The United States today unveiled sanctions and indictments against the alleged proprietor of Joker’s Stash, a now-defunct cybercrime store that peddled tens of millions of payment cards stolen in some of the largest data breaches of the past decade. The government also indicted and sanctioned a top Russian cybercriminal known as Taleon, whose cryptocurrency exchange Cryptex has evolved into one of Russia’s most active money laundering networks.
A 2016 screen shot of the Joker’s Stash homepage. The links have been redacted.
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) today unsealed an indictment against a 38-year-old man from Novosibirsk, Russia for allegedly operating Joker’s Stash, an extremely successful carding shop that came online in late 2014. Joker’s sold cards stolen in a steady drip of breaches at U.S. retailers, including Saks Fifth Avenue, Lord and Taylor, Bebe Stores, Hilton Hotels, Jason’s Deli, Whole Foods, Chipotle, Wawa, Sonic Drive-In, the Hy-Vee supermarket chain, Buca Di Beppo, and Dickey’s BBQ.
The government believes the brains behind Joker’s Stash is Timur Kamilevich Shakhmametov, an individual who is listed in Russian incorporation documents as the owner of Arpa Plus, a Novosibirsk company that makes mobile games.
Early in his career (circa 2000) Shakhmametov was known as “v1pee” and was the founder of the Russian hacker group nerf[.]ru, which periodically published hacking tools and exploits for software vulnerabilities.

The Russian hacker group Nerf as described in a March 2006 article in the Russian hacker magazine xakep.ru.
By 2004, v1pee had adopted the moniker “Vega” on the exclusive Russian language hacking forum Mazafaka, where this user became one of the more reliable vendors of stolen payment cards.
In the years that followed, Vega would cement his reputation as a top carder on other forums, including Verified, DirectConnection, and Carder[.]pro.
Vega also became known as someone who had the inside track on “unlimited cashouts,” a globally coordinated cybercrime scheme in which crooks hack a bank or payment card processor and use cloned cards at cash machines to rapidly withdraw millions of dollars in just a few hours.
“Hi, there is work on d+p, unlimited,” Vega wrote in a private message to another user on Verified in Dec. 2012, referring to “dumps and PINs,” the slang term for stolen debit cards with the corresponding PINs that would allow ATM withdrawals.
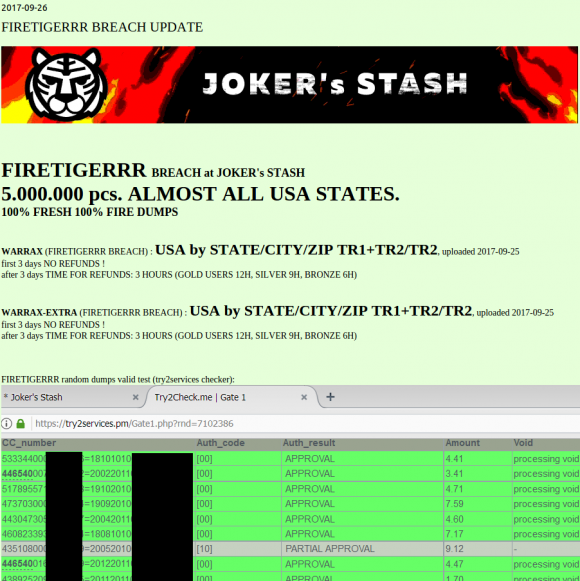
This batch of some five million cards put up for sale Sept. 26, 2017 on the now-defunct carding site Joker’s Stash has been tied to a breach at Sonic Drive-In.
Joker’s Stash came online in the wake of several enormous card breaches at retailers like Target and Home Depot, and the resulting glut of inventory had depressed prices for stolen cards. But Joker’s would distinguish itself by catering to high-roller customers — essentially street gangs in the United States that would purchase thousands of stolen payment cards in one go.
Faced with a buyer’s market, Joker’s Stash set themselves apart by focusing on loyalty programs, frequent buyer discounts, money-back guarantees, and just plain good customer service. Big spenders were given access to the most freshly hacked payment cards, and were offered the ability to get free replacement cards if any turned out to be duds.
