
It’s no longer possible to deny that your life in the physical world and your digital life are one and the same. Coming to terms with this reality will help you make better decisions in many aspects of your life.
The same identity you use at work, at home, and with friends also exists in apps, inboxes, accounts, devices, and databases, whether you actively post online or prefer to stay quiet. Every purchase, login, location ping, and message leaves a trail. And that trail shapes what people, companies, and scammers can learn about you, how they can reach you, and what they might try to take.
That’s why digital security isn’t just an IT or a “tech person” problem. It’s a daily life skill. When you understand how your digital life works, what information you’re sharing, where it’s stored, and how it can be misused, you make better decisions. This guide is designed to help you build that awareness and translate it into practical habits: protecting your data, securing your accounts, and staying in control of your privacy in a world that’s always connected.
Being digitally secure doesn’t mean hiding from the internet or using complicated tools you don’t understand. It means having intentional control over your digital life to reduce risks while still being able to live, work, and communicate online safely. A digitally secure person focuses on four interconnected areas:
Your personal data is the foundation of your digital identity. Protecting it includes limiting how much data you share, understanding where it’s stored, and reducing how easily it can be collected, sold, or stolen. At its heart, personal information falls into two critical categories that require different levels of protection:
Account security ensures that only you can access them. Strong, unique passwords, multi-factor authentication, and secure recovery options prevent criminals from hijacking your email, banking, cloud storage, social media, and other online accounts, often the gateway to everything else in your digital life.
Privacy control means setting boundaries and deciding who can see what about you, and under what circumstances. This includes managing social media visibility, app permissions, browser tracking, and third-party access to your data.
Digital security is an ongoing effort as threats evolve, platforms change their policies, and new technologies introduce new risks. Staying digitally secure requires periodic check-ins, learning to recognize scams and manipulation, and adjusting your habits as the digital landscape changes.
Your personal information faces exposure risks through multiple channels during routine digital activities, often without your explicit knowledge.
Implementing comprehensive personal data protection requires a systematic approach that addresses the common exposure points. These practical steps provide layers of security that work together to minimize your exposure to identity theft and fraud.
Start by conducting a thorough audit of your online accounts and subscriptions to identify where you have unnecessarily shared more data than needed. Remove or minimize details that aren’t essential for the service to function. Moving forward, provide only the minimum required information to new accounts and avoid linking them across different platforms unless necessary.
Be particularly cautious with loyalty programs, surveys, and promotional offers that ask for extensive personal information, as they may share it with third parties. Read privacy policies carefully, focusing on sections that describe data sharing, retention periods, and your rights regarding your personal information.
If possible, consider using separate email addresses for different accounts to limit cross-platform tracking and reduce the impact if one account is compromised. Create dedicated email addresses for shopping, social media, newsletters, and important accounts like banking and healthcare.
Privacy protection requires regular attention to your account settings across all platforms and services you use. Social media platforms frequently update their privacy policies and settings, often defaulting to less private configurations that allow them to collect and share your data. For this reason, it is a good idea to review your privacy settings at least quarterly. Limit who can see your posts, contact information, and friend lists. Disable location tracking, facial recognition, and advertising customization features that rely on your personal data. Turn off automatic photo tagging and prevent search engines from indexing your profile.
On Google accounts, visit your Activity Controls and disable Web & App Activity, Location History, and YouTube History to stop this data from being saved. You can even opt out of ad personalization entirely if desired by adjusting Google Ad Settings. If you are more tech savvy, Google Takeout allows you to export and review what data Google has collected about you.
For Apple ID accounts, you can navigate to System Preferences on Mac or Settings on iOS devices to disable location-based Apple ads, limit app tracking, and review which apps have access to your contacts, photos, and other personal data.
Meanwhile, Amazon accounts store extensive purchase history, voice recordings from Alexa devices, and browsing behavior. Review your privacy settings to limit data sharing with third parties, delete voice recordings, and manage your advertising preferences.
Regularly audit the permissions you’ve granted to installed applications. Many apps request far more permissions to your location, contacts, camera, and microphone even though they don’t need them. Cancel these unnecessary permissions, and be particularly cautious about granting access to sensitive data.
Create passwords that actually protect you; they should be long and complex enough that even sophisticated attacks can’t easily break them. Combine uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to make it harder for attackers to crack.
Aside from passwords, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your most critical accounts: banking and financial services, email, cloud storage, social media, work, and healthcare. Use authenticator apps such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy rather than SMS-based authentication when possible, as text messages can be intercepted through SIM swapping attacks. When setting up MFA, ensure you save backup codes in a secure location and register multiple devices when possible to keep you from being locked out of your accounts if your primary authentication device is lost, stolen, or damaged.
Alternatively, many services now offer passkeys which use cryptographic keys stored on your device, providing stronger security than passwords while being more convenient to use. Consider adopting passkeys for accounts that support them, particularly for your most sensitive accounts.
Device encryption protects your personal information if your smartphone, tablet, or laptop is lost, stolen, or accessed without authorization. Modern devices typically offer built-in encryption options that are easy to enable and don’t noticeably impact performance.
You can implement automatic backup systems such as secure cloud storage services, and ensure backup data is protected. iOS users can utilize encrypted iCloud backups, while Android users should enable Google backup with encryption. Regularly test your backup systems to ensure they’re working correctly and that you can successfully restore your data when needed.
Identify major data brokers that likely have your information and look for their privacy policy or opt-out procedures, which often involves submitting a request with your personal information and waiting for confirmation that your data has been removed.
In addition, review your subscriptions and memberships to identify services you no longer use. Request account deletion rather than simply closing accounts, as many companies retain data from closed accounts. When requesting deletion, ask specifically for all personal data to be removed from their systems, including backups and archives.
Keep records of your opt-out and deletion requests, and follow up if you don’t receive confirmation within the stated timeframe. In the United States, key data broker companies include Acxiom, LexisNexis, Experian, Equifax, TransUnion, Whitepages, Spokeo, BeenVerified, and PeopleFinder. Visit each company’s website.
Connect only to trusted, secure networks to reduce the risk of your data being intercepted by attackers lurking behind unsecured or fake Wi-Fi connections. Avoid logging into sensitive accounts on public networks in coffee shops, airports, or hotels, and use encrypted connections such as HTTPS or a virtual private network to hide your IP address and block third parties from monitoring your online activities.
Rather than using a free VPN service that often collects and sells your data to generate revenue, it is better to choose a premium, reputable VPN service that doesn’t log your browsing activities and offers servers in multiple locations.
Cyber threats evolve constantly, privacy policies change, and new services collect different types of personal information, making personal data protection an ongoing process rather than a one-time task. Here are measures to help regularly maintain your personal data protection:
By implementing these systematic approaches and maintaining regular attention to your privacy settings and data sharing practices, you significantly reduce your risk of identity theft and fraud while maintaining greater control over your digital presence and personal information.
You don’t need to dramatically overhaul your entire digital security in one day, but you can start making meaningful improvements right now. Taking action today, even small steps, builds the foundation for stronger personal data protection and peace of mind in your digital life. Choose one critical account, update its password, enable multi-factor authentication, and you’ll already be significantly more secure than you were this morning. Your future self will thank you for taking these proactive steps to protect what matters most to you.
Every step you take toward better privacy protection strengthens your overall digital security and reduces your risk of becoming a victim of scams, identity theft, or unwanted surveillance. You’ve already taken the first step by learning about digital security risks and solutions. Now it’s time to put that knowledge into action with practical steps that fit seamlessly into your digital routine.
The post What Does It Take To Be Digitally Secure? appeared first on McAfee Blog.

