The Russia-based cybercrime group dubbed “Fin7,” known for phishing and malware attacks that have cost victim organizations an estimated $3 billion in losses since 2013, was declared dead last year by U.S. authorities. But experts say Fin7 has roared back to life in 2024 — setting up thousands of websites mimicking a range of media and technology companies — with the help of Stark Industries Solutions, a sprawling hosting provider that is a persistent source of cyberattacks against enemies of Russia.
In May 2023, the U.S. attorney for Washington state declared “Fin7 is an entity no more,” after prosecutors secured convictions and prison sentences against three men found to be high-level Fin7 hackers or managers. This was a bold declaration against a group that the U.S. Department of Justice described as a criminal enterprise with more than 70 people organized into distinct business units and teams.
The first signs of Fin7’s revival came in April 2024, when Blackberry wrote about an intrusion at a large automotive firm that began with malware served by a typosquatting attack targeting people searching for a popular free network scanning tool.
Now, researchers at security firm Silent Push say they have devised a way to map out Fin7’s rapidly regrowing cybercrime infrastructure, which includes more than 4,000 hosts that employ a range of exploits, from typosquatting and booby-trapped ads to malicious browser extensions and spearphishing domains.
Silent Push said it found Fin7 domains targeting or spoofing brands including American Express, Affinity Energy, Airtable, Alliant, Android Developer, Asana, Bitwarden, Bloomberg, Cisco (Webex), CNN, Costco, Dropbox, Grammarly, Google, Goto.com, Harvard, Lexis Nexis, Meta, Microsoft 365, Midjourney, Netflix, Paycor, Quickbooks, Quicken, Reuters, Regions Bank Onepass, RuPay, SAP (Ariba), Trezor, Twitter/X, Wall Street Journal, Westlaw, and Zoom, among others.
Zach Edwards, senior threat analyst at Silent Push, said many of the Fin7 domains are innocuous-looking websites for generic businesses that sometimes include text from default website templates (the content on these sites often has nothing to do with the entity’s stated business or mission).
Edwards said Fin7 does this to “age” the domains and to give them a positive or at least benign reputation before they’re eventually converted for use in hosting brand-specific phishing pages.
“It took them six to nine months to ramp up, but ever since January of this year they have been humming, building a giant phishing infrastructure and aging domains,” Edwards said of the cybercrime group.
In typosquatting attacks, Fin7 registers domains that are similar to those for popular free software tools. Those look-alike domains are then advertised on Google so that sponsored links to them show up prominently in search results, which is usually above the legitimate source of the software in question.
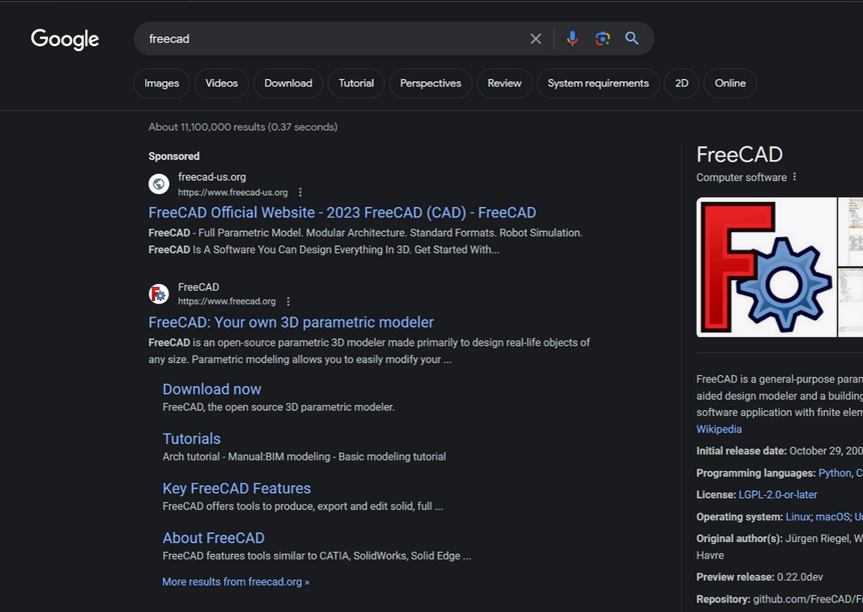
A malicious site spoofing FreeCAD showed up prominently as a sponsored result in Google search results earlier this year.
According to Silent Push, the software currently being targeted by Fin7 includes 7-zip, PuTTY, ProtectedPDFViewer, AIMP, Notepad++, Advanced IP Scanner, AnyDesk, pgAdmin, AutoDesk, Bitwarden, Rest Proxy, Python, Sublime Text, and Node.js.
