One of the most notorious providers of abuse-friendly “bulletproof” web hosting for cybercriminals has started routing its operations through networks run by the Russian antivirus and security firm Kaspersky Lab, KrebsOnSecurity has learned.
Security experts say the Russia-based service provider Prospero OOO (the triple O is the Russian version of “LLC”) has long been a persistent source of malicious software, botnet controllers, and a torrent of phishing websites. Last year, the French security firm Intrinsec detailed Prospero’s connections to bulletproof services advertised on Russian cybercrime forums under the names Securehost and BEARHOST.
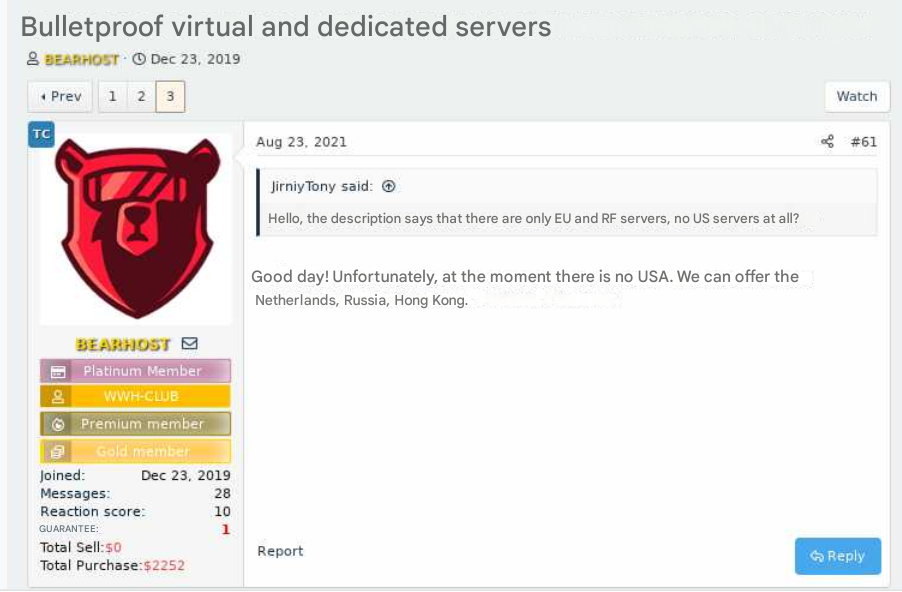
The bulletproof hosting provider BEARHOST. This screenshot has been machine-translated from Russian. Image: Ke-la.com.
Bulletproof hosts are so named when they earn or cultivate a reputation for ignoring legal demands and abuse complaints. And BEARHOST has been cultivating its reputation since at least 2019.
“If you need a server for a botnet, for malware, brute, scan, phishing, fakes and any other tasks, please contact us,” BEARHOST’s ad on one forum advises. “We completely ignore all abuses without exception, including SPAMHAUS and other organizations.”
Intrinsec found Prospero has courted some of Russia’s nastiest cybercrime groups, hosting control servers for multiple ransomware gangs over the past two years. Intrinsec said its analysis showed Prospero frequently hosts malware operations such as SocGholish and GootLoader, which are spread primarily via fake browser updates on hacked websites and often lay the groundwork for more serious cyber intrusions — including ransomware.
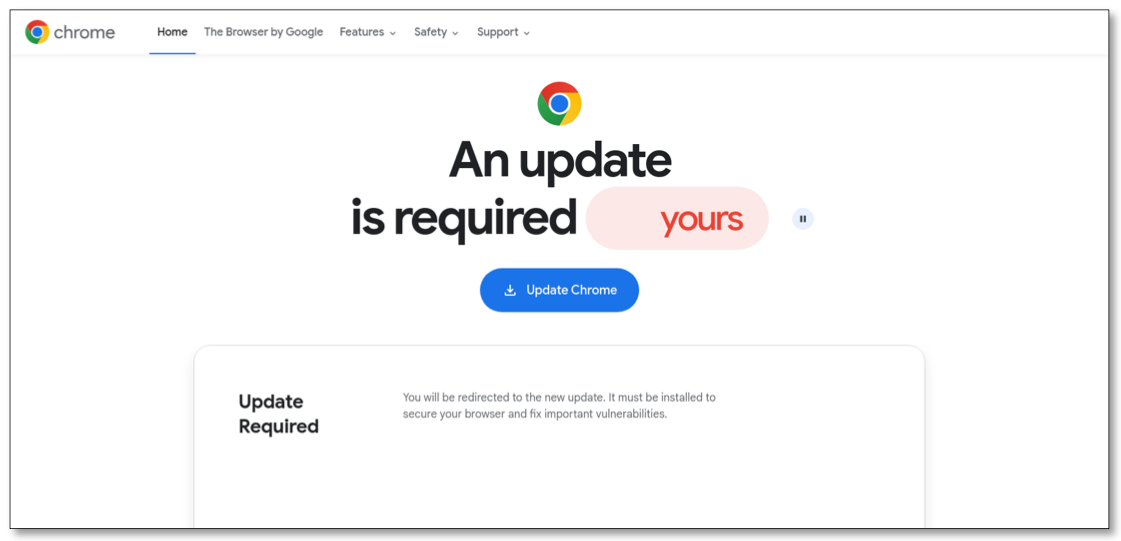
A fake browser update page pushing mobile malware. Image: Intrinsec.