Joker’s Stash also was unique because it claimed to sell only payment cards that its own hackers had stolen directly from merchants. At the time, card shops typically resold payment cards that were stolen and supplied by many third-party hackers of unknown reliability or reputation.
In January 2021, Joker’s Stash announced it was closing up shop, after European authorities seized a number of servers for the fraud store, and its proprietor came down with the Coronavirus.
A DOJ statement credits the U.S. Secret Service for leading the years-long investigations (the Service’s original mandate was not protecting the president; it was pursuing counterfeiters, and modern-day carders definitely qualify as that). Prosecutors allege Joker’s Stash earned revenues of at least $280 million, but possibly more than $1 billion (the broad range is a consequence of several variables, including the rapid fluctuation in the price of bitcoin and the stolen goods they were peddling).
The proprietors of Joker’s Stash may have sold tens of millions of stolen payment cards, but Taleon is by far the bigger fish in this law enforcement action because his various cryptocurrency and cash exchanges have allegedly helped to move billions of dollars into and out of Russia over the past 20 years.
An indictment unsealed today names Taleon as Sergey Sergeevich Ivanov, 44, of Saint Petersburg, Russia. The government says Ivanov, who likely changed his surname from Omelnitskii at some point, laundered money for Joker’s Stash, among many other cybercrime stores.
In a statement today, the Treasury Department said Ivanov has laundered hundreds of millions of dollars’ worth of virtual currency for ransomware actors, initial access brokers, darknet marketplace vendors, and other criminal actors for approximately the last 20 years.
First appearing on Mazafaka in the early 2000s, Taleon was known on the forums as someone who could reliably move large amounts of physical cash. Sources familiar with the investigation said Taleon’s service emerged as one of the few remaining domestic cash delivery services still operating after Russia invaded Ukraine in Feb. 2022.
Taleon set up his service to facilitate transfers between Moscow, St. Petersburg and financial institutions in the West. Taleon’s private messages on some hacker forums have been leaked over the years and indexed by the cyber intelligence platform Intel 471. Those messages indicate Taleon worked on many of the same ATM cashouts as Vegas, so it’s clear the two had an established business relationship well before Joker’s Stash came into being.
Sometime around 2013, Taleon launched a partnership with a money transfer business called pm2btc[.]me. PM2BTC allowed customers to convert funds from the virtual currency Perfect Money (PM) into bitcoin, and then have the balance (minus a processing fee) available on a physical debit card that could be used at ATMs, for shopping online, or at retail stores.
A screenshot of a website reviewing PM2BTC.
The U.S. government itself set things in motion for Taleon’s nascent cryptocurrency exchange business in 2013 after the DOJ levied money laundering charges against the proprietors of Liberty Reserve, one of the largest virtual currencies in operation at the time. Liberty Reserve was heavily used by cybercriminals of all stripes. The government said the service had more than a million users worldwide, and laundered in excess of $6 billion in suspected criminal proceeds.
In the days following the takedown of Liberty Reserve, KrebsOnSecurity ran a story that examined discussions across multiple top Russian cybercrime forums about where crooks could feel safe parking their stolen funds. The answer involved Bitcoin, but also Taleon’s new service.
Part of the appeal of Taleon’s exchange was that it gave its vetted customers an “application programming interface” or API that made it simple for dodgy online shops selling stolen goods and cybercrime services to accept cryptocurrency deposits from their customers, and to manage payouts to any suppliers and affiliates.
This API is synonymous with a service Taleon and friends operate in the background called UAPS, short for “Universal Anonymous Payment System.” UAPS has gone by several other names including “Pinpays,” and in October 2014 it landed Joker’s Stash as its first big client.
A source with knowledge of the investigation told KrebsOnSecurity that Taleon is a pilot who owns and flies around in his own helicopter.
Ivanov appears to have little to no social media presence, but the 40-year-old woman he lives with in St. Petersburg does, and she has a photo on her Vktontake page that shows the two of them in 2019 flying over Lake Ladoga, a large body of water directly north of St. Petersburg.