Unfortunately, scammers today are coming at us from all angles, trying to trick us into giving up our hard-earned money. We all need to be vigilant in protecting ourselves online. If you aren’t paying attention, even if you know what to look for, they can still catch you off guard. There are numerous ways to detect fake sites, phishing, and other scams, including emails.
Before we delve into the signs of fake websites, we will first take a closer look at the common types of scams that use websites, what happens when you accidentally access a fake website, and what you can do in case you unknowingly purchased items from it.
Fake or scam websites are fraudulent sites that look legitimate while secretly attempting to steal your personal information, money, or account access.
These deceptive platforms masquerade as trustworthy businesses or organizations, sending urgent messages that appear to be from popular shopping websites offering fantastic limited-time deals, banking websites requesting immediate account verification, government portals claiming you owe taxes or are eligible for refunds, and shipping companies asking for delivery fees.
The urgency aims to trick you into logging in and sharing sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, Social Security details, login credentials, and personal data. Once you submit your data, the scammers will steal your identity, drain your accounts, or sell your details to other criminals on the dark web.
These scam websites have become increasingly prevalent because they’re relatively inexpensive to create and can reach millions of potential victims quickly through email and text campaigns, social media ads, and search engine manipulation.
Cybersecurity researchers and consumer protection agencies discover these fraudulent sites through various methods, including monitoring suspicious domain registrations, analyzing reported phishing attempts, and tracking unusual web traffic patterns. According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center, losses from cyber-enabled fraud totaled $13.7 billion, with fake websites accounting for a significant portion of these losses.
Visiting a fake website, accidentally or intentionally, can expose you to several serious security risks that can impact your digital life and financial well-being:
Scammers employ various tactics to create fake websites that appear authentic, but most of these techniques follow familiar patterns. Knowing the main types of scam sites helps you recognize danger faster. This section lists the most common categories of scam websites, explains how they operate, and identifies the red flags that alert you before they can steal your information or money.
Understanding these common scam types helps you recognize fake sites before they can steal your information or money. When in doubt, verify legitimacy by visiting official websites directly through bookmarks or search engines rather than clicking suspicious links.
For the latest warnings and protection guidance, check resources from the Federal Trade Commission and the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
You can protect yourself by learning to recognize the warning signs of fake sites. By understanding what these scams look like and how they operate, you’ll be better equipped to shop, bank, and browse online with confidence. Remember, legitimate companies will never pressure you to provide sensitive information through unsolicited emails or urgent pop-up messages.
Most scams typically start with social engineering tactics, such as phishing, smishing, and fake social media messages containing suspicious links, before directing you to a fake website.
From these communications, the scammers impersonate legitimate organizations before finally executing their malevolent intentions. To avoid being tricked, it is essential to recognize the warning signs wherever you encounter them.
Fake emails are among the most common phishing attempts you’ll encounter. If you see any of these signs in an unsolicited email, it is best not to engage:
Smishing messages bear the same signs as phishing emails and have become increasingly sophisticated. These fake messages often appear to come from delivery services, banks, or government agencies. Common tactics include fake package delivery notifications, urgent banking alerts, or messages claiming you’ve won prizes or need to verify account information.
Legitimate organizations typically don’t include clickable links in unsolicited text messages, especially for account-related actions. When in doubt, don’t click the link—instead, open your banking app directly or visit the official website by typing the URL manually.
Social media platforms give scammers new opportunities to create convincing fake profiles and pages. They might impersonate customer service accounts, create fake giveaways, or send direct messages requesting personal information. These fake sites often use profile pictures and branding that closely resemble legitimate companies.
Unusual sender behavior is another indicator of a scam across all platforms. This includes messages from contacts you haven’t heard from in years, communications from brands you don’t typically interact with, or requests that seem out of character for the supposed sender.
Scammers have become increasingly cunning in creating fake websites that closely mimic legitimate businesses and services. Here are some real-life examples of how cybercriminals use fake websites to victimize consumers:
Scammers exploit your trust in the United States Postal Service (USPS), designing sophisticated fake websites to steal your personal information, payment details, or money. They know you’re expecting a package or need to resolve a delivery issue, making you more likely to enter sensitive information without carefully verifying the site’s authenticity.
USPS-themed smishing attacks arrive as text messages stating your package is delayed, undeliverable, or requires immediate action. Common phrases include “Pay $1.99 to reschedule delivery” or “Your package is held – click here to release.”
Scammers use various URL manipulation techniques to make their fake sites appear official. Watch for these red flags:
Always verify package information and delivery issues through official USPS channels before taking any action on suspicious websites or messages:
Reporting fake USPS websites helps protect others from falling victim to these scams and assists law enforcement in tracking down perpetrators.
Remember that legitimate USPS services are free for standard delivery confirmation and tracking. Any website demanding payment for basic package tracking or delivery should be treated as suspicious and verified through official USPS channels before providing any personal or financial information.
According to the Federal Trade Commission, tech support scams cost Americans nearly $1.5 billion in 2024. These types of social engineering attacks are increasingly becoming sophisticated, making it more important than ever to verify security alerts through official channels.
Sadly, many scammers are misusing the McAfee name to create fake tech support pop-up scams and trick you into believing your computer is infected or your protection has expired, and hoping you’ll act without thinking.
These pop-ups typically appear while you’re browsing and claim your computer is severely infected with viruses, malware, or other threats. They use official-looking McAfee logos, colors, and messaging to appear legitimate to get you to call a fake support number, download malicious software, or pay for unnecessary services.
Learning to detect fake sites and pop-ups protects you from scams. Be on the lookout for these warning signs:
If you see a suspicious pop-up claiming to be from McAfee, here’s exactly what you should do:
To check if your McAfee protection is genuinely active and up-to-date:
Remember, legitimate McAfee software updates and notifications come through the installed program itself, not through random browser pop-ups. Your actual McAfee protection works quietly in the background without bombarding you with alarming messages.
Stay protected by trusting your installed McAfee software and always verifying security alerts through official McAfee channels, such as your installed McAfee dashboard or the official website.
Be prepared and know how to respond quickly when something doesn’t feel right. If you suspect you’ve encountered a fake website, trust your instincts and take these protective steps immediately.
Recognizing fake sites and emails becomes easier with practice. The key is to trust your instincts—if something feels suspicious or too good to be true, take a moment to verify through official channels. With the simple verification techniques covered in this guide, you can confidently navigate the digital world and spot fake sites and emails before they cause harm.
Your best defense is to make these quick security checks a regular habit—verify URLs, look for secure connections, and trust your instincts when something feels off. Go directly to the source or bookmark your most frequently used services and always navigate to them. Enable two-factor authentication on important accounts, and remember that legitimate companies will never ask for sensitive information via email. Maintaining healthy skepticism about unsolicited communications will protect not only your personal information but also help create a safer online environment for everyone.
For the latest information on fake websites and scams and to report them, visit the Federal Trade Commission’s scam alerts or the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
The post Ways to Tell if a Website Is Fake appeared first on McAfee Blog.
On the surface, the Superbox media streaming devices for sale at retailers like BestBuy and Walmart may seem like a steal: They offer unlimited access to more than 2,200 pay-per-view and streaming services like Netflix, ESPN and Hulu, all for a one-time fee of around $400. But security experts warn these TV boxes require intrusive software that forces the user’s network to relay Internet traffic for others, traffic that is often tied to cybercrime activity such as advertising fraud and account takeovers.
