your profile is broken down, cataloged, and disseminated. Your name, age, address, email, phone number, contacts, income status, job description, and other personal details are of use to anyone targeting your wallet.
However, legitimate advertisers aren’t the only ones targeting social networks. Criminal hackers and identity thieves are accessing your data, either through the public portion of these sites or by hacking through the back door. The bad guy is using your profile information to come up with an answer to your password reset question, or to trick you into opening your wallet or entering login credentials that might allow them to take over your existing accounts.
Amid all these developments, the National Cyber Security Alliance established Data Privacy Day, an annual awareness event observed every January 28, which encourages you to take control of your personal information and understand your online privacy rights. Initially launched in 2008, this important day coincides with the anniversary of the signing of Convention 108, the first legally binding international treaty dealing with privacy and data protection.
As a U.S. consumer, Data Privacy Day matters to you more than ever because your personal information has become incredibly valuable and, unfortunately, increasingly vulnerable. Every day, you share personal details through social media, shopping websites, mobile apps, and online services, often without realizing how this information is collected, used, or shared.
The observance of this day highlights several key risks that affect your daily digital life. Data misuse occurs when companies collect more information than necessary or use your personal details in ways you haven’t explicitly approved. Identity theft remains a significant threat, with criminals using stolen personal information to open fraudulent accounts, make unauthorized purchases, or even file fake tax returns. Additionally, data breaches continue to expose millions of Americans’ personal information each year, from social security numbers to financial details.
What makes Data Privacy Day empowering is its focus on actionable steps you can take immediately. Rather than feeling overwhelmed by privacy concerns, you can use this day as motivation to review and strengthen your digital privacy habits. The day is a reminder that privacy and data protection aren’t just technical concepts. They’re fundamental rights that help you maintain control over your digital life.
Before delving deeper into regulations and best practices, let’s take a look at the core concepts. The Federal Trade Commission defines data privacy as the reasonable expectation that your personal information will be handled appropriately by the organizations that collect it. It is your fundamental right to control how your personal information is collected, used, shared, and retained by the companies and services you interact with every day. At its heart, data privacy ensures that you have a say in what happens to details about your life, from your name and email address to your online shopping preferences, videos watched, social media usage, and down to your browsing habits and location data.
Your data follows a path that starts with collection, when companies gather information directly from you, such as when you fill out a form, or indirectly through cookies and tracking pixels. The use phase refers to how organizations process your information, whether to improve their services, target advertisements, or analyze user behavior. Sharing involves passing your data to third parties, from business partners to data brokers. Retention determines how long your information stays in their systems, often well beyond the end of your active relationship with the service.
Throughout this process, your information is governed by three principles of modern data privacy:
When Netflix asks if you want to share viewing data to improve recommendations, that’s consent in action. When Google lets you download your search history or delete location tracking, you’re exercising control. When Apple’s privacy labels show exactly what data an app collects, that’s transparency working for you.
Under these newly instituted state privacy laws, you have several key rights that put you in control of your personal information:
Data protection and data privacy are sometimes used interchangeably, but they serve different but complementary roles in keeping your personal information safe:
Here are some everyday scenarios that show how these concepts work differently:
As a consumer, your data privacy rights translate into real, actionable benefits you can use today. However, the effectiveness of these protections often depends on enforcement and your own awareness of the tools available to you.
U.S. state privacy laws are increasingly giving you the right to know what personal information companies collect, the right to delete your data, and the right to opt out of having your information sold or shared.
America’s privacy framework is built on sector-specific federal regulations combined with increasingly robust state legislation. This approach means your rights and protections can vary significantly depending on where you live and what type of data is being collected.
At the federal level, key laws include the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for healthcare data, the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) for credit information, and the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) for children under 13 years. While these provide important protections in specific areas, they leave significant gaps in comprehensive consumer data privacy protection.
To fill these gaps, California established crucial precedents through the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and its successor, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA). Other states are also now enacting comprehensive privacy laws, including Virginia’s Consumer Data Protection Act, Colorado Privacy Act, Connecticut’s Data Privacy Act, and Utah’s Consumer Privacy Act. Each provides residents with fundamental rights over their personal data while requiring businesses to implement stronger protection measures.
Sensitive personal data represents the most valuable and vulnerable information about you—the details that, if compromised, could cause significant harm to your finances, safety, and peace of mind. Unlike basic contact information, sensitive data requires stronger legal protections and your extra vigilance because of its potential for misuse.
Your health information deserves particular care because it reveals intimate details about your physical and mental well-being. HIPAA protections cover medical records, but health data collected by fitness apps, mental health platforms, or wellness websites may not receive the same legal safeguards.
Biometric data—your unique physical characteristics such as fingerprints, voice patterns, or facial features—can’t be changed if stolen, making this information particularly precious.
Children’s data receives special attention under privacy laws because minors can’t meaningfully consent to data collection. The Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act requires explicit parental consent before companies can collect information from children under 13, while some state laws extend these protections to older teens.
Meanwhile, global services such as Google, Facebook, or Netflix apply the Europe-established General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) laws worldwide to maintain consistent data practices.
GDPR personal data includes obvious identifiers such as your name, email address, phone number, and Social Security number. But it also covers less obvious information, such as IP addresses, device IDs, location data, and even your online shopping habits or social media activity. Essentially, if data points can be combined to create a profile of you, they qualify as personal data under GDPR standards. This broader definition gives you stronger control over your information and has influenced many U.S. companies to offer the same rights to all users, not just those in the European Union.
Whether a company follows GDPR, California’s privacy laws, or other frameworks, the core principle remains the same: you deserve transparency and control over your personal information.
Your privacy rights are expanding, but exercising them effectively requires staying informed and taking proactive steps. As we celebrate Data Privacy Day, we recommend you participate by taking simple, practical steps to exercise your data privacy rights.
Start with the platforms and services you use most frequently. Look for the privacy or data protection section in your account settings and review the information being collected and shared.
Many major companies now provide online forms or dedicated email addresses for privacy requests. Take advantage of these to understand what data they have about you. Popular platforms such as Google, Facebook, and Amazon have streamlined processes for data downloads.
Look for “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” links on websites, typically found in footers or privacy policy pages. You can also use opt-out tools such as the Global Privacy Control browser setting that automatically signals your opt-out preferences.
Many data brokers now offer opt-out mechanisms, though the process can be time-consuming. Consider using privacy services that handle multiple opt-out requests on your behalf.
Regularly search for your name and personal information online. Set up Google Alerts for your name and key personal details to stay informed about new appearances of your information. In addition, monitor your credit reports for unauthorized changes, and use identity monitoring services that watch for your personal information appearing in data breaches or on the dark web.
When sharing sensitive information online, verify that websites use https:// in the address bar and read privacy policies before providing personal details. Only use well-established, privacy-focused health, financial, and communication platforms with a strong track record of privacy and data protection.
For children’s data, maintaining active oversight will help you stay ahead of potential problems in their online activities. Review the apps and websites they use, understand what information these platforms collect, and use parental controls to limit data sharing. Teach your children about privacy and the risks of sharing personal information online.
Protecting your personal data doesn’t have to feel like a giant, technical project. Most privacy wins come from small, repeatable habits that you can do in minutes to shrink your digital footprint, and use the internet on your terms.
Your personal information has value, so make sure you’re getting a fair return through services that respect your privacy.
Personal data includes any information that can directly or indirectly identify you. This covers obvious details such as your name, email, and Social Security number, but also extends to IP addresses, device identifiers, location data, browsing history, and even inferences about your preferences or behavior.
On company websites, look for “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” or “Your Privacy Choices” links, usually found in the footer. You can also use the Global Privacy Control browser signal to send opt-out requests automatically. Services such as DeleteMe or manual removal requests can help you reclaim control of your information from data brokers and multiple platforms.
First, change passwords for affected accounts and enable two-factor authentication. Next, monitor your credit reports and bank statements for unusual activity. If Social Security numbers or financial data were involved, place a credit freeze with all three major credit bureaus. Sign up for identity monitoring services if offered by the breached company. Be sure to document everything and report identity theft to the FTC if you notice fraudulent activity.
Watch for manipulative design tricks that push you toward sharing more data. Red flags include pre-checked boxes for marketing emails, making privacy-friendly options harder to find or understand, using confusing language that hides the intent, or making it much easier to accept all cookies than to customize your preferences. Legitimate consent should be freely given, specific, informed, and easily withdrawn.
Depending on your location, you may have the right to know what data companies collect about you, request copies of your data, correct inaccurate information, delete your data, and opt out of its sale or use for targeted advertising. Some laws also give you the right to data portability and protect you from discrimination for exercising these rights. Check if your state has comprehensive privacy laws or if you’re covered by GDPR.
To stay current with your privacy rights and the evolving legal landscape, bookmark these authoritative resources:
Data Privacy Day serves as an important annual reminder, but your commitment to privacy and data protection shouldn’t end when January 28th passes. The digital threats we face continue to evolve throughout the year, making ongoing vigilance essential to protect your personal details.
Small, consistent habits can make a profound difference in your digital security. By regularly updating your passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, reviewing privacy settings on your accounts, and staying informed about emerging threats, you create layers of protection that work together to safeguard your information.
Invest in McAfee+ identity protection, which includes proactive identity surveillance to monitor subscribers’ credit and personal information, as well as access to live fraud resolution agents who help subscribers work through the process of resolving identity theft issues.
The post Celebrate Data Privacy Day by Applying These Best Practices appeared first on McAfee Blog.

The malware landscape is growing more complex and costly by the minute, as indicated by the rising number of cyberattacks that grow each year. According to the Federal Bureau of Investigation, in 2024, approximately $1.4 million in losses were reported due to malware. Meanwhile, complaints of ransomware, a type of malware that locks your files until a ransom is paid to release them, rose by 9% from the year prior, with losses totaling nearly $12.5 million.
With the continued growth of e-commerce, online banking, and artificial intelligence, we can count on even more new cyber threats for all kinds of devices—be it Android, iPhone, PC, or Mac. No device under your family’s roof is immune to cyberattacks. As we speak, one or more of your devices may have already been infected. But would you know it?
In this blog, we’ll dive into the types of viruses and malware that infiltrate devices and their indications, the ways you can remove them, and tips to protect your phones moving forward.
Malware is malicious software designed to harm your device, steal your personal information, or disrupt your digital life. On mobile devices, malware can take many forms—from apps that secretly collect your data to programs that bombard you with unwanted ads or even lock your device for ransom.
Mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets, can be infected with malware and other digital threats, even when their operating systems have built-in security features. How does this happen? Your phone can catch viruses and malware in several ways:
Malware doesn’t always announce itself with a big flashing sign. On the contrary, it slips quietly into your devices and starts causing trouble behind the scenes. Before long, you will see noticeable changes in its behavior. Here are five key signs of malware or a virus to watch for and catch the problem early, before the damage spreads:
As our phones and tablets become extensions of our daily lives, cybercriminals have developed sophisticated malware explicitly designed to infiltrate them, such as:
Sometimes the warning signs are obvious, but at other times, malware operates quietly in the background, stealing data or draining resources without drawing attention. Find out for sure if your device has a virus or malware by following these steps:
Here are more specific measures to ascertain the presence of a virus or malware, based on your mobile device’s operating system:
If you discover malicious apps and profiles in your phone, a clear, step-by-step action plan will help you remove them and restore your device to a secure state. Here’s how to tackle mobile malware confidently and get your device back to normal:
With a few smart habits and simple tools, you can create a safer digital environment for your family members. Here are some practical ways to safeguard family devices and keep threats at bay.
While the threat of malware and viruses continues to evolve, you now have the knowledge and tools to stay digitally protected. The signs we’ve discussed—from unexpected device behavior to suspicious pop-ups—serve as warnings, helping you catch problems before they escalate into major security incidents.
Your best defense combines proactive security measures and vigilant behavior. Applying simple, solid digital habits such as updating software, using strong passwords, and staying alert to suspicious activity will thwart the vast majority of common threats. By incorporating these practices into your routine, along with the right online security tools, you are building a robust defense that works around the clock.
The post 5 Signs Your Device May be Infected with Malware or a Virus appeared first on McAfee Blog.

It’s the screen you never want to see.
Something is seriously wrong with your phone. Or is it? You might not have a broken phone at all. Instead, you might have a hacked phone.

What you see above is a form of scareware, an attack that frightens you into thinking your device is broken or infected with a virus. What the hacker wants you to do next is panic. They want you to tap on a bogus link that says it’ll run a security check, remove a virus, or otherwise fix your phone before the problem gets worse.
Of course, tapping that link takes you to a malware or phishing site, where the hacker takes the next step and installs an even nastier form of malware on your phone. In other cases, they steal your personal info under the guise of a virus removal service. (And yes, sometimes they pose as McAfee when they pull that move. In fact,
Note that in this example above, the hacker behind the phony broken screen is arguably going for a user who’s perhaps less tech savvy. After all, the message atop the “broken” screen appears clear as day. Still, in the heat of the moment, it can be convincing enough.
Scareware typically finds its way onto phones through misleading ads, fake security alerts, or hacked websites. In other cases, downloading apps from places other than an official app store can lead to scareware (and other forms of malware too).
As for malware on phones, you’ll find different risk levels between Android and iOS phones. While neither platform is completely immune to threats, Android phones are reportedly more susceptible to viruses than iPhones due to differences in their app downloading policies. On Android phones, you can install apps from third-party sources outside the official Google Play Store, which increases the risk of downloading malicious software.
In contrast, Apple restricts app installations to its official App Store, making it harder for malware to get on iOS devices. (That’s if you haven’t taken steps to jailbreak your iPhone, which removes the software restrictions imposed by Apple on its iOS operating system. We absolutely don’t recommend jailbreaking because it may void warranties and make it easier for malware, including scareware, to end up on your phone.)
If you think you’ve wound up with a case of scareware, stay calm. The first thing the hacker wants you to do is panic and click that link. Let’s go over the steps you can take.
If you don’t already have mobile security and antivirus for your phone, your best bet is to get the latest virus removal guidance from Android, which you can find on this help page.
Moving forward, you can get protection that helps you detect and steer clear of potential threats as you use your phone. You can pick up McAfee Security: Antivirus VPN in the Google Play store, which also includes our Scam Detector and Identity Monitoring. You can also get it as part of your McAfee+
Step 1: Restart your phone
Hold down the iPhone power button until you see slide to power off on your screen. Slide it, wait for the phone to power down, and then press the power button to restart your iPhone.
Step 2: Download updates
Having the latest version of iOS on your phone ensures you have the best protection in place. Open the Settings app. Look for Software Update in the General tab. Select Software Update. Tap Download and Install to the latest iPhone update.
Step 3: Delete suspicious apps
Press a suspicious app icon on your screen and wait for the Remove App to pop up. Remove it and repeat that as needed for any other suspicious apps.
More steps you can take …
If those steps don’t take care of the issue, there are two stronger steps you can take. The first involves restoring your phone from a backup as described by Apple here.
The most aggressive step you can take is to reset your phone entirely. You can return it to the original factory settings (with the option to keep your content) by following the steps in this help article from Apple.
Clearly these attacks play on fear that one of the most important devices in your life has a problem—your phone.
Comprehensive online protection software can secure your phone in the same ways that it secures your laptops and computers. Installing it can protect your privacy, keep you safe from attacks on public Wi-Fi, automatically block unsafe websites and links, and detect scams, just to name a few things it can do.
Along with installing security software, keeping your phone’s operating system up to date can greatly improve your security. Updates can fix vulnerabilities that hackers rely on to pull off their malware-based attacks. It’s another tried-and-true method of keeping yourself safe—and for keeping your phone running great too.
Google Play and Apple’s App Store have measures in place to review and vet apps to help ensure that they are safe and secure. Third-party sites might very well not, and they might intentionally host malicious apps as part of a front. Further, Google and Apple are quick to remove malicious apps from their stores when discovered, making shopping there safer still.
The post Black or Scrambled Phone Screen? Here’s How to Spot a Hacked vs Broken Phone appeared first on McAfee Blog.

They came by phone, by text, by email, and they even weaseled their way into people’s love lives—an entire host of scams that we covered here in our blogs throughout the year.
Today, we look back, picking five noteworthy scams that firmly established new trends, along with one in particular that gives us a hint at the face of scams to come.
Let’s start it off with one scam that pinged plenty of phones over the spring and summer: those toll road texts.
It was the hot new scam of 2025 that increased by 900% in one year: the toll road scam.
There’s a good chance you got a few of these this year,scam texts that say you have an unpaid tab for tolls and that you need to pay right away. And as always, they come with a handy link where you can pay up and avoid that threat of a “late fee.”

Of course, links like those took people to phishing sites where people gave scammers their payment info, which led to fraudulent charges on their cards. In some instances, the scammers took it a step further by asking for driver’s license and Social Security numbers, key pieces of info for big-time identity theft.
Who knows what the hot new text scam for 2026 will be, yet here are several ways you can stop text scams in their tracks, no matter what form they take:
Don’t click on any links in unexpected texts (or respond to them, either). Scammers want you to react quickly, but it’s best to stop and check it out.
Check to see if the text is legit. Reach out to the company that apparently contacted you using a phone number or website you know is real—not the info from the text.
Get our Scam Detector. It automatically detects scams by scanning URLs in your text messages. If you accidentally tap or click? Don’t worry, it blocks risky sites if you follow a suspicious link.
It started with a DM. And a few months later, it cost her $1,200.
Earlier this year, we brought you the story of 25-year-old computer programmer Maggie K. who fell for a romance scam on Instagram. Her story played out like so many. When she and her online boyfriend finally agreed to meet in person, he claimed he missed his flight and needed money to rebook. Desperate to finally see him, she sent the money and never heard from him again.
But here’s the twist—he wasn’t real in the first place.
When she reported the scam to police, they determined his images were all made with AI. In Maggie’s words, “That was the scariest part—I had trusted someone who never even existed.”
Maggie isn’t alone. Our own research earlier this year revealed that more than half (52%) of people have been scammed out of money or pressured to send money or gifts by someone they met online.
Moreover, we found that scammers have fueled those figures with the use of AI. Of people we surveyed, more than 1 in 4 (26%) said they—or someone they know—have been approached by an AI chatbot posing as a real person on a dating app or social media.
We expect this trend will only continue, as AI tools make it easier and more efficient to pull off romance scams on an increasingly larger scale.
Even so, the guidelines for avoiding romance scams remain the same:
The job offer sounds simple enough … go online, review products, like videos, or do otherwise simple tasks and get paid doing it—until it’s time to get paid.
It’s a new breed of job scam that took root this spring, one where victims found themselves “paying to get paid.”
The FTC dubbed these scams as “gamified job scams” or “task scams.” Given the way these scams work, the naming fits.
It starts with a text or direct message from a “recruiter” offering work with the promise of making good money by “liking” or “rating” sets of videos or product images in an app, all with the vague purpose of “product optimization.” With each click, you earn a “commission” and see your “earnings” rack up in the app. You might even get a payout, somewhere between $5 and $20, just to earn your trust.
Then comes the hook.
Like a video game, the scammer sweetens the deal by saying the next batch of work can “level up” your earnings. But if you want to claim your “earnings” and book more work, you need to pay up. So you make the deposit, complete the task set, and when you try to get your pay the scammer and your money are gone. It was all fake.
This scam and others like it fall right in line with McAfee data that uncovered a spike in job-related scams of 1,000% between May and July,which undoubtedly built on 2024’s record-setting job scam losses of $501 million.
A proper recruiter will reach out to you by email or via a job networking site. Moreover, per the FTC, any job that pays you to “like” or “rate” content is against the law. That alone says it’s a scam.
In the case of job offers in general, look up the company. Check out their background and see if it matches up with the job they’re pitching. In the U.S., The Better Business Bureau (BBB) offers a list of businesses you can search.
Any case where you’re asked to pay to up front, with any form of payment, refuse, whether that’s for “training,” “equipment,” or more work. It’s a sign of a scam.
Prince Harry, Taylor Swift, and now the Today show’s Al Roker, too, they’ve all found themselves as the AI-generated spokesperson for deepfake scams.
In the past, a deepfake Prince Harry pushed bogus investments, while another deepfake of Taylor Swift hawked a phony cookware deal. Then, this spring, a deepfake of Al Roker used his image and voice to promote a bogus hypertension cure—claiming, falsely, that he had suffered “a couple of heart attacks.”
The fabricated clip appeared on Facebook, which appeared convincing enough to fool plenty of people, including some of Roker’s own friends. “I’ve had some celebrity friends call because their parents got taken in by it,” said Roker.
While Meta quickly removed the video from Facebook after being contacted by TODAY, the damage was done. The incident highlights a growing concern in the digital age: how easy it is to create—and believe—convincing deepfakes.
Roker put it plainly, “We used to say, ‘Seeing is believing.’ Well, that’s kind of out the window now.”
In all, this stands as a good reminder to be skeptical of celebrity endorsements on social media. If public figure fronts an apparent deal for an investment, cookware, or a hypertension “cure” in your feed, think twice. And better yet, let our Scam Detector help you spot what’s real and what’s fake out there.
And to close things out, a look at some recent news, which also serves as a look ahead.
Last September, researchers spotted something unseen before:a cyberattack almost entirely run by agentic AI.
What is Agentic AI?
Definition: Artificial intelligence systems that can independently plan, make decisions, and work toward specific goals with minimal human intervention; in this way, it executes complex tasks by adapting to new info and situations on its own.
Reported by AI researcher Anthropic, a Chinese state-sponsored group allegedly used the company’s Claude Code agent to automate most of an espionage campaign across nearly thirty organizations. Attackers allegedly bypassed guardrails that typically prevent such malicious use with jailbreaking techniques, which broke down their attacks into small, seemingly innocent tasks. That way, Claude orchestrated a large-scale attack it wouldn’t otherwise execute.
Once operational, the agent performed reconnaissance, wrote exploit code, harvested credentials, identified high-value databases, created backdoors, and generated documentation of the intrusion. By Anthropic’s estimate, they completed 80–90% of the work without any human involvement.
According to Anthropic: “At the peak of its attack, the AI made thousands of requests, often multiple per second—an attack speed that would have been, for human hackers, simply impossible to match.”
We knew this moment was coming, and now the time has arrived: what once took weeks of human effort to execute a coordinated attack now boils down to minutes as agentic AI does the work on someone’s behalf.
In 2026, we can expect to see more attacks led by agentic AI, along with AI-led scams as well, which raises an important question that Anthropic answers head-on:
If AI models can be misused for cyberattacks at this scale, why continue to develop and release them? The answer is that the very abilities that allow Claude to be used in these attacks also make it crucial for cyber defense. When sophisticated cyberattacks inevitably occur, our goal is for Claude—into which we’ve built strong safeguards—to assist cybersecurity professionals to detect, disrupt, and prepare for future versions of the attack.
That gets to the heart of security online: it’s an ever-evolving game. As new technologies arise, those who protect and those who harm one-up each other in a cycle of innovation and exploits. As we’re on the side of innovation here, you can be sure we’ll continue to roll out protections that keep you safer out there. Even as AI changes the game, our commitment remains the same.
We’re taking a little holiday break here and we’ll be back with our weekly roundups again in 2026. Looking forward to catching up with you then and helping you stay safer in the new year.
The post This Year in Scams: A 2025 Retrospective, and a Look Ahead at 2026 appeared first on McAfee Blog.

If you’re in the market for insurance right now, keep an eye out for scammers in the mix. They’re out in full force once again this open enrollment season.
As people across the U.S. sign up for, renew, or change their health insurance plans, scammers want to cash in as people rush to get their coverage set. And scammers have several factors working in their favor.
For starters, many people find the insurance marketplace confusing, frustrating, and even intimidating, all feelings that scammers can take advantage of. Moreover, concerns about getting the right level of coverage at an affordable price also play into the hands of scammers.
Amidst all this uncertainty and time pressure, health insurance scams crop up online. Whether under the guise of helping people navigate the complex landscape or by offering seemingly low-cost quotes, scammers prey on insurance seekers by stealing their personal information, Social Security numbers, and money.
According to the FBI, health insurance scams cost families millions each year. In some cases, the costs are up front. People pay for fraudulent insurance and have their personal info stolen. And for many, the follow-on costs are far worse, where victims go in for emergency care and find that their treatment isn’t covered—leaving them with a hefty bill.
Like so many of the scams we cover here in our blogs, you can spot health insurance scams relatively quickly once you get to know their ins and outs.
Here’s how some of those scams can play out.
Some are “one and done scams” where the scammer promises a policy or service and then disappears after stealing money and personal info—much like an online shopping scam. It’s a quick and dirty hit where scammers quickly get what they want by reaching victims the usual ways, such as through texts, emails, paid search results, and social media. In the end, victims end up on a phishing site where they think they’re locking in a good deal but handing over their info to scammers instead.
Other scams play a long con game, milking victims for thousands and thousands of dollars over time. The following complaint lodged by one victim in Washington state provides a typical example:
A man purchased a plan to cover himself, his wife, and his two children, only to learn there was no coverage. He was sold a second policy, with the same result, and offered a refund if he purchased a third policy. When he filed a complaint, his family still had no coverage, and he was seeking a refund for more than $20,000 and reimbursement for $55,000 in treatments and prescriptions he’d paid out of pocket.
Scams like these are known as ghost broker scams where scammers pose as insurance brokers who take insurance premiums and pocket the money, leaving victims thinking they have coverage when they don’t. In some cases, scammers initially apply for a genuine policy with a legitimate carrier, only to cancel it later, while still taking premiums from the victim as their “broker.” Many victims only find out that they got scammed when they attempt to file a claim.
Another type of scam comes in the form of policy cancellation scams. These work like any number of other account-based scams, where a scammer pretends to be a customer service rep at a bank, utility, or credit card company. In the insurance version of it, scammers email, text, or call with some bad news—the person’s policy is about to get cancelled. Yet not to worry, the victim can keep the policy active they hand over some personal and financial info. It’s just one more way that scammers use urgency and fear to steal to commit identity theft and fraud.
As said, health insurance scams become relatively easy to spot once you know the tricks that scammers use. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) offers up its list of the ones they typically use the most:
1)Someone says they’re from the government and need money or your personal info.Government agencies don’t call people out of the blue to ask them for money or personal info. No one from the government will ask you to verify your Social Security, bank account, or credit card number, and they won’t ask you to wire money or pay by gift card or cryptocurrency.
If you have a question about Health Insurance Marketplace®, contact the government directly at: HealthCare.gov or 1-800-318-2596
2) Someone tries to sell you a medical discount plan. Legitimate medical discount plans differ from health insurance. They supplement it. In that way, they don’t pay for any of your medical expenses. Rather, they’re membership programs where you pay a recurring fee for access to a network of providers who offer their services at pre-negotiated, reduced rates. The FTC strongly advises thorough research before participating in one, as some take people’s money and offer very little in return. Call your caregiver and see if they really participate in the program and in what way. And always review the details of any medical discount plan in writing before you sign up.
3) Someone wants your sensitive personal info in exchange for a price quote. The Affordable Care Act’s (ACA’s) official government site is HealthCare.gov. It lets you compare prices on health insurance plans, check your eligibility for healthcare subsidies, and begin enrollment. But HealthCare.gov will only ask for your monthly income and your age to give you a price quote. Never enter personal financial info like your Social Security number, bank account, or credit card number to get a quote for health insurance.
4) Someone wants money to help you navigate the Health Insurance Marketplace. The people who offer legitimate help with the Health Insurance Marketplace (sometimes called Navigators or Assisters) are not allowed to charge you and won’t ask you for personal or financial info. If they ask for money, it’s a scam. Go to HealthCare.govand click “Find Local Help” to learn more.
1)For health insurance, visit a trusted source like HealthCare.gov or your state marketplace. Doing so helps guarantee that you’ll get the kind of fully compliant coverage you want.
2) Make sure the insurance covers you in your state. Not every insurer is licensed to operate in your state. Double-check that the one you’re dealing with is. A good place to start is to visit the site for your state’s insurance commission. It should have resources that let you look up the insurance companies, agents, and brokers in your state.
3) For any insurance, research the company offering it. Run a search with the company name and add “scam” or “fraud” to it. See if any relevant news or complaints show up. And if the plan you’re being offered sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
4) Watch out for high-pressure sales. Don’t pay anything up front and be cautious if a company is forcing you to make quick decisions.
5) Guard your personal info. Never share your personal info, account details, or Social Security number over text or email. Make sure you’re really working with a legitimate company and that you submit any info through a secure submissions process.
6) Block bad links to phishing sites. Many insurance scams rely on phishing sites to steal personal info. A combination of our Web Protection and Scam Detector can steer you clear of them. They’ll alert you if a link might take you to one. It’ll also block those sites if you accidentally tap or click on a bad link.
7) Monitor your identity and credit. In some health insurance scams, your personal info winds up in wrong hands, which can lead to identity fraud and theft. And the problem is that you only find out once the damage is done. Actively monitoring your identity and credit can spot a problem before it becomes an even bigger one. You can take care of both easily with our identity monitoring and credit monitoring.
Additionally, our identity theft coverage can help if the unexpected happens with up to $2 million in identity theft coverage and identity restoration support if determined you’re a victim of identity theft.
You’ll find these protections and more in McAfee+.
The post How To Spot Health Insurance Scams This Open Enrollment Season appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Imagine a day where you didn’t have to juggle passwords.
No more sticky notes. No more notebooks with dozens of passwords scribbled in, crossed out, and scribbled in again. No more forgetting and resetting. No more typing them in all the time.
And even better, imagine secure accounts, likely even more secure than you could keep them on your own.
That’s the power of a password manager in your life.
A password manager does the work of creating strong, unique passwords for each and every one of your accounts. And considering the hundred or so accounts you have, that’s something that would take plenty of time if you did all that work on your own.
In all, a password manager can turn the pain of juggling passwords into a real comfort.
Before we get into how a password manager can make your life easier while making your accounts more secure, let’s look at what makes up a bad password. Here are a few examples:
Obvious passwords: Password-cracking programs start by entering a list of common (and arguably lazy) passwords. These may include the simple “password” or “1234567”. Others include common keyboard paths like “qwerty.” Even longer keyboard paths like “qwertyuiop” are well known to hackers and their tools as well.
Dictionary words: Hacking tools also look for common dictionary words strung together, which helps them crack longer passwords in chunks. The same goes for passwords that contain the name of the app or service in them. These are “no brainer” words found in passwords that make passwords even easier to crack.
Repeated passwords: You may think you have such an unbreakable password that you want to use it for all your accounts. However, this means that if hackers compromise one of your accounts, all your other accounts are vulnerable. This is a favorite tactic of hackers. They’ll target less secure accounts and services and then attempt to re-use those credentials on more secure services like online bank and credit card companies.
Personal information passwords: Passwords that include your birthday, dog’s name, or nickname leave you open to attack. While they’re easy for you to remember, they’re also easy for a hacker to discover—such as with a quick trip to your social media profile, particularly if it is not set to private.
If any of the above sounds familiar, you’ll want to replace any of your bad passwords with strong ones.
We can point to three things that make up a strong password, which makes it difficult to hack.
Your password is:
Long: A longer password is potentially a stronger password when it comes to a “brute force” attack, where a hacker uses an automated trial-and-error system to break it. For example, an eight-character password using uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols can get hacked in minutes. Kick it up to 16 characters and it becomes incredibly more difficult to break—provided it doesn’t rely on common words or phrases. McAfee can help you generate a strong password, for stronger security with our random password generator.
Complex: To increase the security of your password, it should have a combination of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, symbols, and numbers like mentioned above.
Unique: Every one of your accounts should have its own password.
Now, apply this to the hundred or so accounts you keep and creating strong passwords for all of them really does call for a lot of work.
Given its ease of use and the big security boost it gives you and all your accounts, the answer is yes.
A password manager does the work of creating strong, unique passwords for your accounts. These will take the form of a string of random numbers, letters, and characters. They won’t be memorable, but the manager does the memorizing for you. You only need to remember a single password to access the tools of your manager.
A strong password manager also stores your passwords securely. Our password manager protects your passwords by scrambling them with AES-256, one of the strongest encryption algorithms available. Only you can decrypt and access your info with the factors you choose. Additionally, our password manager uses multi-factor authentication (MFA), so you’ll be verified by at least two factors before being signed in.
Aside from the comfort of convenience a password manager can give you, it gives you another level of assurance—extra protection in an age of data breaches, because you’ll have unique passwords where one compromise won’t lead to others.
And whether or not you go with a password manager to create those strong and unique passwords, make sure you use MFA on every account that offers it. MFA offers another layer of protection by adding another factor into the login process, such as something you own like a text to your phone or notification to an authentication app. That way if a hacker has your password, they’ll still be locked out of your account because they lack that MFA code.
In some cases, you really don’t need some of your old accounts and the passwords that come along with them. Maybe they’re old and unused. Or maybe they were for a one-time purchase at an online store you won’t visit again. Deleting these accounts is a smart move because they’re yet more places where your personal info is stored—and subject to a data breach.
Our Online Account Cleanup can help, which you can find in all our McAfee+ plans. It scans for accounts in your name, gives you a full list, and shows you which types of accounts might be riskier than others. From there you can decide which ones you want to delete, along with the personal info linked to them. In our McAfee+ Ultimate plans, you get full-service Online Account Cleanup, which sends the data deletion requests for you.
Between this and a password manager, you’ll have one less thing to juggle—your passwords, and one less thing to worry about—if they’re secure from hackers.
The post Why “Strong Passwords” Aren’t Enough Anymore—and What to Do Instead appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Pets, poisoned AI search results, and a phone call that sounds like it’s coming straight from the federal government, this week’s scams don’t have much in common except one thing: they’re getting harder to spot.
In today’s edition of This Week in Scams, we’re breaking down the biggest security lapses and the tactics scammers used to exploit them, and what you can do to stay ahead of the latest threats.
If you’re a Petco customer, you’ll want to know about not one but two data security lapses in the past week.
First, as reported by TechCrunch on Monday, Petco followed Texas data privacy laws by filing a data breach with the attorney general’s office. In that filing, Petco reported that the affected data included names, Social Security numbers, and driver’s license numbers. Further info including account numbers, credit and debit card numbers, and dates of birth were also mentioned in the filing.
Also according to Techcrunch, the company filed similar notices in California and Massachusetts.
To date, Petco has not made a comment about the size of the breach and the number of people affected.
Different states have different policies for reporting data breaches. In some cases, that helps us put a figure to the size of the breach, as some states require companies to disclose the total number of people caught up in the breach. That’s not the case here, so the full scope of the attack remains in question, at least for right now.
As of Thursday, we know Petco reported that 329 Texans were affected along with seven Massachusetts residents, per the respective reports filed. California’s report does not contain the number of Californians affected, yet laws in that state require businesses to report breaches that affect 500 or more people, so at least 500 people were affected there.
Below you can see the form letter Petco sent to affected Californians in accordance with California’s data privacy laws:

In it, you can see that Petco discovered that “a setting within one of our software applications … inadvertently allowed certain files to become accessible online.” Further, Petco said that it “immediately took steps to correct the issue and to remove the files from further online access,” and that it “corrected” the setting and implemented unspecified “additional security measures.”
So while no foul play appears to have been behind the breach, it’s still no less risky and concerning for Petco’s customers. We’ll cover what you can do about that in a moment after we cover yet another data issue at Petco through its Vetco clinics.
Also within the same timeframe, yet more research and reporting from Techcrunch uncovered a second security lapse that exposed personal info online. From their article:
“TechCrunch identified a vulnerability in how Vetco’s website generates copies of PDF documents for its customers.
“Vetco’s customer portal, located at petpass.com, allows customers to log in and obtain veterinary records and other documents relating to their pet’s care. But TechCrunch found that the PDF generating page on Vetco’s website was public and not protected with a password.
“As such, it was possible for anyone on the internet to access sensitive customer files directly from Vetco’s servers by modifying the web address to input a customer’s unique identification number. Vetco customer numbers are sequential, which means one could access other customers’ data simply by changing a customer number by one or two digits.”
With the size and reach of the Petco breach still unknown, and the impact of the Vetco security lapse also unknown, we advise caution for all Petco customers. At minimum, monitor transactions and keep an eye on your credit report for any suspicious activity. And it’s always a good time to update a weak password.
For those who received a notification, we advise the following:
Check your credit, consider a security freeze, and get ID theft protection. You can get all three working for you with McAfee+ Advanced or McAfee+ Ultimate.
Monitor transactions across your accounts, also available in McAfee+ Advanced and Ultimate.
Keep an eye out for phishing attacks. Use our Scam Detector to spot any follow-on attacks.
Update your passwords. Strong and unique passwords are best. Our password manager can help you create and store them securely.
And use two-factor authentication on all your accounts. Enabling two-factor authentication provides an added layer of security.

What to do if your Social Security number was breached.
If you think your Social Security number was caught up in the breach, act quickly.
You might want to be careful when searching for customer service numbers while in AI mode. Or with an AI search engine. It could connect you to a scammer.
From The Times comes reports of scammers manipulating the AI in platforms like Google and Perplexity so that their search results return scam numbers instead of a proper customer service numbers for, say, British Airways.
How do they manipulate those results? By spamming the internet with false info that gets picked up and then amplified by AI.
“[S]cammers have started seeding fake call center numbers on the web so the AI is tricked into thinking it is genuine …
“Criminals have set up YouTube channels with videos claiming to help with customer support, which are packed with airline brand names and scam numbers designed to be scraped and reused by the AI.
“Bot-generated reviews on Yelp or video descriptions on YouTube are filled with fraudulent numbers as are airline and travel web forums.”
And with these tactics, scammers could poison the results for just about any organization, business, or brand. Not just airlines. Per The Times, “The scammers have also hijacked government sites, university domains, and even fitness sites to place scam numbers, which fools the AI into thinking they are genuine.”
This reveals a current limitation with many AI platforms. Largely they can’t distinguish when people deliberately feed them bad info, as seen in the case here.
Yet even as this attack is new, our advice remains the same: any time you want to ring up a customer service line, get the number directly from the company’s official website. Not from AI search and not by clicking a paid search result that shows up first (scammers can poison them too).
Are you under investigation for money laundering? Of course not. But this scam wants you to think so—and to pay up.
On Tuesday, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) issued a consumer alert warning that people are reporting getting unexpected calls from someone saying they’re “FTC agent” John Krebs. Apparently “Agent Krebs” is telling people that they’re under investigation for money laundering—and that a deposit to a Bitcoin ATM can resolve the matter.
Of course, it’s a scam.
For starters, the FTC doesn’t have “agents.” And the idea of clearing one’s name in an investigation with a Bitcoin payment is a sure-fire sign of a scam. Lastly, any time someone asks for payment with Bitcoin or other payment methods that are near-impossible to recover (think wire transfers and gift cards), those are big red flags.
Apart from hanging up and holding on to your money, the FTC offers the following guidance, which holds true for any scam call:
As always, here’s a quick list of a few stories that caught our eye this week:
AI tools transform Christmas shopping as people turn to chatbots
National cybercrime network operating for 14 years dismantled in Indonesia
Why is AI becoming the go-to support for our children’s mental health?
We’ll see you next Friday with a special edition to close out 2025 … This Year in Scams.
The post This Week in Scams: Petco Breach Warning, and Watch Out for Fake Federal Calls appeared first on McAfee Blog.

It looks harmless enough.
A digital party invitation lands in your inbox or phone. You click to see the details. Then it asks you to log in or create an account before revealing the event.
That’s where the scam begins.
Fake e-vite phishing scams are on the rise, and they take advantage of something simple: social trust. You’re far more likely to click an invitation than a generic “account alert” or “delivery notice.”
And that’s exactly why scammers are using them.
In fact, here’s a screenshot of a fake phishing email I recently got this holiday season:

When you click the “open invitation” link, it immediately asks you to sign in or create an account with your personal information. That’s the step where scammers steal your private data.
A fake e-vite scam is a phishing attack that pretends to be a real invitation from platforms like Paperless Post or other digital invitation services.
The goal is to trick you into:
Once scammers have your login information, they can:
Here’s the most common flow:
Because this starts with something familiar and social, many people don’t realize it’s phishing until accounts are already compromised. Plus, scammers then use your email and name to trick friends and family into trusting more fake e-vites from your account.
Paperless Post has publicly acknowledged these scams and shared what legitimate messages actually look like.
Legitimate Paperless Post Emails Will Never:
Official Paperless Post Email Domains:
Legitimate invitations and account messages only come from:
Official support emails only come from:
If the sender does not match one of these exactly, it’s a scam.
Paperless Post also notes that verified emails may display a blue checkmark in supported inboxes to confirm authenticity.
If you see any of the following, do not click:
Modern phishing attacks don’t rely on sloppy design anymore. Many now use:
Invitation phishing is especially powerful because:
If you entered any information into a suspicious invitation page:
The faster you act, the more damage you can prevent.
The post Think That Party Invite Is Real? Fake E-Vite Scams Are the New Phishing Trap appeared first on McAfee Blog.

AI-powered browsers give you much more than a window to the web. They represent an entirely new way to experience the internet, with an AI “agent” working by your side.
We’re entering an age where you can delegate all kinds of tasks to a browser, and with that comes a few things you’ll want to keep in mind when using AI browsers like ChatGPT’s Atlas, Perplexity’s Comet, and others.
So, what’s the allure of this new breed of browser? The answer is that it’s highly helpful, and plenty more.
By design, these “agentic” AI browsers actively assist you with the things you do online. They can automate tasks and interpret your intentions when you make a request. Further, they can work proactively by anticipating things you might need or by offering suggestions.
In a way, an AI browser works like a personal assistant. It can summarize the pages in several open tabs, conduct research on just about any topic you ask it to, or even track down the lowest airfare to Paris in the month of May. Want it to order ink for your printer and some batteries for your remote? It can do that too. And that’s just to name a few possibilities.
As you can see, referring to the AI in these browsers as “agentic” fits. It truly works like an agent on your behalf, a capability that promises to get more powerful over time.
But as with any new technology, early adopters should balance excitement with awareness, especially when it comes to privacy and security. You might have seen some recent headlines that shared word of security concerns with these browsers.
The reported exploits vary, as does the harm they can potentially inflict. That ranges from stealing personal info, gaining access to Gmail and Google Drive files, installing malware, and injecting the AI’s “memory” with malicious instructions, which can follow from session to session and device to device, wherever a user logs in.
Our own research has shown that some of these attacks are now tougher to pull off than they were initially, particularly as the AI browser companies continue to put guardrails in place. If anything, this reinforces a long-standing truth about online security, it’s a cat-and-mouse game. Tech companies put protections in place, bad actors discover an exploit, companies put further protections in place, new exploits crop up, and so on. It’s much the same in the rapidly evolving space of AI browsers. The technology might be new, but the game certainly isn’t.
While these reports don’t mean AI browsers are necessarily unsafe to use, they do underscore how fast this space is evolving…and why caution is smart as the tech matures.
It’s still early days for AI-powered browsers and understanding the security and privacy implications of their use. With that, we strongly recommend the following to help reduce your risk:
Don’t let an AI browser do what you wouldn’t let a stranger do. Handle things like your banking, finances, and health on your own. And the same certainly goes for all the info tied to those aspects of your life.
Pay attention to confirmations. As of today, agentic browsers still require some level of confirmation from the user to perform key actions (like processing a payment, sending an email, or updating a calendar entry). Pay close attention to them, so you can prevent your browser from doing something you don’t want it to do.
Use the “logged out” mode, if possible. As of this writing, at least one AI browser, Atlas, gives you the option to use the agent in the logged-out mode.i This limits its access to sensitive data and the risk of it taking actions on your behalf with your credentials.
If possible, disable “model learning.” By turning it off, you reduce the amount of personal info stored and processed by the AI provider for AI training purposes, which can minimize security and privacy risks.
Set privacy controls to the strictest options available. Further, understand what privacy policies the AI developer has in place. For example, some AI providers have policies that allow people to review your interactions with the AI as part of its training. These policies vary from company to company, and they tend to undergo changes. Keeping regular tabs on the privacy policy of the AI browser you use makes for a privacy-smart move.
Keep yourself informed. The capabilities, features, and privacy policies of AI-powered browsers continue to evolve rapidly. Set up news alerts about the AI browser you use and see if any issues get reported and, if so, how the AI developer has responded. Do routine searches pairing the name of the AI browser with “privacy.”
McAfee’s award-winning protection helps you browse safer, whether you’re testing out new AI tools or just surfing the web.
McAfee offers comprehensive privacy services, including personal info scans and removal plus a secure VPN.
Plus, protections like McAfee’s Scam Detector automatically alert you to suspicious texts, emails, and videos before harm can happen—helping you manage your online presence confidently and safeguard your digital life for the long term. Likewise, Web Protection can help you steer you clear of suspicious websites that might take advantage of AI browsers.
The post How to Stay Safe on Your New AI Browser appeared first on McAfee Blog.

For this week in scams, we have fake AI-generated shopping images that could spoil your holidays, scammers use an Apple Support ticket in a takeover attempt, and a PlayStation scam partly powered by AI.
Let’s start with those fake ads, because holiday shopping is in full swing.
Turns out that three-quarters of people (74%) can’t correctly identify a fake AI-generated social media ad featuring popular holiday gifts—which could leave them open to online shopping scams.
That finding, and several others, comes by way of research from Santander, a financial services company in the UK.
Here’s a quick rundown of what else they found:
From the study … could you tell these ads are both fake?


In all, cheap and readily available AI tools make spinning up fake ads quick and easy work. The same goes for launching websites where those “goods” can get sold. In the past, we’ve seen scammers take two different approaches when they use social media ads and websites to lure in their victims:
During the holidays, scammers pump out ads that offer seemingly outstanding deals on hot items. Of course, the offer and the site where it’s “sold” is fake. Victims hand over their personal info and credit card number, never to see the items they thought they’d purchased. On top of the money a victim loses, the scammer also has their card info and can run up its tab or sell it to others on the dark web.
In this case, the scammer indeed sells and delivers something. But you don’t get what you paid for. The item looks, feels, fits, or works entirely differently than what was advertised. In this way, people wind up with a cheaply made item cobbled together with inferior materials. Worse yet, these scams potentially prop up sweatshops, child labor, and other illegal operations in the process. Nothing about these sites and the things they sell on them are genuine.
So, fake AI shopping ads are out there. What should you look out for? Here’s a quick list:
“I almost lost everything—my photos, my email, my entire digital life.”
So opens a recent Medium post from Eric Moret recounting how he almost handed over his Apple Account to a scammer armed with a real Apple Support ticket to make this elaborate phishing attack look legit.
Over the course of nearly 30 minutes, a scammer calmly and professionally walked Moret through a phony account takeover attempt.
It started with two-factor authentication notifications that claimed someone was trying to access his iCloud account. Three minutes later, he got a call from an Atlanta-based number. The caller said they were with Apple Support. “Your account is under attack. We’re opening a ticket to help you. Someone will contact you shortly.”
Seconds later came another call from the same number, which is where the scam fully kicked in. The person also said they were from Apple Support and that they’d opened a case on Moret’s behalf. Sure enough, when directed, Moret opened his email and saw a legitimate case number from a legitimate Apple address.
The caller then told him to reset his password, which he did. Moret received a text with a link to a site where he could, apparently, close his case.
Note that at no time did the scammers ask him for his two-factor authentication code throughout this process, which is always the sign of a scam. However, the scammers had another way to get it.
The link took him to a site called “appeal-apple dot com,” which was in fact a scam site. However, the page looked official to him, and he entered a six-digit code “confirmation code” sent by text to finish the process.
That “confirmation code” was actually a fresh two-factor authentication code. With that finally in hand, the scammers signed in. Moret received a notice that a new device had logged into his account. Moret quickly reset his password again, which kicked them out and stopped the attack.
Maybe you didn’t get a scam call from “Emma” or “Carl” at Wal-Mart, but plenty of people did. Around eight million in all. Now the Federal Communications Commission’s (FCC) Enforcement Bureau wants to put a stop to them.
“Emma” and “Carl” are in fact a couple of AI voices fronting a scam framed around the bogus purchase of a PlayStation. It’s garnered its share of complaints, so much that the FCC has stepped in. It alleges that SK Teleco, a voice service provider, provisioned at least some of these calls, and that it must immediately stop.
According to the FCC, the call plays out like this:
“A preauthorized purchase of PlayStation 5 special edition with Pulse 3D headset is being ordered from your Walmart account for an amount of 919 dollars 45 cents. To cancel your order or to connect with one of our customer support representatives, please press ‘1.’ Thank you.”
Pressing “1” connects you to a live operator who asks for personal identifiable such as Social Security numbers to cancel the “purchase.”
If you were wondering, it’s unlawful to place calls to cellphones containing artificial or prerecorded voice messages absent an emergency purpose or prior express consent. According to the FCC’s press release, SK Teleco didn’t respond to a request to investigate the calls. The FCC further alleges that it’s unlikely the company has any such consent.
Per the FCC, “If SK Teleco fails to take swift action to prevent scam calls, the FCC will require all other providers to no longer accept call traffic from SK Teleco.”
We’ll see how this plays out, yet it’s a good reminder to report scam calls. When it comes to any kind of scam, law enforcement and federal agencies act on complaints.
Here’s a quick list of a few stories that caught our eye this week:
Scammers pose as law enforcement, threaten jail time if you don’t pay (with audio)
Deepfake of North Carolina lawmaker used in award-winning Brazilian Whirlpool video
What happens when you kick millions of teens off social media? Australia’s about to find out
We’ll see you next Friday with more updates, scam news, and ways you can stay safer out there.
The post This Week in Scams: Phony AI Ads, Apple Account Takeover Attempts, and a PlayStation Scam appeared first on McAfee Blog.
China-based phishing groups blamed for non-stop scam SMS messages about a supposed wayward package or unpaid toll fee are promoting a new offering, just in time for the holiday shopping season: Phishing kits for mass-creating fake but convincing e-commerce websites that convert customer payment card data into mobile wallets from Apple and Google. Experts say these same phishing groups also are now using SMS lures that promise unclaimed tax refunds and mobile rewards points.
Over the past week, thousands of domain names were registered for scam websites that purport to offer T-Mobile customers the opportunity to claim a large number of rewards points. The phishing domains are being promoted by scam messages sent via Apple’s iMessage service or the functionally equivalent RCS messaging service built into Google phones.
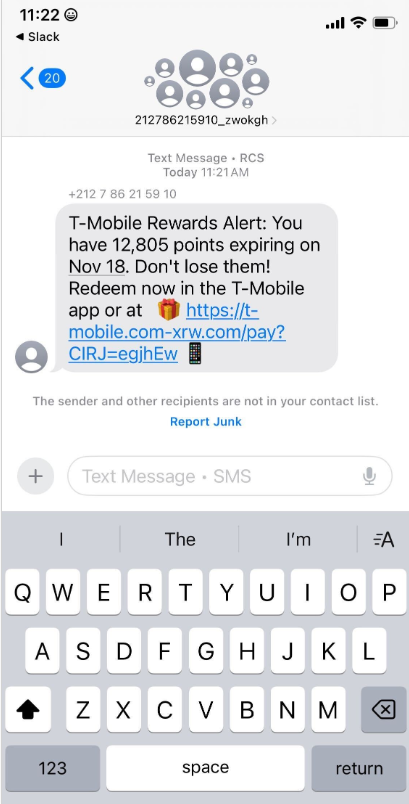
An instant message spoofing T-Mobile says the recipient is eligible to claim thousands of rewards points.
The website scanning service urlscan.io shows thousands of these phishing domains have been deployed in just the past few days alone. The phishing websites will only load if the recipient visits with a mobile device, and they ask for the visitor’s name, address, phone number and payment card data to claim the points.
A phishing website registered this week that spoofs T-Mobile.
If card data is submitted, the site will then prompt the user to share a one-time code sent via SMS by their financial institution. In reality, the bank is sending the code because the fraudsters have just attempted to enroll the victim’s phished card details in a mobile wallet from Apple or Google. If the victim also provides that one-time code, the phishers can then link the victim’s card to a mobile device that they physically control.
Pivoting off these T-Mobile phishing domains in urlscan.io reveals a similar scam targeting AT&T customers:
An SMS phishing or “smishing” website targeting AT&T users.
Ford Merrill works in security research at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group company. Merrill said multiple China-based cybercriminal groups that sell phishing-as-a-service platforms have been using the mobile points lure for some time, but the scam has only recently been pointed at consumers in the United States.
“These points redemption schemes have not been very popular in the U.S., but have been in other geographies like EU and Asia for a while now,” Merrill said.
A review of other domains flagged by urlscan.io as tied to this Chinese SMS phishing syndicate shows they are also spoofing U.S. state tax authorities, telling recipients they have an unclaimed tax refund. Again, the goal is to phish the user’s payment card information and one-time code.
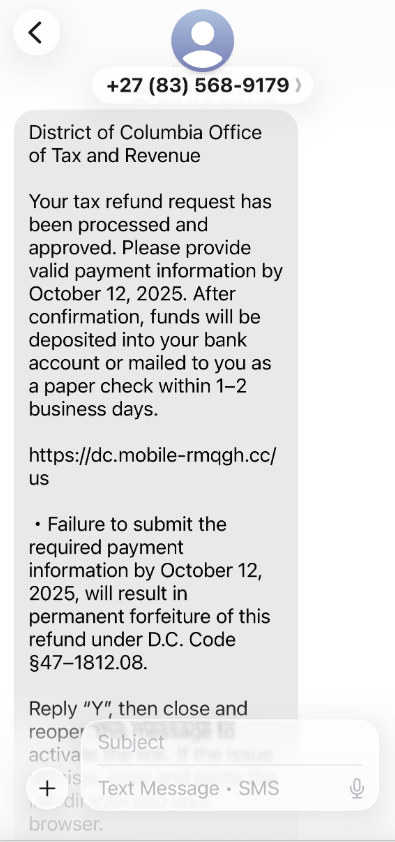
A text message that spoofs the District of Columbia’s Office of Tax and Revenue.
Many SMS phishing or “smishing” domains are quickly flagged by browser makers as malicious. But Merrill said one burgeoning area of growth for these phishing kits — fake e-commerce shops — can be far harder to spot because they do not call attention to themselves by spamming the entire world.
Merrill said the same Chinese phishing kits used to blast out package redelivery message scams are equipped with modules that make it simple to quickly deploy a fleet of fake but convincing e-commerce storefronts. Those phony stores are typically advertised on Google and Facebook, and consumers usually end up at them by searching online for deals on specific products.
A machine-translated screenshot of an ad from a China-based phishing group promoting their fake e-commerce shop templates.
With these fake e-commerce stores, the customer is supplying their payment card and personal information as part of the normal check-out process, which is then punctuated by a request for a one-time code sent by your financial institution. The fake shopping site claims the code is required by the user’s bank to verify the transaction, but it is sent to the user because the scammers immediately attempt to enroll the supplied card data in a mobile wallet.
According to Merrill, it is only during the check-out process that these fake shops will fetch the malicious code that gives them away as fraudulent, which tends to make it difficult to locate these stores simply by mass-scanning the web. Also, most customers who pay for products through these sites don’t realize they’ve been snookered until weeks later when the purchased item fails to arrive.
“The fake e-commerce sites are tough because a lot of them can fly under the radar,” Merrill said. “They can go months without being shut down, they’re hard to discover, and they generally don’t get flagged by safe browsing tools.”
Happily, reporting these SMS phishing lures and websites is one of the fastest ways to get them properly identified and shut down. Raymond Dijkxhoorn is the CEO and a founding member of SURBL, a widely-used blocklist that flags domains and IP addresses known to be used in unsolicited messages, phishing and malware distribution. SURBL has created a website called smishreport.com that asks users to forward a screenshot of any smishing message(s) received.
“If [a domain is] unlisted, we can find and add the new pattern and kill the rest” of the matching domains, Dijkxhoorn said. “Just make a screenshot and upload. The tool does the rest.”
The SMS phishing reporting site smishreport.com.
Merrill said the last few weeks of the calendar year typically see a big uptick in smishing — particularly package redelivery schemes that spoof the U.S. Postal Service or commercial shipping companies.
“Every holiday season there is an explosion in smishing activity,” he said. “Everyone is in a bigger hurry, frantically shopping online, paying less attention than they should, and they’re just in a better mindset to get phished.”
As we can see, adopting a shopping strategy of simply buying from the online merchant with the lowest advertised prices can be a bit like playing Russian Roulette with your wallet. Even people who shop mainly at big-name online stores can get scammed if they’re not wary of too-good-to-be-true offers (think third-party sellers on these platforms).
If you don’t know much about the online merchant that has the item you wish to buy, take a few minutes to investigate its reputation. If you’re buying from an online store that is brand new, the risk that you will get scammed increases significantly. How do you know the lifespan of a site selling that must-have gadget at the lowest price? One easy way to get a quick idea is to run a basic WHOIS search on the site’s domain name. The more recent the site’s “created” date, the more likely it is a phantom store.
If you receive a message warning about a problem with an order or shipment, visit the e-commerce or shipping site directly, and avoid clicking on links or attachments — particularly missives that warn of some dire consequences unless you act quickly. Phishers and malware purveyors typically seize upon some kind of emergency to create a false alarm that often causes recipients to temporarily let their guard down.
But it’s not just outright scammers who can trip up your holiday shopping: Often times, items that are advertised at steeper discounts than other online stores make up for it by charging way more than normal for shipping and handling.
So be careful what you agree to: Check to make sure you know how long the item will take to be shipped, and that you understand the store’s return policies. Also, keep an eye out for hidden surcharges, and be wary of blithely clicking “ok” during the checkout process.
Most importantly, keep a close eye on your monthly statements. If I were a fraudster, I’d most definitely wait until the holidays to cram through a bunch of unauthorized charges on stolen cards, so that the bogus purchases would get buried amid a flurry of other legitimate transactions. That’s why it’s key to closely review your credit card bill and to quickly dispute any charges you didn’t authorize.