BEARHOST prides itself on the ability to evade blocking by Spamhaus, an organization that many Internet service providers around the world rely on to help identify and block sources of malware and spam. Earlier this week, Spamhaus said it noticed that Prospero was suddenly connecting to the Internet by routing through networks operated by Kaspersky Lab in Moscow.
Update, March 1, 9:43 a.m. ET: In a written statement, Kaspersky said it is aware of the public claim about the company allegedly providing services to a “bulletproof” web hosting provider. Here is their full statement:
“Kaspersky denies these claims as the company does not work and has never worked with the service provider in question. The routing through networks operated by Kaspersky doesn’t by default mean provision of the company’s services, as Kaspersky’s automatic system (AS) path might appear as a technical prefix in the network of telecom providers the company works with and provides its DDoS services.”
“Kaspersky pays great attention to conducting business ethically and ensuring that its solutions are used for their original purpose of providing cybersecurity protection. The company is currently investigating the situation to inform the company whose network could have served as a transit for a “bulletproof” web hosting provider so that the former takes the necessary measures.”
Kaspersky began selling antivirus and security software in the United States in 2005, and the company’s malware researchers have earned accolades from the security community for many important discoveries over the years. But in September 2017, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) barred U.S. federal agencies from using Kaspersky software, mandating its removal within 90 days.
Cybersecurity reporter Kim Zetter notes that DHS didn’t cite any specific justification for its ban in 2017, but media reports quoting anonymous government officials referenced two incidents. Zetter wrote:
According to one story, an NSA contractor developing offensive hacking tools for the spy agency had Kaspersky software installed on his home computer where he was developing the tools, and the software detected the source code as malicious code and extracted it from his computer, as antivirus software is designed to do. A second story claimed that Israeli spies caught Russian government hackers using Kaspersky software to search customer systems for files containing U.S. secrets.
Kaspersky denied that anyone used its software to search for secret information on customer machines and said that the tools on the NSA worker’s machine were detected in the same way that all antivirus software detects files it deems suspicious and then quarantines or extracts them for analysis. Once Kaspersky discovered that the code its antivirus software detected on the NSA worker’s machine were not malicious programs but source code in development by the U.S. government for its hacking operations, CEO Eugene Kaspersky says he ordered workers to delete the code.
Last year, the U.S. Commerce Department banned the sale of Kaspersky software in the U.S. effective July 20, 2024. U.S. officials argued the ban was needed because Russian law requires domestic companies to cooperate in all official investigations, and thus the Russian government could force Kaspersky to secretly gather intelligence on its behalf.
Phishing data gathered last year by the Interisle Consulting Group ranked hosting networks by their size and concentration of spambot hosts, and found Prospero had a higher spam score than any other provider by far.
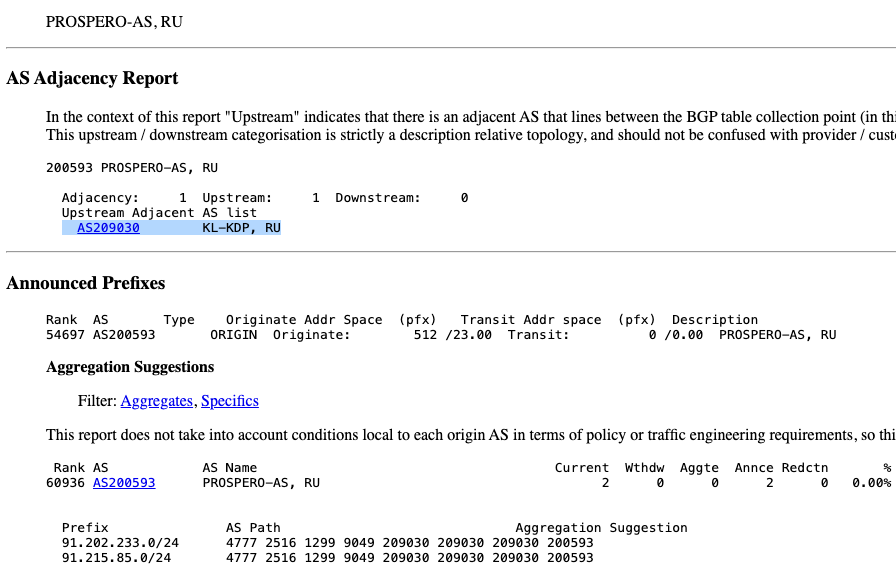
AS209030, owned by Kaspersky Lab, is providing connectivity to the bulletproof host Prospero (AS200593). Image: cidr-report.org.