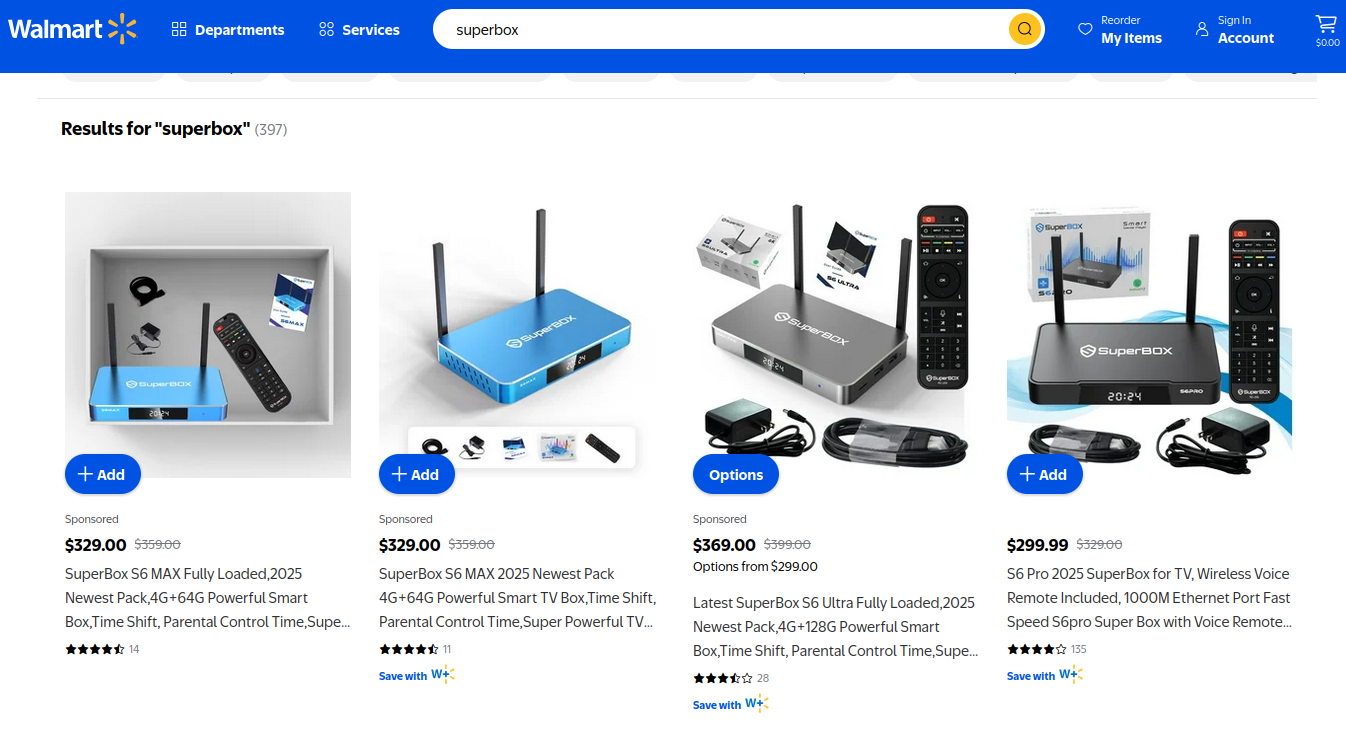
Superbox media streaming boxes for sale on Walmart.com.
Superbox bills itself as an affordable way for households to stream all of the television and movie content they could possibly want, without the hassle of monthly subscription fees — for a one-time payment of nearly $400.
“Tired of confusing cable bills and hidden fees?,” Superbox’s website asks in a recent blog post titled, “Cheap Cable TV for Low Income: Watch TV, No Monthly Bills.”
“Real cheap cable TV for low income solutions does exist,” the blog continues. “This guide breaks down the best alternatives to stop overpaying, from free over-the-air options to one-time purchase devices that eliminate monthly bills.”
Superbox claims that watching a stream of movies, TV shows, and sporting events won’t violate U.S. copyright law.
“SuperBox is just like any other Android TV box on the market, we can not control what software customers will use,” the company’s website maintains. “And you won’t encounter a law issue unless uploading, downloading, or broadcasting content to a large group.”

A blog post from the Superbox website.
There is nothing illegal about the sale or use of the Superbox itself, which can be used strictly as a way to stream content at providers where users already have a paid subscription. But that is not why people are shelling out $400 for these machines. The only way to watch those 2,200+ channels for free with a Superbox is to install several apps made for the device that enable them to stream this content.
Superbox’s homepage includes a prominent message stating the company does “not sell access to or preinstall any apps that bypass paywalls or provide access to unauthorized content.” The company explains that they merely provide the hardware, while customers choose which apps to install.
“We only sell the hardware device,” the notice states. “Customers must use official apps and licensed services; unauthorized use may violate copyright law.”
Superbox is technically correct here, except for maybe the part about how customers must use official apps and licensed services: Before the Superbox can stream those thousands of channels, users must configure the device to update itself, and the first step involves ripping out Google’s official Play store and replacing it with something called the “App Store” or “Blue TV Store.”
Superbox does this because the device does not use the official Google-certified Android TV system, and its apps will not load otherwise. Only after the Google Play store has been supplanted by this unofficial App Store do the various movie and video streaming apps that are built specifically for the Superbox appear available for download (again, outside of Google’s app ecosystem).
Experts say while these Android streaming boxes generally do what they advertise — enabling buyers to stream video content that would normally require a paid subscription — the apps that enable the streaming also ensnare the user’s Internet connection in a distributed residential proxy network that uses the devices to relay traffic from others.
Ashley is a senior solutions engineer at Censys, a cyber intelligence company that indexes Internet-connected devices, services and hosts. Ashley requested that only her first name be used in this story.
In a recent video interview, Ashley showed off several Superbox models that Censys was studying in the malware lab — including one purchased off the shelf at BestBuy.
“I’m sure a lot of people are thinking, ‘Hey, how bad could it be if it’s for sale at the big box stores?'” she said. “But the more I looked, things got weirder and weirder.”
Ashley said she found the Superbox devices immediately contacted a server at the Chinese instant messaging service Tencent QQ, as well as a residential proxy service called Grass IO.
Also known as getgrass[.]io, Grass says it is “a decentralized network that allows users to earn rewards by sharing their unused Internet bandwidth with AI labs and other companies.”
“Buyers seek unused internet bandwidth to access a more diverse range of IP addresses, which enables them to see certain websites from a retail perspective,” the Grass website explains. “By utilizing your unused internet bandwidth, they can conduct market research, or perform tasks like web scraping to train AI.” 
Reached via Twitter/X, Grass founder Andrej Radonjic told KrebsOnSecurity he’d never heard of a Superbox, and that Grass has no affiliation with the device maker.
“It looks like these boxes are distributing an unethical proxy network which people are using to try to take advantage of Grass,” Radonjic said. “The point of grass is to be an opt-in network. You download the grass app to monetize your unused bandwidth. There are tons of sketchy SDKs out there that hijack people’s bandwidth to help webscraping companies.”
Radonjic said Grass has implemented “a robust system to identify network abusers,” and that if it discovers anyone trying to misuse or circumvent its terms of service, the company takes steps to stop it and prevent those users from earning points or rewards.
Superbox’s parent company, Super Media Technology Company Ltd., lists its street address as a UPS store in Fountain Valley, Calif. The company did not respond to multiple inquiries.
According to this teardown by behindmlm.com, a blog that covers multi-level marketing (MLM) schemes, Grass’s compensation plan is built around “grass points,” which are earned through the use of the Grass app and through app usage by recruited affiliates. Affiliates can earn 5,000 grass points for clocking 100 hours usage of Grass’s app, but they must progress through ten affiliate tiers or ranks before they can redeem their grass points (presumably for some type of cryptocurrency). The 10th or “Titan” tier requires affiliates to accumulate a whopping 50 million grass points, or recruit at least 221 more affiliates.
Radonjic said Grass’s system has changed in recent months, and confirmed the company has a referral program where users can earn Grass Uptime Points by contributing their own bandwidth and/or by inviting other users to participate.