Unfortunately, scammers today are coming at us from all angles, trying to trick us into giving up our hard-earned money. We all need to be vigilant in protecting ourselves online. If you aren’t paying attention, even if you know what to look for, they can still catch you off guard. There are numerous ways to detect fake sites, phishing, and other scams, including emails.
Before we delve into the signs of fake websites, we will first take a closer look at the common types of scams that use websites, what happens when you accidentally access a fake website, and what you can do in case you unknowingly purchased items from it.
Fake or scam websites are fraudulent sites that look legitimate while secretly attempting to steal your personal information, money, or account access.
These deceptive platforms masquerade as trustworthy businesses or organizations, sending urgent messages that appear to be from popular shopping websites offering fantastic limited-time deals, banking websites requesting immediate account verification, government portals claiming you owe taxes or are eligible for refunds, and shipping companies asking for delivery fees.
The urgency aims to trick you into logging in and sharing sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, Social Security details, login credentials, and personal data. Once you submit your data, the scammers will steal your identity, drain your accounts, or sell your details to other criminals on the dark web.
These scam websites have become increasingly prevalent because they’re relatively inexpensive to create and can reach millions of potential victims quickly through email and text campaigns, social media ads, and search engine manipulation.
Cybersecurity researchers and consumer protection agencies discover these fraudulent sites through various methods, including monitoring suspicious domain registrations, analyzing reported phishing attempts, and tracking unusual web traffic patterns. According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center, losses from cyber-enabled fraud totaled $13.7 billion, with fake websites accounting for a significant portion of these losses.
Visiting a fake website, accidentally or intentionally, can expose you to several serious security risks that can impact your digital life and financial well-being:
Scammers employ various tactics to create fake websites that appear authentic, but most of these techniques follow familiar patterns. Knowing the main types of scam sites helps you recognize danger faster. This section lists the most common categories of scam websites, explains how they operate, and identifies the red flags that alert you before they can steal your information or money.
Understanding these common scam types helps you recognize fake sites before they can steal your information or money. When in doubt, verify legitimacy by visiting official websites directly through bookmarks or search engines rather than clicking suspicious links.
For the latest warnings and protection guidance, check resources from the Federal Trade Commission and the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
You can protect yourself by learning to recognize the warning signs of fake sites. By understanding what these scams look like and how they operate, you’ll be better equipped to shop, bank, and browse online with confidence. Remember, legitimate companies will never pressure you to provide sensitive information through unsolicited emails or urgent pop-up messages.
Most scams typically start with social engineering tactics, such as phishing, smishing, and fake social media messages containing suspicious links, before directing you to a fake website.
From these communications, the scammers impersonate legitimate organizations before finally executing their malevolent intentions. To avoid being tricked, it is essential to recognize the warning signs wherever you encounter them.
Fake emails are among the most common phishing attempts you’ll encounter. If you see any of these signs in an unsolicited email, it is best not to engage:
Smishing messages bear the same signs as phishing emails and have become increasingly sophisticated. These fake messages often appear to come from delivery services, banks, or government agencies. Common tactics include fake package delivery notifications, urgent banking alerts, or messages claiming you’ve won prizes or need to verify account information.
Legitimate organizations typically don’t include clickable links in unsolicited text messages, especially for account-related actions. When in doubt, don’t click the link—instead, open your banking app directly or visit the official website by typing the URL manually.
Social media platforms give scammers new opportunities to create convincing fake profiles and pages. They might impersonate customer service accounts, create fake giveaways, or send direct messages requesting personal information. These fake sites often use profile pictures and branding that closely resemble legitimate companies.
Unusual sender behavior is another indicator of a scam across all platforms. This includes messages from contacts you haven’t heard from in years, communications from brands you don’t typically interact with, or requests that seem out of character for the supposed sender.
Scammers have become increasingly cunning in creating fake websites that closely mimic legitimate businesses and services. Here are some real-life examples of how cybercriminals use fake websites to victimize consumers:
Scammers exploit your trust in the United States Postal Service (USPS), designing sophisticated fake websites to steal your personal information, payment details, or money. They know you’re expecting a package or need to resolve a delivery issue, making you more likely to enter sensitive information without carefully verifying the site’s authenticity.
USPS-themed smishing attacks arrive as text messages stating your package is delayed, undeliverable, or requires immediate action. Common phrases include “Pay $1.99 to reschedule delivery” or “Your package is held – click here to release.”
Scammers use various URL manipulation techniques to make their fake sites appear official. Watch for these red flags:
Always verify package information and delivery issues through official USPS channels before taking any action on suspicious websites or messages:
Reporting fake USPS websites helps protect others from falling victim to these scams and assists law enforcement in tracking down perpetrators.
Remember that legitimate USPS services are free for standard delivery confirmation and tracking. Any website demanding payment for basic package tracking or delivery should be treated as suspicious and verified through official USPS channels before providing any personal or financial information.
According to the Federal Trade Commission, tech support scams cost Americans nearly $1.5 billion in 2024. These types of social engineering attacks are increasingly becoming sophisticated, making it more important than ever to verify security alerts through official channels.
Sadly, many scammers are misusing the McAfee name to create fake tech support pop-up scams and trick you into believing your computer is infected or your protection has expired, and hoping you’ll act without thinking.
These pop-ups typically appear while you’re browsing and claim your computer is severely infected with viruses, malware, or other threats. They use official-looking McAfee logos, colors, and messaging to appear legitimate to get you to call a fake support number, download malicious software, or pay for unnecessary services.
Learning to detect fake sites and pop-ups protects you from scams. Be on the lookout for these warning signs:
If you see a suspicious pop-up claiming to be from McAfee, here’s exactly what you should do:
To check if your McAfee protection is genuinely active and up-to-date:
Remember, legitimate McAfee software updates and notifications come through the installed program itself, not through random browser pop-ups. Your actual McAfee protection works quietly in the background without bombarding you with alarming messages.
Stay protected by trusting your installed McAfee software and always verifying security alerts through official McAfee channels, such as your installed McAfee dashboard or the official website.
Be prepared and know how to respond quickly when something doesn’t feel right. If you suspect you’ve encountered a fake website, trust your instincts and take these protective steps immediately.
Recognizing fake sites and emails becomes easier with practice. The key is to trust your instincts—if something feels suspicious or too good to be true, take a moment to verify through official channels. With the simple verification techniques covered in this guide, you can confidently navigate the digital world and spot fake sites and emails before they cause harm.
Your best defense is to make these quick security checks a regular habit—verify URLs, look for secure connections, and trust your instincts when something feels off. Go directly to the source or bookmark your most frequently used services and always navigate to them. Enable two-factor authentication on important accounts, and remember that legitimate companies will never ask for sensitive information via email. Maintaining healthy skepticism about unsolicited communications will protect not only your personal information but also help create a safer online environment for everyone.
For the latest information on fake websites and scams and to report them, visit the Federal Trade Commission’s scam alerts or the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
The post Ways to Tell if a Website Is Fake appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Leading off our news on scams this week, a heads-up for DoorDash users, merchants, and Dashers too. A data breach of an undisclosed size may have impacted you.
Per an email sent by the company to “affected DoorDash users where required,” a third party gained access to data that may have included a mix of the following:
You might have got the email too. And even if you didn’t, anyone who’s used DoorDash should take note.
As to the potential scope of the breach, DoorDash made no comment in its email or a post on their help site. Of note, though, is that one of the help lines cited in their post mentions a French-language number—implying that the breach might affect Canadian users as well. Any reach beyond the U.S. and Canada remains unclear.
Per the company’s Q2 financial report this year, “hundreds of thousands of merchants, tens of millions of consumers, and millions of Dashers across over 30 countries every month.” Stats published elsewhere put the user base at more than 40 million people, which includes some 600,000 merchants.
The company underscored that no “sensitive” info like Social Security Numbers (and potentially Canadian Social Insurance Numbers) were involved in the breach. This marks the third notable breach by the well-known delivery service, with incidents in 2019 and 2022

While the types of info involved here appear to be limited, any time there’s a breach, we suggest the following:
Protect your credit and identity. Checking your credit and getting identity theft protection can help keep you safer in the aftermath of a breach. Further, a security freeze can help prevent identity theft if you spot any unusual activity. You can get all three in place with our McAfee+ Advanced or Ultimate plans.
Keep an eye out for phishing attacks. With some personal info in hand, bad actors might seek out more. They might follow up a breach with rounds of phishing attacks that direct you to bogus sites designed to steal your personal info. As with any text or email you get from a company, make sure it’s legitimate before clicking or tapping on any links. Instead, go straight to the appropriate website or contact them by phone directly. Also, protections like our Scam Detector and Web Protection can alert you to scams and sketchy links before they take you somewhere you don’t want to go.
Update your passwords and use two-factor authentication. Changing your password is a strong preventive measure. Strong and unique passwords are best, which means never reusing your passwords across different sites and platforms. Using a password manager helps you stay on top of it all while also storing your passwords securely.
Even as the FAA lifted recent flight restrictions on Monday morning, scammers are still taking advantage of lingering uncertainty, and upcoming holiday travel, with a spate of flight cancellation scams.
Fake cancellation texts
The first comes via a text message saying that your flight has been cancelled and you must call or rebook quickly to avoid losing your seat—usually in 30 minutes. It’s a typical scammer trick, where they hook you with a combination of bad news and urgency. Of course, the phone number and the site don’t connect you with your airline. They connect you to a scammer, who walks away with your money and your card info to potentially rip you off again.
Fake airline sites in search results
The second uses paid search results. We’ve talked about this trick in our blogs before. Because paid search results appear ahead of organic results, scammers spin up bogus sites that mirror legitimate ones and promote them in paid search. In this way, they can look like a certain well-known airline and appear in search before the real airline’s listing. With that, people often mistakenly click the first link they see. From there, the scam plays out just as above as the scammer comes away with your money and card info.
Q: How can I confirm whether my flight is really canceled?
A: Check directly in your airline’s official app or website. Never click links in texts or emails.
Q: How can I spot a fake airline search result?
A: Look for “Ad”/“Sponsored,” confirm the URL, and check that the site uses HTTPS, not HTTP.
Q: Is there a tool that flags fake booking sites?
A: Scam-spotting tools like Scam Detector and Web Protection can identify sketchy links before you click.
In search, first isn’t always best.
Look closely to see if your top results are tagged with “Sponsored” or “Ad” in some way, realizing it might be in fine print. Further, look at the web address. Does it start with “https” (the “s” means secure), because many scam sites simply use an unsecured “http” site. Also, does the link look right? For example, if you’re searching for “Generic Airlines,” is the link the expected “genericairlines dot-com” or something else? Scammers often try to spoof it in some way by adding to the name or by creating a subdomain like this: “genericairlines.rebookyourflight dot-com.”
Get a scam detector to spot bogus links for you.
Even with these tips and tools, spotting bogus links with the naked eye can get tricky. Some look “close enough” to a legitimate link that you might overlook it. Yet a combination of features in our McAfee+ plans can help do that work for you. Our Scam Detector helps you stay safer with advanced scam detection technology built to spot and stop scams across text messages, emails, and videos. Likewise, our Web Protection will alert you if a link might take you to a sketchy site. It’ll also block those sites if you accidentally tap or click on a bad link.
You’ve probably seen plenty of messages sent by short code numbers. They’re the five- or six-digit codes used to send texts instead of by a phone number. For example, your cable company might use one to send a text for resetting a streaming password, the same goes for your pharmacy to let you know a prescription is ready or your state’s DoT to issue a winter travel alert, and so on.
According to NBC News, scammers sent hundreds of thousands of texts using codes used by the state of New York, a charity, and a political organizing group. The article also cites an email sent to messaging providers by the U.S. Short Code Registry, an industry nonprofit that maintains those codes in the U.S. In the email, the registry said attempted attacks on messaging providers are on the rise.
What this means for the rest of us is that just about any text from an unknown number, and now short codes, might contain malicious links and content. It’s one more reason to arm yourself with the one-two punch of our Scam Detector and Web Protection.
What are short codes?
Short codes are 5–6 digit numbers used by pharmacies, utilities, banks, and government agencies to send official alerts.
Why this attack is unusual
Scammers didn’t spoof short codes—they gained access to real ones used by:
Why this matters
Even texts from legitimate short-code numbers can no longer be trusted at face value.
Consumers warned over AI chatbots giving inaccurate financial advice
Why our own clicks are often cybercrime’s greatest allies
TikTok malware scam uses fake software activation guides to steal data
We’ll be back after the Thanksgiving weekend with more updates, scam news, and ways to stay cyber safe.
The post This Week in Scams: DoorDash Breach and Fake Flight Cancellation Texts appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Contactless payments make everyday purchases fast and easy. Yet with that convenience comes a risk: ghost tapping.
In crowded spaces or rushed moments, a scammer could trigger a small tap-to-pay charge or push through a higher amount without your clear consent. Understanding what ghost tapping is, how it happens, and what to do next helps you keep your money and identity secure.
Ghost tapping is a form of contactless fraud where someone attempts to initiate a tap-to-pay transaction without your approval.
Tap-to-pay cards and mobile wallets on phones use a technology called “near-field communication,” or NFC. That lets them communicate with things like a point-of-sale device for payment at a very close range. It’s generally quite safe, particularly because of the “near” part. You have to get very close to make the connection.
Even so, proximity and distraction can be exploited. Attackers may try to skim limited details from RFID (Radio Frequency Identification technology) cards or NFC cards, or nudge you into approving a payment you didn’t intend. If you’ve ever wondered what ghost tapping is, think of it as an opportunistic, in-person scam that abuses the tap-to-pay moment rather than a remote hack.
Most schemes rely on getting close and catching you off guard. A criminal might carry a portable reader, press into a pocket or bag, and attempt a low-value charge. Others set up tampered terminals, rushing you so you don’t check the amount.
You’re at a busy farmer’s market. A scammer with a phone equipped with a point-of-sale app stumbles into you and gets close enough to your card to trigger a transaction. It’s almost like a modern-day pickpocket move, where the bump distracts the victim from the theft as it happens.
In another case, you might come across a phony vendor. Maybe someone’s selling cheap hats outside a football game or someone’s going around your neighborhood selling candy, supposedly to support a charity. In scenarios like these, you tap to pay with your phone just as you’d expect… but with one exception: the “vendor” jacks up the purchase price. They hurry you through the transaction, so quickly that you don’t review the screen before you confirm payment.
We’ve also seen reports of people getting Apple Pay scammed by impostor merchants who exploit quick taps and small screens. While mobile wallets add strong safeguards, poor visibility and social pressure can still lead to losses.
A report posted on the Scam Tracker at the Better Business Bureau (BBB) shows how the phony vendor version of this scam allegedly played out:
“An individual is going door to door in [location redacted] claiming to be selling chocolate on behalf of [redacted] to support special needs students. He says that he can only accept tap-to-pay to get people to pay with a card. He then charges large amounts to the card without the cardholder being able to see the amount. He got my mother for $537… Another victim for $1100… He changes neighborhoods frequently to avoid getting caught.”
Early ghost detecting starts with vigilance. Watch for unfamiliar small charges, especially after crowded events, and alerts tied to contactless transactions. If you see odd activity tied to RFID cards or NFC cards, act quickly.
Common myths persist. Attackers can’t drain accounts from far away, clone full cards via a tap, or bypass wallet protections easily. Most successful cases hinge on proximity, distraction, and human error. Meanwhile, Apple Pay scam stories often involve rushed taps and unverified totals.
Effective ghost detecting focuses on timely alerts, careful review, and immediate response.
The BBB, which recently broke the story of these scams, offers several pieces of advice. We have some advice we can add as well.
From the BBB…
From us at McAfee…
The problem with many card scams is that they can lead to further identity theft and fraud, which you only find out about once the damage is done. Actively monitoring your identity and credit goes beyond single transaction alerts from your bank and can spot an emerging problem before it becomes an even bigger one. You can take care of both easily with timely notifications from our credit monitoring and identity monitoring features, all as part of our McAfee+ plans.
The physical safety of your phone and cards counts as well. While ghost tapping scams are new, old-school physical pickpocketing attempts persist. When it comes to devices and things like debit cards, credit cards, and even cash, keep what you bring with you to the bare minimum when you go out. This can cut your losses if the unfortunate happens. If you have a credit card and ID holder attached to the back of your phone, you may want to remove your cards from it. That way, if your phone gets snatched, those important cards don’t get snatched as well.
In the U.S., credit cards offer you additional protection that debit cards don’t. That’s thanks to the Fair Credit Billing Act (FCBA). It limits your liability to $50 for fraudulent charges on a credit card if you report the loss to your issuer within 60 days.
The post Ghost Tapping: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Stay Safe appeared first on McAfee Blog.

As the holiday season ramps up, so do group dinners, shared travel costs, gift exchanges, and all the little moments where someone says, “Just Venmo me.”
With more people sending and splitting money this time of year, scammers know it’s prime time to target payment apps. Here’s how to keep your Venmo transactions safe during one of the busiest — and riskiest — payment seasons.
Venmo scams come in all shapes, and many of them look like variations of email phishing and text scams. The scammers behind them will pose as Venmo customer service reps who ask for your login credentials. Other scammers offer bogus cash prizes and pyramid schemes that lure in victims with the promise of quick cash. Some scammers will use the app itself to impersonate friends and family to steal money.
Venmo has a dedicated web page on the topic of scams, and lists the following as the top Venmo scams out there:
| · Fake Prize or Cash Reward
· Call from Venmo · Call from Tech Support · Fake Payment Confirmation · Pre-payment for Goods and Services |
· Stranger Posing as a Friend
· Payments from Strangers · Offers to Make Money Fast · Paper Check Scam · Romance Scam |
Venmo has thorough instructions to combat these scams and breaks them down in detail on its site. They also provide preventative tips and steps to take if you unfortunately fall victim to one of these scams. Broadly speaking, though, avoiding Venmo scams breaks down into a few straightforward steps.
1) Never share private details.
Scammers often pose as customer service reps to pump info out of their victims. They’ll ask for things like bank account info, debit card or credit card numbers, or even passwords and authentication codes sent to your phone. Never share this info. Legitimate reps from legitimate companies like Venmo won’t request it.
2) Know when Venmo might ask for your Social Security number.
In the U.S., Venmo is regulated by the Treasury Department. As such, Venmo might require your SSN in certain circumstances. Venmo details the cases where they might need your SSN for reporting, here on their website. Note that this is an exception to what we say about sharing SSNs and tax ID numbers. As a payment app, Venmo might have legitimate reasons to request it. However, don’t send this info by email or text (any email or text that asks you to do that is a scam). Instead, always use the mobile app by going to Settings –> Identity Verification.
3) Keep an eye out for scam emails and texts.
Venmo always sends communications through its official “venmo.com” domain name. If you receive an email that claims to be from Venmo but that doesn’t use “venmo.com,” it’s a scam. Never click or tap on links in emails or texts supposedly sent by Venmo.
4) Be suspicious of the messages you get. Imposters are afoot.
Another broad category of scams includes people who aren’t who they say they are. In the case of Venmo, scammers will create imposter accounts that look like they might be a friend or family member but aren’t. If you receive an unexpected and likely urgent-sounding request for payment, contact that person outside the app. See if it’s really them.
5) When sending money, keep an eye open for alerts from the app.
Just recently, Venmo added a new feature, dynamic alerts, which helps protect people when sending money via the “Friends and Family” option. It pops up an alert if the app detects a potentially fraudulent transaction and includes info that describes the level of risk involved. In the cases of highly risky payments, Venmo might decline the transaction altogether. This adds another level of protection to Friends and Family payments, which are non-refundable in cases of fraud. Further, this underscores another important point about using Venmo: only pay people you absolutely know and trust.
Keep your transactions private. Venmo has a social component that can display a transaction between two people and allow others to comment on it. Payment amounts are always secret. Yet you have control over who sees what by adjusting your privacy settings:
This brings up the question, what if the participants in the transaction have different privacy settings? Venmo uses the most restrictive one. So, if you’re paying someone who has their privacy set to “Public” and you have yours set to “Private,” the transaction will indeed be private.
We suggest going private with your account. The less financial information you share, the better. You can set your transactions to private by heading into the Settings of the Venmo app, tapping on Privacy, and then selecting Private.
In short, just because something is designed to be social doesn’t mean it should become a treasure trove of personal data about your spending habits.
Add extra layers of security. Take extra precautions that make it difficult for others to access your Venmo app.
Online protection software like ours offers several additional layers of security when it comes to your safety and finances online.
For starters, it includes Web Protection and Scam Detector that can block malicious and questionable links that might lead you down the road to malware or a phishing scam, such as a phony Venmo link designed to steal your login credentials. It also includes a password manager that creates and stores strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts.
Moreover, it further protects you by locking down your identity online. Transaction Monitoring and Credit Monitoring help you spot any questionable financial activity quickly. And if identity theft unfortunately happens to you, up to $2 million in ID theft coverage & restoration can help you recover quickly.
The post Venmo 101: Making Safer Payments with the App appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Welcome back to another This Week in Scams.
This week, have attacks that take over Androids and iPhones, plus news that Google has gone on the offensive against phishing websites.
First up, a heads-up for iPhone owners.
In the hands of a scammer, “Find My” can quickly turn into “Scam Me.”
Switzerland’s National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) shared word this week of a new scam that turns the otherwise helpful “Find My” iOS feature into an avenue of attack.
Now, the thought of losing your phone, along with all the important and precious things you have on it, is enough to give you goosebumps. Luckily, the “Find My” can help you track it down and even post a personalized message on the lock screen to help with its return. And that’s where the scam kicks in.
From the NCSC:
When a device is marked as lost, the owner can display a message on the lock screen containing contact details, such as a phone number or email address. This can be very helpful if the finder is honest – but in dishonest hands, the same information can be used to launch a targeted phishing attack.
With that, scammers send a targeted phishing text, as seen in the sample provided by the NCSC below …

What do the scammers want once you tap that link? They request your Apple ID and password, which effectively hands your phone over to them—along with everything on it and everything else that’s associated with your Apple ID.
It’s a scam you can easily avoid. So even if you’re still stuck with a lost phone that’s likely in the hands of a scammer the point of consolation is that, without your ID, the phone is useless to them.
Ignore such messages. The most important rule is Apple will never contact you by text message or email to inform you that a lost device has been found.
Never click on links in unsolicited messages or enter your Apple ID credentials on a linked website.
If you lose your device, act immediately. Enable Lost Mode straight away via the Find My app on another device or at iCloud.com/find. This will lock the device.
Be careful about which contact details you show on your lost device’s lock screen. For example, use a dedicated email address created specifically for this purpose. Never remove the device from your Apple account, as this would disable the Activation Lock.
Make sure your SIM card is protected with a PIN. This simple yet effective measure prevents criminals from gaining access to your phone number.
Now, a different attack aimed at Android owners …
A story shared on Fox this week breaks down how a combination of paid search ads, remote access tools, and social engineering have led to hijacked Android phones.
It starts with a search, where an Android owner looks up a bank, a tech support company, or what have you. Instead of getting a legitimate result, they get a link to a bogus site via paid search results that appear above organic search results. The link, and the page it takes them to, look quite convincing, given the ease with which scammers can spin up ads and sites today. (More on that next.)
Once there, they call a support number and get connected to a phony agent. The agent convinces the victim to download an app that will help the “agent” solve their issue with their account or phone. In fact, the app is a remote access tool that gives control of the phone, and everything on it, to the scammer. That means they can steal passwords, send messages to friends, family, or anyone at all, and even go so far as to lock you out.
Basically, this scam hands over one of your most precious possessions to a scammer.
Skip paid search results for extra security. That’s particularly true when contacting your bank or other companies you’re doing business with. Look for their official website in the organic search results below paid ads. Better yet, contact places like your bank or credit card company by calling the number on the back of your card.
Get a scam detector. A combination of our Scam Detector and Web Protection can call out sketchy links, like the bogus paid links here. They’ll even block malicious sites if you accidentally tap a bad link.
Never download apps from third-party sites outside of the Google Play Store. Google has checks in place to spot malicious apps in its store.
Lastly, never give anyone access to your phone. No bank rep needs it. So if someone on a call asks you to download an app like TeamViewer, AnyDesk, or AirDroid, it’s a scam. Hang up.
Beyond that, you can protect yourself further by installing an app like our McAfee Security: Antivirus VPN. You can pick it up in the Google Play store, which also includes our Scam Detector and Identity Monitoring. You can also get it as part of your McAfee+ protection.
Just Wednesday, Google took a first step toward making the internet safer from bogus sites, per a story filed by National Public Radio.
A lawsuit alleges that a China-based company called “Lighthouse” runs a “Phishing-as-a-Service” operation that outfits scammers with quick and easy tools and templates for creating convincing-looking websites. According to Google’s general counsel, these sites could “compromise between 12.7 and 115 million credit cards in the U.S. alone.”
The suit was filed in the U.S. District Court in the Southern District of New York, which, of course, has no jurisdiction over a China-based company. The aim, per Google’s counsel, is deterrence. From the article:
“It allows us a legal basis on which to go to other platforms and services and ask for their assistance in taking down different components of this particular illegal infrastructure,” she said, without naming which platforms or services Google might focus on. “Even if we can’t get to the individuals, the idea is to deter the overall infrastructure in some cases.”
We’ll keep an eye on this case as it progresses. And in the meantime, it’s a good reminder to get Scam Detector and Web Protection on all your devices so you don’t get hoodwinked by these increasingly convincing-looking scam sites.
Again, scammers can roll them out so quickly and easily today.
Here’s a quick list of a few stories that caught our eye this week:
Alarmingly realistic deepfake threats now target banks in South Africa
Hyundai data breach exposes 2.7 million Social Security numbers
And that’s it for this week! We’ll see you next Friday with more updates, scam news, and ways you can stay safer out there.
The post This Week in Scams: New Alerts for iPhone and Android Users and a Major Google Crackdown appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Google is suing more than two dozen unnamed individuals allegedly involved in peddling a popular China-based mobile phishing service that helps scammers impersonate hundreds of trusted brands, blast out text message lures, and convert phished payment card data into mobile wallets from Apple and Google.
In a lawsuit filed in the Southern District of New York on November 12, Google sued to unmask and disrupt 25 “John Doe” defendants allegedly linked to the sale of Lighthouse, a sophisticated phishing kit that makes it simple for even novices to steal payment card data from mobile users. Google said Lighthouse has harmed more than a million victims across 120 countries.
A component of the Chinese phishing kit Lighthouse made to target customers of The Toll Roads, which refers to several state routes through Orange County, Calif.
Lighthouse is one of several prolific phishing-as-a-service operations known as the “Smishing Triad,” and collectively they are responsible for sending millions of text messages that spoof the U.S. Postal Service to supposedly collect some outstanding delivery fee, or that pretend to be a local toll road operator warning of a delinquent toll fee. More recently, Lighthouse has been used to spoof e-commerce websites, financial institutions and brokerage firms.
Regardless of the text message lure or brand used, the basic scam remains the same: After the visitor enters their payment information, the phishing site will automatically attempt to enroll the card as a mobile wallet from Apple or Google. The phishing site then tells the visitor that their bank is going to verify the transaction by sending a one-time code that needs to be entered into the payment page before the transaction can be completed.
If the recipient provides that one-time code, the scammers can link the victim’s card data to a mobile wallet on a device that they control. Researchers say the fraudsters usually load several stolen wallets onto each mobile device, and wait 7-10 days after that enrollment before selling the phones or using them for fraud.
Google called the scale of the Lighthouse phishing attacks “staggering.” A May 2025 report from Silent Push found the domains used by the Smishing Triad are rotated frequently, with approximately 25,000 phishing domains active during any 8-day period.
Google’s lawsuit alleges the purveyors of Lighthouse violated the company’s trademarks by including Google’s logos on countless phishing websites. The complaint says Lighthouse offers over 600 templates for phishing websites of more than 400 entities, and that Google’s logos were featured on at least a quarter of those templates.
Google is also pursuing Lighthouse under the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations (RICO) Act, saying the Lighthouse phishing enterprise encompasses several connected threat actor groups that work together to design and implement complex criminal schemes targeting the general public.
According to Google, those threat actor teams include a “developer group” that supplies the phishing software and templates; a “data broker group” that provides a list of targets; a “spammer group” that provides the tools to send fraudulent text messages in volume; a “theft group,” in charge of monetizing the phished information; and an “administrative group,” which runs their Telegram support channels and discussion groups designed to facilitate collaboration and recruit new members.
“While different members of the Enterprise may play different roles in the Schemes, they all collaborate to execute phishing attacks that rely on the Lighthouse software,” Google’s complaint alleges. “None of the Enterprise’s Schemes can generate revenue without collaboration and cooperation among the members of the Enterprise. All of the threat actor groups are connected to one another through historical and current business ties, including through their use of Lighthouse and the online community supporting its use, which exists on both YouTube and Telegram channels.”
Silent Push’s May report observed that the Smishing Triad boasts it has “300+ front desk staff worldwide” involved in Lighthouse, staff that is mainly used to support various aspects of the group’s fraud and cash-out schemes.
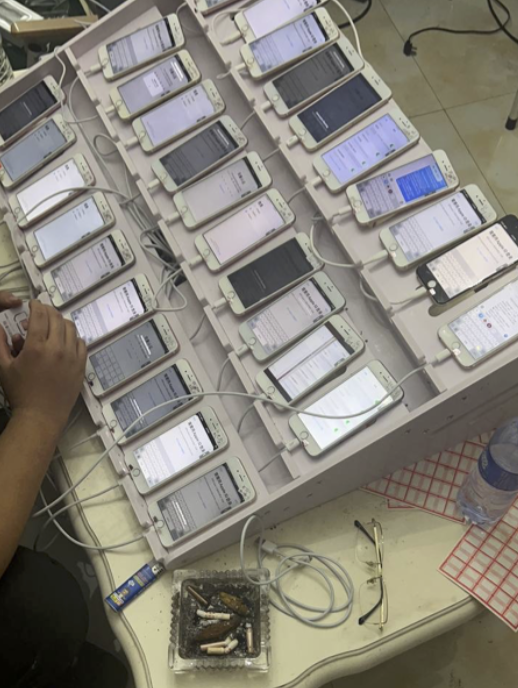

An image shared by an SMS phishing group shows a panel of mobile phones responsible for mass-sending phishing messages. These panels require a live operator because the one-time codes being shared by phishing victims must be used quickly as they generally expire within a few minutes.
Google alleges that in addition to blasting out text messages spoofing known brands, Lighthouse makes it easy for customers to mass-create fake e-commerce websites that are advertised using Google Ads accounts (and paid for with stolen credit cards). These phony merchants collect payment card information at checkout, and then prompt the customer to expect and share a one-time code sent from their financial institution.
Once again, that one-time code is being sent by the bank because the fake e-commerce site has just attempted to enroll the victim’s payment card data in a mobile wallet. By the time a victim understands they will likely never receive the item they just purchased from the fake e-commerce shop, the scammers have already run through hundreds of dollars in fraudulent charges, often at high-end electronics stores or jewelers.
Ford Merrill works in security research at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group company, and he’s been tracking Chinese SMS phishing groups for several years. Merrill said many Lighthouse customers are now using the phishing kit to erect fake e-commerce websites that are advertised on Google and Meta platforms.
“You find this shop by searching for a particular product online or whatever, and you think you’re getting a good deal,” Merrill said. “But of course you never receive the product, and they will phish that one-time code at checkout.”
Merrill said some of the phishing templates include payment buttons for services like PayPal, and that victims who choose to pay through PayPal can also see their PayPal accounts hijacked.

A fake e-commerce site from the Smishing Triad spoofing PayPal on a mobile device.
“The main advantage of the fake e-commerce site is that it doesn’t require them to send out message lures,” Merrill said, noting that the fake vendor sites have more staying power than traditional phishing sites because it takes far longer for them to be flagged for fraud.
Merrill said Google’s legal action may temporarily disrupt the Lighthouse operators, and could make it easier for U.S. federal authorities to bring criminal charges against the group. But he said the Chinese mobile phishing market is so lucrative right now that it’s difficult to imagine a popular phishing service voluntarily turning out the lights.
Merrill said Google’s lawsuit also can help lay the groundwork for future disruptive actions against Lighthouse and other phishing-as-a-service entities that are operating almost entirely on Chinese networks. According to Silent Push, a majority of the phishing sites created with these kits are sitting at two Chinese hosting companies: Tencent (AS132203) and Alibaba (AS45102).
“Once Google has a default judgment against the Lighthouse guys in court, theoretically they could use that to go to Alibaba and Tencent and say, ‘These guys have been found guilty, here are their domains and IP addresses, we want you to shut these down or we’ll include you in the case.'”
If Google can bring that kind of legal pressure consistently over time, Merrill said, they might succeed in increasing costs for the phishers and more frequently disrupting their operations.
“If you take all of these Chinese phishing kit developers, I have to believe it’s tens of thousands of Chinese-speaking people involved,” he said. “The Lighthouse guys will probably burn down their Telegram channels and disappear for a while. They might call it something else or redevelop their service entirely. But I don’t believe for a minute they’re going to close up shop and leave forever.”