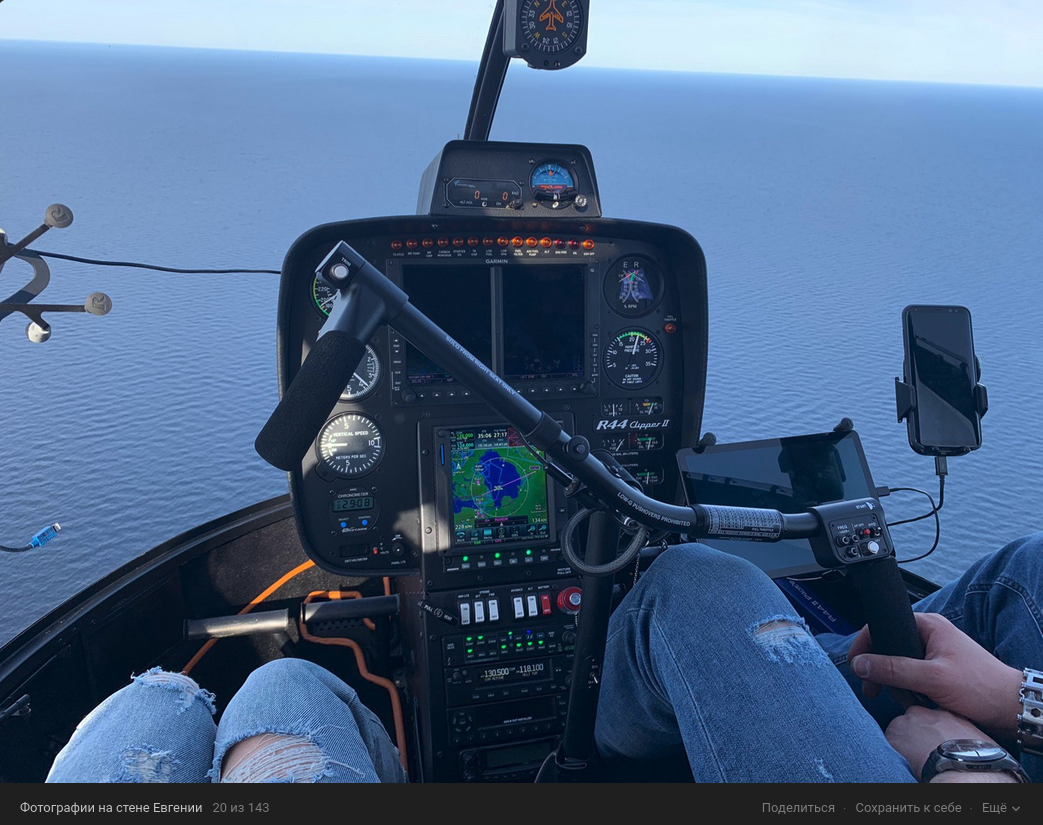

Sergey “Taleon” Ivanov (right) in 2019 in his helicopter with the woman he lives with, flying over a lake north of St. Petersburg, Russia.
In late 2015, a major competitor to Joker’s Stash emerged using UAPS for its back-end payments: BriansClub. BriansClub sullies this author’s name, photos and reputation to peddle millions of credit and debit cards stolen from merchants in the United States and around the world.

An ad for BriansClub has been using my name and likeness for years to peddle millions of stolen credit cards.
In 2019, someone hacked BriansClub and relieved the fraud shop of more than 26 million stolen payment cards — an estimated one-third of the 87 million payment card accounts that were on sale across all underground shops at that time. An anonymous source shared that card data with KrebsOnSecurity, which ultimately shared it with a consortium of financial institutions that issued most of the cards.
After that incident, the administrator of BriansClub changed the site’s login page so that it featured a copy of my phone bill, Social Security card, and a link to my full credit report [to this day, random cybercriminals confuse Yours Truly with the proprietor of BriansClub].
Alex Holden is founder of the Milwaukee-based cybersecurity firm Hold Security. Holden has long maintained visibility into cryptocurrency transactions made by BriansClub.
Holden said those records show BriansClub sells tens of thousands of dollars worth of stolen credit cards every day, and that in the last two years alone the BriansClub administrator has removed more than $242 million worth of cryptocurrency revenue from the UAPS platform.