“Users are not required to participate in the referral program to earn Grass Uptime Points or to receive Grass Tokens,” Radonjic said. “Grass is in the process of phasing out the referral program and has introduced an updated Grass Points model.”
A review of the Terms and Conditions page for getgrass[.]io at the Wayback Machine shows Grass’s parent company has changed names at least five times in the course of its two-year existence. Searching the Wayback Machine on getgrass[.]io shows that in June 2023 Grass was owned by a company called Wynd Network. By March 2024, the owner was listed as Lower Tribeca Corp. in the Bahamas. By August 2024, Grass was controlled by a Half Space Labs Limited, and in November 2024 the company was owned by Grass OpCo (BVI) Ltd. Currently, the Grass website says its parent is just Grass OpCo Ltd (no BVI in the name).
Radonjic acknowledged that Grass has undergone “a handful of corporate clean-ups over the last couple of years,” but described them as administrative changes that had no operational impact. “These reflect normal early-stage restructuring as the project moved from initial development…into the current structure under the Grass Foundation,” he said.
Censys’s Ashley said the phone home to China’s Tencent QQ instant messaging service was the first red flag with the Superbox devices she examined. She also discovered the streaming boxes included powerful network analysis and remote access tools, such as Tcpdump and Netcat.
“This thing DNS hijacked my router, did ARP poisoning to the point where things fall off the network so they can assume that IP, and attempted to bypass controls,” she said. “I have root on all of them now, and they actually have a folder called ‘secondstage.’ These devices also have Netcat and Tcpdump on them, and yet they are supposed to be streaming devices.”
A quick online search shows various Superbox models and many similar Android streaming devices for sale at a wide range of top retail destinations, including Amazon, BestBuy, Newegg, and Walmart. Newegg.com, for example, currently lists more than three dozen Superbox models. In all cases, the products are sold by third-party merchants on these platforms, but in many instances the fulfillment comes from the e-commerce platform itself.
“Newegg is pretty bad now with these devices,” Ashley said. “Ebay is the funniest, because they have Superbox in Spanish — the SuperCaja — which is very popular.”
Ashley said Amazon recently cracked down on Android streaming devices branded as Superbox, but that those listings can still be found under the more generic title “modem and router combo” (which may be slightly closer to the truth about the device’s behavior).
Superbox doesn’t advertise its products in the conventional sense. Rather, it seems to rely on lesser-known influencers on places like Youtube and TikTok to promote the devices. Meanwhile, Ashley said, Superbox pays those influencers 50 percent of the value of each device they sell.
“It’s weird to me because influencer marketing usually caps compensation at 15 percent, and it means they don’t care about the money,” she said. “This is about building their network.”
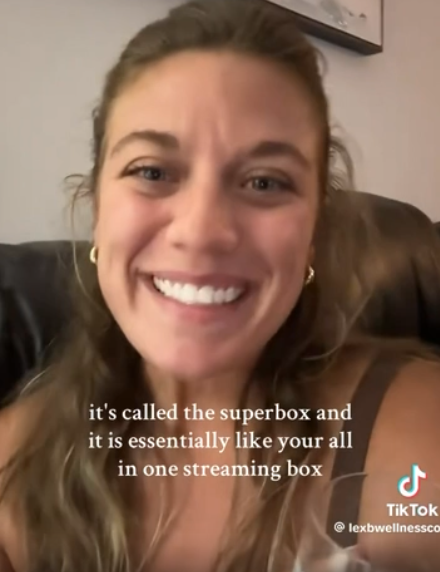
A TikTok influencer casually mentions and promotes Superbox while chatting with her followers over a glass of wine.
As plentiful as the Superbox is on e-commerce sites, it is just one brand in an ocean of no-name Android-based TV boxes available to consumers. While these devices generally do provide buyers with “free” streaming content, they also tend to include factory-installed malware or require the installation of third-party apps that engage the user’s Internet address in advertising fraud.
In July 2025, Google filed a “John Doe” lawsuit (PDF) against 25 unidentified defendants dubbed the “BadBox 2.0 Enterprise,” which Google described as a botnet of over ten million Android streaming devices that engaged in advertising fraud. Google said the BADBOX 2.0 botnet, in addition to compromising multiple types of devices prior to purchase, can also infect devices by requiring the download of malicious apps from unofficial marketplaces.

Some of the unofficial Android devices flagged by Google as part of the Badbox 2.0 botnet are still widely for sale at major e-commerce vendors. Image: Google.
Several of the Android streaming devices flagged in Google’s lawsuit are still for sale on top U.S. retail sites. For example, searching for the “X88Pro 10” and the “T95” Android streaming boxes finds both continue to be peddled by Amazon sellers.
Google’s lawsuit came on the heels of a June 2025 advisory from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which warned that cyber criminals were gaining unauthorized access to home networks by either configuring the products with malicious software prior to the user’s purchase, or infecting the device as it downloads required applications that contain backdoors, usually during the set-up process.
“Once these compromised IoT devices are connected to home networks, the infected devices are susceptible to becoming part of the BADBOX 2.0 botnet and residential proxy services known to be used for malicious activity,” the FBI said.
The FBI said BADBOX 2.0 was discovered after the original BADBOX campaign was disrupted in 2024. The original BADBOX was identified in 2023, and primarily consisted of Android operating system devices that were compromised with backdoor malware prior to purchase.
Riley Kilmer is founder of Spur, a company that tracks residential proxy networks. Kilmer said Badbox 2.0 was used as a distribution platform for IPidea, a China-based entity that is now the world’s largest residential proxy network.
Kilmer and others say IPidea is merely a rebrand of 911S5 Proxy, a China-based proxy provider sanctioned last year by the U.S. Department of the Treasury for operating a botnet that helped criminals steal billions of dollars from financial institutions, credit card issuers, and federal lending programs (the U.S. Department of Justice also arrested the alleged owner of 911S5).
How are most IPidea customers using the proxy service? According to the proxy detection service Synthient, six of the top ten destinations for IPidea proxies involved traffic that has been linked to either ad fraud or credential stuffing (account takeover attempts).
Kilmer said companies like Grass are probably being truthful when they say that some of their customers are companies performing web scraping to train artificial intelligence efforts, because a great deal of content scraping which ultimately benefits AI companies is now leveraging these proxy networks to further obfuscate their aggressive data-slurping activity. By routing this unwelcome traffic through residential IP addresses, Kilmer said, content scraping firms can make it far trickier to filter out.
“Web crawling and scraping has always been a thing, but AI made it like a commodity, data that had to be collected,” Kilmer told KrebsOnSecurity. “Everybody wanted to monetize their own data pots, and how they monetize that is different across the board.”
Products like Superbox are drawing increased interest from consumers as more popular network television shows and sportscasts migrate to subscription streaming services, and as people begin to realize they’re spending as much or more on streaming services than they previously paid for cable or satellite TV.
These streaming devices from no-name technology vendors are another example of the maxim, “If something is free, you are the product,” meaning the company is making money by selling access to and/or information about its users and their data.
Superbox owners might counter, “Free? I paid $400 for that device!” But remember: Just because you paid a lot for something doesn’t mean you are done paying for it, or that somehow you are the only one who might be worse off from the transaction.
It may be that many Superbox customers don’t care if someone uses their Internet connection to tunnel traffic for ad fraud and account takeovers; for them, it beats paying for multiple streaming services each month. My guess, however, is that quite a few people who buy (or are gifted) these products have little understanding of the bargain they’re making when they plug them into an Internet router.