If you’ve been watching the news, you’ve probably seen the headlines out of Paris: one of the most audacious heists in decades took place at the Louvre, where thieves made off with centuries-old crown jewels worth tens of millions of dollars.
But amid the cinematic drama, a quieter detail emerged that’s almost harder to believe—according to French newspaper Libération (via PC Gamer), auditors discovered that the password protecting the museum’s video surveillance system was simply “Louvre.”
While it’s not yet confirmed whether this played a direct role in the robbery, cybersecurity experts point out that weak or reused passwords remain one of the easiest ways for criminals—digital or otherwise—to get inside.
The Louvre’s cybersecurity audits, dating back to 2014, reportedly revealed a pattern of outdated software and simple passwords that hadn’t been updated in years. Subsequent reviews noted “serious shortcomings,” including security systems running on decades-old software no longer supported by developers.
That situation mirrors one of the most common security issues individuals face at home. Whether it’s an email account, a social media login, or your home Wi-Fi router, using an easy or repeated password is like leaving the front door open. Hackers don’t need to break in when they can just walk through.
As experts here at McAfee have explained, cybercriminals routinely rely on “credential stuffing” attacks, in which they test stolen passwords from one breach against other sites to see what else they can access. If you’ve used the same password for your streaming account and your online banking, it’s not hard to imagine what could go wrong.
A strong password is long, complex, and unique. Cybersecurity experts recommend at least 12–16 characters that mix uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. A short password can be guessed in minutes; a long one can take decades to crack.
If that sounds like a lot to juggle, you’re not alone. That’s why password managers exist.
A password manager takes the work—and the guesswork—out of creating and remembering complex passwords. It generates random combinations that are nearly impossible to crack, then stores them securely using advanced encryption.
The added bonus? You’ll never have to reuse a password again. Even if one account is theoretically compromised in a breach, your others remain protected because each password is unique.
McAfee’s password manager also uses multi-factor authentication (MFA), meaning you’ll need at least two forms of verification before signing in—like a code sent to your phone. That extra step can stop hackers cold, even if they somehow get your password.
To keep your digital treasures safer than the Louvre’s jewels:
Reports of the Louvre’s weak password might make for an easy punchline, but the truth is that millions of people make the same mistake every day—reusing simple passwords across dozens of accounts. Strong, unique passwords (and the right tools to manage them) are still one of the most powerful defenses against data theft and identity fraud.
As scams and breaches continue to evolve, your best defense is awareness and protection that adapts just as fast. McAfee’s built-in Scam Detector, included in all core plans, automatically detects scams across text, email, and video, blocks dangerous links, and identifies deepfakes—stopping harm before it happens.
The post The Louvre Used Its Own Name as a Password. Here’s What to Learn From It appeared first on McAfee Blog.

They’re not hiding in dark alleys—they’re hiding in plain sight. Airports, cafés, hotels, even libraries can harbor dangerous Vampire Wi-Fi networks.
These vampires pass themselves off as legitimate public Wi-Fi hotspots, using names that look innocent enough, such as “FREE_WIFI” and “AT&T_FREE_WIFI”. These can potentially be “evil twin networks,” they often mimic the name of the airport you’re in, or the place where you’re grabbing a quick coffee and some laptop time while you’re on the road. In fact, when you connect to a vampire or evil twin network, you’re connecting to a hacker.
These networks are relatively easy to set up. With just a few hundred dollars of gear, attackers can set up these digital bloodsuckers anywhere. The moment you log on, they begin feeding on your data, using tools called packet sniffers to capture and analyze every bit you send.
So say you’re on the road and log into one of these networks, a hacker on the network can see what you’re connecting to and what data you’re passing along. Your credit card number while you shop. Your password when you bank. That confidential contract you just sent to a client. And your email password when your app regularly checks for mail every few minutes or so.
What tools let hackers snoop? Network analyzers, or packet sniffers as many call them. A bad actor can gather up data with a packet sniffer, analyze it, and pluck out the sensitive bits of info that are of value. Before you know it, you’re a victim of identity theft.
Another common vampire Wi-Fi ploy is to set up a phony login screen that asks for a username and password, often for popular online services like Google and Apple. In this case, the hacker gets the keys to all the personal info, apps, files, and financial info connected to them.
Hackers typically take lengths to make these networks look legitimate, but they may give off signs:
Still, even with some of these flags, they can be tough to spot. And that’s a reason why our mobile security apps for iOS and Android analyze Wi-Fi networks before you connect to them—letting you know if a connection is Safe, Risky, or altogether Unsafe.
Your best bet when using any public Wi-Fi at all is to use a VPN.
A VPN is an app that you install on your device to help keep your data safe as you browse the internet. With your VPN on, your device makes a secure connection to a VPN server that routes internet traffic through an encrypted “tunnel.” This keeps your online activity private on any network, shielding it from prying eyes.
While you’re on a VPN, you can browse and bank with the confidence that your passwords, credentials, and financial info are secure. If a hacker attempts to intercept your web traffic, they’ll only see garbled content, thanks to your VPN’s encryption functionality.
With that, choosing a secure and trustworthy VPN provider is a must. A VPN like ours has both your security and privacy in mind. In a VPN, look for:
Not every VPN offers these features. Selecting one that does gives you the protection you want paired with the privacy you want. You’ll find them all in our VPN, which is also included as part of our McAfee+ plans.
Several other straightforward steps can keep you safer from vampire and evil twin Wi-Fi—and safer while using public Wi-Fi in general:
Vampire Wi-Fi networks aren’t going anywhere. Hackers will keep setting up these traps because they work. People see “free Wi-Fi” and click without thinking twice. But now you know better. You’ve got the tools to spot the red flags, the habits to stay protected, and most importantly, you understand why a quality VPN isn’t optional anymore—it’s essential.
McAfee+ gives you everything we’ve talked about: bank-level encryption, zero-logging policies, independent security audits, and that smart auto-connect feature that kicks in when you need it most. Plus, unlimited data across all your devices, because who has time to ration their security?
Your personal information is worth protecting. Your financial data, your work files, your private conversations, they’re all valuable to the wrong people. Don’t hand them over just because someone dangled “free Wi-Fi” in front of you.
Ready to stop gambling with your data? Get comprehensive protection with McAfee+ and never worry about vampire networks again.
The post Vampire Wifi: How Public Wi-Fi Traps Travelers in Cyber Attacks appeared first on McAfee Blog.
The world’s largest and most disruptive botnet is now drawing a majority of its firepower from compromised Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices hosted on U.S. Internet providers like AT&T, Comcast and Verizon, new evidence suggests. Experts say the heavy concentration of infected devices at U.S. providers is complicating efforts to limit collateral damage from the botnet’s attacks, which shattered previous records this week with a brief traffic flood that clocked in at nearly 30 trillion bits of data per second.
Since its debut more than a year ago, the Aisuru botnet has steadily outcompeted virtually all other IoT-based botnets in the wild, with recent attacks siphoning Internet bandwidth from an estimated 300,000 compromised hosts worldwide.
The hacked systems that get subsumed into the botnet are mostly consumer-grade routers, security cameras, digital video recorders and other devices operating with insecure and outdated firmware, and/or factory-default settings. Aisuru’s owners are continuously scanning the Internet for these vulnerable devices and enslaving them for use in distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks that can overwhelm targeted servers with crippling amounts of junk traffic.
As Aisuru’s size has mushroomed, so has its punch. In May 2025, KrebsOnSecurity was hit with a near-record 6.35 terabits per second (Tbps) attack from Aisuru, which was then the largest assault that Google’s DDoS protection service Project Shield had ever mitigated. Days later, Aisuru shattered that record with a data blast in excess of 11 Tbps.
By late September, Aisuru was publicly flexing DDoS capabilities topping 22 Tbps. Then on October 6, its operators heaved a whopping 29.6 terabits of junk data packets each second at a targeted host. Hardly anyone noticed because it appears to have been a brief test or demonstration of Aisuru’s capabilities: The traffic flood lasted less only a few seconds and was pointed at an Internet server that was specifically designed to measure large-scale DDoS attacks.
A measurement of an Oct. 6 DDoS believed to have been launched through multiple botnets operated by the owners of the Aisuru botnet. Image: DDoS Analyzer Community on Telegram.
Aisuru’s overlords aren’t just showing off. Their botnet is being blamed for a series of increasingly massive and disruptive attacks. Although recent assaults from Aisuru have targeted mostly ISPs that serve online gaming communities like Minecraft, those digital sieges often result in widespread collateral Internet disruption.
For the past several weeks, ISPs hosting some of the Internet’s top gaming destinations have been hit with a relentless volley of gargantuan attacks that experts say are well beyond the DDoS mitigation capabilities of most organizations connected to the Internet today.
Steven Ferguson is principal security engineer at Global Secure Layer (GSL), an ISP in Brisbane, Australia. GSL hosts TCPShield, which offers free or low-cost DDoS protection to more than 50,000 Minecraft servers worldwide. Ferguson told KrebsOnSecurity that on October 8, TCPShield was walloped with a blitz from Aisuru that flooded its network with more than 15 terabits of junk data per second.
Ferguson said that after the attack subsided, TCPShield was told by its upstream provider OVH that they were no longer welcome as a customer.
“This was causing serious congestion on their Miami external ports for several weeks, shown publicly via their weather map,” he said, explaining that TCPShield is now solely protected by GSL.
Traces from the recent spate of crippling Aisuru attacks on gaming servers can be still seen at the website blockgametracker.gg, which indexes the uptime and downtime of the top Minecraft hosts. In the following example from a series of data deluges on the evening of September 28, we can see an Aisuru botnet campaign briefly knocked TCPShield offline.
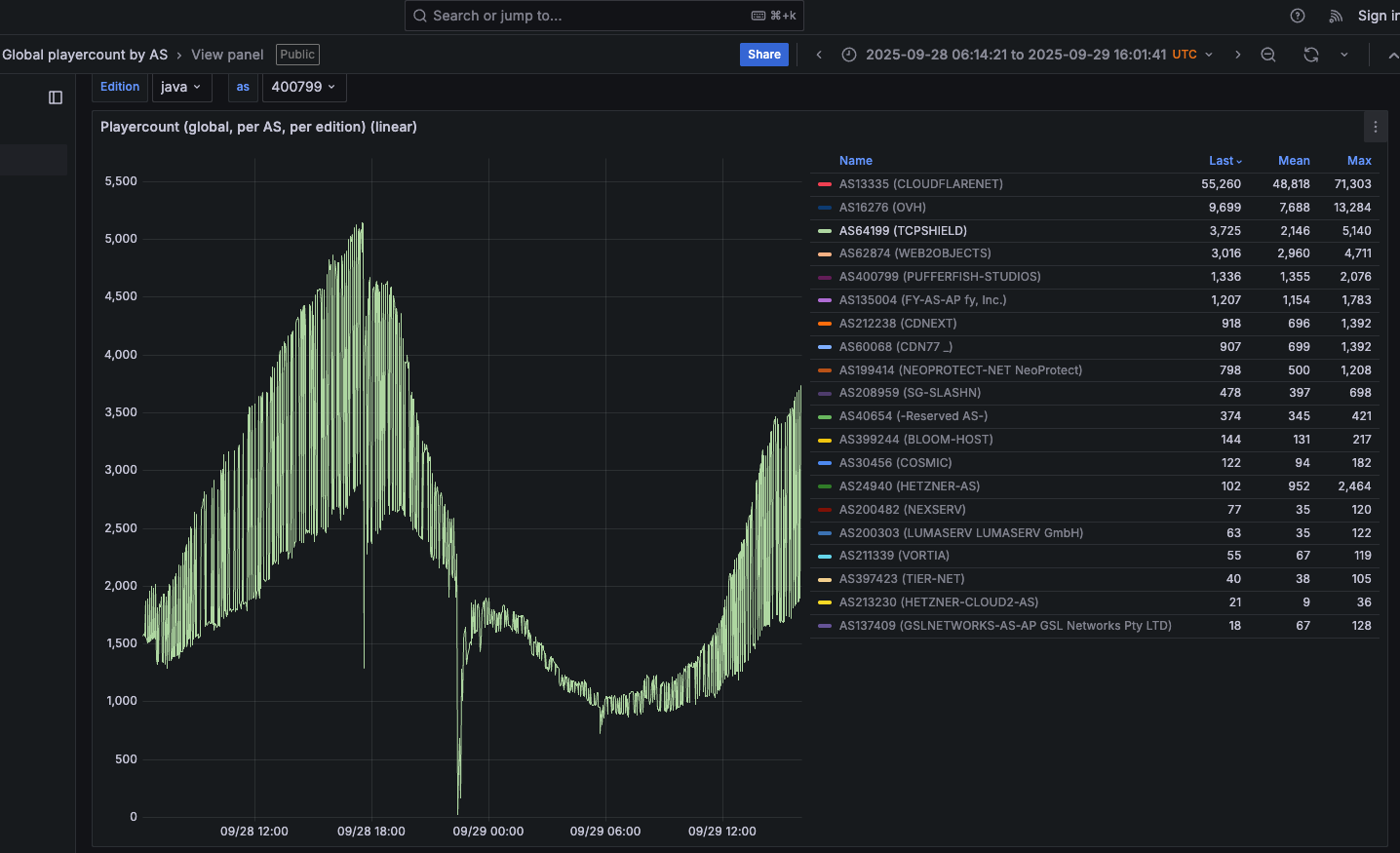
An Aisuru botnet attack on TCPShield (AS64199) on Sept. 28 can be seen in the giant downward spike in the middle of this uptime graphic. Image: grafana.blockgametracker.gg.
Paging through the same uptime graphs for other network operators listed shows almost all of them suffered brief but repeated outages around the same time. Here is the same uptime tracking for Minecraft servers on the network provider Cosmic (AS30456), and it shows multiple large dips that correspond to game server outages caused by Aisuru.
Multiple DDoS attacks from Aisuru can be seen against the Minecraft host Cosmic on Sept. 28. The sharp downward spikes correspond to brief but enormous attacks from Aisuru. Image: grafana.blockgametracker.gg.
Ferguson said he’s been tracking Aisuru for about three months, and recently he noticed the botnet’s composition shifted heavily toward infected systems at ISPs in the United States. Ferguson shared logs from an attack on October 8 that indexed traffic by the total volume sent through each network provider, and the logs showed that 11 of the top 20 traffic sources were U.S. based ISPs.
AT&T customers were by far the biggest U.S. contributors to that attack, followed by botted systems on Charter Communications, Comcast, T-Mobile and Verizon, Ferguson found. He said the volume of data packets per second coming from infected IoT hosts on these ISPs is often so high that it has started to affect the quality of service that ISPs are able to provide to adjacent (non-botted) customers.
“The impact extends beyond victim networks,” Ferguson said. “For instance we have seen 500 gigabits of traffic via Comcast’s network alone. This amount of egress leaving their network, especially being so US-East concentrated, will result in congestion towards other services or content trying to be reached while an attack is ongoing.”
Roland Dobbins is principal engineer at Netscout. Dobbins said Ferguson is spot on, noting that while most ISPs have effective mitigations in place to handle large incoming DDoS attacks, many are far less prepared to manage the inevitable service degradation caused by large numbers of their customers suddenly using some or all available bandwidth to attack others.
“The outbound and cross-bound DDoS attacks can be just as disruptive as the inbound stuff,” Dobbin said. “We’re now in a situation where ISPs are routinely seeing terabit-per-second plus outbound attacks from their networks that can cause operational problems.”
“The crying need for effective and universal outbound DDoS attack suppression is something that is really being highlighted by these recent attacks,” Dobbins continued. “A lot of network operators are learning that lesson now, and there’s going to be a period ahead where there’s some scrambling and potential disruption going on.”
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment from the ISPs named in Ferguson’s report. Charter Communications pointed to a recent blog post on protecting its network, stating that Charter actively monitors for both inbound and outbound attacks, and that it takes proactive action wherever possible.
“In addition to our own extensive network security, we also aim to reduce the risk of customer connected devices contributing to attacks through our Advanced WiFi solution that includes Security Shield, and we make Security Suite available to our Internet customers,” Charter wrote in an emailed response to questions. “With the ever-growing number of devices connecting to networks, we encourage customers to purchase trusted devices with secure development and manufacturing practices, use anti-virus and security tools on their connected devices, and regularly download security patches.”
A spokesperson for Comcast responded, “Currently our network is not experiencing impacts and we are able to handle the traffic.”
Aisuru is built on the bones of malicious code that was leaked in 2016 by the original creators of the Mirai IoT botnet. Like Aisuru, Mirai quickly outcompeted all other DDoS botnets in its heyday, and obliterated previous DDoS attack records with a 620 gigabit-per-second siege that sidelined this website for nearly four days in 2016.
The Mirai botmasters likewise used their crime machine to attack mostly Minecraft servers, but with the goal of forcing Minecraft server owners to purchase a DDoS protection service that they controlled. In addition, they rented out slices of the Mirai botnet to paying customers, some of whom used it to mask the sources of other types of cybercrime, such as click fraud.
A depiction of the outages caused by the Mirai botnet attacks against the internet infrastructure firm Dyn on October 21, 2016. Source: Downdetector.com.
Dobbins said Aisuru’s owners also appear to be renting out their botnet as a distributed proxy network that cybercriminal customers anywhere in the world can use to anonymize their malicious traffic and make it appear to be coming from regular residential users in the U.S.
“The people who operate this botnet are also selling (it as) residential proxies,” he said. “And that’s being used to reflect application layer attacks through the proxies on the bots as well.”
The Aisuru botnet harkens back to its predecessor Mirai in another intriguing way. One of its owners is using the Telegram handle “9gigsofram,” which corresponds to the nickname used by the co-owner of a Minecraft server protection service called Proxypipe that was heavily targeted in 2016 by the original Mirai botmasters.
Robert Coelho co-ran Proxypipe back then along with his business partner Erik “9gigsofram” Buckingham, and has spent the past nine years fine-tuning various DDoS mitigation companies that cater to Minecraft server operators and other gaming enthusiasts. Coelho said he has no idea why one of Aisuru’s botmasters chose Buckingham’s nickname, but added that it might say something about how long this person has been involved in the DDoS-for-hire industry.
“The Aisuru attacks on the gaming networks these past seven day have been absolutely huge, and you can see tons of providers going down multiple times a day,” Coelho said.
Coelho said the 15 Tbps attack this week against TCPShield was likely only a portion of the total attack volume hurled by Aisuru at the time, because much of it would have been shoved through networks that simply couldn’t process that volume of traffic all at once. Such outsized attacks, he said, are becoming increasingly difficult and expensive to mitigate.
“It’s definitely at the point now where you need to be spending at least a million dollars a month just to have the network capacity to be able to deal with these attacks,” he said.
Aisuru has long been rumored to use multiple zero-day vulnerabilities in IoT devices to aid its rapid growth over the past year. XLab, the Chinese security company that was the first to profile Aisuru’s rise in 2024, warned last month that one of the Aisuru botmasters had compromised the firmware distribution website for Totolink, a maker of low-cost routers and other networking gear.
“Multiple sources indicate the group allegedly compromised a router firmware update server in April and distributed malicious scripts to expand the botnet,” XLab wrote on September 15. “The node count is currently reported to be around 300,000.”
A malicious script implanted into a Totolink update server in April 2025. Image: XLab.
Aisuru’s operators received an unexpected boost to their crime machine in August when the U.S. Department Justice charged the alleged proprietor of Rapper Bot, a DDoS-for-hire botnet that competed directly with Aisuru for control over the global pool of vulnerable IoT systems.
Once Rapper Bot was dismantled, Aisuru’s curators moved quickly to commandeer vulnerable IoT devices that were suddenly set adrift by the government’s takedown, Dobbins said.
“Folks were arrested and Rapper Bot control servers were seized and that’s great, but unfortunately the botnet’s attack assets were then pieced out by the remaining botnets,” he said. “The problem is, even if those infected IoT devices are rebooted and cleaned up, they will still get re-compromised by something else generally within minutes of being plugged back in.”
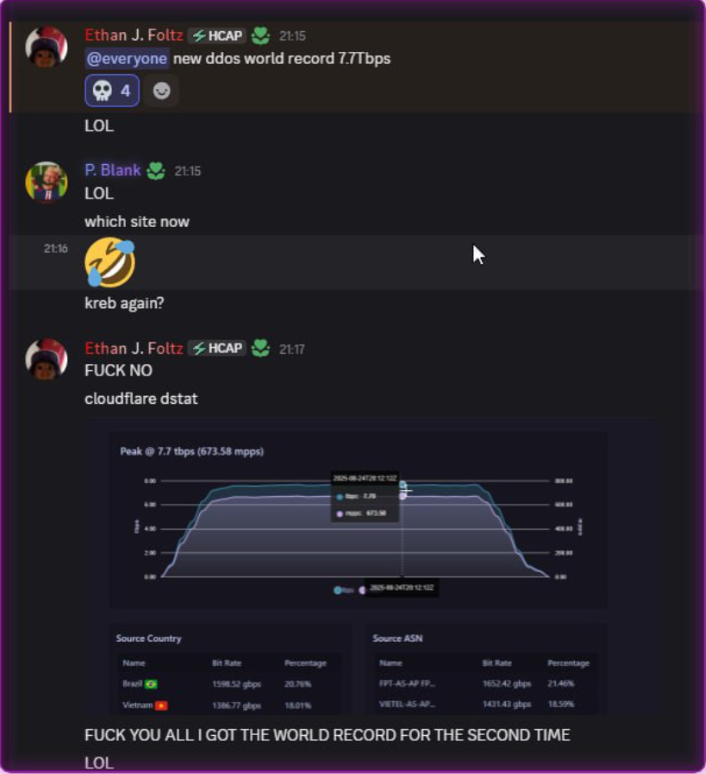
A screenshot shared by XLabs showing the Aisuru botmasters recently celebrating a record-breaking 7.7 Tbps DDoS. The user at the top has adopted the name “Ethan J. Foltz” in a mocking tribute to the alleged Rapper Bot operator who was arrested and charged in August 2025.
XLab’s September blog post cited multiple unnamed sources saying Aisuru is operated by three cybercriminals: “Snow,” who’s responsible for botnet development; “Tom,” tasked with finding new vulnerabilities; and “Forky,” responsible for botnet sales.
KrebsOnSecurity interviewed Forky in our May 2025 story about the record 6.3 Tbps attack from Aisuru. That story identified Forky as a 21-year-old man from Sao Paulo, Brazil who has been extremely active in the DDoS-for-hire scene since at least 2022. The FBI has seized Forky’s DDoS-for-hire domains several times over the years.

Like the original Mirai botmasters, Forky also operates a DDoS mitigation service called Botshield. Forky declined to discuss the makeup of his ISP’s clientele, or to clarify whether Botshield was more of a hosting provider or a DDoS mitigation firm. However, Forky has posted on Telegram about Botshield successfully mitigating large DDoS attacks launched against other DDoS-for-hire services.
In our previous interview, Forky acknowledged being involved in the development and marketing of Aisuru, but denied participating in attacks launched by the botnet.
Reached for comment earlier this month, Forky continued to maintain his innocence, claiming that he also is still trying to figure out who the current Aisuru botnet operators are in real life (Forky said the same thing in our May interview).
But after a week of promising juicy details, Forky came up empty-handed once again. Suspecting that Forky was merely being coy, I asked him how someone so connected to the DDoS-for-hire world could still be mystified on this point, and suggested that his inability or unwillingness to blame anyone else for Aisuru would not exactly help his case.
At this, Forky verbally bristled at being pressed for more details, and abruptly terminated our interview.
“I’m not here to be threatened with ignorance because you are stressed,” Forky replied. “They’re blaming me for those new attacks. Pretty much the whole world (is) due to your blog.”
U.S. prosecutors last week levied criminal hacking charges against 19-year-old U.K. national Thalha Jubair for allegedly being a core member of Scattered Spider, a prolific cybercrime group blamed for extorting at least $115 million in ransom payments from victims. The charges came as Jubair and an alleged co-conspirator appeared in a London court to face accusations of hacking into and extorting several large U.K. retailers, the London transit system, and healthcare providers in the United States.
At a court hearing last week, U.K. prosecutors laid out a litany of charges against Jubair and 18-year-old Owen Flowers, accusing the teens of involvement in an August 2024 cyberattack that crippled Transport for London, the entity responsible for the public transport network in the Greater London area.

A court artist sketch of Owen Flowers (left) and Thalha Jubair appearing at Westminster Magistrates’ Court last week. Credit: Elizabeth Cook, PA Wire.
On July 10, 2025, KrebsOnSecurity reported that Flowers and Jubair had been arrested in the United Kingdom in connection with recent Scattered Spider ransom attacks against the retailers Marks & Spencer and Harrods, and the British food retailer Co-op Group.
That story cited sources close to the investigation saying Flowers was the Scattered Spider member who anonymously gave interviews to the media in the days after the group’s September 2023 ransomware attacks disrupted operations at Las Vegas casinos operated by MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment.
The story also noted that Jubair’s alleged handles on cybercrime-focused Telegram channels had far lengthier rap sheets involving some of the more consequential and headline-grabbing data breaches over the past four years. What follows is an account of cybercrime activities that prosecutors have attributed to Jubair’s alleged hacker handles, as told by those accounts in posts to public Telegram channels that are closely monitored by multiple cyber intelligence firms.
Jubair is alleged to have been a core member of the LAPSUS$ cybercrime group that broke into dozens of technology companies beginning in late 2021, stealing source code and other internal data from tech giants including Microsoft, Nvidia, Okta, Rockstar Games, Samsung, T-Mobile, and Uber.
That is, according to the former leader of the now-defunct LAPSUS$. In April 2022, KrebsOnSecurity published internal chat records taken from a server that LAPSUS$ used, and those chats indicate Jubair was working with the group using the nicknames Amtrak and Asyntax. In the middle of the gang’s cybercrime spree, Asyntax told the LAPSUS$ leader not to share T-Mobile’s logo in images sent to the group because he’d been previously busted for SIM-swapping and his parents would suspect he was back at it again.
The leader of LAPSUS$ responded by gleefully posting Asyntax’s real name, phone number, and other hacker handles into a public chat room on Telegram:
In March 2022, the leader of the LAPSUS$ data extortion group exposed Thalha Jubair’s name and hacker handles in a public chat room on Telegram.
That story about the leaked LAPSUS$ chats also connected Amtrak/Asyntax to several previous hacker identities, including “Everlynn,” who in April 2021 began offering a cybercriminal service that sold fraudulent “emergency data requests” targeting the major social media and email providers.
In these so-called “fake EDR” schemes, the hackers compromise email accounts tied to police departments and government agencies, and then send unauthorized demands for subscriber data (e.g. username, IP/email address), while claiming the information being requested can’t wait for a court order because it relates to an urgent matter of life and death.
The roster of the now-defunct “Infinity Recursion” hacking team, which sold fake EDRs between 2021 and 2022. The founder “Everlynn” has been tied to Jubair. The member listed as “Peter” became the leader of LAPSUS$ who would later post Jubair’s name, phone number and hacker handles into LAPSUS$’s chat channel.
Prosecutors in New Jersey last week alleged Jubair was part of a threat group variously known as Scattered Spider, 0ktapus, and UNC3944, and that he used the nicknames EarthtoStar, Brad, Austin, and Austistic.
Beginning in 2022, EarthtoStar co-ran a bustling Telegram channel called Star Chat, which was home to a prolific SIM-swapping group that relentlessly used voice- and SMS-based phishing attacks to steal credentials from employees at the major wireless providers in the U.S. and U.K.

