On the surface, the Superbox media streaming devices for sale at retailers like BestBuy and Walmart may seem like a steal: They offer unlimited access to more than 2,200 pay-per-view and streaming services like Netflix, ESPN and Hulu, all for a one-time fee of around $400. But security experts warn these TV boxes require intrusive software that forces the user’s network to relay Internet traffic for others, traffic that is often tied to cybercrime activity such as advertising fraud and account takeovers.
Superbox media streaming boxes for sale on Walmart.com.
Superbox bills itself as an affordable way for households to stream all of the television and movie content they could possibly want, without the hassle of monthly subscription fees — for a one-time payment of nearly $400.
“Tired of confusing cable bills and hidden fees?,” Superbox’s website asks in a recent blog post titled, “Cheap Cable TV for Low Income: Watch TV, No Monthly Bills.”
“Real cheap cable TV for low income solutions does exist,” the blog continues. “This guide breaks down the best alternatives to stop overpaying, from free over-the-air options to one-time purchase devices that eliminate monthly bills.”
Superbox claims that watching a stream of movies, TV shows, and sporting events won’t violate U.S. copyright law.
“SuperBox is just like any other Android TV box on the market, we can not control what software customers will use,” the company’s website maintains. “And you won’t encounter a law issue unless uploading, downloading, or broadcasting content to a large group.”

A blog post from the Superbox website.
There is nothing illegal about the sale or use of the Superbox itself, which can be used strictly as a way to stream content at providers where users already have a paid subscription. But that is not why people are shelling out $400 for these machines. The only way to watch those 2,200+ channels for free with a Superbox is to install several apps made for the device that enable them to stream this content.
Superbox’s homepage includes a prominent message stating the company does “not sell access to or preinstall any apps that bypass paywalls or provide access to unauthorized content.” The company explains that they merely provide the hardware, while customers choose which apps to install.
“We only sell the hardware device,” the notice states. “Customers must use official apps and licensed services; unauthorized use may violate copyright law.”
Superbox is technically correct here, except for maybe the part about how customers must use official apps and licensed services: Before the Superbox can stream those thousands of channels, users must configure the device to update itself, and the first step involves ripping out Google’s official Play store and replacing it with something called the “App Store” or “Blue TV Store.”
Superbox does this because the device does not use the official Google-certified Android TV system, and its apps will not load otherwise. Only after the Google Play store has been supplanted by this unofficial App Store do the various movie and video streaming apps that are built specifically for the Superbox appear available for download (again, outside of Google’s app ecosystem).
Experts say while these Android streaming boxes generally do what they advertise — enabling buyers to stream video content that would normally require a paid subscription — the apps that enable the streaming also ensnare the user’s Internet connection in a distributed residential proxy network that uses the devices to relay traffic from others.
Ashley is a senior solutions engineer at Censys, a cyber intelligence company that indexes Internet-connected devices, services and hosts. Ashley requested that only her first name be used in this story.
In a recent video interview, Ashley showed off several Superbox models that Censys was studying in the malware lab — including one purchased off the shelf at BestBuy.
“I’m sure a lot of people are thinking, ‘Hey, how bad could it be if it’s for sale at the big box stores?'” she said. “But the more I looked, things got weirder and weirder.”
Ashley said she found the Superbox devices immediately contacted a server at the Chinese instant messaging service Tencent QQ, as well as a residential proxy service called Grass IO.
Also known as getgrass[.]io, Grass says it is “a decentralized network that allows users to earn rewards by sharing their unused Internet bandwidth with AI labs and other companies.”
“Buyers seek unused internet bandwidth to access a more diverse range of IP addresses, which enables them to see certain websites from a retail perspective,” the Grass website explains. “By utilizing your unused internet bandwidth, they can conduct market research, or perform tasks like web scraping to train AI.” 
Reached via Twitter/X, Grass founder Andrej Radonjic told KrebsOnSecurity he’d never heard of a Superbox, and that Grass has no affiliation with the device maker.
“It looks like these boxes are distributing an unethical proxy network which people are using to try to take advantage of Grass,” Radonjic said. “The point of grass is to be an opt-in network. You download the grass app to monetize your unused bandwidth. There are tons of sketchy SDKs out there that hijack people’s bandwidth to help webscraping companies.”
Radonjic said Grass has implemented “a robust system to identify network abusers,” and that if it discovers anyone trying to misuse or circumvent its terms of service, the company takes steps to stop it and prevent those users from earning points or rewards.