It remains unclear why Kaspersky is providing transit to Prospero. Doug Madory, director of Internet analysis at Kentik, said routing records show the relationship between Prospero and Kaspersky started at the beginning of December 2024.
Madory said Kaspersky’s network appears to be hosting several financial institutions, including Russia’s largest — Alfa-Bank. Kaspersky sells services to help protect customers from distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and Madory said it could be that Prospero is simply purchasing that protection from Kaspersky.
But if that is the case, it doesn’t make the situation any better, said Zach Edwards, a senior threat researcher at the security firm Silent Push.
“In some ways, providing DDoS protection to a well-known bulletproof hosting provider may be even worse than just allowing them to connect to the rest of the Internet over your infrastructure,” Edwards said.
Malicious hackers are targeting people in the cryptocurrency space in attacks that start with a link added to the target’s calendar at Calendly, a popular application for scheduling appointments and meetings. The attackers impersonate established cryptocurrency investors and ask to schedule a video conference call. But clicking the meeting link provided by the scammers prompts the user to run a script that quietly installs malware on macOS systems.
KrebsOnSecurity recently heard from a reader who works at a startup that is seeking investment for building a new blockchain platform for the Web. The reader spoke on condition that their name not be used in this story, so for the sake of simplicity we’ll call him Doug.
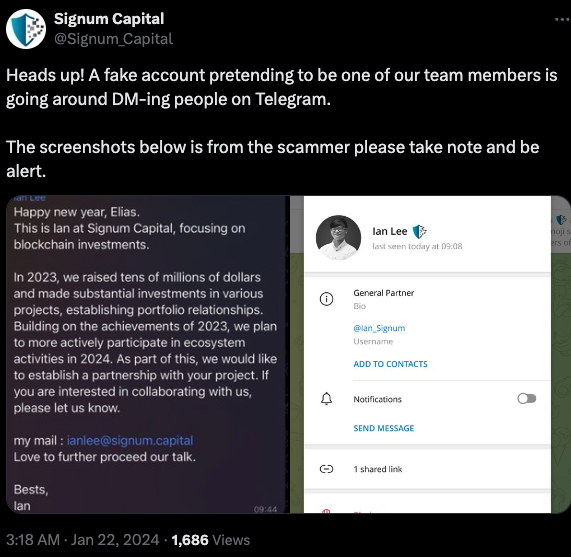
Being in the cryptocurrency scene, Doug is also active on the instant messenger platform Telegram. Earlier this month, Doug was approached by someone on Telegram whose profile name, image and description said they were Ian Lee, from Signum Capital, a well-established investment firm based in Singapore. The profile also linked to Mr. Lee’s Twitter/X account, which features the same profile image.
The investor expressed interest in financially supporting Doug’s startup, and asked if Doug could find time for a video call to discuss investment prospects. Sure, Doug said, here’s my Calendly profile, book a time and we’ll do it then.
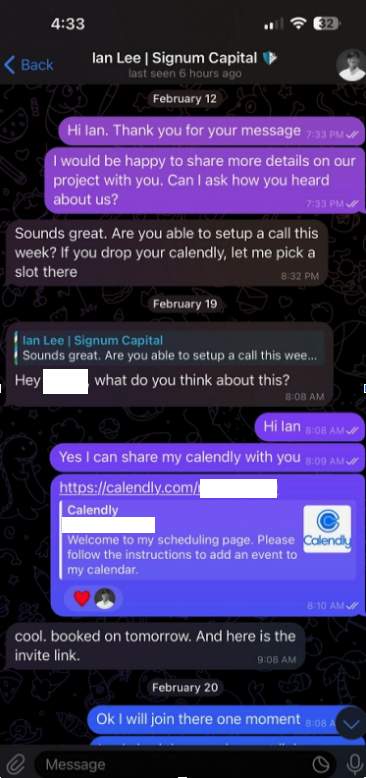
When the day and time of the scheduled meeting with Mr. Lee arrived, Doug clicked the meeting link in his calendar but nothing happened. Doug then messaged the Mr. Lee account on Telegram, who said there was some kind of technology issue with the video platform, and that their IT people suggested using a different meeting link.