Jubair allegedly used the handle “Earth2Star,” a core member of a prolific SIM-swapping group operating in 2022. This ad produced by the group lists various prices for SIM swaps.
The group would then use that access to sell a SIM-swapping service that could redirect a target’s phone number to a device the attackers controlled, allowing them to intercept the victim’s phone calls and text messages (including one-time codes). Members of Star Chat targeted multiple wireless carriers with SIM-swapping attacks, but they focused mainly on phishing T-Mobile employees.
In February 2023, KrebsOnSecurity scrutinized more than seven months of these SIM-swapping solicitations on Star Chat, which almost daily peppered the public channel with “Tmo up!” and “Tmo down!” notices indicating periods wherein the group claimed to have active access to T-Mobile’s network.
A redacted receipt from Star Chat’s SIM-swapping service targeting a T-Mobile customer after the group gained access to internal T-Mobile employee tools.
The data showed that Star Chat — along with two other SIM-swapping groups operating at the same time — collectively broke into T-Mobile over a hundred times in the last seven months of 2022. However, Star Chat was by far the most prolific of the three, responsible for at least 70 of those incidents.
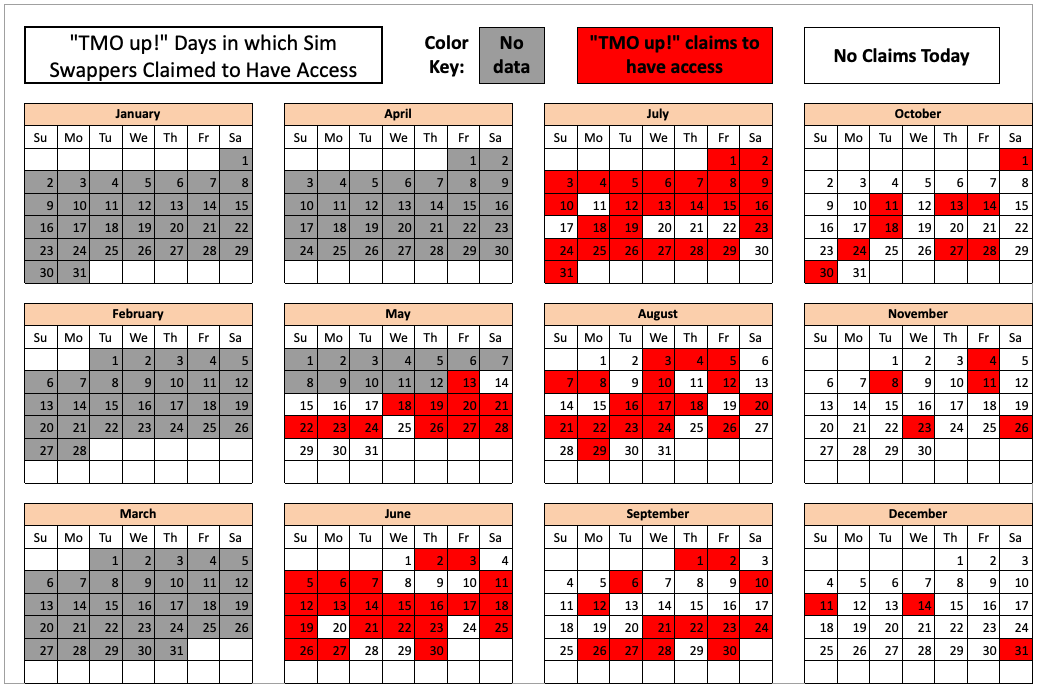
The 104 days in the latter half of 2022 in which different known SIM-swapping groups claimed access to T-Mobile employee tools. Star Chat was responsible for a majority of these incidents. Image: krebsonsecurity.com.
A review of EarthtoStar’s messages on Star Chat as indexed by the threat intelligence firm Flashpoint shows this person also sold “AT&T email resets” and AT&T call forwarding services for up to $1,200 per line. EarthtoStar explained the purpose of this service in post on Telegram:
“Ok people are confused, so you know when u login to chase and it says ‘2fa required’ or whatever the fuck, well it gives you two options, SMS or Call. If you press call, and I forward the line to you then who do you think will get said call?”
New Jersey prosecutors allege Jubair also was involved in a mass SMS phishing campaign during the summer of 2022 that stole single sign-on credentials from employees at hundreds of companies. The text messages asked users to click a link and log in at a phishing page that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication page, saying recipients needed to review pending changes to their upcoming work schedules.
The phishing websites used a Telegram instant message bot to forward any submitted credentials in real-time, allowing the attackers to use the phished username, password and one-time code to log in as that employee at the real employer website.
That weeks-long SMS phishing campaign led to intrusions and data thefts at more than 130 organizations, including LastPass, DoorDash, Mailchimp, Plex and Signal.
A visual depiction of the attacks by the SMS phishing group known as 0ktapus, ScatterSwine, and Scattered Spider. Image: Amitai Cohen twitter.com/amitaico.
EarthtoStar’s group Star Chat specialized in phishing their way into business process outsourcing (BPO) companies that provide customer support for a range of multinational companies, including a number of the world’s largest telecommunications providers. In May 2022, EarthtoStar posted to the Telegram channel “Frauwudchat”:
“Hi, I am looking for partners in order to exfiltrate data from large telecommunications companies/call centers/alike, I have major experience in this field, [including] a massive call center which houses 200,000+ employees where I have dumped all user credentials and gained access to the [domain controller] + obtained global administrator I also have experience with REST API’s and programming. I have extensive experience with VPN, Citrix, cisco anyconnect, social engineering + privilege escalation. If you have any Citrix/Cisco VPN or any other useful things please message me and lets work.”
At around the same time in the Summer of 2022, at least two different accounts tied to Star Chat — “RocketAce” and “Lopiu” — introduced the group’s services to denizens of the Russian-language cybercrime forum Exploit, including:
-SIM-swapping services targeting Verizon and T-Mobile customers;
-Dynamic phishing pages targeting customers of single sign-on providers like Okta;
-Malware development services;
-The sale of extended validation (EV) code signing certificates.
The user “Lopiu” on the Russian cybercrime forum Exploit advertised many of the same unique services offered by EarthtoStar and other Star Chat members. Image source: ke-la.com.
These two accounts on Exploit created multiple sales threads in which they claimed administrative access to U.S. telecommunications providers and asked other Exploit members for help in monetizing that access. In June 2022, RocketAce, which appears to have been just one of EarthtoStar’s many aliases, posted to Exploit:
Hello. I have access to a telecommunications company’s citrix and vpn. I would like someone to help me break out of the system and potentially attack the domain controller so all logins can be extracted we can discuss payment and things leave your telegram in the comments or private message me ! Looking for someone with knowledge in citrix/privilege escalation
On Nov. 15, 2022, EarthtoStar posted to their Star Sanctuary Telegram channel that they were hiring malware developers with a minimum of three years of experience and the ability to develop rootkits, backdoors and malware loaders.
“Optional: Endorsed by advanced APT Groups (e.g. Conti, Ryuk),” the ad concluded, referencing two of Russia’s most rapacious and destructive ransomware affiliate operations. “Part of a nation-state / ex-3l (3 letter-agency).”
The Telegram and Discord chat channels wherein Flowers and Jubair allegedly planned and executed their extortion attacks are part of a loose-knit network known as the Com, an English-speaking cybercrime community consisting mostly of individuals living in the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia.
Many of these Com chat servers have hundreds to thousands of members each, and some of the more interesting solicitations on these communities are job offers for in-person assignments and tasks that can be found if one searches for posts titled, “If you live near,” or “IRL job” — short for “in real life” job.
These “violence-as-a-service” solicitations typically involve “brickings,” where someone is hired to toss a brick through the window at a specified address. Other IRL jobs for hire include tire-stabbings, molotov cocktail hurlings, drive-by shootings, and even home invasions. The people targeted by these services are typically other criminals within the community, but it’s not unusual to see Com members asking others for help in harassing or intimidating security researchers and even the very law enforcement officers who are investigating their alleged crimes.
It remains unclear what precipitated this incident or what followed directly after, but on January 13, 2023, a Star Sanctuary account used by EarthtoStar solicited the home invasion of a sitting U.S. federal prosecutor from New York. That post included a photo of the prosecutor taken from the Justice Department’s website, along with the message:
“Need irl niggas, in home hostage shit no fucking pussies no skinny glock holding 100 pound niggas either”
Throughout late 2022 and early 2023, EarthtoStar’s alias “Brad” (a.k.a. “Brad_banned”) frequently advertised Star Chat’s malware development services, including custom malicious software designed to hide the attacker’s presence on a victim machine:
We can develop KERNEL malware which will achieve persistence for a long time,
bypass firewalls and have reverse shell access.This shit is literally like STAGE 4 CANCER FOR COMPUTERS!!!
Kernel meaning the highest level of authority on a machine.
This can range to simple shells to Bootkits.Bypass all major EDR’s (SentinelOne, CrowdStrike, etc)
Patch EDR’s scanning functionality so it’s rendered useless!Once implanted, extremely difficult to remove (basically impossible to even find)
Development Experience of several years and in multiple APT Groups.Be one step ahead of the game. Prices start from $5,000+. Message @brad_banned to get a quote
In September 2023 , both MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment suffered ransomware attacks at the hands of a Russian ransomware affiliate program known as ALPHV and BlackCat. Caesars reportedly paid a $15 million ransom in that incident.
Within hours of MGM publicly acknowledging the 2023 breach, members of Scattered Spider were claiming credit and telling reporters they’d broken in by social engineering a third-party IT vendor. At a hearing in London last week, U.K. prosecutors told the court Jubair was found in possession of more than $50 million in ill-gotten cryptocurrency, including funds that were linked to the Las Vegas casino hacks.
The Star Chat channel was finally banned by Telegram on March 9, 2025. But U.S. prosecutors say Jubair and fellow Scattered Spider members continued their hacking, phishing and extortion activities up until September 2025.
In April 2025, the Com was buzzing about the publication of “The Com Cast,” a lengthy screed detailing Jubair’s alleged cybercriminal activities and nicknames over the years. This account included photos and voice recordings allegedly of Jubair, and asserted that in his early days on the Com Jubair used the nicknames Clark and Miku (these are both aliases used by Everlynn in connection with their fake EDR services).

Thalha Jubair (right), without his large-rimmed glasses, in an undated photo posted in The Com Cast.
More recently, the anonymous Com Cast author(s) claimed, Jubair had used the nickname “Operator,” which corresponds to a Com member who ran an automated Telegram-based doxing service that pulled consumer records from hacked data broker accounts. That public outing came after Operator allegedly seized control over the Doxbin, a long-running and highly toxic community that is used to “dox” or post deeply personal information on people.
“Operator/Clark/Miku: A key member of the ransomware group Scattered Spider, which consists of a diverse mix of individuals involved in SIM swapping and phishing,” the Com Cast account stated. “The group is an amalgamation of several key organizations, including Infinity Recursion (owned by Operator), True Alcorians (owned by earth2star), and Lapsus, which have come together to form a single collective.”
The New Jersey complaint (PDF) alleges Jubair and other Scattered Spider members committed computer fraud, wire fraud, and money laundering in relation to at least 120 computer network intrusions involving 47 U.S. entities between May 2022 and September 2025. The complaint alleges the group’s victims paid at least $115 million in ransom payments.
U.S. authorities say they traced some of those payments to Scattered Spider to an Internet server controlled by Jubair. The complaint states that a cryptocurrency wallet discovered on that server was used to purchase several gift cards, one of which was used at a food delivery company to send food to his apartment. Another gift card purchased with cryptocurrency from the same server was allegedly used to fund online gaming accounts under Jubair’s name. U.S. prosecutors said that when they seized that server they also seized $36 million in cryptocurrency.
The complaint also charges Jubair with involvement in a hacking incident in January 2025 against the U.S. courts system that targeted a U.S. magistrate judge overseeing a related Scattered Spider investigation. That other investigation appears to have been the prosecution of Noah Michael Urban, a 20-year-old Florida man charged in November 2024 by prosecutors in Los Angeles as one of five alleged Scattered Spider members.
Urban pleaded guilty in April 2025 to wire fraud and conspiracy charges, and in August he was sentenced to 10 years in federal prison. Speaking with KrebsOnSecurity from jail after his sentencing, Urban asserted that the judge gave him more time than prosecutors requested because he was mad that Scattered Spider hacked his email account.
Noah “Kingbob” Urban, posting to Twitter/X around the time of his sentencing on Aug. 20.
A court transcript (PDF) from a status hearing in February 2025 shows Urban was telling the truth about the hacking incident that happened while he was in federal custody. The judge told attorneys for both sides that a co-defendant in the California case was trying to find out about Mr. Urban’s activity in the Florida case, and that the hacker accessed the account by impersonating a judge over the phone and requesting a password reset.
Allison Nixon is chief research officer at the New York based security firm Unit 221B, and easily one of the world’s leading experts on Com-based cybercrime activity. Nixon said the core problem with legally prosecuting well-known cybercriminals from the Com has traditionally been that the top offenders tend to be under the age of 18, and thus difficult to charge under federal hacking statutes.
In the United States, prosecutors typically wait until an underage cybercrime suspect becomes an adult to charge them. But until that day comes, she said, Com actors often feel emboldened to continue committing — and very often bragging about — serious cybercrime offenses.
“Here we have a special category of Com offenders that effectively enjoy legal immunity,” Nixon told KrebsOnSecurity. “Most get recruited to Com groups when they are older, but of those that join very young, such as 12 or 13, they seem to be the most dangerous because at that age they have no grounding in reality and so much longevity before they exit their legal immunity.”
Nixon said U.K. authorities face the same challenge when they briefly detain and search the homes of underage Com suspects: Namely, the teen suspects simply go right back to their respective cliques in the Com and start robbing and hurting people again the minute they’re released.
Indeed, the U.K. court heard from prosecutors last week that both Scattered Spider suspects were detained and/or searched by local law enforcement on multiple occasions, only to return to the Com less than 24 hours after being released each time.
“What we see is these young Com members become vectors for perpetrators to commit enormously harmful acts and even child abuse,” Nixon said. “The members of this special category of people who enjoy legal immunity are meeting up with foreign nationals and conducting these sometimes heinous acts at their behest.”
Nixon said many of these individuals have few friends in real life because they spend virtually all of their waking hours on Com channels, and so their entire sense of identity, community and self-worth gets wrapped up in their involvement with these online gangs. She said if the law was such that prosecutors could treat these people commensurate with the amount of harm they cause society, that would probably clear up a lot of this problem.
“If law enforcement was allowed to keep them in jail, they would quit reoffending,” she said.
The Times of London reports that Flowers is facing three charges under the Computer Misuse Act: two of conspiracy to commit an unauthorized act in relation to a computer causing/creating risk of serious damage to human welfare/national security and one of attempting to commit the same act. Maximum sentences for these offenses can range from 14 years to life in prison, depending on the impact of the crime.
Jubair is reportedly facing two charges in the U.K.: One of conspiracy to commit an unauthorized act in relation to a computer causing/creating risk of serious damage to human welfare/national security and one of failing to comply with a section 49 notice to disclose the key to protected information.
In the United States, Jubair is charged with computer fraud conspiracy, two counts of computer fraud, wire fraud conspiracy, two counts of wire fraud, and money laundering conspiracy. If extradited to the U.S., tried and convicted on all charges, he faces a maximum penalty of 95 years in prison.
In July 2025, the United Kingdom barred victims of hacking from paying ransoms to cybercriminal groups unless approved by officials. U.K. organizations that are considered part of critical infrastructure reportedly will face a complete ban, as will the entire public sector. U.K. victims of a hack are now required to notify officials to better inform policymakers on the scale of Britain’s ransomware problem.
For further reading (bless you), check out Bloomberg’s poignant story last week based on a year’s worth of jailhouse interviews with convicted Scattered Spider member Noah Urban.
A 20-year-old Florida man at the center of a prolific cybercrime group known as “Scattered Spider” was sentenced to 10 years in federal prison today, and ordered to pay roughly $13 million in restitution to victims.
Noah Michael Urban of Palm Coast, Fla. pleaded guilty in April 2025 to charges of wire fraud and conspiracy. Florida prosecutors alleged Urban conspired with others to steal at least $800,000 from five victims via SIM-swapping attacks that diverted their mobile phone calls and text messages to devices controlled by Urban and his co-conspirators.

A booking photo of Noah Michael Urban released by the Volusia County Sheriff.
Although prosecutors had asked for Urban to serve eight years, Jacksonville news outlet News4Jax.com reports the federal judge in the case today opted to sentence Urban to 120 months in federal prison, ordering him to pay $13 million in restitution and undergo three years of supervised release after his sentence is completed.
In November 2024 Urban was charged by federal prosecutors in Los Angeles as one of five members of Scattered Spider (a.k.a. “Oktapus,” “Scatter Swine” and “UNC3944”), which specialized in SMS and voice phishing attacks that tricked employees at victim companies into entering their credentials and one-time passcodes at phishing websites. Urban pleaded guilty to one count of conspiracy to commit wire fraud in the California case, and the $13 million in restitution is intended to cover victims from both cases.
The targeted SMS scams spanned several months during the summer of 2022, asking employees to click a link and log in at a website that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication page. Some SMS phishing messages told employees their VPN credentials were expiring and needed to be changed; other missives advised employees about changes to their upcoming work schedule.
That phishing spree netted Urban and others access to more than 130 companies, including Twilio, LastPass, DoorDash, MailChimp, and Plex. The government says the group used that access to steal proprietary company data and customer information, and that members also phished people to steal millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency.
For many years, Urban’s online hacker aliases “King Bob” and “Sosa” were fixtures of the Com, a mostly Telegram and Discord-based community of English-speaking cybercriminals wherein hackers boast loudly about high-profile exploits and hacks that almost invariably begin with social engineering. King Bob constantly bragged on the Com about stealing unreleased rap music recordings from popular artists, presumably through SIM-swapping attacks. Many of those purloined tracks or “grails” he later sold or gave away on forums.

Noah “King Bob” Urban, posting to Twitter/X around the time of his sentencing today.
Sosa also was active in a particularly destructive group of accomplished criminal SIM-swappers known as “Star Fraud.” Cyberscoop’s AJ Vicens reported in 2023 that individuals within Star Fraud were likely involved in the high-profile Caesars Entertainment and MGM Resorts extortion attacks that same year.
The Star Fraud SIM-swapping group gained the ability to temporarily move targeted mobile numbers to devices they controlled by constantly phishing employees of the major mobile providers. In February 2023, KrebsOnSecurity published data taken from the Telegram channels for Star Fraud and two other SIM-swapping groups showing these crooks focused on SIM-swapping T-Mobile customers, and that they collectively claimed internal access to T-Mobile on 100 separate occasions over a 7-month period in 2022.
Reached via one of his King Bob accounts on Twitter/X, Urban called the sentence unjust, and said the judge in his case discounted his age as a factor.
“The judge purposefully ignored my age as a factor because of the fact another Scattered Spider member hacked him personally during the course of my case,” Urban said in reply to questions, noting that he was sending the messages from a Florida county jail. “He should have been removed as a judge much earlier on. But staying in county jail is torture.”
A court transcript (PDF) from a status hearing in February 2025 shows Urban was telling the truth about the hacking incident that happened while he was in federal custody. It involved an intrusion into a magistrate judge’s email account, where a copy of Urban’s sealed indictment was stolen. The judge told attorneys for both sides that a co-defendant in the California case was trying to find out about Mr. Urban’s activity in the Florida case.
“What it ultimately turned into a was a big faux pas,” Judge Harvey E. Schlesinger said. “The Court’s password…business is handled by an outside contractor. And somebody called the outside contractor representing Judge Toomey saying, ‘I need a password change.’ And they gave out the password change. That’s how whoever was making the phone call got into the court.”

How do hackers hack phones? In several ways. But also, there are several ways you can prevent it from happening to you. The thing is that our phones are like little treasure chests. They’re loaded with plenty of personal data, and we use them to shop, bank, and take care of other personal and financial matters—all of which are of high value to identity thieves. However, you can protect yourself and your phone by knowing what to look out for and by taking a few simple steps. Let’s break it down by first understanding what phone hacking is, taking a look at some common attacks, and learning how you can prevent it.
Phone hacking refers to any method where an unauthorized third party gains access to your smartphone and its data. This isn’t just one single technique; it covers a wide range of cybercrimes. A phone hack can happen through software vulnerabilities, like the spyware campaigns throughout the years that could monitor calls and messages. It can also occur over unsecured networks, such as a hacker intercepting your data on public Wi-Fi. Sometimes, it’s as simple as physical access, where someone installs tracking software on an unattended device.
Hackers have multiple avenues of attacking your phone. Among these common methods are using malicious apps disguised as legitimate software, exploiting the vulnerabilities of unsecure public Wi-Fi networks, or deploying sophisticated zero-click exploits that require no interaction from you at all. The most common method, however, remains social engineering, where they trick you into giving them access. Let’s further explore these common hacking techniques below.
Whether hackers sneak it onto your phone by physically accessing your phone or by tricking you into installing it via a phony app, a sketchy website, or a phishing attack, hacking software can create problems for you in a couple of ways:
Some possible signs of hacking software on your phone include:
In all, hacking software can eat up system resources, create conflicts with other apps, and use your data or internet connection to pass your personal information into the hands of hackers.
This classic form of attack has been leveled at our computers for years. Phishing is where hackers impersonate a company or trusted individual to get access to your accounts or personal info or both. These attacks take many forms such as emails, texts, instant messages, and so forth, some of which can look really legitimate. Common to them are links to bogus sites that attempt to trick you into handing over personal info or that install malware to wreak havoc on your device or likewise steal information. Learning to spot a phishing attack is one way to keep yourself from falling victim to one.
Professional hackers can use dedicated technologies that search for vulnerable mobile devices with an open Bluetooth connection. Hackers can pull off these attacks when they are within range of your phone, up to 30 feet away, usually in a populated area. When hackers make a Bluetooth connection to your phone, they might access your data and info, yet that data and info must be downloaded while the phone is within range. This is a more sophisticated attack given the effort and technology involved.
In August of 2019, then CEO of Twitter had his phone hacked by SIM card swapping scam. In this type of scam, a hacker contacts your phone provider, pretends to be you, then asks for a replacement SIM card. Once the provider sends the new SIM to the hacker, the old SIM card is deactivated, and your phone number will be effectively stolen. This enables the hacker to take control of your phone calls, messages, among others. The task of impersonating someone else seems difficult, yet it happened to the CEO of a major tech company, underscoring the importance of protecting your personal info and identity online to prevent hackers from pulling off this and other crimes.
While a phone call itself cannot typically install malware on your device, it is a primary tool for social engineering, known as vishing or voice phishing. A hacker might call, impersonating your bank or tech support company, and trick you into revealing sensitive information like passwords or financial details. They might also try to convince you to install a malicious app. Another common tactic is the “one-ring” scam, where they hang up hoping you’ll call back a premium-rate number. To stay safe, be wary of unsolicited calls, never provide personal data, block suspicious numbers, and check that your call forwarding isn’t enabled.
Generally, a phone that is powered off is a difficult target for remote hackers. However, modern smartphones aren’t always truly off. Features like Apple’s Find My network can operate in a low-power mode, keeping certain radios active. Furthermore, if a device has been previously compromised with sophisticated firmware-level malware, it could activate upon startup. The more common risk involves data that was already stolen before the phone was turned off or if the device is physically stolen. While it’s an uncommon scenario, the only sure way to take a device offline and completely sever all power is by removing the battery, where possible.
Hacking a phone’s camera is referred to as camfecting, usually done through malware or spyware hidden within a rogue application. Once installed, these apps can gain unauthorized permission to access your camera and record video or capture images without your knowledge. Occasionally, vulnerabilities in a phone’s operating system (OS) have been discovered that could allow for this, though these are rare and usually patched quickly. Protect yourself by regularly reviewing app permissions in your phone’s settings—for both iOS and Android—and revoking camera access for any app that doesn’t absolutely need it. Always keep your OS and apps updated to the latest versions.
This is a long-standing debate with no simple answer. iPhones are generally considered more secure due to Apple’s walled garden approach: a closed ecosystem, a strict vetting process for the App Store, and timely security updates for all supported devices. Android’s open-source nature offers more flexibility but also creates a more fragmented ecosystem, where security updates can be delayed depending on the device manufacturer. However, both platforms use powerful security features like application sandboxing.
The most important factor is not the brand but your behavior. A user who practices good digital hygiene—using strong passwords, avoiding suspicious links, and vetting apps—is well-protected on any platform.
Detecting a phone hack early can save you from significant trouble. Watch for key red flags: your battery draining much faster than usual, unexpected spikes in your mobile data usage, a persistently hot device even when idle, or a sudden barrage of pop-up ads. You might also notice apps you don’t remember installing or find that your phone is running unusually slow. To check, go into your settings to review your battery and data usage reports for any strange activity. The most effective step you can take is to install a comprehensive security app, like McAfee® Mobile Security, to run an immediate scan and detect any threats.
Discovering that your phone has been hacked can be alarming, but acting quickly can help you regain control and protect your personal information. Here are the urgent steps to take so you can remove the hacker, secure your accounts, and prevent future intrusions.
While there are several ways a hacker can get into your phone and steal personal and critical information, here are a few tips to keep that from happening:
Your smartphone is central to your life, so protecting it is essential. Ultimately, your proactive security habits are your strongest defense against mobile hacking. Make a habit of keeping your operating system and apps updated, be cautious about the links you click and the networks you join, and use a comprehensive security solution like McAfee® Mobile Security.
By staying vigilant and informed, you can enjoy all the benefits of your mobile device with confidence and peace of mind. Stay tuned to McAfee for the latest on how to protect your digital world from emerging threats.
The post How Do Hackers Hack Phones and How Can I Prevent It? appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Malicious software, also called malware, refers to any program or code engineered to harm or exploit computer systems, networks and devices. It affects your phone’s functionality, especially if you jailbreak your device—that is, opening your iOS to additional features, apps, and themes.
The risks associated with a malware infection can range from poor device performance to stolen data. Cybercriminals typically use it to extract data—from financial data and healthcare records to emails and passwords—that they can leverage over victims for financial gain.
Thanks to their closed ecosystem, built-in security features, and strict policies on third-party apps, Apple devices tend to be generally resilient against malware infections. It’s important to note, however, that they’re not completely without vulnerabilities.
Read on to learn how you can detect malware on your iPhone and how to remove these infections so you can get back to enjoying your digital activities.
While traditional self-replicating viruses are rare on iPhones, malware is a genuine threat for Apple devices. Malware typically enters through links in deceptive texts or emails or through downloaded, unvetted apps rather than system-wide infection. These are some types of malware that could infect your iPhone:
To keep you safe against malware and other threats, Apple engineers the iPhone with multiple security layers, including:
Together, these features create a highly secure environment for iPhones. However, this robust shield does not eliminate all risks, as threats can still bypass these defenses through phishing scams or by tricking a user into installing a malicious configuration profile.
If your iPhone is exhibiting these odd activities listed below, a manual scan is your first point of order. These quick actions are free to do as they are already integrated into your device.
The disadvantage of doing a manual scan is that it requires effort. In addition, it does not detect sophisticated malware, and only identifies symptoms rather than root causes.
If your iPhone persistently exhibits any of the red flags above despite your quick actions, you may have to investigate using a third-party security app to find the threats that manual checks don’t catch.
Compared with manual or built-in scans, third-party solutions like McAfee Mobile Security offer automated, comprehensive malware scans by detecting a wider range of threats before they enter your digital space. While available at a premium, third-party security suites offer great value as they include full-scale protection that includes a safe browsing feature to protect your digital life and a virtual private network (VPN) for a more secure internet connection.
If the scan confirms the presence of malware on your iPhone, don’t worry. There’s still time to protect yourself and your data. Below is an action plan you can follow to remove malware from your device.
In many cases, hackers exploit outdated versions of iOS to launch malware attacks. If you don’t have the latest version of your operating system, it’s a good idea to update your iOS immediately to close this potential vulnerability. To do this, go to Settings > General > Software Update and follow the instructions to update your iPhone.
It might sound simple, but restarting your device can fix certain issues. The system will restart on its own when updating the iOS. If you already have the latest version, restart your iPhone now.
If updating the iOS and restarting your device didn’t fix the issue, try clearing your phone’s browsing history and data. If you’re using Safari, go to Settings > Clear History and Website Data > Clear History and Data. Keep in mind that the process is similar for Google Chrome and most other popular web browsers.
Malicious software, such as spyware and ransomware, often end up on phones by masquerading as legitimate apps. To err on the side of caution, delete any apps that you don’t remember downloading or installing.
The option to restore to a previous backup is one of the most valuable features found on the iPhone and iPad. This allows you to restore your device to an iCloud backup version that was made before the malware infection. Go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Erase All Content and Settings > Restore from iCloud Backup.
A factory reset should be your last resort when other removal methods have failed, as it is a complete data wipe. That means it will erase all content and settings, including any malicious apps, profiles, or files, returning the software to its original, out-of-the-box state. That’s why it’s crucial to back up your essential data such as photos and contacts first. Also, remember to restore to an iCloud backup version *before* the malware infection to avoid reintroducing the infection. For the highest level of security, set the iPhone up as new and manually redownload trusted apps from the App Store. When you are ready to reset, go to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Erase All Content and Settings > Set Up as New iPhone.
Spyware is designed to be sneaky, but it leaves subtle traces. Pay attention to your iPhone’s behavior, such as the camera or microphone unexpectedly activating as indicated by a green or orange dot in the status bar, sudden battery drain, or your device overheating for no reason. Another major red flag is a spike in data usage when you aren’t actively using your phone.
For a deeper look, do this 5-minute check to see which apps have accessed your data, camera, and microphone. Look for any activity that seems suspicious or that you don’t recall authorizing.
If you suspect your iPhone has been compromised, it’s important to act quickly. Here’s a step-by-step process to remove it, restore your privacy, and prevent future threats.
A common tactic used by scammers is the fake virus pop-up. These alarming messages appear while you are browsing, often using logos from Apple or other trusted companies, and claim your iPhone is infected. Their goal is to create panic, urging you to click a link, download a fake app, or call a fraudulent support number. Never interact with these pop-ups. Here’s a quick response plan when dealing with fake virus pop-up ads:
Never enter personal information, passwords, or payment details on a page that appears from a pop-up ad.
The best way to protect your iOS device is to avoid malware in the first place. Follow these security measures to safeguard your device:
Can my iPhone get a virus from opening an email?
Simply opening an email is very unlikely to infect your iPhone. However, clicking a malicious link or downloading an attachment from a phishing email can lead you to a harmful website or trick you into compromising your information. It’s the action you take, not opening the email itself, that creates the risk.
How do I know if a virus warning is real or fake?
Any pop-up in your browser that claims your iPhone has a virus is fake. Apple does not send notifications like this. These are scare tactics designed to trick you into clicking a link or calling a fake support number. The safest response is to close the browser tab and clear your browsing data.
Does my iPhone really need antivirus software?
It’s a misconception that iPhones are immune to all viruses. While Apple’s built-in security provides a strong defense, it doesn’t offer complete protection. Cybercriminals are increasingly using phishing, smishing, AI voice cloning, deepfake videos and other social engineering methods to target iPhone users. A comprehensive security app provides layered protection beyond the iOS integrated security. Think of it as adding a professional security guard to already-strong walls.
What is the best way to check my iPhone for a virus or malware for free?
You can perform manual checks for free by looking for suspicious apps, checking for unusual battery drain and data usage, and reviewing your App Privacy Report. While helpful for spotting obvious issues, these manual checks aren’t foolproof. A dedicated security app offers a more reliable and thorough analysis.
Can an iPhone get malware without jailbreaking it?
Yes. While jailbreaking significantly increases the risk, malware can still infect a non-jailbroken iPhone. This typically happens through sophisticated phishing attacks, installing malicious configuration profiles from untrusted sources, or, in very rare cases, by exploiting an unknown vulnerability in iOS, known as a “zero-day” attack.
Is an iPhone malware scan truly necessary?
Given the value of the personal data on our phones, a regular malware scan provides significant peace of mind. A reputable security app can identify vulnerabilities you might miss, such as outdated software or risky system settings, helping you maintain a strong security posture.
Keeping your iPhone secure from malware is an achievable goal that puts you in control of your digital safety. By combining smart habits with powerful security tools, you can confidently protect your personal information from emerging threats.
McAfee is committed to empowering you with the resources and protection needed to navigate the online world safely. McAfee Mobile Security provides full protection against various types of malware targeting the Apple ecosystem. With safe browsing features, a secure VPN, and antivirus software, McAfee Security for iOS delivers protection against emerging threats, so you can continue to use your iPhone with peace of mind. Download the McAfee Mobile Security app today and get all-in-one protection.
The post A Guide to Remove Malware From Your iPhone appeared first on McAfee Blog.