Superbox’s parent company, Super Media Technology Company Ltd., lists its street address as a UPS store in Fountain Valley, Calif. The company did not respond to multiple inquiries.
According to this teardown by behindmlm.com, a blog that covers multi-level marketing (MLM) schemes, Grass’s compensation plan is built around “grass points,” which are earned through the use of the Grass app and through app usage by recruited affiliates. Affiliates can earn 5,000 grass points for clocking 100 hours usage of Grass’s app, but they must progress through ten affiliate tiers or ranks before they can redeem their grass points (presumably for some type of cryptocurrency). The 10th or “Titan” tier requires affiliates to accumulate a whopping 50 million grass points, or recruit at least 221 more affiliates.
Radonjic said Grass’s system has changed in recent months, and confirmed the company has a referral program where users can earn Grass Uptime Points by contributing their own bandwidth and/or by inviting other users to participate.
“Users are not required to participate in the referral program to earn Grass Uptime Points or to receive Grass Tokens,” Radonjic said. “Grass is in the process of phasing out the referral program and has introduced an updated Grass Points model.”
A review of the Terms and Conditions page for getgrass[.]io at the Wayback Machine shows Grass’s parent company has changed names at least five times in the course of its two-year existence. Searching the Wayback Machine on getgrass[.]io shows that in June 2023 Grass was owned by a company called Wynd Network. By March 2024, the owner was listed as Lower Tribeca Corp. in the Bahamas. By August 2024, Grass was controlled by a Half Space Labs Limited, and in November 2024 the company was owned by Grass OpCo (BVI) Ltd. Currently, the Grass website says its parent is just Grass OpCo Ltd (no BVI in the name).
Radonjic acknowledged that Grass has undergone “a handful of corporate clean-ups over the last couple of years,” but described them as administrative changes that had no operational impact. “These reflect normal early-stage restructuring as the project moved from initial development…into the current structure under the Grass Foundation,” he said.
Censys’s Ashley said the phone home to China’s Tencent QQ instant messaging service was the first red flag with the Superbox devices she examined. She also discovered the streaming boxes included powerful network analysis and remote access tools, such as Tcpdump and Netcat.
“This thing DNS hijacked my router, did ARP poisoning to the point where things fall off the network so they can assume that IP, and attempted to bypass controls,” she said. “I have root on all of them now, and they actually have a folder called ‘secondstage.’ These devices also have Netcat and Tcpdump on them, and yet they are supposed to be streaming devices.”
A quick online search shows various Superbox models and many similar Android streaming devices for sale at a wide range of top retail destinations, including Amazon, BestBuy, Newegg, and Walmart. Newegg.com, for example, currently lists more than three dozen Superbox models. In all cases, the products are sold by third-party merchants on these platforms, but in many instances the fulfillment comes from the e-commerce platform itself.
“Newegg is pretty bad now with these devices,” Ashley said. “Ebay is the funniest, because they have Superbox in Spanish — the SuperCaja — which is very popular.”
Ashley said Amazon recently cracked down on Android streaming devices branded as Superbox, but that those listings can still be found under the more generic title “modem and router combo” (which may be slightly closer to the truth about the device’s behavior).
Superbox doesn’t advertise its products in the conventional sense. Rather, it seems to rely on lesser-known influencers on places like Youtube and TikTok to promote the devices. Meanwhile, Ashley said, Superbox pays those influencers 50 percent of the value of each device they sell.
“It’s weird to me because influencer marketing usually caps compensation at 15 percent, and it means they don’t care about the money,” she said. “This is about building their network.”
A TikTok influencer casually mentions and promotes Superbox while chatting with her followers over a glass of wine.
As plentiful as the Superbox is on e-commerce sites, it is just one brand in an ocean of no-name Android-based TV boxes available to consumers. While these devices generally do provide buyers with “free” streaming content, they also tend to include factory-installed malware or require the installation of third-party apps that engage the user’s Internet address in advertising fraud.
In July 2025, Google filed a “John Doe” lawsuit (PDF) against 25 unidentified defendants dubbed the “BadBox 2.0 Enterprise,” which Google described as a botnet of over ten million Android streaming devices that engaged in advertising fraud. Google said the BADBOX 2.0 botnet, in addition to compromising multiple types of devices prior to purchase, can also infect devices by requiring the download of malicious apps from unofficial marketplaces.

Some of the unofficial Android devices flagged by Google as part of the Badbox 2.0 botnet are still widely for sale at major e-commerce vendors. Image: Google.