Superbox performs some serious linguistic gymnastics to claim its products don’t violate copyright laws, and that its customers alone are responsible for understanding and observing any local laws on the matter. However, buyer beware: If you’re a resident of the United States, you should know that using these devices for unauthorized streaming violates the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), and can incur legal action, fines, and potential warnings and/or suspension of service by your Internet service provider.
According to the FBI, there are several signs to look for that may indicate a streaming device you own is malicious, including:
-The presence of suspicious marketplaces where apps are downloaded.
-Requiring Google Play Protect settings to be disabled.
-Generic TV streaming devices advertised as unlocked or capable of accessing free content.
-IoT devices advertised from unrecognizable brands.
-Android devices that are not Play Protect certified.
-Unexplained or suspicious Internet traffic.
This explainer from the Electronic Frontier Foundation delves a bit deeper into each of the potential symptoms listed above.
Aisuru, the botnet responsible for a series of record-smashing distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks this year, recently was overhauled to support a more low-key, lucrative and sustainable business: Renting hundreds of thousands of infected Internet of Things (IoT) devices to proxy services that help cybercriminals anonymize their traffic. Experts say a glut of proxies from Aisuru and other sources is fueling large-scale data harvesting efforts tied to various artificial intelligence (AI) projects, helping content scrapers evade detection by routing their traffic through residential connections that appear to be regular Internet users.
First identified in August 2024, Aisuru has spread to at least 700,000 IoT systems, such as poorly secured Internet routers and security cameras. Aisuru’s overlords have used their massive botnet to clobber targets with headline-grabbing DDoS attacks, flooding targeted hosts with blasts of junk requests from all infected systems simultaneously.
In June, Aisuru hit KrebsOnSecurity.com with a DDoS clocking at 6.3 terabits per second — the biggest attack that Google had ever mitigated at the time. In the weeks and months that followed, Aisuru’s operators demonstrated DDoS capabilities of nearly 30 terabits of data per second — well beyond the attack mitigation capabilities of most Internet destinations.
These digital sieges have been particularly disruptive this year for U.S.-based Internet service providers (ISPs), in part because Aisuru recently succeeded in taking over a large number of IoT devices in the United States. And when Aisuru launches attacks, the volume of outgoing traffic from infected systems on these ISPs is often so high that it can disrupt or degrade Internet service for adjacent (non-botted) customers of the ISPs.
“Multiple broadband access network operators have experienced significant operational impact due to outbound DDoS attacks in excess of 1.5Tb/sec launched from Aisuru botnet nodes residing on end-customer premises,” wrote Roland Dobbins, principal engineer at Netscout, in a recent executive summary on Aisuru. “Outbound/crossbound attack traffic exceeding 1Tb/sec from compromised customer premise equipment (CPE) devices has caused significant disruption to wireline and wireless broadband access networks. High-throughput attacks have caused chassis-based router line card failures.”
The incessant attacks from Aisuru have caught the attention of federal authorities in the United States and Europe (many of Aisuru’s victims are customers of ISPs and hosting providers based in Europe). Quite recently, some of the world’s largest ISPs have started informally sharing block lists identifying the rapidly shifting locations of the servers that the attackers use to control the activities of the botnet.
Experts say the Aisuru botmasters recently updated their malware so that compromised devices can more easily be rented to so-called “residential proxy” providers. These proxy services allow paying customers to route their Internet communications through someone else’s device, providing anonymity and the ability to appear as a regular Internet user in almost any major city worldwide.
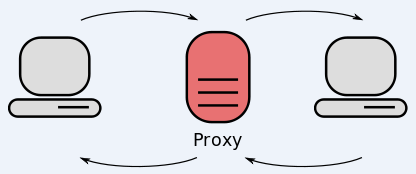
From a website’s perspective, the IP traffic of a residential proxy network user appears to originate from the rented residential IP address, not from the proxy service customer. Proxy services can be used in a legitimate manner for several business purposes — such as price comparisons or sales intelligence. But they are massively abused for hiding cybercrime activity (think advertising fraud, credential stuffing) because they can make it difficult to trace malicious traffic to its original source.
And as we’ll see in a moment, this entire shadowy industry appears to be shifting its focus toward enabling aggressive content scraping activity that continuously feeds raw data into large language models (LLMs) built to support various AI projects.
Riley Kilmer is co-founder of spur.us, a service that tracks proxy networks. Kilmer said all of the top proxy services have grown substantially over the past six months.
“I just checked, and in the last 90 days we’ve seen 250 million unique residential proxy IPs,” Kilmer said. “That is insane. That is so high of a number, it’s unheard of. These proxies are absolutely everywhere now.”
Today, Spur says it is tracking an unprecedented spike in available proxies across all providers, including;
LUMINATI_PROXY 11,856,421
NETNUT_PROXY 10,982,458
ABCPROXY_PROXY 9,294,419
OXYLABS_PROXY 6,754,790
IPIDEA_PROXY 3,209,313
EARNFM_PROXY 2,659,913
NODEMAVEN_PROXY 2,627,851
INFATICA_PROXY 2,335,194
IPROYAL_PROXY 2,032,027
YILU_PROXY 1,549,155
Reached for comment about the apparent rapid growth in their proxy network, Oxylabs (#4 on Spur’s list) said while their proxy pool did grow recently, it did so at nowhere near the rate cited by Spur.
“We don’t systematically track other providers’ figures, and we’re not aware of any instances of 10× or 100× growth, especially when it comes to a few bigger companies that are legitimate businesses,” the company said in a written statement.
Bright Data was formerly known as Luminati Networks, the name that is currently at the top of Spur’s list of the biggest residential proxy networks. Bright Data likewise told KrebsOnSecurity that Spur’s current estimates of its proxy network are dramatically overstated and inaccurate.
“We did not actively initiate nor do we see any 10x or 100x expansion of our network, which leads me to believe that someone might be presenting these IPs as Bright Data’s in some way,” said Rony Shalit, Bright Data’s chief compliance and ethics officer. “In many cases in the past, due to us being the leading data collection proxy provider, IPs were falsely tagged as being part of our network, or while being used by other proxy providers for malicious activity.”
“Our network is only sourced from verified IP providers and a robust opt-in only residential peers, which we work hard and in complete transparency to obtain,” Shalit continued. “Every DC, ISP or SDK partner is reviewed and approved, and every residential peer must actively opt in to be part of our network.”
Even Spur acknowledges that Luminati and Oxylabs are unlike most other proxy services on their top proxy providers list, in that these providers actually adhere to “know-your-customer” policies, such as requiring video calls with all customers, and strictly blocking customers from reselling access.
Benjamin Brundage is founder of Synthient, a startup that helps companies detect proxy networks. Brundage said if there is increasing confusion around which proxy networks are the most worrisome, it’s because nearly all of these lesser-known proxy services have evolved into highly incestuous bandwidth resellers. What’s more, he said, some proxy providers do not appreciate being tracked and have been known to take aggressive steps to confuse systems that scan the Internet for residential proxy nodes.
Brundage said most proxy services today have created their own software development kit or SDK that other app developers can bundle with their code to earn revenue. These SDKs quietly modify the user’s device so that some portion of their bandwidth can be used to forward traffic from proxy service customers.
“Proxy providers have pools of constantly churning IP addresses,” he said. “These IP addresses are sourced through various means, such as bandwidth-sharing apps, botnets, Android SDKs, and more. These providers will often either directly approach resellers or offer a reseller program that allows users to resell bandwidth through their platform.”
Many SDK providers say they require full consent before allowing their software to be installed on end-user devices. Still, those opt-in agreements and consent checkboxes may be little more than a formality for cybercriminals like the Aisuru botmasters, who can earn a commission each time one of their infected devices is forced to install some SDK that enables one or more of these proxy services.