We use our smartphones for everything under the sun, from work-related communication to online shopping, banking transactions, and social media. For this reason, our phones store a lot of personal data, including contacts, account details, and bank account logins.
High online usage also makes your devices vulnerable to viruses, a type of malware that replicate themselves and spread throughout the entire system. They can affect your phone’s performance or, worse, compromise your sensitive information so that hackers can benefit monetarily.
In this article, we will give you a rundown of viruses that can infect your phone and how you can identify and eliminate them. We will also provide some tips for protecting your phone from viruses in the first place.
iPhones and Android devices run on different operating systems, hence differences in how they resist viruses and how these affect each system.
While iOS hacks can still happen, Apple’s operating system is reputed to be highly resistant to viruses because of its design. By restricting interactions between apps, Apple’s operating system limits the movement of a virus across the device. However, if you jailbreak your iPhone or iPad to unlock other capabilities or install third-party apps, then the security restrictions set by Apple’s OS won’t work. This exposes your iPhone and you to vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
Android phones, while also designed with cybersecurity in mind, rely on open-source code, making them an easier target for hackers. Additionally, giving users the capability to install third-party apps from alternative app stores, such as the Amazon or Samsung Galaxy app stores, makes Android devices open to viruses.
Cybercriminals today are sophisticated and can launch a variety of cyberattacks on your smartphone. Some viruses that can infect your phone include:
Ultimately, contracting a virus on your phone or computer comes down to your browsing and downloading habits. These are the most common ways it could happen:
Now that you know how your phone could be infected by a virus, look out for these seven signs that occur when malicious software is present:
Most pop-up ads don’t carry viruses but are only used as marketing tools. However, if you find yourself closing pop-up ads more often than usual, it might indicate a virus on your phone. These ads might be coming from apps in your library that you didn’t install. In this case, uninstall them immediately as they tend to carry malware that’s activated when the app is opened or used.
When you accidentally download apps that contain malware, your device has to work harder to continue functioning. Since your phone isn’t built to support malware, there is a good chance it will overheat.
If your contacts receive unsolicited scam emails or messages on social media from your account, especially those containing suspicious links, a virus may have accessed your contact list. It’s best to let all the recipients know that your phone has been hacked so that they don’t download any malware themselves or forward those links to anybody else.
An unusually slow-performing device is a hint of suspicious activity on your phone. The device may be slowing down because it is working harder to support the downloaded virus. Alternatively, unfamiliar apps might be taking up storage space and running background tasks, causing your phone to run more slowly.
Are you finding credit card transactions in your banking statements that you don’t recognize? It could be an unfamiliar app or malware making purchases through your account without your knowledge.
A sudden rise in your data usage or phone bill can be suspicious. A virus might be running background processes or using your internet connection to transfer data out of your device for malicious purposes.
An unusually quick battery drain may also cause concern. Your phone will be trying to meet the energy requirements of the virus, so this problem is likely to persist for as long as the virus is on the device.
You may have an inkling that a virus resides in your phone, but the only way to be sure is to check. An easy way to do this is by downloading a trustworthy antivirus app that will prevent suspicious apps from attaching themselves to your phone and secure any public connections you might be using.
Another way to check your phone is to follow these step-by-step processes, depending on the type of phone you use:
Once you have determined that a virus is present on your iPhone or Android device, there are several things you can do.
Caring for your phone is a vital practice to protect your information. Follow these tips to stay safe online and help reduce the risk of your phone getting a virus.
You have come to rely heavily on your smartphones for many online activities and storage of much of your personal data, including contacts, account details, and bank account logins. This puts your devices at high risk of being infected by viruses that impact not just your phone’s performance but also of being compromised by cybercriminals.
To help you protect your device and personal information, the award-winning McAfee Mobile Security solution regularly scans for threats transmitted through suspicious links in text messages, emails, or downloads, and blocks them in real time. McAfee Mobile Security is a reputable security application that filters risky emails and phishing attempts, so your inbox stays secure while providing a secure virtual private network. It is also capable of spotting deepfake videos, so you can stay ahead of misinformation. With McAfee, you can rest easy knowing your mobile phone is protected from the latest cyberthreats.
The post 7 Signs Your Phone Is Infected With a Virus appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Cybercriminals are getting smarter. They’re now using a development toolkit called .NET MAUI to create fake apps that look and feel like the real thing—banking apps, dating apps, and even social media. But instead of helping you, these apps secretly steal your private info.
We break down the full research from McAfee Labs here:
.NET MAUI is a tool used by developers to build apps that work on many devices—like phones, tablets, and computers—all from one set of code.
That’s great for app creators. But now, hackers are using it too. While McAfee is able to detect this malware, the decision to build with .NET MAUI helps hide their dangerous code from most antivirus software. Think of it like a thief wearing an invisibility cloak—unless you’re really looking, you won’t see them.
Hackers are creating apps that look like they’re from real companies. For example, one fake app pretended to be IndusInd Bank, asking users to enter sensitive information like:
Once you hit submit, that info goes straight to the hacker’s server.

Figure 1. Fake IndusInd Bank app’s screen requesting user information
Normal Android apps have code in a format security tools can scan. These fake apps hide their code in binary files so it can’t be easily detected. That lets them stay on your phone longer—stealing quietly in the background.
In another case, hackers made an app that pretended to be a social media platform. This one targeted Chinese-speaking users and was even trickier than the fake bank app.
Here’s what it did:
And instead of using regular internet traffic, it sent stolen data through secret encrypted channels—so even if someone intercepted it, they couldn’t read it.

Figure 2. Various fake apps using the same technique
These apps aren’t in the Google Play Store. Instead, hackers are sharing them on:
So if someone sends you a link to a cool new app that’s not from the Play Store—be extra careful.
Here are a few easy ways to stay safe:
Hackers are getting creative, but you can stay one step ahead. These new .NET MAUI-based threats are sneaky—but they’re not unstoppable.
With smart habits and the right tools, you can keep your phone and your personal info safe. Want real-time protection on your phone? Download McAfee+ and get ahead of the latest threats.
The post New Android Malware Sneaks Past Security by Pretending to Be Real Apps appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Social media connects us to friends, trends, and news in real time—but it also opens the door to scammers looking to exploit trust and curiosity. From fake giveaways to impersonation scams, fraudsters use sophisticated tactics to trick users into handing over personal information, money, or access to their accounts.
Even the most internet-savvy users can fall victim to these deceptive schemes. That’s why it’s crucial to recognize the red flags before it’s too late. Whether it’s a DM from a “friend” in trouble, a deal that seems too good to be true, or a sudden request to verify your account, scammers prey on urgency and emotion to pull you in.
Here’s a look at some of the most common social media scams—and how you can stay one step ahead to protect yourself and your accounts.
Fraudsters use various tactics to lure unsuspecting users into their schemes, including:
Recognizing these red flags can help you stay safe:
Follow these precautions to reduce your risk of falling victim:
If you suspect you’ve fallen victim to a social media scam, take immediate action:
Social media scams are becoming more sophisticated, but you can protect yourself by staying informed and cautious.
Always verify messages, be skeptical of too-good-to-be-true offers, and use strong security measures to safeguard your accounts.
By recognizing these scams early, you can avoid financial loss and keep your personal information safe online.
McAfee helps protect you from online threats with advanced security tools, including identity monitoring, safe browsing features, and real-time malware protection. Stay one step ahead of scammers with trusted cybersecurity solutions.
The post The 9 Most Common Social Media Scams—and How to Spot Them Before It’s Too Late appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Authored by Anuradha, Sakshi Jaiswal
In 2024, scams in India have continued to evolve, leveraging sophisticated methods and technology to exploit unsuspecting individuals. These fraudulent activities target people across demographics, causing financial losses and emotional distress. This blog highlights some of the most prevalent scams this year, how they operate, some real-world scenarios, tips to stay vigilant and what steps to be taken if you become a victim.

This blog covers the following scams:
Scam Tactics:
Fraudsters on WhatsApp employ deceptive tactics to steal personal information, financial data, or gain unauthorized access to accounts. Common tactics include:
Case 1: In the figure below, a user is being deceived by a message originating from the +244 country code, assigned to Angola. The message offers an unrealistic investment opportunity promising a high return in just four days, which is a common scam tactic. It uses pressure and informal language, along with a link for immediate action.

Case 2: In the figure below, a user is being deceived by a message originating from the +261 country code, assigned to Madagascar. The message claims that you have been hired and asks you to click a link to view the offer or contact the sender which is a scam.

Case 3: In the figure below, a user is being deceived by a message originating from the +91 country code, assigned to India. Scammers may contact you, posing as representatives of a legitimate company, offering a job opportunity. The recruiter offers an unrealistic daily income (INR 2000–8000) for vague tasks like searching keywords, which is suspicious. Despite requests, they fail to provide official company details or an email ID, raising credibility concerns. They also ask for personal information prematurely, a common red flag.

Case 4: In the figure below, a user is being deceived by a message originating from the +84 country code, assigned to Vietnam. The offer to earn money by watching a video for just a few seconds and providing a screenshot is a common tactic used by scammers to exploit individuals. They may use the link to gather personal information, or your action could lead to phishing attempts.

Case 5: In the figure below, a user is being misled by a message originating from the country codes +91, +963, and +27, corresponding to India, Syria, and South Africa, respectively. The message claims to offer a part-time job with a high salary for minimal work, which is a common tactic used by scammers to lure individuals. The use of popular names like “Amazon” and promises of easy money are red flags. The link provided might lead to phishing attempts or data theft. It’s important not to click on any links, share personal details, or respond to such unsolicited offers.

Case 6: The messages encourage you to post fake 5-star reviews for businesses in exchange for a small payment, which is unethical and often illegal. Scammers use such tactics to manipulate online ratings, and the provided links could lead to phishing sites or malware. Avoid engaging with these messages, clicking on the links, or participating in such activities.

How to Identify WhatsApp Scams:
Impact:
Prevention:

Scam Tactics:
How to Identify Instant Loan Scam:

Impact:
Prevention:

Voice-cloning scams use advanced AI technology to replicate the voices of familiar people, such as friends, family members, or colleagues, to manipulate victims into transferring money or providing sensitive information.
Scam Tactics:
How to Identify AI Voice-Cloning Scams:
Impact:
Prevention

Scam Tactics
Scammers use various methods to deceive victims into revealing credit card information or making unauthorized payments:
How to identify Credit card scam:
Impact:
Prevention:

Scam Tactics:
In fake delivery scams, fraudsters pose as delivery services to trick you into providing personal information, card details, or payment. Common tactics include:
How to Identify Fake Delivery Scams:
Impact:
Prevention:

Scam Tactics:
Scammers pose as police officers or government officials, accusing victims of being involved in illegal activities like money laundering or cybercrime. They intimidate victims by threatening arrest or legal action unless immediate payment is made to “resolve the matter.”
How to Identify Digital Arrest Scam:
Impact: Daily losses from such scams run into lakhs, as victims panic and transfer money or provide sensitive information under pressure.
Prevention:
What to Do if You Fall Victim
If you’ve fallen victim to any of the mentioned scams—Digital Arrest Scam, Instant Loan Scam, Voice Cloning Scam, WhatsApp Scam, Fake Delivery Scam or Credit Card Scam—it’s important to take immediate action to minimize damage and protect your finances and personal information. Here are common tips and steps to follow for all these scams:
As scams in India continue to grow in number and sophistication, it is crucial to raise awareness to protect individuals and businesses from falling victim to these fraudulent schemes. Scams such as phishing, fake job offers, credit card scams, loan scams, investment frauds and online shopping frauds are increasingly targeting unsuspecting victims, causing significant financial loss and emotional harm.
By raising awareness of scam warning signs and encouraging vigilance, we can equip individuals to make safer, more informed decisions online. Simple precautions, such as verifying sources, being cautious of unsolicited offers, and safeguarding personal and financial information, can go a long way in preventing scams.
It is essential for both individuals and organizations to stay informed and updated on emerging scam tactics. Through continuous awareness and proactive security measures, we can reduce the impact of scams, ensuring a safer and more secure digital environment for everyone in India.
The post Rising Scams in India: Building Awareness and Prevention appeared first on McAfee Blog.

It’s an increasingly common surprise: a package shows up at your door with your name and your address…but you never ordered it.
These unsolicited deliveries may seem harmless, but they’re often tied to a scheme called a brushing scam. These scams occur year-round but tend to pick up around the holidays or peak shopping seasons, when shipping volume spikes and it’s easier for suspicious packages to blend in.
Below is everything you need to know: how brushing scams work, what they mean for your personal information, and the exact steps to take if one shows up at your doorstep.
A brushing scam is when sellers send you unsolicited items so they can post fake reviews using your name, boosting their product’s ranking and credibility without your consent.
A typical brushing scam looks like this:
In one sentence: Your delivery confirmation becomes their proof that a real customer received the item—even though you never ordered it.
The term comes from e-commerce, where sellers would “brush up” their sales by generating fake orders and reviews. Today, brushing scams are a global issue affecting major online marketplaces.
If the item feels random or unusually cheap, it fits the profile.
Personal Data Exposure
The biggest red flag is that someone had your name and address, and possibly more. Brushing scams often follow data breaches or third-party leaks.
Account Risk
Some platforms may temporarily flag or freeze your account if someone posts fake reviews under your name.
Misleading Products
Fake reviews inflate trust and push low-quality items higher in search results. That misleads other shoppers and props up fraudulent sellers.
Potential Safety Hazards
Some unsolicited items—cosmetics, supplements, electronics, or seeds—may be unsafe, expired, counterfeit, or banned.
Generally: No.
You are not legally required to return or pay for an unsolicited package. But reporting it helps platforms investigate fraudulent sellers.
This helps platforms identify abusive sellers.
Genuine reviews mention specific details; fake ones are vague, repetitive, or overly positive.
Avoid newly created storefronts with few verified reviews.
Why am I receiving random packages from overseas?
It’s often part of a brushing scam where sellers need a “delivered” status to post fake reviews.
Is a brushing scam identity theft?
Not exactly, but it does mean someone had access to your personal data, which increases your overall risk.
Should I throw the item away?
You can safely discard most brushing-scam items, but avoid using them and report the incident first.
Should I worry if I get seeds or soil?
Yes—never plant or dispose of unknown seeds improperly. Report them to the USDA or your state agriculture office.
Brushing scams may seem like a harmless freebie, but they’re a sign that your personal information was exposed and could potentially be misused.
Stay cautious, secure your accounts, report any unsolicited packages, and trust only reputable sellers. With simple steps, you can protect your identity, and avoid being pulled into a scammer’s fake review scheme.
The post Brushing Scams: What They Are and How to Stay Safe From Unsolicited Packages appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Phishing attacks increased nearly 40 percent in the year ending August 2024, with much of that growth concentrated at a small number of new generic top-level domains (gTLDs) — such as .shop, .top, .xyz — that attract scammers with rock-bottom prices and no meaningful registration requirements, new research finds. Meanwhile, the nonprofit entity that oversees the domain name industry is moving forward with plans to introduce a slew of new gTLDs.

Image: Shutterstock.
A study on phishing data released by Interisle Consulting finds that new gTLDs introduced in the last few years command just 11 percent of the market for new domains, but accounted for roughly 37 percent of cybercrime domains reported between September 2023 and August 2024.
Interisle was sponsored by several anti-spam organizations, including the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG), the Coalition Against Unsolicited Commercial Email (CAUCE), and the Messaging, Malware, and Mobile Anti-Abuse Working Group (M3AAWG).
The study finds that while .com and .net domains made up approximately half of all domains registered in the past year (more than all of the other TLDs combined) they accounted for just over 40 percent of all cybercrime domains. Interisle says an almost equal share — 37 percent — of cybercrime domains were registered through new gTLDs.
Spammers and scammers gravitate toward domains in the new gTLDs because these registrars tend to offer cheap or free registration with little to no account or identity verification requirements. For example, among the gTLDs with the highest cybercrime domain scores in this year’s study, nine offered registration fees for less than $1, and nearly two dozen offered fees of less than $2.00. By comparison, the cheapest price identified for a .com domain was $5.91.
Currently, there are around 2,500 registrars authorized to sell domains by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), the California nonprofit that oversees the domain industry.
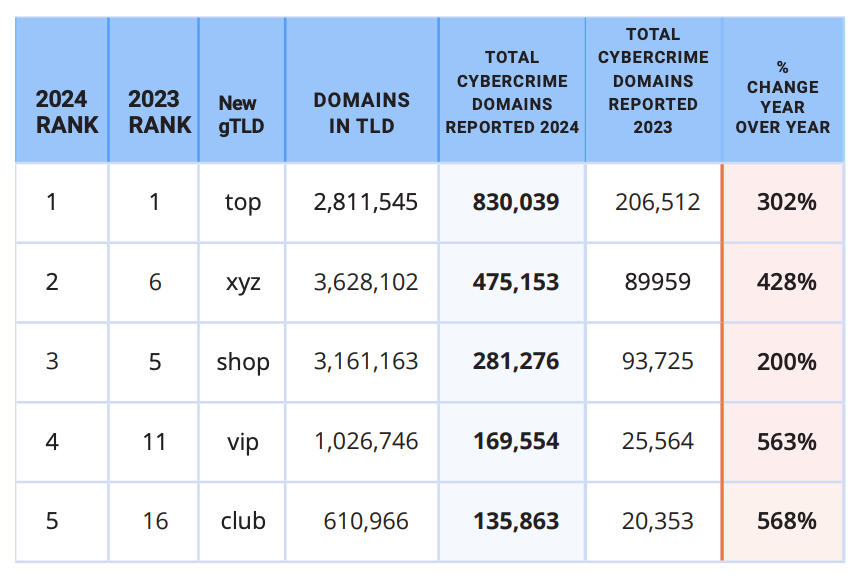
The top 5 new gTLDs, ranked by cybercrime domains reported. Image: Interisle Cybercrime Supply Chain 2014.
Incredibly, despite years of these reports showing phishers heavily abusing new gTLDs, ICANN is shuffling forward on a plan to introduce even more of them. ICANN’s proposed next round envisions accepting applications for new gTLDs in 2026.
John Levine is author of the book “The Internet for Dummies” and president of CAUCE. Levine said adding more TLDs without a much stricter registration policy will likely further expand an already plentiful greenfield for cybercriminals.
“The problem is that ICANN can’t make up their mind whether they are the neutral nonprofit regulator or just the domain speculator trade association,” Levine told KrebsOnSecurity. “But they act a lot more like the latter.”
Levine said the vast majority of new gTLDs have a few thousand domains — a far cry from the number of registrations they would need just to cover the up-front costs of operating a new gTLD (~$180,000-$300,000). New gTLD registrars can quickly attract customers by selling domains cheaply to customers who buy domains in bulk, but that tends to be a losing strategy.
“Selling to criminals and spammers turns out to be lousy business,” Levine said. “You can charge whatever you want on the first year, but you have to charge list price on domain renewals. And criminals and spammers never renew. So if it sounds like the economics makes no sense it’s because the economics makes no sense.”
In virtually all previous spam reports, Interisle found the top brands referenced in phishing attacks were the largest technology companies, including Apple, Facebook, Google and PayPal. But this past year, Interisle found the U.S. Postal Service was by far the most-phished entity, with more than four times the number of phishing domains as the second most-frequent target (Apple).
At least some of that increase is likely from a prolific cybercriminal using the nickname Chenlun, who has been selling phishing kits targeting domestic postal services in the United States and at least a dozen other countries.
Interisle says an increasing number of phishers are eschewing domain registrations altogether, and instead taking advantage of subdomain providers like blogspot.com, pages.dev, and weebly.com. The report notes that cyberattacks hosted at subdomain provider services can be tough to mitigate, because only the subdomain provider can disable malicious accounts or take down malicious web pages.
“Any action upstream, such as blocking the second-level domain, would have an impact across the provider’s whole customer base,” the report observes.
Interisle tracked more than 1.18 million instances of subdomains used for phishing in the past year (a 114 percent increase), and found more than half of those were subdomains at blogspot.com and other services operated by Google.
“Many of these services allow the creation of large numbers of accounts at one time, which is highly exploited by criminals,” the report concludes. “Subdomain providers should limit the number of subdomains (user accounts) a customer can create at one time and suspend automated, high-volume automated account sign-ups – especially using free services.”
Dec. 4, 10:21 a.m. ET: Corrected link to report.

McAfee threat researchers have identified several consumer brands and product categories most frequently used by cybercriminals to trick consumers into clicking on malicious links in the first weeks of this holiday shopping season. As holiday excitement peaks and shoppers hunt for the perfect gifts and amazing deals, scammers are taking advantage of the buzz. The National Retail Federation projects holiday spending will reach between $979.5 and $989 billion this year, and cybercriminals are capitalizing by creating scams that mimic the trusted brands and categories consumers trust. From October 1 to November 12, 2024, McAfee safeguarded its customers from 624,346 malicious or suspicious URLs tied to popular consumer brand names – a clear indication that bad actors are exploiting trusted brand names to deceive holiday shoppers.
McAfee’s threat research also reveals a 33.82% spike in malicious URLs targeting consumers with these brands’ names in the run-up to Black Friday and Cyber Monday. This rise in fraudulent activity aligns with holiday shopping patterns during a time when consumers may be more susceptible to clicking on offers from well-known brands like Apple, Yeezy, and Louis Vuitton, especially when deals seem too good to be true – pointing to the need for consumers to stay vigilant, especially with offers that seem unusually generous or come from unverified sources.
McAfee threat researchers have identified a surge in counterfeit sites and phishing scams that use popular luxury brands and tech products to lure consumers into “deals” on fake e-commerce sites designed to appear as official brand pages. While footwear and handbags were identified as the top two product categories exploited by cybercrooks during this festive time, the list of most exploited brands extends beyond those borders:
By mimicking trusted brands like these, offering unbelievable deals, or posing as legitimate customer service channels, cybercrooks create convincing traps designed to steal personal information or money. Here are some of the most common tactics scammers are using this holiday season:
With holiday shopping in full swing, it’s essential for consumers to stay one step ahead of scammers. By understanding the tactics cybercriminals use and taking a few precautionary measures, shoppers can protect themselves from falling victim to fraud. Here are some practical tips for safe shopping this season:
McAfee’s threat research team analyzed malicious or suspicious URLs that McAfee’s web reputation technology identified as targeting customers, by using a list of key company and product brand names—based on insights from a Potter Clarkson report on frequently faked brands—to query the URLs. This methodology captures instances where users either clicked on or were directed to dangerous sites mimicking trusted brands. Additionally, the team queried anonymized user activity from October 1st through November 12th.
The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: Yeezy is a popular product brand formerly from Adidas found in multiple Malicious/Suspicious URLs. Often, they present themselves as official Yeezy and/or Adidas shopping sites.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: The Apple brand was a popular target for scammers. Many sites were either knock offs, scams, or in this case, a fake customer service page designed to lure users into a scam.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: This particular (fake) Apple sales site used Apple within its URL and name to appear more official. Oddly, this site also sells Samsung Android phones.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: This site, now taken down, is a scam site purporting to sell Nike shoes.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: Louis Vuitton is a popular brand for counterfeit and scams. Particularly their handbags. Here is one site that was entirely focused on Louis Vuitton Handbags.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: This site presents itself as the official Louis Vuitton site selling handbags and clothes.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: This site uses too-good-to-be-true deals on branded items including this Louis Vuitton Bomber jacket.

The image below is a screenshot of a fake / malicious / scam site: Rolex is a popular watch brand for counterfeits and scams. This site acknowledges it sells counterfeits and makes no effort to indicate this on the product.

The post This Holiday Season, Watch Out for These Cyber-Grinch Tricks Used to Scam Holiday Shoppers appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Two-step verification, two-factor authentication, multi-factor authentication…whatever your social media platform calls it, it’s an excellent way to protect your accounts.
There’s a good chance you’re already using multi-factor verification with your other accounts — for your bank, your finances, your credit card, and any number of things. The way it requires an extra one-time code in addition to your login and password makes life far tougher for hackers.
It’s increasingly common to see nowadays, where all manner of online services only allow access to your accounts after you’ve provided a one-time passcode sent to your email or smartphone. That’s where two-step verification comes in. You get sent a code as part of your usual login process (usually a six-digit number), and then you enter that along with your username and password.
Some online services also offer the option to use an authenticator app, which sends the code to a secure app rather than via email or your smartphone. Authenticator apps work much in the same way, yet they offer three unique features:
Google, Microsoft, and others offer authenticator apps if you want to go that route. You can get a good list of options by checking out the “editor’s picks” at your app store or in trusted tech publications.
Whichever form of authentication you use, always keep that secure code to yourself. It’s yours and yours alone. Anyone who asks for that code, say someone masquerading as a customer service rep, is trying to scam you. With that code, and your username/password combo, they can get into your account.
Passwords and two-step verification work hand-in-hand to keep you safer. Yet not any old password will do. You’ll want a strong, unique password. Here’s how that breaks down:
Now, with strong passwords in place, you can get to setting up multi-factor verification on your social media accounts.
When you set up two-factor authentication on Facebook, you’ll be asked to choose one of three security methods:
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://www.facebook.com/help/148233965247823
When you set up two-factor authentication on Instagram, you’ll be asked to choose one of three security methods: an authentication app, text message, or WhatsApp.
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://help.instagram.com/566810106808145
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://faq.whatsapp.com/1920866721452534
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://support.google.com/accounts/answer/185839?hl=en&co=GENIE.Platform%3DDesktop
1. TapProfileat the bottom of the screen.
2. Tap the Menu button at the top.
3. Tap Settings and Privacy, then Security.
4. Tap 2-step verification and choose at least two verification methods: SMS (text), email, and authenticator app.
5. Tap Turn on to confirm.
And here’s a link to the company’s full walkthrough: https://support.tiktok.com/en/account-and-privacy/personalized-ads-and-data/how-your-phone-number-is-used-on-tiktok
The post How to Protect Your Social Media Passwords with Multi-factor Verification appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Federal prosecutors in Los Angeles this week unsealed criminal charges against five men alleged to be members of a hacking group responsible for dozens of cyber intrusions at major U.S. technology companies between 2021 and 2023, including LastPass, MailChimp, Okta, T-Mobile and Twilio.

A visual depiction of the attacks by the SMS phishing group known as Scattered Spider, and Oktapus. Image: Amitai Cohen twitter.com/amitaico.
The five men, aged 20 to 25, are allegedly members of a hacking conspiracy dubbed “Scattered Spider” and “Oktapus,” which specialized in SMS-based phishing attacks that tricked employees at tech firms into entering their credentials and one-time passcodes at phishing websites.
The targeted SMS scams asked employees to click a link and log in at a website that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication page. Some SMS phishing messages told employees their VPN credentials were expiring and needed to be changed; other phishing messages advised employees about changes to their upcoming work schedule.
These attacks leveraged newly-registered domains that often included the name of the targeted company, such as twilio-help[.]com and ouryahoo-okta[.]com. The phishing websites were normally kept online for just one or two hours at a time, meaning they were often yanked offline before they could be flagged by anti-phishing and security services.
The phishing kits used for these campaigns featured a hidden Telegram instant message bot that forwarded any submitted credentials in real-time. The bot allowed the attackers to use the phished username, password and one-time code to log in as that employee at the real employer website.
In August 2022, multiple security firms gained access to the server that was receiving data from that Telegram bot, which on several occasions leaked the Telegram ID and handle of its developer, who used the nickname “Joeleoli.”
The Telegram username “Joeleoli” can be seen sandwiched between data submitted by people who knew it was a phish, and data phished from actual victims. Click to enlarge.
That Joeleoli moniker registered on the cybercrime forum OGusers in 2018 with the email address joelebruh@gmail.com, which also was used to register accounts at several websites for a Joel Evans from North Carolina. Indeed, prosecutors say Joeleoli’s real name is Joel Martin Evans, and he is a 25-year-old from Jacksonville, North Carolina.
One of Scattered Spider’s first big victims in its 2022 SMS phishing spree was Twilio, a company that provides services for making and receiving text messages and phone calls. The group then used their access to Twilio to attack at least 163 of its customers. According to prosecutors, the group mainly sought to steal cryptocurrency from victim companies and their employees.
“The defendants allegedly preyed on unsuspecting victims in this phishing scheme and used their personal information as a gateway to steal millions in their cryptocurrency accounts,” said Akil Davis, the assistant director in charge of the FBI’s Los Angeles field office.
Many of the hacking group’s phishing domains were registered through the registrar NameCheap, and FBI investigators said records obtained from NameCheap showed the person who managed those phishing websites did so from an Internet address in Scotland. The feds then obtained records from Virgin Media, which showed the address was leased for several months to Tyler Buchanan, a 22-year-old from Dundee, Scotland.
A Scattered Spider phishing lure sent to Twilio employees.
As first reported here in June, Buchanan was arrested in Spain as he tried to board a flight bound for Italy. The Spanish police told local media that Buchanan, who allegedly went by the alias “Tylerb,” at one time possessed Bitcoins worth $27 million.
The government says much of Tylerb’s cryptocurrency wealth was the result of successful SIM-swapping attacks, wherein crooks transfer the target’s phone number to a device they control and intercept any text messages or phone calls sent to the victim — including one-time passcodes for authentication, or password reset links sent via SMS.
According to several SIM-swapping channels on Telegram where Tylerb was known to frequent, rival SIM-swappers hired thugs to invade his home in February 2023. Those accounts state that the intruders assaulted Tylerb’s mother in the home invasion, and that they threatened to burn him with a blowtorch if he didn’t give up the keys to his cryptocurrency wallets. Tylerb was reputed to have fled the United Kingdom after that assault.