In May 2024, security firm eSentire warned that Fin7 was spotted using sponsored Google ads to serve pop-ups prompting people to download phony browser extensions that install malware. Malwarebytes blogged about a similar campaign in April, but did not attribute the activity to any particular group.
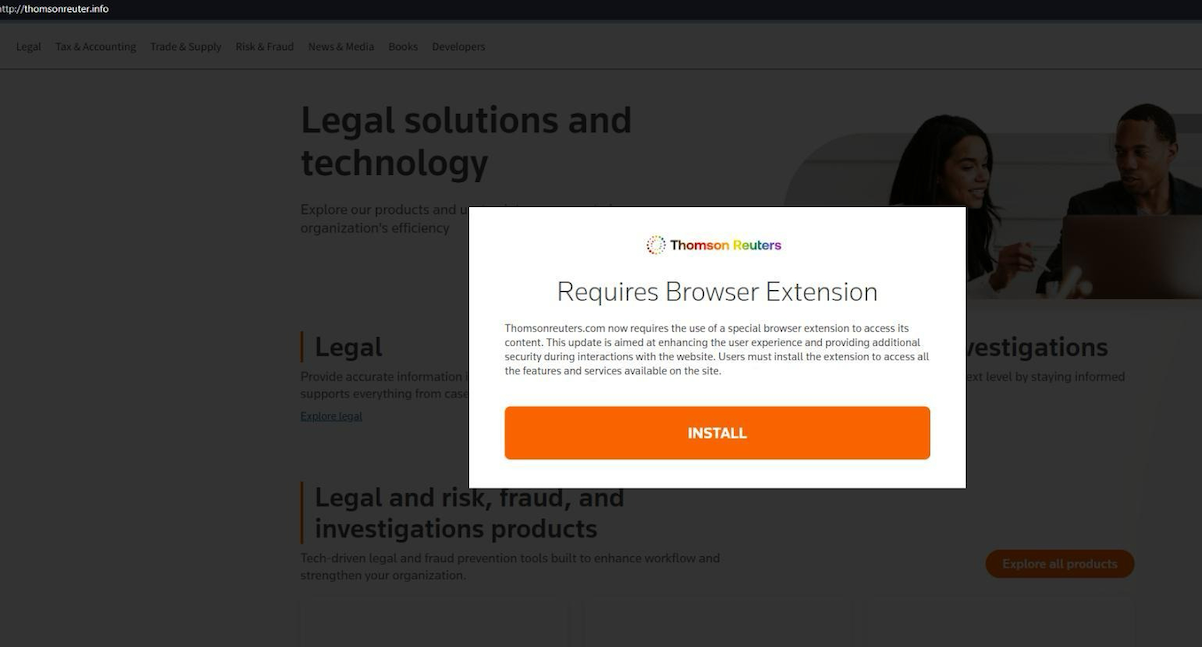
A pop-up at a Thomson Reuters typosquatting domain telling visitors they need to install a browser extension to view the news content.
Edwards said Silent Push discovered the new Fin7 domains after a hearing from an organization that was targeted by Fin7 in years past and suspected the group was once again active. Searching for hosts that matched Fin7’s known profile revealed just one active site. But Edwards said that one site pointed to many other Fin7 properties at Stark Industries Solutions, a large hosting provider that materialized just two weeks before Russia invaded Ukraine.
As KrebsOnSecurity wrote in May, Stark Industries Solutions is being used as a staging ground for wave after wave of cyberattacks against Ukraine that have been tied to Russian military and intelligence agencies.
“FIN7 rents a large amount of dedicated IP on Stark Industries,” Edwards said. “Our analysts have discovered numerous Stark Industries IPs that are solely dedicated to hosting FIN7 infrastructure.”
Fin7 once famously operated behind fake cybersecurity companies — with names like Combi Security and Bastion Secure — which they used for hiring security experts to aid in ransomware attacks. One of the new Fin7 domains identified by Silent Push is cybercloudsec[.]com, which promises to “grow your business with our IT, cyber security and cloud solutions.”

The fake Fin7 security firm Cybercloudsec.
Like other phishing groups, Fin7 seizes on current events, and at the moment it is targeting tourists visiting France for the Summer Olympics later this month. Among the new Fin7 domains Silent Push found are several sites phishing people seeking tickets at the Louvre.
“We believe this research makes it clear that Fin7 is back and scaling up quickly,” Edwards said. “It’s our hope that the law enforcement community takes notice of this and puts Fin7 back on their radar for additional enforcement actions, and that quite a few of our competitors will be able to take this pool and expand into all or a good chunk of their infrastructure.”
Further reading:
Stark Industries Solutions: An Iron Hammer in the Cloud.
A 2022 deep dive on Fin7 from the Swiss threat intelligence firm Prodaft (PDF).