Depending on its structure, a single provider may operate hundreds of different proxy pools at a time — all maintained through other means, Brundage said.
“Often, you’ll see resellers maintaining their own proxy pool in addition to an upstream provider,” he said. “It allows them to market a proxy pool to high-value clients and offer an unlimited bandwidth plan for cheap reduce their own costs.”
Some proxy providers appear to be directly in league with botmasters. Brundage identified one proxy seller that was aggressively advertising cheap and plentiful bandwidth to content scraping companies. After scanning that provider’s pool of available proxies, Brundage said he found a one-to-one match with IP addresses he’d previously mapped to the Aisuru botnet.
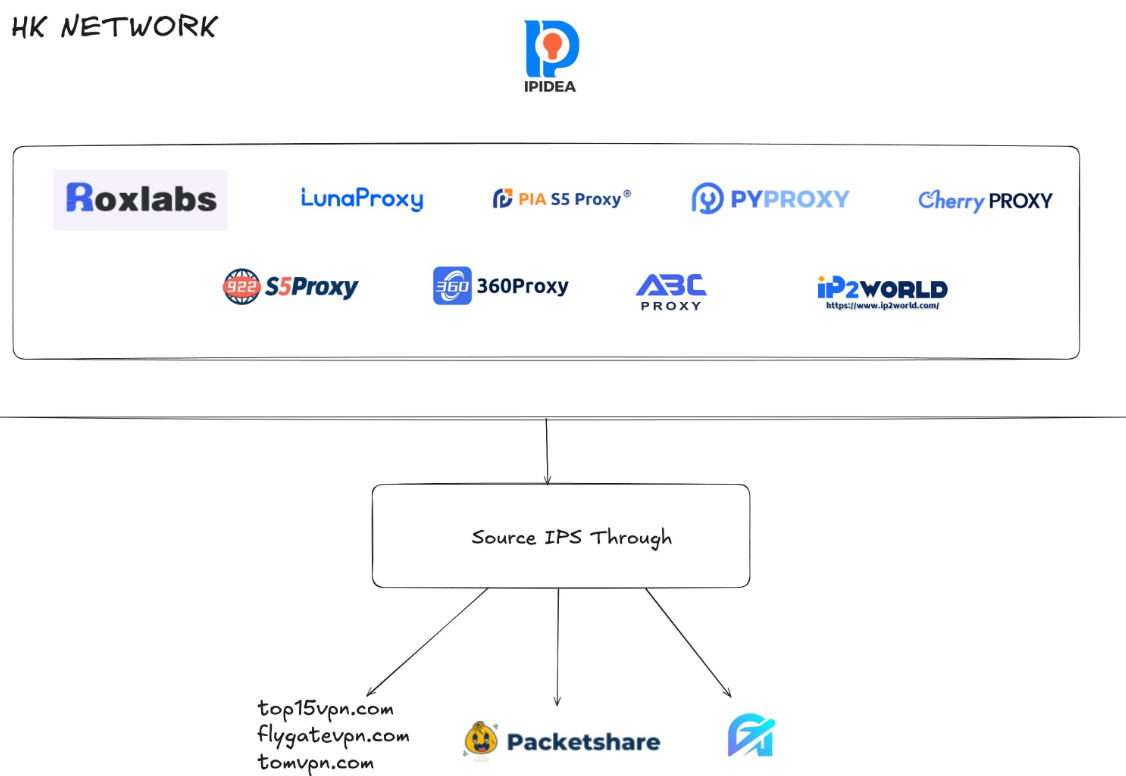
Brundage says that by almost any measurement, the world’s largest residential proxy service is IPidea, a China-based proxy network. IPidea is #5 on Spur’s Top 10, and Brundage said its brands include ABCProxy (#3), Roxlabs, LunaProxy, PIA S5 Proxy, PyProxy, 922Proxy, 360Proxy, IP2World, and Cherry Proxy. Spur’s Kilmer said they also track Yilu Proxy (#10) as IPidea.
Brundage said all of these providers operate under a corporate umbrella known on the cybercrime forums as “HK Network.”
“The way it works is there’s this whole reseller ecosystem, where IPidea will be incredibly aggressive and approach all these proxy providers with the offer, ‘Hey, if you guys buy bandwidth from us, we’ll give you these amazing reseller prices,'” Brundage explained. “But they’re also very aggressive in recruiting resellers for their apps.”
A graphic depicting the relationship between proxy providers that Synthient found are white labeling IPidea proxies. Image: Synthient.com.
Those apps include a range of low-cost and “free” virtual private networking (VPN) services that indeed allow users to enjoy a free VPN, but which also turn the user’s device into a traffic relay that can be rented to cybercriminals, or else parceled out to countless other proxy networks.
“They have all this bandwidth to offload,” Brundage said of IPidea and its sister networks. “And they can do it through their own platforms, or they go get resellers to do it for them by advertising on sketchy hacker forums to reach more people.”
One of IPidea’s core brands is 922S5Proxy, which is a not-so-subtle nod to the 911S5Proxy service that was hugely popular between 2015 and 2022. In July 2022, KrebsOnSecurity published a deep dive into 911S5Proxy’s origins and apparent owners in China. Less than a week later, 911S5Proxy announced it was closing down after the company’s servers were massively hacked.
That 2022 story named Yunhe Wang from Beijing as the apparent owner and/or manager of the 911S5 proxy service. In May 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice arrested Mr Wang, alleging that his network was used to steal billions of dollars from financial institutions, credit card issuers, and federal lending programs. At the same time, the U.S. Treasury Department announced sanctions against Wang and two other Chinese nationals for operating 911S5Proxy.
The website for 922Proxy.
In recent months, multiple experts who track botnet and proxy activity have shared that a great deal of content scraping which ultimately benefits AI companies is now leveraging these proxy networks to further obfuscate their aggressive data-slurping activity. That’s because by routing it through residential IP addresses, content scraping firms can make their traffic far trickier to filter out.
“It’s really difficult to block, because there’s a risk of blocking real people,” Spur’s Kilmer said of the LLM scraping activity that is fed through individual residential IP addresses, which are often shared by multiple customers at once.
Kilmer says the AI industry has brought a veneer of legitimacy to residential proxy business, which has heretofore mostly been associated with sketchy affiliate money making programs, automated abuse, and unwanted Internet traffic.
“Web crawling and scraping has always been a thing, but AI made it like a commodity, data that had to be collected,” Kilmer said. “Everybody wanted to monetize their own data pots, and how they monetize that is different across the board.”
Kilmer said many LLM-related scrapers rely on residential proxies in cases where the content provider has restricted access to their platform in some way, such as forcing interaction through an app, or keeping all content behind a login page with multi-factor authentication.
“Where the cost of data is out of reach — there is some exclusivity or reason they can’t access the data — they’ll turn to residential proxies so they look like a real person accessing that data,” Kilmer said of the content scraping efforts.
Aggressive AI crawlers increasingly are overloading community-maintained infrastructure, causing what amounts to persistent DDoS attacks on vital public resources. A report earlier this year from LibreNews found some open-source projects now see as much as 97 percent of their traffic originating from AI company bots, dramatically increasing bandwidth costs, service instability, and burdening already stretched-thin maintainers.
Cloudflare is now experimenting with tools that will allow content creators to charge a fee to AI crawlers to scrape their websites. The company’s “pay-per-crawl” feature is currently in a private beta, and it lets publishers set their own prices that bots must pay before scraping content.
On October 22, the social media and news network Reddit sued Oxylabs (PDF) and several other proxy providers, alleging that their systems enabled the mass-scraping of Reddit user content even though Reddit had taken steps to block such activity.