A still frame from a video released by the Spanish national police, showing Tyler Buchanan being taken into custody at the airport.
Prosecutors allege Tylerb worked closely on SIM-swapping attacks with Noah Michael Urban, another alleged Scattered Spider member from Palm Coast, Fla. who went by the handles “Sosa,” “Elijah,” and “Kingbob.”
Sosa was known to be a top member of the broader cybercriminal community online known as “The Com,” wherein hackers boast loudly about high-profile exploits and hacks that almost invariably begin with social engineering — tricking people over the phone, email or SMS into giving away credentials that allow remote access to corporate networks.
In January 2024, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that Urban had been arrested in Florida in connection with multiple SIM-swapping attacks. That story noted that Sosa’s alter ego Kingbob routinely targeted people in the recording industry to steal and share “grails,” a slang term used to describe unreleased music recordings from popular artists.
FBI investigators identified a fourth alleged member of the conspiracy – Ahmed Hossam Eldin Elbadawy, 23, of College Station, Texas — after he used a portion of cryptocurrency funds stolen from a victim company to pay for an account used to register phishing domains.
The indictment unsealed Wednesday alleges Elbadawy controlled a number of cryptocurrency accounts used to receive stolen funds, along with another Texas man — Evans Onyeaka Osiebo, 20, of Dallas.
Members of Scattered Spider are reputed to have been involved in a September 2023 ransomware attack against the MGM Resorts hotel chain that quickly brought multiple MGM casinos to a standstill. In September 2024, KrebsOnSecurity reported that a 17-year-old from the United Kingdom was arrested last year by U.K. police as part of an FBI investigation into the MGM hack.
Evans, Elbadawy, Osiebo and Urban were all charged with one count of conspiracy to commit wire fraud, one count of conspiracy, and one count of aggravated identity theft. Buchanan, who is named as an indicted co-conspirator, was charged with conspiracy to commit wire fraud, conspiracy, wire fraud, and aggravated identity theft.
A Justice Department press release states that if convicted, each defendant would face a statutory maximum sentence of 20 years in federal prison for conspiracy to commit wire fraud, up to five years in federal prison for the conspiracy count, and a mandatory two-year consecutive prison sentence for aggravated identity theft. Buchanan would face up to 20 years in prison for the wire fraud count as well.
Further reading:

So, what does your phone know about you? Taken all together it knows plenty — sometimes in ways that feel like your phone is watching you.
It all comes down to the data that courses through your phone and your apps, along with a phone’s built-in tracking capabilities. Indeed, your phone certainly knows plenty about you. And companies keep tabs on that. Here’s how…
The apps on our phones entertain us, inform us, and help us shop. Many of them also track our activities and location — and then sell or share that info with third parties. From there, that info can end up with data brokers who sell that info to anyone who’ll pay. That includes advertisers, spammers, insurance companies, hackers, law enforcement, private investigators, and so on. It’s all legal, and it’s all part of a multi-billion-dollar industry worldwide.
Still, you can take charge of your privacy amidst all this data and info gathering. Several steps can reduce what your phone collects and shares with others.
For starters, though, let’s look at several of the things your phone knows about you.
Unless you’ve turned it off completely, your phone can track you in several ways with several degrees of accuracy:
GPS: The Global Positioning System, or GPS as many of us know it, is a system of satellites run by the U.S. government for navigation purposes. First designed for national defense, the system became available for public use in the 1980s. It’s highly accurate, to anywhere between nine to 30 feet depending on conditions and technology used, making it one of the strongest tools for determining a phone’s location. This is what powers location services on cell phones, and thus can help an app recommend a great burger joint nearby.
Cell towers: Cell phone providers can track a phone’s location by the distance it is to various cell phone towers and by the strength of its signal. The location info this method provides is a bit coarser than GPS, providing results that can place a phone within 150 feet. It’s most accurate in urban areas with high densities of cell phone towers, although it does not always work well indoors as some buildings can weaken or block cell phone signals.
One of the most significant public benefits of this method is that it automatically routes emergency service calls (like 911 in the U.S.) to the proper local authorities without any guesswork from the caller.
Public Wi-Fi: Larger tech companies and internet providers will sometimes provide free public Wi-Fi hotspots that people can tap into at airports, restaurants, coffeehouses, and such. It’s a nice convenience, but connecting to their Wi-Fi might share a phone’s MAC address, a unique identifier for connected devices, along with other identifiers on the smartphone.
Taken together, this can allow the Wi-Fi hosting company to gather location and behavioral data while you use your phone on their Wi-Fi network.
Bluetooth: Like with public Wi-Fi, companies can use strategically placed Bluetooth devices to gather location info as well. If Bluetooth is enabled on a phone, it will periodically seek out Bluetooth-enabled devices to connect to while the phone is awake. This way, a Bluetooth receiver can then capture that phone’s unique MAC address. This provides highly exact location info to within just a few feet because of Bluetooth’s short broadcast range.
In the past, we’ve seen retailers use this method to track customers in their physical stores to better understand their shopping habits. However, newer phones often create dummy MAC addresses when they seek out Bluetooth connections, which helps thwart this practice.
Certain apps pair location info with other info they collect while you use that app. In some cases, an app shares that precise combination of info with third parties. (It all depends on the terms in the user agreement you accepted once you installed it.)
What does that look like in the real world? Third parties might know:
Those are just a few examples of many.
Just to emphasize what we said above, not every app sells shares or sells your info to third parties. However, that gets into the complicated nature of user agreements. The language that covers what’s collected, for what reasons, what’s done with it, and who it’s shared can be tough to tease out because it’s often written in some form of legalese.
Broadly though, apps need to request permission to access location tracking services. In the past, we’ve seen some sketchy apps request location permissions even though they have no reason to. Examples include coupon apps, wallpaper apps, productivity apps, and plenty of games too. When apps like those ask for permission to access location tracking services, raises a red flag that your privacy is in jeopardy.
Depending on what apps and services you use, your phone might know a lot about your health. That can include range of info, as apps can track things like step counts, vital signs, and menstrual cycles. Other apps manage health conditions or work as symptom checkers. In all, this data can get very private. Unfortunately, sometimes that data winds up in the hands of third parties.
With that, we’ve seen cases where people’s medical info was shared without their knowledge by medical apps and services.
In April 2024, The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) ruled against an online mental health service that “disclosed consumers’ sensitive personal health information and other sensitive data to third parties for advertising purposes…”[i] Also according to the complaint, the company gave third parties personal data about its users including names, medical and prescription histories, pharmacy and health insurance info, and other health info.
Also in April 2024, U.S. healthcare provider Kaiser Permanente disclosed that more than 13 million people had some of their personal data shared by third parties via tracking technologies on its websites and apps. Companies such as Microsoft (Bing), Google, and X (Twitter) were all named.[ii] That info possibly included how people interacted with and navigated through their website or mobile app, along with search terms used in Kaiser’s health encyclopedia.
So, is someone on the other end of your smartphone listening to your recordings when you use Siri or Google Assistant? Possibly, yes. Companies make constant improvements to their devices and services, which may include the review of commands from users to make sure they are interpreted correctly. There are typically two types of review — machine and human. As the names suggest, a machine review is a digital analysis. Human reviews entail someone listening to and evaluating a recorded command or reading and evaluating a transcript of a written command.
However, several manufacturers let you opt out of those reviews. In fact, you’ll find that they post a fair share of articles about this collection and review process, along with your choices for opting in or out as you wish:
Turn off your phone or switch to Airplane Mode. Disconnect. Without a Wi-Fi or data connection, you can’t get tracked. While this makes you unreachable, it also makes you untraceable, which you might want to consider if you’d rather keep your whereabouts and travels to yourself for periods of time.
Turn off location services altogether. As noted above, your smartphone can get tracked by other means, yet disabling location services in your phone settings shuts down a primary avenue of location data collection. Note that your maps apps won’t offer directions, and your restaurant app won’t point you toward that tasty burger when location services are off, but you’ll be more private than with them turned on.
Provide permissions on an app-by-app basis. Another option is to go into your phone settings and enable location services for specific apps in specific cases. For example, you can set your map app to enable location services only while in use. For other apps, you can disable location services entirely. Yet another option is to have the app ask for permissions each time. Note that this is a great way to discover if apps have defaulted to using location services without your knowledge when you installed them.
On an iPhone, you can find this in Settings -> Privacy & Security -> Location Services. On an Android, go to Settings -> Locations -> App Locations Permissions.
Turn off app tracking. As you’ve seen, some apps will ask to track your activity and potentially share it with data brokers and other third parties. You can halt this by turning off app tracking. On an iPhone, go to Settings -> Privacy & Security -> Tracking and disable “Allow Apps to Request to Track.” On an Android phone, go to Settings -> Privacy and Security, then turn on “Do Not Track.”
And just as you can with location services, you can set apps to make tracking requests on an app-by-app basis. You’ll see it on the same screen that has the global “Do Not Track” option.
Opt yourself out of cell phone carrier ad programs. Different cell phone carriers have different user agreements, yet some might allow the carrier to share insights about you with third parties based on browsing and usage history. Opting out of these programs might not stop your cell phone carrier from collecting data about you, but it might prevent it from sharing insights about you with others.
To see if you take part in one of these programs, log into your account portal or app. Look for settings around “relevant advertising,” “custom experience,” or even “advertising,” and then figure out if these programs are worth it.
Delete old apps. And be choosy about new ones. Fewer apps mean fewer avenues of potential data collection. If you have old, unused apps, consider deleting them, along with the accounts and data associated with them. Our Online Account Cleanup Online Account Cleanup can make quick work of it. It scans for accounts you no longer use, shows how risky they are, and helps you delete them, along with your personal info. In all, breaches and leaks are a numbers game. The fewer you keep, the better, when it comes to protecting your personal info.
Remove your info from data broker sites. As we’ve seen, the personal info on your smartphone can wind up on data broker sites. And they’ll sell it to practically anyone. Our Personal Data Cleanup can help you remove your personal info from several of the sketchiest brokers out there. Running it periodically can help keep your info off those sites if it crops up again.
[i] https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/press-releases/2024/04/proposed-ftc-order-will-prohibit-telehealth-firm-cerebral-using-or-disclosing-sensitive-data?utm_source=govdelivery
[ii] https://www.hipaajournal.com/kaiser-permanente-website-tracker-breach-affects-13-4-million-individuals/
The post Every Step You Take, Every Call You Make: Is Your Phone Tracking You? appeared first on McAfee Blog.

It usually starts with something small.
You’re scrolling TikTok or Instagram, half-paying attention, when a Black Friday ad pops up. It looks like the brand you love—same logo, same photos, same “limited-time deal” language you’ve seen in real promos. The link takes you to a site that looks identical to the real one. The checkout page works. The confirmation email looks legit.
Then the payment clears, and the merchant name on your bank statement doesn’t match the store at all.
That moment, wait, what did I just buy from?, is becoming the defining holiday-shopping scam of 2025.
This year, fake ads and cloned storefronts aren’t sketchy one-offs or typo-filled red flags. They’re polished. They’re identical. And increasingly, they’re powered by AI.
McAfee’s 2025 holiday research found that nearly half of Americans (46%) have already encountered AI-altered or AI-generated scams while shopping. And with 96% of people planning to shop online, many doing so daily, scammers know this is peak opportunity.
Here’s how fraudsters are blending into the busiest shopping season of the year, what the data shows, and how to stay one step ahead.
A perfect storm is happening:
People are shopping more often.
Nearly half of U.S. adults expect to shop online daily or multiple times per day during the holidays.
People are rushed.
From early Black Friday “price drop” alerts to Cyber Monday countdowns, shoppers don’t slow down to verify what they’re seeing.
AI makes scam content nearly flawless.
McAfee found technology email scams surging ~85%, retail email scams rising ~50%, and fraudulent URLs climbing across the board—from counterfeit Apple support pages to fake Costco refund portals.
Holiday deals are already rolling out—and so are the scams.
McAfee’s 2025 holiday research shows major spikes in email scams (~50% increase), technology scams (~85% increase), and fake storefronts that mimic trusted retailers. AI tools are making these scams faster, more realistic, and harder to spot.
It’s not that shoppers suddenly got careless.
It’s that scammers suddenly got good.

This is the big one, and it’s getting cleaner every year.
Scammers lift entire storefronts:
The only giveaway? A URL that’s juuust slightly off—“target-sale.com” instead of “target.com,” or a link ending in “.shop” or “.store” rather than a brand’s normal domain.
Once you enter your payment info, it goes directly into a database that criminals resell or use to make purchases.
How to spot and avoid this scam: Skip the ad. Type the retailer’s name into your browser yourself. If it’s a real deal, you’ll find it on their actual site.
Short-form videos are now a prime scam vehicle.
Scammers steal influencer footage, use AI voice clones, or generate deepfake “promo” videos with celebrities offering huge holiday discounts. When someone clicks the link, it leads straight to a counterfeit store.
How to spot and avoid this scam: Check the creator’s account history. Real brands don’t drop one-off promo videos from accounts you’ve never seen before. Same as our initial advice, skip the ad entirely and go directly to the official brand website rather than clicking any links.
The classic delivery scam is back, with McAfee researchers finding dozens of examples of fake messages attempting to scam holiday shoppers.
You’ll receive a text saying a package can’t be delivered or that a small fee is needed to confirm your address.
McAfee found that 43% of people have encountered fake delivery notifications, and many victims say they entered credit card information thinking they were resolving a legitimate issue.
How to spot and avoid this scam: UPS, USPS, and FedEx will never send a clickable payment link in a text. If you’re wondering about a specific delivery, go directly to the site you ordered it from, or your original receipt in your email to find your tracking information.
These hit during the weeks leading up to the holidays.
Messages claim:
How to spot and avoid this scam:
No legitimate company will ever resolve account issues through gift cards or text-confirmation codes.
Not long ago, scam emails had broken English and pixelated logos.
Now scammers use generative AI to:
And people are noticing.
57% of shoppers say they’re more concerned about AI scams this year than last.
Yet 38% believe they can spot scams—even though 22% have fallen for one.
Confidence ≠ protection.

If something feels off—a message, a link, a charge on your bank statement—don’t panic. Most holiday scams rely on speed and confusion. Slowing down and taking a few simple steps can keep a bad situation from turning into real damage.
Close the tab, delete the message, and don’t click anything else.
Scammers often stack multiple pop-ups or redirects to pressure you into acting fast.
If you started typing in a password or card number but didn’t hit “submit,” back out.
If you did enter details, move to the next steps right away.
Use a strong, unique password—especially for accounts tied to:
A reused password is how one compromised login unlocks everything else. McAfee offers a password manager to help you make and store strong, unique passwords.
Fraud usually starts small: $1–$5 “test” charges, odd merchant names, or tiny withdrawals.
If you see anything suspicious, contact your bank and request:
Some fake sites drop malware or spyware quietly in the background.
A quick scan can detect:
McAfee offers a free antivirus trial that you can use to scan your device and check for compromises.
Reporting helps stop other shoppers from being targeted.
You can report scams to:
McAfee can automatically detect whether the link, message, or site you interacted with is malicious—and alert you if your information may have been exposed.
Tools like:
can help contain an issue before it turns into identity theft.

There’s always someone on your holiday list who doesn’t want more stuff, they want something useful. The friend who loves a clean inbox. The sibling who’s constantly traveling. The parent who keeps forwarding you suspicious texts asking, “Is this real?”
For them, security might actually be the most thoughtful gift you can give this year.
Online safety tools aren’t flashy, but they are the thing people reach for the moment they click the wrong link, lose a password, or get a sketchy delivery text. And with scams more believable than ever, digital protection has quietly become a new “practical essential,” like a good VPN or a reliable password manager.
Gifting McAfee means giving someone:
Scam protection that works quietly in the background
Scam Detector flags dangerous messages, deepfake-style content, and fake shopping sites before they ever interact with them.
Identity & financial monitoring
A huge help for anyone who’s been burned by fraud in the past — or is tired of checking bank statements manually.
Password security that doesn’t require them to remember anything
Perfect for the person who uses the same password everywhere (and you know exactly who I mean).
Device protection for laptops, phones, and tablets
Which is especially relevant for people shopping, traveling, or working remotely through the holiday season.
It’s practical. It’s protective. And unlike most presents, it’s something they’ll use all year.
The post How To Protect Yourself from Black Friday and Cyber Monday AI Scams appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Not long ago, the ability to digitally track someone’s daily movements just by knowing their home address, employer, or place of worship was considered a dangerous power that should remain only within the purview of nation states. But a new lawsuit in a likely constitutional battle over a New Jersey privacy law shows that anyone can now access this capability, thanks to a proliferation of commercial services that hoover up the digital exhaust emitted by widely-used mobile apps and websites.

Image: Shutterstock, Arthimides.
Delaware-based Atlas Data Privacy Corp. helps its users remove their personal information from the clutches of consumer data brokers, and from people-search services online. Backed by millions of dollars in litigation financing, Atlas so far this year has sued 151 consumer data brokers on behalf of a class that includes more than 20,000 New Jersey law enforcement officers who are signed up for Atlas services.
Atlas alleges all of these data brokers have ignored repeated warnings that they are violating Daniel’s Law, a New Jersey statute allowing law enforcement, government personnel, judges and their families to have their information completely removed from commercial data brokers. Daniel’s Law was passed in 2020 after the death of 20-year-old Daniel Anderl, who was killed in a violent attack targeting a federal judge — his mother.
Last week, Atlas invoked Daniel’s Law in a lawsuit (PDF) against Babel Street, a little-known technology company incorporated in Reston, Va. Babel Street’s core product allows customers to draw a digital polygon around nearly any location on a map of the world, and view a slightly dated (by a few days) time-lapse history of the mobile devices seen coming in and out of the specified area.
Babel Street’s LocateX platform also allows customers to track individual mobile users by their Mobile Advertising ID or MAID, a unique, alphanumeric identifier built into all Google Android and Apple mobile devices.
Babel Street can offer this tracking capability by consuming location data and other identifying information that is collected by many websites and broadcast to dozens and sometimes hundreds of ad networks that may wish to bid on showing their ad to a particular user.

This image, taken from a video recording Atlas made of its private investigator using Babel Street to show all of the unique mobile IDs seen over time at a mosque in Dearborn, Michigan. Each red dot represents one mobile device.
In an interview, Atlas said a private investigator they hired was offered a free trial of Babel Street, which the investigator was able to use to determine the home address and daily movements of mobile devices belonging to multiple New Jersey police officers whose families have already faced significant harassment and death threats.
Atlas said the investigator encountered Babel Street while testing hundreds of data broker tools and services to see if personal information on its users was being sold. They soon discovered Babel Street also bundles people-search services with its platform, to make it easier for customers to zero in on a specific device.
The investigator contacted Babel Street about possibly buying home addresses in certain areas of New Jersey. After listening to a sales pitch for Babel Street and expressing interest, the investigator was told Babel Street only offers their service to the government or to “contractors of the government.”
“The investigator (truthfully) mentioned that he was contemplating some government contract work in the future and was told by the Babel Street salesperson that ‘that’s good enough’ and that ‘they don’t actually check,’” Atlas shared in an email with reporters.
KrebsOnSecurity was one of five media outlets invited to review screen recordings that Atlas made while its investigator used a two-week trial version of Babel Street’s LocateX service. References and links to reporting by other publications, including 404 Media, Haaretz, NOTUS, and The New York Times, will appear throughout this story.
Collectively, these stories expose how the broad availability of mobile advertising data has created a market in which virtually anyone can build a sophisticated spying apparatus capable of tracking the daily movements of hundreds of millions of people globally.
The findings outlined in Atlas’s lawsuit against Babel Street also illustrate how mobile location data is set to massively complicate several hot-button issues, from the tracking of suspected illegal immigrants or women seeking abortions, to harassing public servants who are already in the crosshairs over baseless conspiracy theories and increasingly hostile political rhetoric against government employees.
Atlas says the Babel Street trial period allowed its investigator to find information about visitors to high-risk targets such as mosques, synagogues, courtrooms and abortion clinics. In one video, an Atlas investigator showed how they isolated mobile devices seen in a New Jersey courtroom parking lot that was reserved for jurors, and then tracked one likely juror’s phone to their home address over several days.
While the Atlas investigator had access to its trial account at Babel Street, they were able to successfully track devices belonging to several plaintiffs named or referenced in the lawsuit. They did so by drawing a digital polygon around the home address or workplace of each person in Babel Street’s platform, which focused exclusively on the devices that passed through those addresses each day.

Each red dot in this Babel Street map represents a unique mobile device that has been seen since April 2022 at a Jewish synagogue in Los Angeles, Calif. Image: Atlas Data Privacy Corp.
One unique feature of Babel Street is the ability to toggle a “night” mode, which makes it relatively easy to determine within a few meters where a target typically lays their head each night (because their phone is usually not far away).
Atlas plaintiffs Scott and Justyna Maloney are both veteran officers with the Rahway, NJ police department who live together with their two young children. In April 2023, Scott and Justyna became the target of intense harassment and death threats after Officer Justyna responded to a routine call about a man filming people outside of the Motor Vehicle Commission in Rahway.
The man filming the Motor Vehicle Commission that day is a social media personality who often solicits police contact and then records himself arguing about constitutional rights with the responding officers.
Officer Justyna’s interaction with the man was entirely peaceful, and the episode appeared to end without incident. But after a selectively edited video of that encounter went viral, their home address and unpublished phone numbers were posted online. When their tormentors figured out that Scott was also a cop (a sergeant), the couple began receiving dozens of threatening text messages, including specific death threats.
According to the Atlas lawsuit, one of the messages to Mr. Maloney demanded money, and warned that his family would “pay in blood” if he didn’t comply. Sgt. Maloney said he then received a video in which a masked individual pointed a rifle at the camera and told him that his family was “going to get [their] heads cut off.”
Maloney said a few weeks later, one of their neighbors saw two suspicious individuals in ski masks parked one block away from the home and alerted police. Atlas’s complaint says video surveillance from neighboring homes shows the masked individuals circling the Maloney’s home. The responding officers arrested two men, who were armed, for unlawful possession of a firearm.

According to Google Maps, Babel Street shares a corporate address with Google and the consumer credit reporting bureau TransUnion.
Atlas said their investigator was not able to conclusively find Scott Maloney’s iPhone in the Babel Street platform, but they did find Justyna’s. Babel Street had nearly 100,000 hits for her phone over several months, allowing Atlas to piece together an intimate picture of Justyna’s daily movements and meetings with others.
An Atlas investigator visited the Maloneys and inspected Justyna’s iPhone, and determined the only app that used her device’s location data was from the department store Macy’s.
In a written response to questions, Macy’s said its app includes an opt-in feature for geo-location, “which allows customers to receive an enhanced shopping experience based on their location.”
“We do not store any customer location information,” Macy’s wrote. “We share geo-location data with a limited number of partners who help us deliver this enhanced app experience. Furthermore, we have no connection with Babel Street” [link added for context].
Justyna’s experience highlights a stark reality about the broad availability of mobile location data: Even if the person you’re looking for isn’t directly identifiable in platforms like Babel Street, it is likely that at least some of that person’s family members are. In other words, it’s often trivial to infer the location of one device by successfully locating another.
The terms of service for Babel Street’s Locate X service state that the product “may not be used as the basis for any legal process in any country, including as the basis for a warrant, subpoena, or any other legal or administrative action.” But Scott Maloney said he’s convinced by their experience that not even law enforcement agencies should have access to this capability without a warrant.
“As a law enforcement officer, in order for me to track someone I need a judge to sign a warrant – and that’s for a criminal investigation after we’ve developed probable cause,” Mr. Maloney said in an interview. “Data brokers tracking me and my family just to sell that information for profit, without our consent, and even after we’ve explicitly asked them not to is deeply disturbing.”
Mr. Maloney’s law enforcement colleagues in other states may see things differently. In August, The Texas Observer reported that state police plan to spend more than $5 million on a contract for a controversial surveillance tool called Tangles from the tech firm PenLink. Tangles is an AI-based web platform that scrapes information from the open, deep and dark web, and it has a premier feature called WebLoc that can be used to geofence mobile devices.
The Associated Press reported last month that law enforcement agencies from suburban Southern California to rural North Carolina have been using an obscure cell phone tracking tool called Fog Reveal — at times without warrants — that gives them the ability to follow people’s movements going back many months.
It remains unclear precisely how Babel Street is obtaining the abundance of mobile location data made available to users of its platform. The company did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
But according to a document (PDF) obtained under a Freedom of Information Act request with the Department of Homeland Security’s Science and Technology directorate, Babel Street re-hosts data from the commercial phone tracking firm Venntel.
On Monday, the Substack newsletter All-Source Intelligence unearthed documents indicating that the U.S. Federal Trade Commission has opened an inquiry into Venntel and its parent company Gravy Analytics.
“Venntel has also been a data partner of the police surveillance contractor Fog Data Science, whose product has been described as ‘mass surveillance on a budget,'” All-Source’s Jack Poulson wrote. “Venntel was also reported to have been a primary data source of the controversial ‘Locate X’ phone tracking product of the American data fusion company Babel Street.”
The Mobile Advertising ID or MAID — the unique alphanumeric identifier assigned to each mobile device — was originally envisioned as a way to distinguish individual mobile customers without relying on personally identifiable information such as phone numbers or email addresses.
However, there is now a robust industry of marketing and advertising companies that specialize in assembling enormous lists of MAIDs that are “enriched” with historical and personal information about the individual behind each MAID.

One of many vendors that “enrich” MAID data with other identifying information, including name, address, email address and phone number.
Atlas said its investigator wanted to know whether they could find enriched MAID records on their New Jersey law enforcement customers, and soon found plenty of ad data brokers willing to sell it.
Some vendors offered only a handful of data fields, such as first and last name, MAID and email address. Other brokers sold far more detailed histories along with their MAID, including each subject’s social media profiles, precise GPS coordinates, and even likely consumer category.
How are advertisers and data brokers gaining access to so much information? Some sources of MAID data can be apps on your phone such as AccuWeather, GasBuddy, Grindr, and MyFitnessPal that collect your MAID and location and sell that to brokers.
A user’s MAID profile and location data also is commonly shared as a consequence of simply using a smartphone to visit a web page that features ads. In the few milliseconds before those ads load, the website will send a “bid request” to various ad exchanges, where advertisers can bid on the chance to place their ad in front of users who match the consumer profiles they’re seeking. A great deal of data can be included in a bid request, including the user’s precise location (the current open standard for bid requests is detailed here).
The trouble is that virtually anyone can access the “bidstream” data flowing through these so-called “realtime bidding” networks, because the information is simultaneously broadcast in the clear to hundreds of entities around the world.
The result is that there are a number of marketing companies that now enrich and broker access to this mobile location information. Earlier this year, the German news outlet netzpolitik.org purchased a bidstream data set containing more than 3.6 billion data points, and shared the information with the German daily BR24. They concluded that the data they obtained (through a free trial, no less) made it possible to establish movement profiles — some of them quite precise — of several million people across Germany.

A screenshot from the BR24/Netzpolitik story about their ability to track millions of Germans, including many employees of the German Federal Police and Interior Ministry.
Politico recently covered startling research from universities in New Hampshire, Kentucky and St. Louis that showed how the mobile advertising data they acquired allowed them to link visits from investigators with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to insiders selling stock before the investigations became public knowledge.
The researchers in that study said they didn’t attempt to use the same methods to track regulators from other agencies, but that virtually anyone could do it.
Justin Sherman, a distinguished fellow at Georgetown Law’s Center for Privacy and Technology, called the research a “shocking demonstration of what happens when companies can freely harvest Americans’ geolocation data and sell it for their chosen price.”
“Politicians should understand how they, their staff, and public servants are threatened by the sale of personal data—and constituent groups should realize that talk of data broker ‘controls’ or ‘best practices” is designed by companies to distract from the underlying problems and the comprehensive privacy and security solutions,” Sherman wrote for Lawfare this week.
The Orwellian nature of modern mobile advertising networks may soon have far-reaching implications for women’s reproductive rights, as more states move to outlaw abortion within their borders. The 2022 Dobbs decision by the U.S. Supreme Court discarded the federal right to abortion, and 14 states have since enacted strict abortion bans.
Anti-abortion groups are already using mobile advertising data to advance their cause. In May 2023, The Wall Street Journal reported that an anti-abortion group in Wisconsin used precise geolocation data to direct ads to women it suspected of seeking abortions.
As it stands, there is little to stop anti-abortion groups from purchasing bidstream data (or renting access to a platform like Babel Street) and using it to geofence abortion clinics, potentially revealing all mobile devices transiting through these locations.
Atlas said its investigator geofenced an abortion clinic and was able to identify a likely employee at that clinic, following their daily route to and from that individual’s home address.
A still shot from a video Atlas shared of its use of Babel Street to identify and track an employee traveling each day between their home and the clinic.
Last year, Idaho became the first state to outlaw “abortion trafficking,” which the Idaho Capital Sun reports is defined as “recruiting, harboring or transporting a pregnant minor to get an abortion or abortion medication without parental permission.” Tennessee now has a similar law, and GOP lawmakers in five other states introduced abortion trafficking bills that failed to advance this year, the Sun reports.
Atlas said its investigator used Babel Street to identify and track a person traveling from their home in Alabama — where abortion is now illegal — to an abortion clinic just over the border in Tallahassee, Fla. — and back home again within a few hours. Abortion rights advocates and providers are currently suing Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall, seeking to block him from prosecuting people who help patients travel out-of-state to end pregnancies.
Eva Galperin, director of cybersecurity at the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), a non-profit digital rights group, said she’s extremely concerned about dragnet surveillance of people crossing state lines in order to get abortions.
“Specifically, Republican officials from states that have outlawed abortion have made it clear that they are interested in targeting people who have gone to neighboring states in order to get abortions, and to make it more difficult for people who are seeking abortions to go to neighboring states,” Galperin said. “It’s not a great leap to imagine that states will do this.”
Atlas found that for the right price (typically $10-50k a year), brokers can provide access to tens of billions of data points covering large swaths of the US population and the rest of the world.
Based on the data sets Atlas acquired — many of which included older MAID records — they estimate they could locate roughly 80 percent of Android-based devices, and about 25 percent of Apple phones. Google refers to its MAID as the “Android Advertising ID,” (AAID) while Apple calls it the “Identifier for Advertisers” (IDFA).
What accounts for the disparity between the number of Android and Apple devices that can be found in mobile advertising data? In April 2021, Apple shipped version 14.5 of its iOS operating system, which introduced a technology called App Tracking Transparency (ATT) that requires apps to get affirmative consent before they can track users by their IDFA or any other identifier.
Apple’s introduction of ATT had a swift and profound impact on the advertising market: Less than a year later Facebook disclosed that the iPhone privacy feature would decrease the company’s 2022 revenues by about $10 billion.