Several of the Android streaming devices flagged in Google’s lawsuit are still for sale on top U.S. retail sites. For example, searching for the “X88Pro 10” and the “T95” Android streaming boxes finds both continue to be peddled by Amazon sellers.
Google’s lawsuit came on the heels of a June 2025 advisory from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which warned that cyber criminals were gaining unauthorized access to home networks by either configuring the products with malicious software prior to the user’s purchase, or infecting the device as it downloads required applications that contain backdoors, usually during the set-up process.
“Once these compromised IoT devices are connected to home networks, the infected devices are susceptible to becoming part of the BADBOX 2.0 botnet and residential proxy services known to be used for malicious activity,” the FBI said.
The FBI said BADBOX 2.0 was discovered after the original BADBOX campaign was disrupted in 2024. The original BADBOX was identified in 2023, and primarily consisted of Android operating system devices that were compromised with backdoor malware prior to purchase.
Riley Kilmer is founder of Spur, a company that tracks residential proxy networks. Kilmer said Badbox 2.0 was used as a distribution platform for IPidea, a China-based entity that is now the world’s largest residential proxy network.
Kilmer and others say IPidea is merely a rebrand of 911S5 Proxy, a China-based proxy provider sanctioned last year by the U.S. Department of the Treasury for operating a botnet that helped criminals steal billions of dollars from financial institutions, credit card issuers, and federal lending programs (the U.S. Department of Justice also arrested the alleged owner of 911S5).
How are most IPidea customers using the proxy service? According to the proxy detection service Synthient, six of the top ten destinations for IPidea proxies involved traffic that has been linked to either ad fraud or credential stuffing (account takeover attempts).
Kilmer said companies like Grass are probably being truthful when they say that some of their customers are companies performing web scraping to train artificial intelligence efforts, because a great deal of content scraping which ultimately benefits AI companies is now leveraging these proxy networks to further obfuscate their aggressive data-slurping activity. By routing this unwelcome traffic through residential IP addresses, Kilmer said, content scraping firms can make it far trickier to filter out.
“Web crawling and scraping has always been a thing, but AI made it like a commodity, data that had to be collected,” Kilmer told KrebsOnSecurity. “Everybody wanted to monetize their own data pots, and how they monetize that is different across the board.”
Products like Superbox are drawing increased interest from consumers as more popular network television shows and sportscasts migrate to subscription streaming services, and as people begin to realize they’re spending as much or more on streaming services than they previously paid for cable or satellite TV.
These streaming devices from no-name technology vendors are another example of the maxim, “If something is free, you are the product,” meaning the company is making money by selling access to and/or information about its users and their data.
Superbox owners might counter, “Free? I paid $400 for that device!” But remember: Just because you paid a lot for something doesn’t mean you are done paying for it, or that somehow you are the only one who might be worse off from the transaction.
It may be that many Superbox customers don’t care if someone uses their Internet connection to tunnel traffic for ad fraud and account takeovers; for them, it beats paying for multiple streaming services each month. My guess, however, is that quite a few people who buy (or are gifted) these products have little understanding of the bargain they’re making when they plug them into an Internet router.
Superbox performs some serious linguistic gymnastics to claim its products don’t violate copyright laws, and that its customers alone are responsible for understanding and observing any local laws on the matter. However, buyer beware: If you’re a resident of the United States, you should know that using these devices for unauthorized streaming violates the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), and can incur legal action, fines, and potential warnings and/or suspension of service by your Internet service provider.
According to the FBI, there are several signs to look for that may indicate a streaming device you own is malicious, including:
-The presence of suspicious marketplaces where apps are downloaded.
-Requiring Google Play Protect settings to be disabled.
-Generic TV streaming devices advertised as unlocked or capable of accessing free content.
-IoT devices advertised from unrecognizable brands.
-Android devices that are not Play Protect certified.
-Unexplained or suspicious Internet traffic.
This explainer from the Electronic Frontier Foundation delves a bit deeper into each of the potential symptoms listed above.
A Ukrainian man indicted in 2012 for conspiring with a prolific hacking group to steal tens of millions of dollars from U.S. businesses was arrested in Italy and is now in custody in the United States, KrebsOnSecurity has learned.
Sources close to the investigation say Yuriy Igorevich Rybtsov, a 41-year-old from the Russia-controlled city of Donetsk, Ukraine, was previously referenced in U.S. federal charging documents only by his online handle “MrICQ.” According to a 13-year-old indictment (PDF) filed by prosecutors in Nebraska, MrICQ was a developer for a cybercrime group known as “Jabber Zeus.”