Doug clicked the new link, but instead of opening up a videoconference app, a message appeared on his Mac saying the video service was experiencing technical difficulties.
“Some of our users are facing issues with our service,” the message read. “We are actively working on fixing these problems. Please refer to this script as a temporary solution.”
Doug said he ran the script, but nothing appeared to happen after that, and the videoconference application still wouldn’t start. Mr. Lee apologized for the inconvenience and said they would have to reschedule their meeting, but he never responded to any of Doug’s follow-up messages.
It didn’t dawn on Doug until days later that the missed meeting with Mr. Lee might have been a malware attack. Going back to his Telegram client to revisit the conversation, Doug discovered his potential investor had deleted the meeting link and other bits of conversation from their shared chat history.
In a post to its Twitter/X account last month, Signum Capital warned that a fake profile pretending to be their employee Mr. Lee was trying to scam people on Telegram.
The file that Doug ran is a simple Apple Script (file extension “.scpt”) that downloads and executes a malicious trojan made to run on macOS systems. Unfortunately for us, Doug freaked out after deciding he’d been tricked — backing up his important documents, changing his passwords, and then reinstalling macOS on his computer. While this a perfectly sane response, it means we don’t have the actual malware that was pushed to his Mac by the script.
But Doug does still have a copy of the malicious script that was downloaded from clicking the meeting link (the online host serving that link is now offline). A search in Google for a string of text from that script turns up a December 2023 blog post from cryptocurrency security firm SlowMist about phishing attacks on Telegram from North Korean state-sponsored hackers.
“When the project team clicks the link, they encounter a region access restriction,” SlowMist wrote. “At this point, the North Korean hackers coax the team into downloading and running a ‘location-modifying’ malicious script. Once the project team complies, their computer comes under the control of the hackers, leading to the theft of funds.”
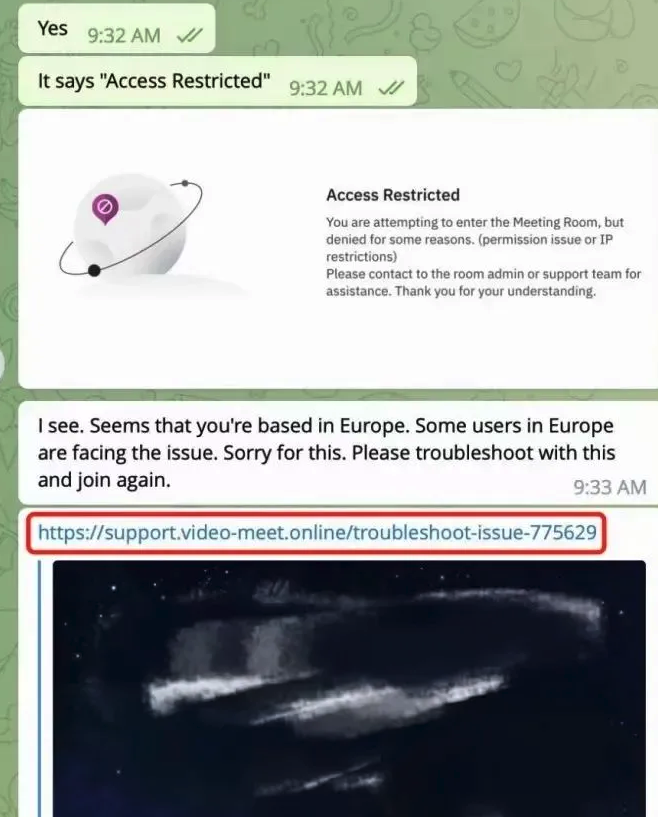
Image: SlowMist.
SlowMist says the North Korean phishing scams used the “Add Custom Link” feature of the Calendly meeting scheduling system on event pages to insert malicious links and initiate phishing attacks.
“Since Calendly integrates well with the daily work routines of most project teams, these malicious links do not easily raise suspicion,” the blog post explains. “Consequently, the project teams may inadvertently click on these malicious links, download, and execute malicious code.”
SlowMist said the malware downloaded by the malicious link in their case comes from a North Korean hacking group dubbed “BlueNoroff, which Kaspersky Labs says is a subgroup of the Lazarus hacking group.