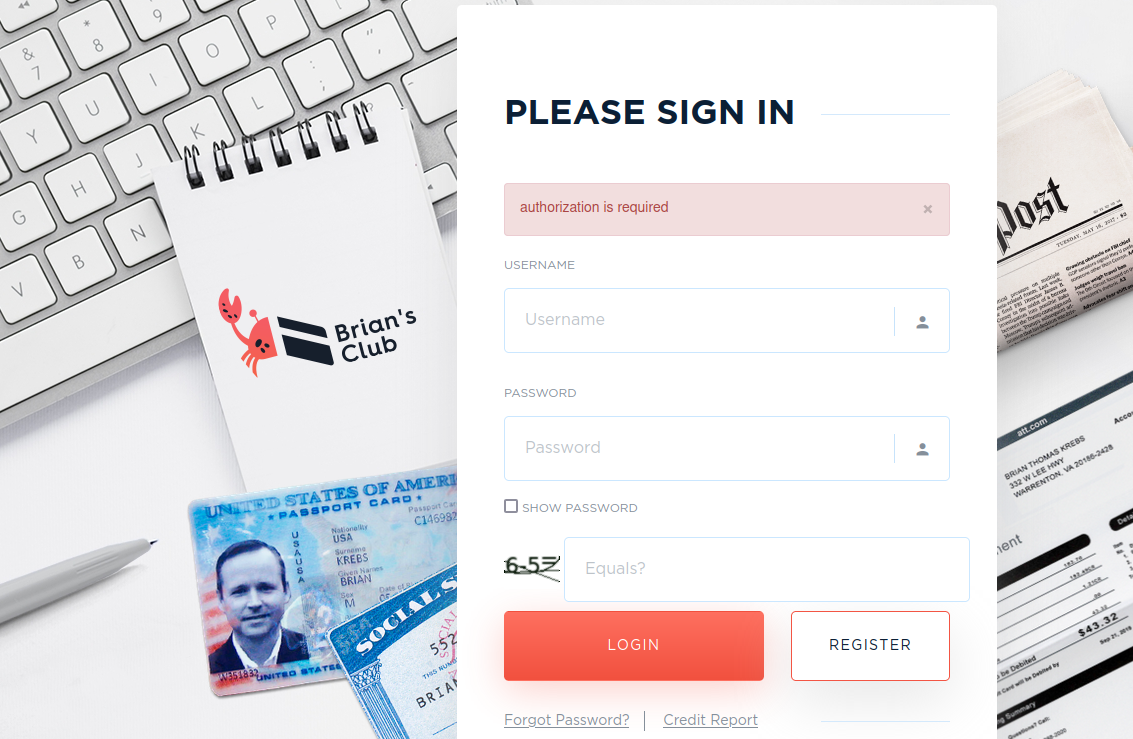
The BriansClub login page, as it looked from late 2019 until recently.
Passive domain name system (DNS) records show that in its early days BriansClub shared a server in Lithuania along with just a handful of other domains, including secure.pinpays[.]com, the crime forum Verified, and a slew of carding shops operating under the banner Rescator.
As KrebsOnSecurity detailed in December 2023, the Rescator shops were directly involved in some of the largest payment card breaches of the past decade. Those include the 2013 breach at Target and the 2014 breach at Home Depot, intrusions that exposed more than 100 million payment card records.
In early 2018, Taleon and the proprietors of UAPS launched a cryptocurrency exchange called Cryptex[.]net that has emerged as a major mover of ill-gotten crypto coins.