Source: cnbc.com.
Google runs by far the world’s largest ad exchange, known as AdX. The U.S. Department of Justice, which has accused Google of building a monopoly over the technology that places ads on websites, estimates that Google’s ad exchange controls 47 percent of the U.S. market and 56 percent globally.
Google’s Android is also the dominant mobile operating system worldwide, with more than 72 percent of the market. In the U.S., however, iPhone users claim approximately 55 percent of the market, according to TechRepublic.
In response to requests for comment, Google said it does not send real time bidding requests to Babel Street, nor does it share precise location data in bid requests. The company added that its policies explicitly prohibit the sale of data from real-time bidding, or its use for any purpose other than advertising.
Google said its MAIDs are randomly generated and do not contain IP addresses, GPS coordinates, or any other location data, and that its ad systems do not share anyone’s precise location data.
“Android has clear controls for users to manage app access to device location, and reset or delete their advertising ID,” Google’s written statement reads. “If we learn that someone, whether an app developer, ad tech company or anyone else, is violating our policies, we take appropriate action. Beyond that, we support legislation and industry collaboration to address these types of data practices that negatively affect the entire mobile ecosystem, including all operating systems.”
In a written statement shared with reporters, Apple said Location Services is not on by default in its devices. Rather, users must enable Location Services and must give permission to each app or website to use location data. Users can turn Location Services off at any time, and can change whether apps have access to location at any time. The user’s choices include precise vs. approximate location, as well as a one-time grant of location access by the app.
“We believe that privacy is a fundamental human right, and build privacy protections into each of our products and services to put the user in control of their data,” an Apple spokesperson said. “We minimize personal data collection, and where possible, process data only on users’ devices.”
Zach Edwards is a senior threat analyst at the cybersecurity firm SilentPush who has studied the location data industry closely. Edwards said Google and Apple can’t keep pretending like the MAIDs being broadcast into the bidstream from hundreds of millions of American devices aren’t making most people trivially trackable.
“The privacy risks here will remain until Apple and Google permanently turn off their mobile advertising ID schemes and admit to the American public that this is the technology that has been supporting the global data broker ecosystem,” he said.
According to Bloomberg Law, between 2019 and 2023, threats against federal judges have more than doubled. Amid increasingly hostile political rhetoric and conspiracy theories against government officials, a growing number of states are seeking to pass their own versions of Daniel’s Law.
Last month, a retired West Virginia police officer filed a class action lawsuit against the people-search service Whitepages for listing their personal information in violation of a statute the state passed in 2021 that largely mirrors Daniel’s Law.
In May 2024, Maryland passed the Judge Andrew F. Wilkinson Judicial Security Act — named after a county circuit court judge who was murdered by an individual involved in a divorce proceeding over which he was presiding. The law allows current and former members of the Maryland judiciary to request their personal information not be made available to the public.
Under the Maryland law, personal information can include a home address; telephone number, email address; Social Security number or federal tax ID number; bank account or payment card number; a license plate or other unique vehicle identifier; a birth or marital record; a child’s name, school, or daycare; place of worship; place of employment for a spouse, child, or dependent.
The law firm Troutman Pepper writes that “so far in 2024, 37 states have begun considering or have adopted similar privacy-based legislation designed to protect members of the judiciary and, in some states, other government officials involved in law enforcement.”
Atlas alleges that in response to requests to have data on its New Jersey law enforcement clients scrubbed from consumer records sold by LexisNexis, the data broker retaliated by freezing the credit of approximately 18,500 people, and falsely reporting them as identity theft victims.
In addition, Atlas said LexisNexis started returning failure codes indicating they had no record of these individuals, resulting in denials when officers attempted to refinance loans or open new bank accounts.
The data broker industry has responded by having at least 70 of the Atlas lawsuits moved to federal court, and challenging the constitutionality of the New Jersey statute as overly broad and a violation of the First Amendment.
Attorneys for the data broker industry argued in their motion to dismiss that there is “no First Amendment doctrine that exempts a content-based restriction from strict scrutiny just because it has some nexus with a privacy interest.”
Atlas’s lawyers responded that data covered under Daniel’s Law — personal information of New Jersey law enforcement officers — is not free speech. Atlas notes that while defending against comparable lawsuits, the data broker industry has argued that home address and phone number data are not “communications.”
“Data brokers should not be allowed to argue that information like addresses are not ‘communications’ in one context, only to turn around and claim that addresses are protectable communications,” Atlas argued (PDF). “Nor can their change of course alter the reality that the data at issue is not speech.”
The judge overseeing the challenge is expected to rule on the motion to dismiss within the next few weeks. Regardless of the outcome, the decision is likely to be appealed all the way to the U.S. Supreme Court.
Meanwhile, media law experts say they’re concerned that enacting Daniel’s Law in other states could limit the ability of journalists to hold public officials accountable, and allow authorities to pursue criminal charges against media outlets that publish the same type of public and government records that fuel the people-search industry.
Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) said Congress’ failure to regulate data brokers, and the administration’s continued opposition to bipartisan legislation that would limit data sales to law enforcement, have created this current privacy crisis.
“Whether location data is being used to identify and expose closeted gay Americans, or to track people as they cross state lines to seek reproductive health care, data brokers are selling Americans’ deepest secrets and exposing them to serious harm, all for a few bucks,” Wyden said in a statement shared with KrebsOnSecurity, 404 Media, Haaretz, NOTUS, and The New York Times.
Sen. Wyden said Google also deserves blame for refusing to follow Apple’s lead by removing companies’ ability to track phones.
“Google’s insistence on uniquely tracking Android users – and allowing ad companies to do so as well – has created the technical foundations for the surveillance economy and the abuses stemming from it,” Wyden said.
Georgetown Law’s Justin Sherman said the data broker and mobile ad industries claim there are protections in place to anonymize mobile location data and restrict access to it, and that there are limits to the kinds of invasive inferences one can make from location data. The data broker industry also likes to tout the usefulness of mobile location data in fighting retail fraud, he said.
“All kinds of things can be inferred from this data, including people being targeted by abusers, or people with a particular health condition or religious belief,” Sherman said. “You can track jurors, law enforcement officers visiting the homes of suspects, or military intelligence people meeting with their contacts. The notion that the sale of all this data is preventing harm and fraud is hilarious in light of all the harm it causes enabling people to better target their cyber operations, or learning about people’s extramarital affairs and extorting public officials.”
Privacy experts say disabling or deleting your device’s MAID will have no effect on how your phone operates, except that you may begin to see far less targeted ads on that device.
Any Android apps with permission to use your location should appear when you navigate to the Settings app, Location, and then App Permissions. “Allowed all the time” is the most permissive setting, followed by “Allowed only while in use,” “Ask every time,” and “Not allowed.”
Android users can delete their ad ID permanently, by opening the Settings app and navigating to Privacy > Ads. Tap “Delete advertising ID,” then tap it again on the next page to confirm. According to the EFF, this will prevent any app on your phone from accessing the ad ID in the future. Google’s documentation on this is here.

Image: eff.org
By default, Apple’s iOS requires apps to ask permission before they can access your device’s IDFA. When you install a new app, it may ask for permission to track you. When prompted to do so by an app, select the “Ask App Not to Track” option. Apple users also can set the “Allow apps to request to track” switch to the “off” position, which will block apps from asking to track you.

Apple’s Privacy and Ad Tracking Settings.
Apple also has its own targeted advertising system which is separate from third-party tracking enabled by the IDFA. To disable it, go to Settings, Privacy, and Apple Advertising, and ensure that the “Personalized Ads” setting is set to “off.”
Finally, if you’re the type of reader who’s the default IT support person for a small group of family or friends (bless your heart), it would be a good idea to set their devices not to track them, and to disable any apps that may have location data sharing turned on 24/7.
There is a dual benefit to this altruism, which is clearly in the device owner’s best interests. Because while your device may not be directly trackable via advertising data, making sure they’re opted out of said tracking also can reduce the likelihood that you are trackable simply by being physically close to those who are.

With its built-in location services, your smartphone can point you to plenty of places. To the location of your vacation rental. To the quickest route around a traffic jam. And to a tasty burger. It’s a tremendous convenience. Yet, there’s a flip side. Your smartphone also tracks your location. Getting to know how your phone tracks you and how you can limit that tracking can make you far more private online.
The basic privacy issue with location services is this: many companies use your activities and apps as a way of gathering info on you. They might collect that info for their own purposes, and they might sell that info to third parties.
As to why some companies do that, the answer typically boils down to a handful of things. They will:
So, it’s a bit of a tradeoff. You might use an app to show you the closest Indian restaurant to your hotel — but depending on the user agreement for that app, the company behind it might collect your info for their own financial gain.
We can boil that down yet further. Sometimes what you gain in convenience you lose in privacy.
Let’s look at how smartphones track your movements and follow that up with ways you can limit that tracking.
Unless you’ve turned it off completely, your phone can track you in several ways with several degrees of accuracy:
GPS: The Global Positioning System, or GPS as many of us know it, is a system of satellites operated by the U.S. government for navigation purposes. First designed for national defense, the system became available for public use in the 1980s. It’s highly accurate, to anywhere between nine to 30 feet depending on conditions and technology used, making it one of the strongest tools for determining a phone’s location. This is what powers location services on cell phones, and thus can help an app recommend a great burger joint nearby.
Cell towers: Cell phone providers can track a phone’s location by the distance it is to various cell phone towers and by the strength of its signal. The location info this method provides is a bit coarser than GPS, providing results that can place a phone within 150 feet. It’s most accurate in urban areas with high densities of cell phone towers, although it does not always work well indoors as some buildings can weaken or block cell phone signals.
One of the most significant public benefits of this method is that it automatically routes emergency services calls (like 911 in the U.S.) to the proper local authorities without any guesswork from the caller.
Public Wi-Fi: Larger tech companies and internet providers will sometimes provide free public Wi-Fi hotspots that people can tap into at airports, restaurants, coffeehouses, and such. It’s a nice convenience, but connecting to their Wi-Fi might share a phone’s MAC address, a unique identifier for connected devices, along with other identifiers on the smartphone.
Taken together, this can allow the Wi-Fi hosting company to gather location and behavioral data while you use your phone on their Wi-Fi network.
Bluetooth: Like with public Wi-Fi, companies can use strategically placed Bluetooth devices to gather location info as well. If Bluetooth is enabled on a phone, it will periodically seek out Bluetooth-enabled devices to connect to while the phone is awake. This way, a Bluetooth receiver can then capture that phone’s unique MAC address. This provides highly accurate location info to within just a few feet because of Bluetooth’s short broadcast range.
In the past, we’ve seen retailers use this method to track customers in their physical stores to better understand their shopping habits. However, newer phones often create dummy MAC addresses when they seek out Bluetooth connections, which helps thwart this practice.
So, just to emphasize what we said above, not every app sells shares or sells your info to third parties. However, that gets into the complicated nature of user agreements. The language that covers what’s collected, for what reasons, what’s done with it, and who it’s shared with often finds itself buried in a wall of legalese.
Ultimately, it’s up to you to determine what your comfort level is in any kind of convenience in exchange for a loss of privacy. Everyone has their own comfort levels.
With that, you can take several steps to limit tracking on your smartphone to various degrees — and boost your privacy to various degrees as a result:
Turn off your phone or switch to Airplane Mode. Disconnect. Without a Wi-Fi or data connection, you can’t get tracked. While this makes you unreachable, it also makes you untraceable, which you might want to consider if you’d rather keep your whereabouts and travels to yourself for periods of time.
Turn off location services altogether. As noted above, your smartphone can get tracked by other means, yet disabling location services in your phone settings shuts down a primary avenue of location data collection. Note that your maps apps won’t offer directions and your restaurant app won’t point you toward that tasty burger when location services are off, but you’ll be more private than with them turned on.
Provide permissions on an app-by-app basis. Another option is to go into your phone settings and enable location services for specific apps in specific cases. For example, you can set your map app to enable location services only while in use. For other apps, you can disable location services entirely. Yet another option is to have the app ask for permissions each time. Note that this is a great way to discover if apps have defaulted to using location services without your knowledge when you installed them.
On an iPhone, you can find this in Settings -> Privacy & Security -> Location Services. On an Android, go to Settings -> Locations -> App Locations Permissions.
Delete old apps. And be choosy about new ones. Fewer apps mean fewer avenues of potential data collection. If you have old, unused apps, consider deleting them, along with the accounts and data associated with them.
Use a VPN. A VPN can make your time online more private and more secure by obscuring things like your IP address and by preventing snoops from monitoring your activity.
Turn off app tracking. As you’ve seen, some apps will ask to track your activity and potentially share it with data brokers and other third parties. You can halt this by turning off app tracking. On an iPhone, go to Settings -> Privacy & Security -> Tracking and disable “Allow Apps to Request to Track.” On an Android phone, go to Settings -> Privacy and Security, then turn on “Do Not Track.”
And just as you can with location services, you can set apps to make tracking requests on an app-by-app basis. You’ll see it on the same screen that has the global “Do Not Track” option.
Opt yourself out of cell phone carrier ad programs. Different cell phone carriers have different user agreements, yet some might allow the carrier to share insights about you with third parties based on browsing and usage history. Opting out of these programs might not stop your cell phone carrier from collecting data about you, but it might prevent it from sharing insights about you with others.
To see if you participate in one of these programs, log into your account portal or app. Look for settings around “relevant advertising,” “custom experience,” or even “advertising,” and then determine if these programs are of worth to you.
The post Location, Location, Location: Three Reasons It Matters for Your Smartphone appeared first on McAfee Blog.

What is malware? A dictionary-like definition is “malicious software that attacks computers, smartphones, and other connected devices.”
In fact, “malware” is a mash-up of “malicious software.” It describes any type of software or code specifically designed to exploit a connected device or network without consent. And, unsurprisingly, hackers design most of it for financial gain.
Think of malware as an umbrella term that covers an entire host of “bad stuff,” such as:
Spyware that tracks activity, like what you type and where you type it. (Think snooping on your bank account logins.
Ransomware that holds devices or the data on them hostage, that hackers only release for a price. (And even so, payment is no guarantee you’ll get back your access.)
Adware that serves up spammy ads on your device. (The hacker gets paid for the number of “impressions” the ads have. The more they show up on people’s devices, the more they get paid.)
Botnet software, that hijacks a device into a remote-controlled network of other devices. (These networks are used to shut down websites or even shut down large portions of the internet, just to mention two of the things they can do.)
Rootkit that attacks that give hackers remote-control access to a device. (And with that control, they can wage all manner of attacks — on the device and on other devices too.)
Viruses that modify the way a device and its apps function. Also, they can effectively bring a device or network to a grinding halt. (Yes, viruses are a subset of malware. They can copy, delete, and steal data, among other things.)
You might know malware by its more commonly used name — viruses.
There’s a pretty good reason why people commonly refer to malware as a “virus.” Viruses have been on our collective minds for some time.
Viruses have a long history. You could call it “the original malware.” And depending on how you define what a virus is, the first one took root in 1971 — more than 50 years ago. It was known as Creeper, and rather than being malicious in nature, the creator designed it to show how a self-replicating program could spot other devices on a network, transfer itself to them, and find yet more devices to repeat the process. Later, the same programmer who created a refined version of Creeper developed Reaper, a program that could remove the Creeper program. In a way, Reaper could be considered the first piece of antivirus software.[i]
From there, it wasn’t until the 1980s that malware started affecting the broader population, a time when computers became more commonplace in businesses and people’s homes.
At first, malware typically spread by infected floppy disks, much like the “Brain” virus in 1986. While recognized today as the first large-scale computer virus, its authors say they never intended it to work that way. Rather, they say they created Brain as an anti-piracy measure to protect their proprietary software from theft. However, Brain got loose. It went beyond their software and affected computers worldwide. Although not malicious or destructive in nature, Brain most certainly put the industry, businesses, and consumers on notice. Computer viruses were a thing.[ii]
Another piece of malware that got passed along via floppy disks was the “PC Cyborg” attack that targeted the medical research community in and around 1989. There, the malware would lie in wait until the user rebooted their computer for the 90th time and was presented with a digital ransom note.[iii]
An early example of ransomware – Source, Wikipedia
Upon that 90th boot, PC Cyborg encrypted the computer’s files, which would only get unencrypted if the victim paid a fee, making it the first documented form of ransomware.
Shortly thereafter, the internet started connecting computers, which opened millions of doors for hackers as people went online. Among the most noteworthy was 1999’s “Melissa” virus, which spread by way of infected email attachments and overloaded hundreds of corporate and governmental email servers worldwide.
It was quickly followed in 2000 by what’s considered among the most damaging malware to date — ILOVEYOU, which also spread by way of an attachment, this one posing as a love letter. Specifically, it was a self-replicating worm that installed itself on the victim’s computer where it destroyed some info and stole other info, then spread to other computers. One estimate put the global cost of ILOVEYOU at $10 billion. It further speculated that it infected 10% of the world’s internet-connected computers at the time.[iv]
With that history, it’s no surprise that anti-malware software is commonly called “antivirus.”
Antivirus forms a major cornerstone of online protection software. It protects your devices against malware through a combination of prevention, detection, and removal. Our antivirus uses AI to detect the absolute latest threats — and has for several years now.
Today, McAfee registers more than a million new malicious programs and potentially unwanted apps (PUA) each day, which contributes to the millions and millions already in existence. Now with the arrival of AI-powered coding tools, hackers can create new strains at rates unseen before.
That’s another reason why we use AI in our antivirus software. We use AI to protect against AI-created malware. It does so in three ways:
Once again, it’s important to remind ourselves that today’s malware is created largely for profit. Hackers use it to gain personal and financial info, either for their own purposes or to sell it for profit. The files you have stored on your devices have a street value. That includes tax returns, financial docs, payment info, and so on. Moreover, when you consider all the important things you keep on your devices, like your photos and documents, those have value too. Should you get caught up in a ransomware attack, a hacker puts a price tag on them for their return.
Needless to say, and you likely know this already, antivirus is essential for you and your devices.
You’ll find our AI-powered antivirus in all our McAfee+ plans. Better yet, our plans have dozens of protections that block the ways hackers distribute malware. To name just a few, our Text Scam Detector blocks links to suspicious sites that host malware and other attacks — and our Web Protection does the same for your browser. It also includes our industry-first online protection score that shows you just how safe you are, along with suggestions that can make you safer still. Together, our McAfee+ plans offer more than just antivirus. They protect your devices, your privacy, and your identity overall.
[i] https://www.historyofinformation.com/detail.php?entryid=2860
[ii] https://www.historyofinformation.com/detail.php?id=1676
[iii] https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2016/05/the-computer-virus-that-haunted-early-aids-researchers/481965/
[iv] https://www.forbes.com/sites/daveywinder/2020/05/04/this-20-year-old-virus-infected-50-million-windows-computers-in-10-days-why-the-iloveyou-pandemic-matters-in-2020
The post What is Malware? appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Microsoft today released security updates to fix at least 117 security holes in Windows computers and other software, including two vulnerabilities that are already seeing active attacks. Also, Adobe plugged 52 security holes across a range of products, and Apple has addressed a bug in its new macOS 15 “Sequoia” update that broke many cybersecurity tools.

One of the zero-day flaws — CVE-2024-43573 — stems from a security weakness in MSHTML, the proprietary engine of Microsoft’s Internet Explorer web browser. If that sounds familiar it’s because this is the fourth MSHTML vulnerability found to be exploited in the wild so far in 2024.
Nikolas Cemerikic, a cybersecurity engineer at Immersive Labs, said the vulnerability allows an attacker to trick users into viewing malicious web content, which could appear legitimate thanks to the way Windows handles certain web elements.
“Once a user is deceived into interacting with this content (typically through phishing attacks), the attacker can potentially gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or manipulate web-based services,” he said.
Cemerikic noted that while Internet Explorer is being retired on many platforms, its underlying MSHTML technology remains active and vulnerable.
“This creates a risk for employees using these older systems as part of their everyday work, especially if they are accessing sensitive data or performing financial transactions online,” he said.
Probably the more serious zero-day this month is CVE-2024-43572, a code execution bug in the Microsoft Management Console, a component of Windows that gives system administrators a way to configure and monitor the system.
Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, observed that the patch for CVE-2024-43572 arrived a few months after researchers at Elastic Security Labs disclosed an attack technique called GrimResource that leveraged an old cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability combined with a specially crafted Microsoft Saved Console (MSC) file to gain code execution privileges.
“Although Microsoft patched a different MMC vulnerability in September (CVE-2024-38259) that was neither exploited in the wild nor publicly disclosed,” Narang said. “Since the discovery of CVE-2024-43572, Microsoft now prevents untrusted MSC files from being opened on a system.”
Microsoft also patched Office, Azure, .NET, OpenSSH for Windows; Power BI; Windows Hyper-V; Windows Mobile Broadband, and Visual Studio. As usual, the SANS Internet Storm Center has a list of all Microsoft patches released today, indexed by severity and exploitability.
Late last month, Apple rolled out macOS 15, an operating system update called Sequoia that broke the functionality of security tools made by a number of vendors, including CrowdStrike, SentinelOne and Microsoft. On Oct. 7, Apple pushed an update to Sequoia users that addresses these compatibility issues.
Finally, Adobe has released security updates to plug a total of 52 vulnerabilities in a range of software, including Adobe Substance 3D Painter, Commerce, Dimension, Animate, Lightroom, InCopy, InDesign, Substance 3D Stager, and Adobe FrameMaker.
Please consider backing up important data before applying any updates. Zero-days aside, there’s generally little harm in waiting a few days to apply any pending patches, because not infrequently a security update introduces stability or compatibility issues. AskWoody.com usually has the skinny on any problematic patches.
And as always, if you run into any glitches after installing patches, leave a note in the comments; chances are someone else is stuck with the same issue and may have even found a solution.

In my world of middle-aged mums (mams), Instagram is by far the most popular social media platform. While many of us still have Facebook, Instagram is where it all happens: messaging, sharing, and yes, of course – shopping!! So, when one of my gal pals discovers that her Instagram account has been hacked, there is understandably a lot of panic!
Believe it or not, Facebook is still hanging onto the top spot as the most popular social media platform with just over 3 billion active monthly users, according to Statista. YouTube comes in 2nd place with 2.5 billion users. Instagram and WhatsApp tie in 3rd place with 2 billion users each. Interestingly, TikTok has 1.5 billion users and is in 4th place – but watch this space, I say!
Despite Facebook having the most monthly users, it isn’t where the personal conversations and engagement take place. That’s Instagram’s sweet spot. Instagram messaging is where links are shared and real personal interaction occurs. In fact, a new report shows that Instagram accounts are targeted more than any other online account and makeup just over a quarter of all social media hacks. So, it makes sense why hackers would expend considerable energy in trying to hack Instagram accounts. They’ll have a much greater chance of success if they use a platform where there is an appetite and trust for sharing links and personal conversations.
But why do they want to get their hands on your account? Well, they may want to steal your personal information, scam your loyal followers by impersonating you, sell your username on the black market or even demand ransoms! Hacking Instagram is big business for professional scammers!!
So, you reach for your phone early one morning to do a quick scroll on Instagram before you start the day, but you can’t seem to log on. Mmmmm. You then see some texts from friends checking whether you have in fact become a cryptocurrency expert overnight. OK – something’s off. You then notice an email from Instagram notifying you that the email linked to your account has been changed. Looks like you’ve been hacked! But please don’t spend any time stressing. The most important thing is to take action ASAP as the longer hackers have access to your account, the greater the chance they can infiltrate your life and create chaos.
The good news is that if you act quickly and strategically, you may be able to get your account back. Here is what I suggest you do – fast!:
1. Change Your Password & Check Your Account
If you are still able to log in to your account then change your password immediately. And ensure it is a password you haven’t used anywhere else. Then do a quick audit of your account and fix any changes the hacker may have made eg remove access to any device you don’t recognise, any apps you didn’t install, and delete any email addresses that aren’t yours.
Next, turn on two-factor authentication (2FA) to make it harder for the hacker to get back into your account. This will take you less than a minute and is absolutely critical. Instagram will give you the option to receive the login code either via text message or via an authentication app. I always recommend the app in case you ever lose control of your phone.
But, if you are locked out of your account then move on to step 2.
2. Locate The Email From Instagram
Every time there is a change to your account details or some new login activity, Instagram will automatically send a message to the email address linked with the account
But there’s good news here. The email from Instagram will ask you if you in fact made the changes and will provide a link to secure your account in case it wasn’t you. Click on this link!! If you can access your account this way, immediately check that the only linked email address and recovery phone number are yours and delete anything that isn’t yours. Then change your password.
But if you’ve had no luck with this step, move on to step 3.
3. Request a Log-In Link
You can also ask Instagram to email or text you a login link. On an iPhone, you just need to select ‘forgot password?’ and on your Android phone, tap ‘get help logging in’. You will need to enter the username, email address, and phone number linked to your account.
No luck? Keep going…
4. Request a Security Code
If the login link won’t get you back in, the next step is to request a security code. Simply enter the username, email address, or phone number associated with your account, then tap on “Need more help?” Select your email address or phone number, then tap “Send security code” and follow the instructions.
5. Video Selfie
If you have exhausted all of these options and you’ve had no luck then chances are you have found your way to the Instagram Support Team. If you haven’t, simply click on the link and it will take you there. Now, if your hacked account contained pictures of you then you might just be in luck! The Support Team may ask you to take a video selfie to confirm who you are and that in fact you are a real person! This process can take a few business days. If you pass the test, you’ll be sent a link to reset your password.
So, you’ve got your Instagram account back – well done! But wouldn’t it be good to avoid all that stress again? Here are my top tips to make it hard for those hackers to take control of your Insta.
1. It’s All About Passwords
I have no doubt you’ve heard this before but it’s essential, I promise! Ensuring you have a complex and unique password for your Instagram account (and all your online accounts) is THE best way of keeping the hackers at bay. And if you’re serious about this you need to get yourself a password manager that can create (and remember) crazily complex and random passwords that are beyond any human ability to create. Check out McAfee’s TrueKey – a complete no-brainer!
2. Turn on Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication adds another layer of security to your account making it that much harder for a hacker to get in. It takes minutes to set up and is essential if you’re serious about protecting yourself. It simply involves using a code to log in, in addition to your password. You can choose to receive the code via a text message or an authenticator app – always choose the app!
3. Choose How To Receive Login Alerts
Acting fast is the name of the game here so ensure your account is set up with your best contact details, so you receive login alerts ASAP. This can be the difference between salvaging your account and not. Ensure the alerts will be sent to where you are most likely to see them first so you can take action straight away!
4. Audit Any Third-Party Apps
Third-party apps that you have connected to your account could potentially be a security risk. So, only ever give third-party apps permission to access your account when absolutely necessary. I suggest taking a few minutes to disconnect any apps you no longer require to keep your private data as secure as possible.
Believe it or not, Instagram is not just an arena for middle-aged mums! I can guarantee that your teens will be on there too. So, next time you’re sharing a family dinner, why not tell them what you’re doing to prevent yourself from getting hacked? And if you’re not convinced they are listening? Perhaps remind them just how devastating it would be to lose access to their pics and their people. I am sure that might just work.
Till next time
Stay safe online!
Alex
The post My Instagram Has Been Hacked – What Do I Do Now? appeared first on McAfee Blog.

All day long, it’s almost always within arm’s reach. Your smartphone. And we rely on it plenty. That makes securing your phone so important. Good thing that some of the best tips for making your phone safer are also some of the easiest.
Here’s a quick rundown:
1. Lock your phone.
Locking your phone is one of the most basic smartphone security measures you can take. Trouble is, few of us do it. Our recent global research showed that only 56% of adults said that they protect their smartphone with a password, passcode, or other form of lock.[i] In effect, an unlocked phone is an open book to anyone who finds or steals a phone.
Setting up a lock screen is easy. It’s a simple feature found on iOS and Android devices. iPhones and Androids have an auto-lock feature that locks your phone after a certain period of inactivity. Keep this time on the low end, one minute or less, to help prevent unauthorized access.
We suggest using a six-digit PIN or passcode rather than using a gesture to unlock your phone. They’re more complex and secure. Researchers proved as much with a little “shoulder surfing” test. They looked at how well one group of subjects could unlock a phone after observing the way another group of subjects unlocked it.[ii]
2. Turn on “Find My Phone.”
Another powerful tool you have at your disposal is the Find My Phone feature made possible thanks to GPS technology. The “find my” feature can help you pinpoint your phone if your lost or stolen phone has an active data or Wi-Fi connection and has its GPS location services enabled. Even if the phone gets powered down or loses connection, it can guide you to its last known location.
Setting up this feature is easy. Apple offers a comprehensive web page on how to enable and use their “Find My” feature for phones (and other devices too). Android users can get a step-by-step walkthrough on Google’s Android support page as well.
3. Learn how to remotely track, lock or erase your phone.
In the event of your phone getting lost or stolen, a combination of device tracking, device locking, and remote erasing can help protect your phone and the data on it.
Different device manufacturers have different ways of going about it. But the result is the same — you can prevent others from using your phone, and even erase it if you’re truly worried that it’s in the wrong hands or gone for good. Apple provides iOS users with a step-by-step guide, and Google offers up a guide for Android users as well.
4. Back up your stuff in the cloud.
Thanks to cloud storage, you might be able to recover your photos, files, apps, notes, contact info, and more if your phone is lost or stolen. Android owners can learn how to set up cloud backup with Google Drive here, and iPhone users can learn the same for iCloud here.
5. Update your phone’s operating system and apps.
Keep your phone’s operating system up to date. Updates can fix vulnerabilities that hackers rely on to pull off their malware-based attacks — it’s another tried-and-true method of keeping yourself safer and your phone running great too.
The same goes for the apps on your phone. Ideally, set them up to update automatically so that you don’t have to take extra time to do it yourself. Also, look for opportunities to delete old apps and any data linked with them. Fewer apps on your phone means fewer vulnerabilities. And less data in fewer places can reduce your exposure to data breaches.
6. Stick with official app stores.
Legitimate app stores like Google Play and Apple’s App Store have measures in place that help ensure that apps are safe and secure. And for the malicious apps that sneak past these processes, Google and Apple are quick to remove them once discovered, making their stores that much safer. Meanwhile, third-party app stores might not have these measures in place. Further, they might be a front for hackers looking to spread mobile malware through malicious apps.
7. Go with a strong app recommendation.
Yet better than combing through user reviews yourself is getting a recommendation from a trusted source, like a well-known publication or from app store editors themselves. In this case, much of the vetting work has been done for you by an established reviewer. A quick online search like “best fitness apps” or “best apps for travelers” should turn up articles from legitimate sites that can suggest good options and describe them in detail before you download.
That’s not to say that you should overlook user reviews. Certainly, legitimate reviews can be a big help. Look closely at the listing, though. Check out the developer’s track record. Have they published several other apps with many downloads and good reviews? A legit app typically has quite a few reviews, whereas malicious apps may have only a handful of (phony) five-star reviews. Lastly, look for typos and poor grammar in both the app description and screenshots. They could be a sign that a hacker slapped the app together and quickly deployed it.
8. Keep an eye on app permissions.
Another way hackers weasel their way into your device is by getting permissions to access things like your location, contacts, and photos — and they’ll use sketchy apps to do it. So check and see what permissions the app is requesting. If it’s asking for way more than you bargained for, like a simple game wanting access to your camera or microphone, it might be a scam.
Delete the app and find a legitimate one that doesn’t ask for invasive permissions. If you’re curious about permissions for apps that are already on your phone, iPhone users can learn how to allow or revoke app permission here, and Android can do the same here.
9. Spot scam texts and their bad links.
Scam texts seem like an unfortunate fact of life. Scammers can blast thousands of phones with texts that contain links to phishing sites and to others that host malware. Our Text Scam Detector puts a stop to scams before you click — detecting any suspicious links and sending you an alert. And if you accidentally tap that bad link, it can still block the site for you.
10. Protect your smartphone with security software.
With all that we do on our phones, it’s important to get security software installed on them, just like we install it on our computers and laptops. Whether you go with comprehensive online protection software that secures all your devices or pick up an app in Google Play or Apple’s App Store, you’ll have malware, web, and device security that’ll help you stay safe on your phone.
[i] https://www.mcafee.com/content/dam/consumer/en-us/docs/reports/rp-connected-family-study-2022-global.pdf
[ii] https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.04959
The post 10 Quick Tips for Mobile Security appeared first on McAfee Blog.