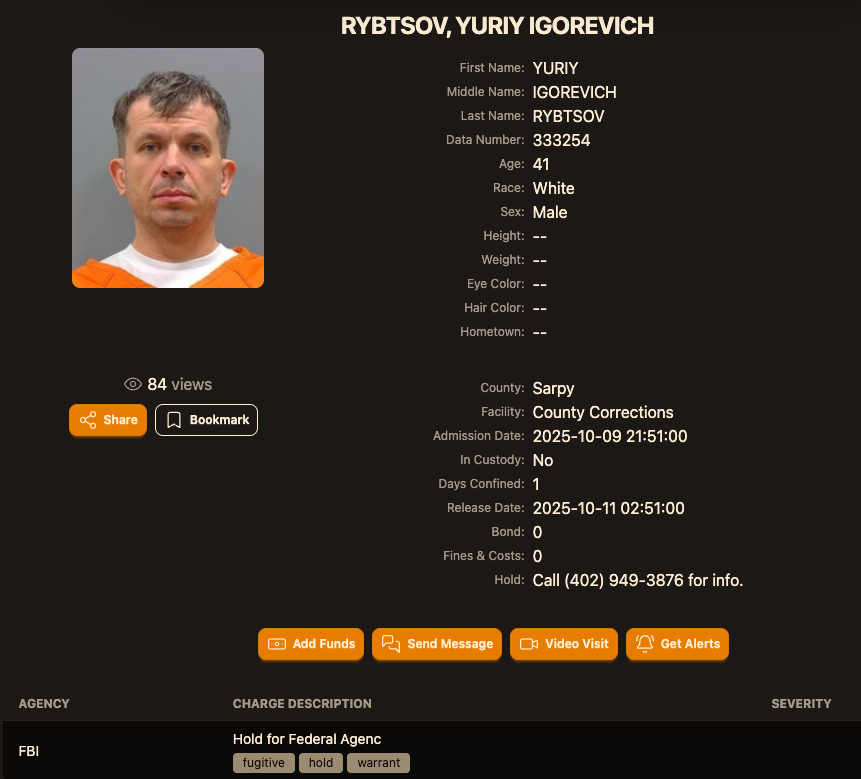
Image: lockedup dot wtf.
The Jabber Zeus name is derived from the malware they used — a custom version of the ZeuS banking trojan — that stole banking login credentials and would send the group a Jabber instant message each time a new victim entered a one-time passcode at a financial institution website. The gang targeted mostly small to mid-sized businesses, and they were an early pioneer of so-called “man-in-the-browser” attacks, malware that can silently intercept any data that victims submit in a web-based form.
Once inside a victim company’s accounts, the Jabber Zeus crew would modify the firm’s payroll to add dozens of “money mules,” people recruited through elaborate work-at-home schemes to handle bank transfers. The mules in turn would forward any stolen payroll deposits — minus their commissions — via wire transfers to other mules in Ukraine and the United Kingdom.
The 2012 indictment targeting the Jabber Zeus crew named MrICQ as “John Doe #3,” and said this person handled incoming notifications of newly compromised victims. The Department of Justice (DOJ) said MrICQ also helped the group launder the proceeds of their heists through electronic currency exchange services.
Two sources familiar with the Jabber Zeus investigation said Rybtsov was arrested in Italy, although the exact date and circumstances of his arrest remain unclear. A summary of recent decisions (PDF) published by the Italian Supreme Court states that in April 2025, Rybtsov lost a final appeal to avoid extradition to the United States.
According to the mugshot website lockedup[.]wtf, Rybtsov arrived in Nebraska on October 9, and was being held under an arrest warrant from the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
The data breach tracking service Constella Intelligence found breached records from the business profiling site bvdinfo[.]com showing that a 41-year-old Yuriy Igorevich Rybtsov worked in a building at 59 Barnaulska St. in Donetsk. Further searching on this address in Constella finds the same apartment building was shared by a business registered to Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, the leader of the Jabber Zeus crew in Ukraine.

Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, seen here performing as “DJ Slava Rich” in Ukraine, in an undated photo from social media.
Penchukov was arrested in 2022 while traveling to meet his wife in Switzerland. Last year, a federal court in Nebraska sentenced Penchukov to 18 years in prison and ordered him to pay more than $73 million in restitution.