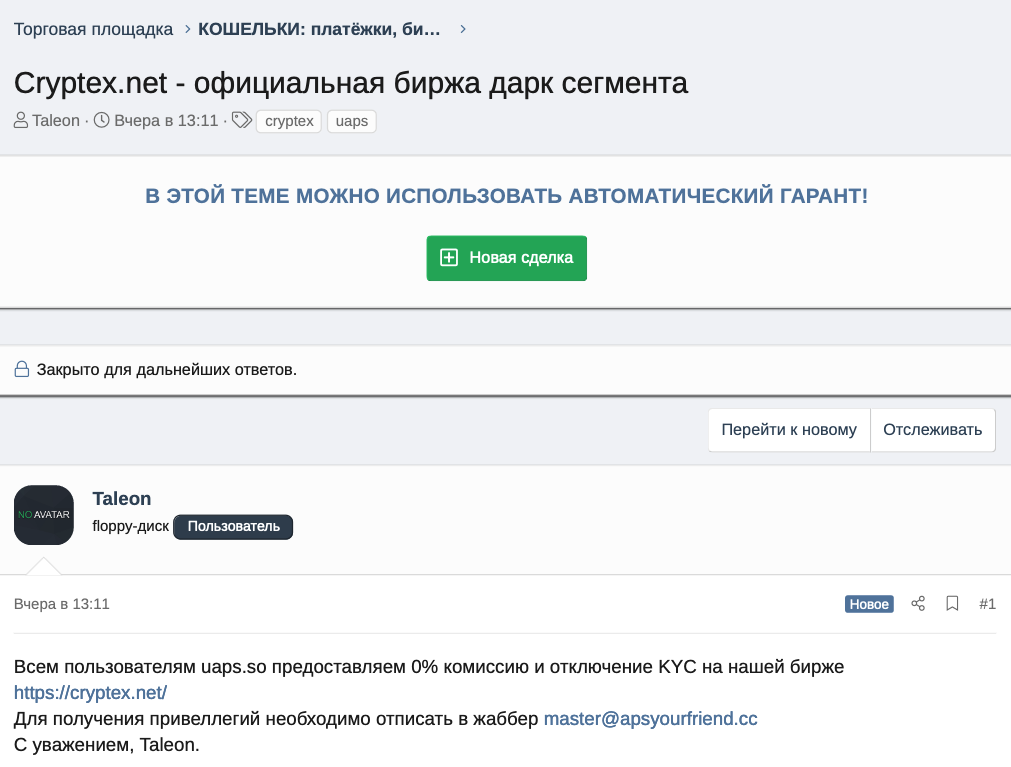
Taleon reminds UAPS customers they will enjoy 0% commission and no “know your customer” (KYC) requirements “on our exchange Cryptex.”
Cryptex has been associated with quite a few ransomware transactions, including the largest known ransomware payment to date. In February 2024, a Fortune 50 ransomware victim paid a record $75 million ransom to a Russian cybercrime group that calls themselves the Dark Angels. A source with knowledge of the investigation said an analysis of that payment shows roughly half of it was processed through Cryptex.
That source provided a screen shot of Cryptex’s sending and receiving exposure as viewed by Chainalysis, a company the U.S. government and many cryptocurrency exchanges rely on to flag transactions associated with suspected money laundering, ransomware payouts, or facilitating payments for darknet websites.
Chainalysis finds that Cryptex has received more than $1.6 billion since its inception, and that this amount is roughly equal to its sending exposure (although the total number of outflows is nearly half of the inflows).
The graphic indicates a great deal of money flowing into Cryptex — roughly a quarter of it — is coming from bitcoin ATMs around the world. Experts say most of those ATM inflows to Cryptex are bitcoin ATM cash deposits from customers of carding websites like BriansClub and Jokers Stash.
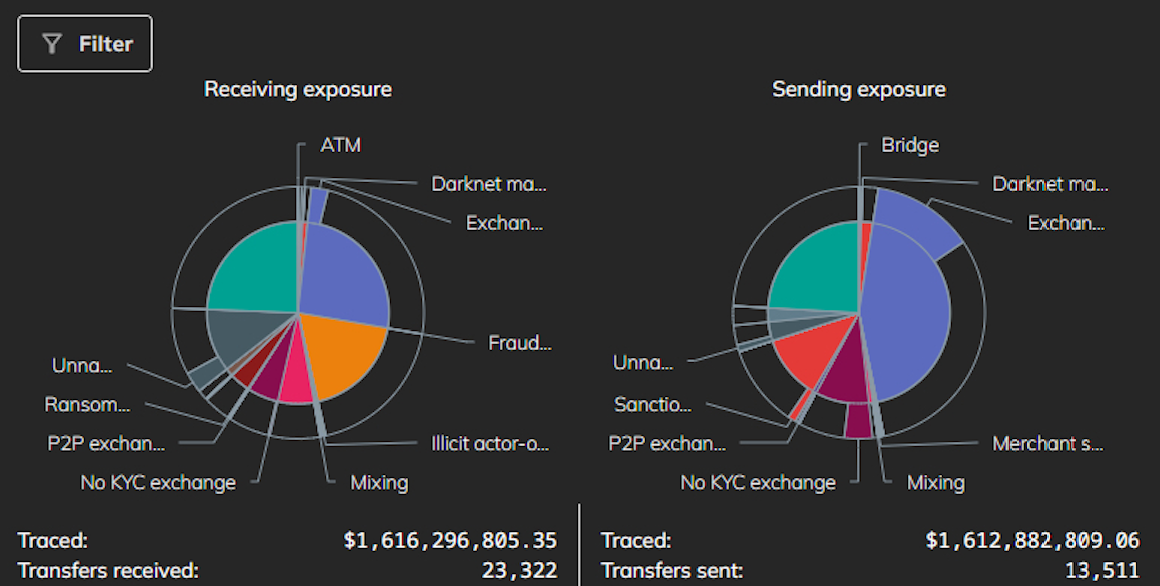
A screenshot of Chainalysis’s summary of illicit activity on Cryptex since the exchange’s inception in 2018.