“Recognizing that Reddit denies scrapers like them access to its site, Defendants scrape the data from Google’s search results instead,” the lawsuit alleges. “They do so by masking their identities, hiding their locations, and disguising their web scrapers as regular people (among other techniques) to circumvent or bypass the security restrictions meant to stop them.”
Denas Grybauskas, chief governance and strategy officer at Oxylabs, said the company was shocked and disappointed by the lawsuit.
“Reddit has made no attempt to speak with us directly or communicate any potential concerns,” Grybauskas said in a written statement. “Oxylabs has always been and will continue to be a pioneer and an industry leader in public data collection, and it will not hesitate to defend itself against these allegations. Oxylabs’ position is that no company should claim ownership of public data that does not belong to them. It is possible that it is just an attempt to sell the same public data at an inflated price.”
As big and powerful as Aisuru may be, it is hardly the only botnet that is contributing to the overall broad availability of residential proxies. For example, on June 5 the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center warned that an IoT malware threat dubbed BADBOX 2.0 had compromised millions of smart-TV boxes, digital projectors, vehicle infotainment units, picture frames, and other IoT devices.
In July, Google filed a lawsuit in New York federal court against the Badbox botnet’s alleged perpetrators. Google said the Badbox 2.0 botnet “compromised more than 10 million uncertified devices running Android’s open-source software, which lacks Google’s security protections. Cybercriminals infected these devices with pre-installed malware and exploited them to conduct large-scale ad fraud and other digital crimes.”
Brundage said the Aisuru botmasters have their own SDK, and for some reason part of its code tells many newly-infected systems to query the domain name fuckbriankrebs[.]com. This may be little more than an elaborate “screw you” to this site’s author: One of the botnet’s alleged partners goes by the handle “Forky,” and was identified in June by KrebsOnSecurity as a young man from Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Brundage noted that only systems infected with Aisuru’s Android SDK will be forced to resolve the domain. Initially, there was some discussion about whether the domain might have some utility as a “kill switch” capable of disrupting the botnet’s operations, although Brundage and others interviewed for this story say that is unlikely.
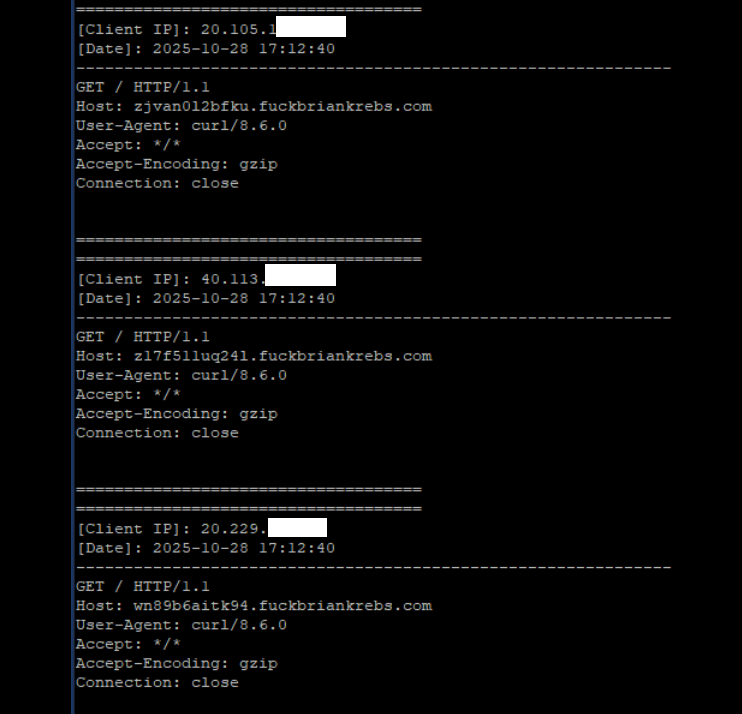
A tiny sample of the traffic after a DNS server was enabled on the newly registered domain fuckbriankrebs dot com. Each unique IP address requested its own unique subdomain. Image: Seralys.
For one thing, they said, if the domain was somehow critical to the operation of the botnet, why was it still unregistered and actively for-sale? Why indeed, we asked. Happily, the domain name was deftly snatched up last week by Philippe Caturegli, “chief hacking officer” for the security intelligence company Seralys.
Caturegli enabled a passive DNS server on that domain and within a few hours received more than 700,000 requests for unique subdomains on fuckbriankrebs[.]com.
But even with that visibility into Aisuru, it is difficult to use this domain check-in feature to measure its true size, Brundage said. After all, he said, the systems that are phoning home to the domain are only a small portion of the overall botnet.
“The bots are hardcoded to just spam lookups on the subdomains,” he said. “So anytime an infection occurs or it runs in the background, it will do one of those DNS queries.”

Caturegli briefly configured all subdomains on fuckbriankrebs dot com to display this ASCII art image to visiting systems today.
The domain fuckbriankrebs[.]com has a storied history. On its initial launch in 2009, it was used to spread malicious software by the Cutwail spam botnet. In 2011, the domain was involved in a notable DDoS against this website from a botnet powered by Russkill (a.k.a. “Dirt Jumper”).
Domaintools.com finds that in 2015, fuckbriankrebs[.]com was registered to an email address attributed to David “Abdilo” Crees, a 27-year-old Australian man sentenced in May 2025 to time served for cybercrime convictions related to the Lizard Squad hacking group.
Update, Nov. 1, 2025, 10:25 a.m. ET: An earlier version of this story erroneously cited Spur’s proxy numbers from earlier this year; Spur said those numbers conflated residential proxies — which are rotating and attached to real end-user devices — with “ISP proxies” located at AT&T. ISP proxies, Spur said, involve tricking an ISP into routing a large number of IP addresses that are resold as far more static datacenter proxies.
KrebsOnSecurity recently heard from a reader whose boss’s email account got phished and was used to trick one of the company’s customers into sending a large payment to scammers. An investigation into the attacker’s infrastructure points to a long-running Nigerian cybercrime ring that is actively targeting established companies in the transportation and aviation industries.

Image: Shutterstock, Mr. Teerapon Tiuekhom.
A reader who works in the transportation industry sent a tip about a recent successful phishing campaign that tricked an executive at the company into entering their credentials at a fake Microsoft 365 login page. From there, the attackers quickly mined the executive’s inbox for past communications about invoices, copying and modifying some of those messages with new invoice demands that were sent to some of the company’s customers and partners.
Speaking on condition of anonymity, the reader said the resulting phishing emails to customers came from a newly registered domain name that was remarkably similar to their employer’s domain, and that at least one of their customers fell for the ruse and paid a phony invoice. They said the attackers had spun up a look-alike domain just a few hours after the executive’s inbox credentials were phished, and that the scam resulted in a customer suffering a six-figure financial loss.
The reader also shared that the email addresses in the registration records for the imposter domain — roomservice801@gmail.com — is tied to many such phishing domains. Indeed, a search on this email address at DomainTools.com finds it is associated with at least 240 domains registered in 2024 or 2025. Virtually all of them mimic legitimate domains for companies in the aerospace and transportation industries worldwide.
An Internet search for this email address reveals a humorous blog post from 2020 on the Russian forum hackware[.]ru, which found roomservice801@gmail.com was tied to a phishing attack that used the lure of phony invoices to trick the recipient into logging in at a fake Microsoft login page. We’ll come back to this research in a moment.
DomainTools shows that some of the early domains registered to roomservice801@gmail.com in 2016 include other useful information. For example, the WHOIS records for alhhomaidhicentre[.]biz reference the technical contact of “Justy John” and the email address justyjohn50@yahoo.com.
A search at DomainTools found justyjohn50@yahoo.com has been registering one-off phishing domains since at least 2012. At this point, I was convinced that some security company surely had already published an analysis of this particular threat group, but I didn’t yet have enough information to draw any solid conclusions.