Lawrence Baldwin is founder of myNetWatchman, a threat intelligence company based in Georgia that began tracking and disrupting the Jabber Zeus gang in 2009. myNetWatchman had secretly gained access to the Jabber chat server used by the Ukrainian hackers, allowing Baldwin to eavesdrop on the daily conversations between MrICQ and other Jabber Zeus members.
Baldwin shared those real-time chat records with multiple state and federal law enforcement agencies, and with this reporter. Between 2010 and 2013, I spent several hours each day alerting small businesses across the country that their payroll accounts were about to be drained by these cybercriminals.
Those notifications, and Baldwin’s tireless efforts, saved countless would-be victims a great deal of money. In most cases, however, we were already too late. Nevertheless, the pilfered Jabber Zeus group chats provided the basis for dozens of stories published here about small businesses fighting their banks in court over six- and seven-figure financial losses.
Baldwin said the Jabber Zeus crew was far ahead of its peers in several respects. For starters, their intercepted chats showed they worked to create a highly customized botnet directly with the author of the original Zeus Trojan — Evgeniy Mikhailovich Bogachev, a Russian man who has long been on the FBI’s “Most Wanted” list. The feds have a standing $3 million reward for information leading to Bogachev’s arrest.

Evgeniy M. Bogachev, in undated photos.
The core innovation of Jabber Zeus was an alert that MrICQ would receive each time a new victim entered a one-time password code into a phishing page mimicking their financial institution. The gang’s internal name for this component was “Leprechaun,” (the video below from myNetWatchman shows it in action). Jabber Zeus would actually re-write the HTML code as displayed in the victim’s browser, allowing them to intercept any passcodes sent by the victim’s bank for multi-factor authentication.
“These guys had compromised such a large number of victims that they were getting buried in a tsunami of stolen banking credentials,” Baldwin told KrebsOnSecurity. “But the whole point of Leprechaun was to isolate the highest-value credentials — the commercial bank accounts with two-factor authentication turned on. They knew these were far juicier targets because they clearly had a lot more money to protect.”
Baldwin said the Jabber Zeus trojan also included a custom “backconnect” component that allowed the hackers to relay their bank account takeovers through the victim’s own infected PC.
“The Jabber Zeus crew were literally connecting to the victim’s bank account from the victim’s IP address, or from the remote control function and by fully emulating the device,” he said. “That trojan was like a hot knife through butter of what everyone thought was state-of-the-art secure online banking at the time.”
Although the Jabber Zeus crew was in direct contact with the Zeus author, the chats intercepted by myNetWatchman show Bogachev frequently ignored the group’s pleas for help. The government says the real leader of the Jabber Zeus crew was Maksim Yakubets, a 38-year Ukrainian man with Russian citizenship who went by the hacker handle “Aqua.”

Alleged Evil Corp leader Maksim “Aqua” Yakubets. Image: FBI
The Jabber chats intercepted by Baldwin show that Aqua interacted almost daily with MrICQ, Tank and other members of the hacking team, often facilitating the group’s money mule and cashout activities remotely from Russia.
The government says Yakubets/Aqua would later emerge as the leader of an elite cybercrime ring of at least 17 hackers that referred to themselves internally as “Evil Corp.” Members of Evil Corp developed and used the Dridex (a.k.a. Bugat) trojan, which helped them siphon more than $100 million from hundreds of victim companies in the United States and Europe.
This 2019 story about the government’s $5 million bounty for information leading to Yakubets’s arrest includes excerpts of conversations between Aqua, Tank, Bogachev and other Jabber Zeus crew members discussing stories I’d written about their victims. Both Baldwin and I were interviewed at length for a new weekly six-part podcast by the BBC that delves deep into the history of Evil Corp. Episode One focuses on the evolution of Zeus, while the second episode centers on an investigation into the group by former FBI agent Jim Craig.

Image: https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/w3ct89y8
Agents with the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) briefed Capitol Hill staff recently on hardening the security of their mobile devices, after a contacts list stolen from the personal phone of the White House Chief of Staff Susie Wiles was reportedly used to fuel a series of text messages and phone calls impersonating her to U.S. lawmakers. But in a letter this week to the FBI, one of the Senate’s most tech-savvy lawmakers says the feds aren’t doing enough to recommend more appropriate security protections that are already built into most consumer mobile devices.

A screenshot of the first page from Sen. Wyden’s letter to FBI Director Kash Patel.