The indictments released today do not definitively connect Taleon to Cryptex. However, PM2BTC (which teamed up with Taleon to launch UAPS and Pinpays) and Cryptex have now been sanctioned by the U.S. Department of the Treasury.
Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) levied sanctions today against PM2BTC under a powerful new “Section 9714” authority included in the Combating Russian Money Laundering Act, changes enacted in 2022 to make it easier to target financial entities involved in laundering money for Russia.
Treasury first used this authority last year against Bitzlato, a cryptocurrency exchange operating in Russia that became a money laundering conduit for ransomware attackers and dark market dealers.
An investigation into the corporate entities behind UAPS and Cryptex reveals an organization incorporated in 2012 in Scotland called Orbest Investments LP. Records from the United Kingdom’s business registry show the owners of Orbest Investments are two entities: CS Proxy Solutions CY, and RM Everton Ltd.
Public business records further reveal that CS Proxy Solutions and RM Everton are co-owners of Progate Solutions, a holding company that featured prominently in a June 2017 report from Bellingcat and Transparency International (PDF) on money laundering networks tied to the Kremlin.
“Law enforcement agencies believe that the total amount laundered through this process could be as high as US$80 billion,” the joint report reads. “Although it is not clear where all of this money came from, investigators claim it includes significant amounts of money that were diverted from the Russian treasury and state contracts.”
Their story built on reporting published earlier that year by the Organized Crime and Corruption Project (OCCRP) and Novaya Gazeta, which found that at least US$20.8 billion was secretly moved out of Russia between 2010 and 2014 through a vast money laundering machine comprising over 5,000 legal entities known as “The Laundromat.”

Image: occrp.org
“Using company records, reporters tracked the names of some clients after executives refused to give them out,” the OCCRP report explains. “They found the heavy users of the scheme were rich and powerful Russians who had made their fortunes from dealing with the Russian state.”
Rich Sanders is a blockchain analyst and investigator who advises the law enforcement and intelligence community. Sanders just returned from a three-week sojourn through Ukraine, traveling with Ukrainian soldiers while mapping out dodgy Russian crypto exchanges that are laundering money for narcotics networks operating in the region. Sanders said today’s sanctions by the Treasury Department will likely have an immediate impact on Cryptex and its customers.
“Whenever an entity is sanctioned, the implications on-chain are immense,” Sanders told KrebsOnSecurity. “Regardless of whether an exchange is actually compliant or just virtue signals it, it is the case across the board that exchanges will pay attention to these sanctions.”
“This action shows these payment processors for illicit platforms will get attention eventually,” Sanders continued. “Even if it took way too long in this case, Cryptex knew the majority of their volume was problematic, knew why it was problematic, and did it anyway. And this should be a wake up call for other exchanges that know full well that most of their volume is problematic.”
The U.S. Department of State is offering a reward of up to $10 million each for information leading to the arrests and/or convictions of Shakhmametov and Ivanov. The State announcement says separate rewards of up to $1 million each are being offered for information leading to the identification of other leaders of the Joker’s Stash criminal marketplace (other than Shakhmametov), as well as the identification of other key leaders of the UAPS, PM2BTC, and PinPays transnational criminal groups (other than Ivanov).

Image: U.S. Secret Service.