“A financially motivated threat actor closely connected with Lazarus that targets banks, casinos, fin-tech companies, POST software and cryptocurrency businesses, and ATMs,” Kaspersky wrote of BlueNoroff in Dec. 2023.
The North Korean regime is known to use stolen cryptocurrencies to fund its military and other state projects. A recent report from Recorded Future finds the Lazarus Group has stolen approximately $3 billion in cryptocurrency over the past six years.
While there is still far more malware out there today targeting Microsoft Windows PCs, the prevalence of information-stealing trojans aimed at macOS users is growing at a steady clip. MacOS computers include X-Protect, Apple’s built-in antivirus technology. But experts say attackers are constantly changing the appearance and behavior of their malware to evade X-Protect.
“Recent updates to macOS’s XProtect signature database indicate that Apple are aware of the problem, but early 2024 has already seen a number of stealer families evade known signatures,” security firm SentinelOne wrote in January.
According to Chris Ueland from the threat hunting platform Hunt.io, the Internet address of the fake meeting website Doug was tricked into visiting (104.168.163,149) hosts or very recently hosted about 75 different domain names, many of which invoke words associated with videoconferencing or cryptocurrency. Those domains indicate this North Korean hacking group is hiding behind a number of phony crypto firms, like the six-month-old website for Cryptowave Capital (cryptowave[.]capital).

In a statement shared with KrebsOnSecurity, Calendly said it was aware of these types of social engineering attacks by cryptocurrency hackers.
“To help prevent these kinds of attacks, our security team and partners have implemented a service to automatically detect fraud and impersonations that could lead to social engineering,” the company said. “We are also actively scanning content for all our customers to catch these types of malicious links and to prevent hackers earlier on. Additionally, we intend to add an interstitial page warning users before they’re redirected away from Calendly to other websites. Along with the steps we’ve taken, we recommend users stay vigilant by keeping their software secure with running the latest updates and verifying suspicious links through tools like VirusTotal to alert them of possible malware. We are continuously strengthening the cybersecurity of our platform to protect our customers.”
The increasing frequency of new Mac malware is a good reminder that Mac users should not depend on security software and tools to flag malicious files, which are frequently bundled with or disguised as legitimate software.
As KrebsOnSecurity has advised Windows users for years, a good rule of safety to live by is this: If you didn’t go looking for it, don’t install it. Following this mantra heads off a great deal of malware attacks, regardless of the platform used. When you do decide to install a piece of software, make sure you are downloading it from the original source, and then keep it updated with any new security fixes.
On that last front, I’ve found it’s a good idea not to wait until the last minute to configure my system before joining a scheduled videoconference call. Even if the call uses software that is already on my computer, it is often the case that software updates are required before the program can be used, and I’m one of those weird people who likes to review any changes to the software maker’s privacy policies or user agreements before choosing to install updates.
Most of all, verify new contacts from strangers before accepting anything from them. In this case, had Doug simply messaged Mr. Lee’s real account on Twitter/X or contacted Signum Capital directly, he would discovered that the real Mr. Lee never asked for a meeting.
If you’re approached in a similar scheme, the response from the would-be victim documented in the SlowMist blog post is probably the best.
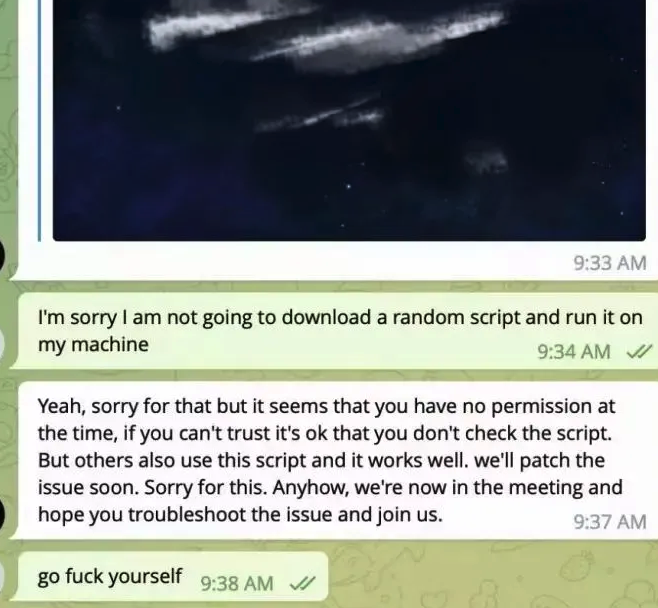
Image: SlowMist.
Update: Added comment from Calendly.