DomainTools says the Justy John email address is tied to more than two dozen domains registered since 2012, but we can find hundreds more phishing domains and related email addresses simply by pivoting on details in the registration records for these Justy John domains. For example, the street address used by the Justy John domain axisupdate[.]net — 7902 Pelleaux Road in Knoxville, TN — also appears in the registration records for accountauthenticate[.]com, acctlogin[.]biz, and loginaccount[.]biz, all of which at one point included the email address rsmith60646@gmail.com.
That Rsmith Gmail address is connected to the 2012 phishing domain alibala[.]biz (one character off of the Chinese e-commerce giant alibaba.com, with a different top-level domain of .biz). A search in DomainTools on the phone number in those domain records — 1.7736491613 — reveals even more phishing domains as well as the Nigerian phone number “2348062918302” and the email address michsmith59@gmail.com.
DomainTools shows michsmith59@gmail.com appears in the registration records for the domain seltrock[.]com, which was used in the phishing attack documented in the 2020 Russian blog post mentioned earlier. At this point, we are just two steps away from identifying the threat actor group.
The same Nigerian phone number shows up in dozens of domain registrations that reference the email address sebastinekelly69@gmail.com, including 26i3[.]net, costamere[.]com, danagruop[.]us, and dividrilling[.]com. A Web search on any of those domains finds they were indexed in an “indicator of compromise” list on GitHub maintained by Palo Alto Networks‘ Unit 42 research team.
According to Unit 42, the domains are the handiwork of a vast cybercrime group based in Nigeria that it dubbed “SilverTerrier” back in 2014. In an October 2021 report, Palo Alto said SilverTerrier excels at so-called “business e-mail compromise” or BEC scams, which target legitimate business email accounts through social engineering or computer intrusion activities. BEC criminals use that access to initiate or redirect the transfer of business funds for personal gain.
Palo Alto says SilverTerrier encompasses hundreds of BEC fraudsters, some of whom have been arrested in various international law enforcement operations by Interpol. In 2022, Interpol and the Nigeria Police Force arrested 11 alleged SilverTerrier members, including a prominent SilverTerrier leader who’d been flaunting his wealth on social media for years. Unfortunately, the lure of easy money, endemic poverty and corruption, and low barriers to entry for cybercrime in Nigeria conspire to provide a constant stream of new recruits.
BEC scams were the 7th most reported crime tracked by the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) in 2024, generating more than 21,000 complaints. However, BEC scams were the second most costly form of cybercrime reported to the feds last year, with nearly $2.8 billion in claimed losses. In its 2025 Fraud and Control Survey Report, the Association for Financial Professionals found 63 percent of organizations experienced a BEC last year.
Poking at some of the email addresses that spool out from this research reveals a number of Facebook accounts for people residing in Nigeria or in the United Arab Emirates, many of whom do not appear to have tried to mask their real-life identities. Palo Alto’s Unit 42 researchers reached a similar conclusion, noting that although a small subset of these crooks went to great lengths to conceal their identities, it was usually simple to learn their identities on social media accounts and the major messaging services.
Palo Alto said BEC actors have become far more organized over time, and that while it remains easy to find actors working as a group, the practice of using one phone number, email address or alias to register malicious infrastructure in support of multiple actors has made it far more time consuming (but not impossible) for cybersecurity and law enforcement organizations to sort out which actors committed specific crimes.
“We continue to find that SilverTerrier actors, regardless of geographical location, are often connected through only a few degrees of separation on social media platforms,” the researchers wrote.
Palo Alto has published a useful list of recommendations that organizations can adopt to minimize the incidence and impact of BEC attacks. Many of those tips are prophylactic, such as conducting regular employee security training and reviewing network security policies.
But one recommendation — getting familiar with a process known as the “financial fraud kill chain” or FFKC — bears specific mention because it offers the single best hope for BEC victims who are seeking to claw back payments made to fraudsters, and yet far too many victims don’t know it exists until it is too late.
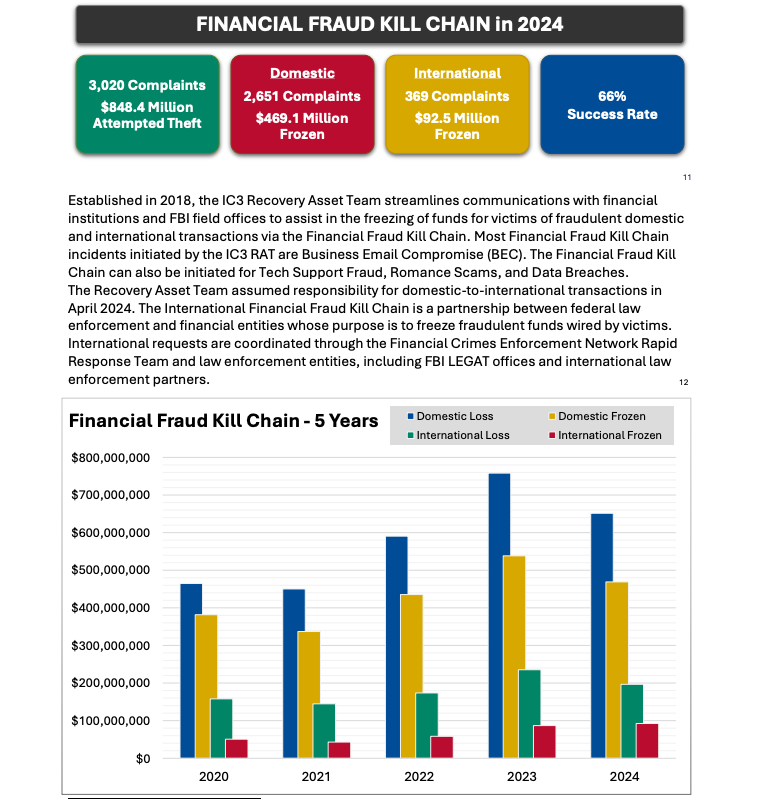
Image: ic3.gov.
As explained in this FBI primer, the International Financial Fraud Kill Chain is a partnership between federal law enforcement and financial entities whose purpose is to freeze fraudulent funds wired by victims. According to the FBI, viable victim complaints filed with ic3.gov promptly after a fraudulent transfer (generally less than 72 hours) will be automatically triaged by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
The FBI noted in its IC3 annual report (PDF) that the FFKC had a 66 percent success rate in 2024. Viable ic3.gov complaints involve losses of at least $50,000, and include all records from the victim or victim bank, as well as a completed FFKC form (provided by FinCEN) containing victim information, recipient information, bank names, account numbers, location, SWIFT, and any additional information.
OWASP Maryam is a modular open-source framework based on OSINT and data gathering. It is designed to provide a robust environment to harvest data from open sources and search engines quickly and thoroughly.
$ pip install maryam
Alternatively, you can install the latest version with the following command (Recommended):
pip install git+https://github.com/saeeddhqan/maryam.git
# Using dns_search. --max means all of resources. --api shows the results as json.
# .. -t means use multi-threading.
maryam -e dns_search -d ibm.com -t 5 --max --api --form
# Using youtube. -q means query
maryam -e youtube -q "<QUERY>"
maryam -e google -q "<QUERY>"
maryam -e dnsbrute -d domain.tld
# Show framework modules
maryam -e show modules
# Set framework options.
maryam -e set proxy ..
maryam -e set agent ..
maryam -e set timeout ..
# Run web API
maryam -e web api 127.0.0.1 1313
Here is a start guide: Development Guide You can add a new search engine to the util classes or use the current search engines to write a new module. The best help to write a new module is checking the current modules.
To report bugs, requests, or any other issues please create an issue.