On May 29, The Wall Street Journal reported that federal authorities were investigating a clandestine effort to impersonate Ms. Wiles via text messages and in phone calls that may have used AI to spoof her voice. According to The Journal, Wiles told associates her cellphone contacts were hacked, giving the impersonator access to the private phone numbers of some of the country’s most influential people.
The execution of this phishing and impersonation campaign — whatever its goals may have been — suggested the attackers were financially motivated, and not particularly sophisticated.
“It became clear to some of the lawmakers that the requests were suspicious when the impersonator began asking questions about Trump that Wiles should have known the answers to—and in one case, when the impersonator asked for a cash transfer, some of the people said,” the Journal wrote. “In many cases, the impersonator’s grammar was broken and the messages were more formal than the way Wiles typically communicates, people who have received the messages said. The calls and text messages also didn’t come from Wiles’s phone number.”
Sophisticated or not, the impersonation campaign was soon punctuated by the murder of Minnesota House of Representatives Speaker Emerita Melissa Hortman and her husband, and the shooting of Minnesota State Senator John Hoffman and his wife. So when FBI agents offered in mid-June to brief U.S. Senate staff on mobile threats, more than 140 staffers took them up on that invitation (a remarkably high number considering that no food was offered at the event).
But according to Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.), the advice the FBI provided to Senate staffers was largely limited to remedial tips, such as not clicking on suspicious links or attachments, not using public wifi networks, turning off bluetooth, keeping phone software up to date, and rebooting regularly.
“This is insufficient to protect Senate employees and other high-value targets against foreign spies using advanced cyber tools,” Wyden wrote in a letter sent today to FBI Director Kash Patel. “Well-funded foreign intelligence agencies do not have to rely on phishing messages and malicious attachments to infect unsuspecting victims with spyware. Cyber mercenary companies sell their government customers advanced ‘zero-click’ capabilities to deliver spyware that do not require any action by the victim.”
Wyden stressed that to help counter sophisticated attacks, the FBI should be encouraging lawmakers and their staff to enable anti-spyware defenses that are built into Apple’s iOS and Google’s Android phone software.
These include Apple’s Lockdown Mode, which is designed for users who are worried they may be subject to targeted attacks. Lockdown Mode restricts non-essential iOS features to reduce the device’s overall attack surface. Google Android devices carry a similar feature called Advanced Protection Mode.
Wyden also urged the FBI to update its training to recommend a number of other steps that people can take to make their mobile devices less trackable, including the use of ad blockers to guard against malicious advertisements, disabling ad tracking IDs in mobile devices, and opting out of commercial data brokers (the suspect charged in the Minnesota shootings reportedly used multiple people-search services to find the home addresses of his targets).
The senator’s letter notes that while the FBI has recommended all of the above precautions in various advisories issued over the years, the advice the agency is giving now to the nation’s leaders needs to be more comprehensive, actionable and urgent.
“In spite of the seriousness of the threat, the FBI has yet to provide effective defensive guidance,” Wyden said.
Nicholas Weaver is a researcher with the International Computer Science Institute, a nonprofit in Berkeley, Calif. Weaver said Lockdown Mode or Advanced Protection will mitigate many vulnerabilities, and should be the default setting for all members of Congress and their staff.
“Lawmakers are at exceptional risk and need to be exceptionally protected,” Weaver said. “Their computers should be locked down and well administered, etc. And the same applies to staffers.”
Weaver noted that Apple’s Lockdown Mode has a track record of blocking zero-day attacks on iOS applications; in September 2023, Citizen Lab documented how Lockdown Mode foiled a zero-click flaw capable of installing spyware on iOS devices without any interaction from the victim.
Earlier this month, Citizen Lab researchers documented a zero-click attack used to infect the iOS devices of two journalists with Paragon’s Graphite spyware. The vulnerability could be exploited merely by sending the target a booby-trapped media file delivered via iMessage. Apple also recently updated its advisory for the zero-click flaw (CVE-2025-43200), noting that it was mitigated as of iOS 18.3.1, which was released in February 2025.
Apple has not commented on whether CVE-2025-43200 could be exploited on devices with Lockdown Mode turned on. But HelpNetSecurity observed that at the same time Apple addressed CVE-2025-43200 back in February, the company fixed another vulnerability flagged by Citizen Lab researcher Bill Marczak: CVE-2025-24200, which Apple said was used in an extremely sophisticated physical attack against specific targeted individuals that allowed attackers to disable USB Restricted Mode on a locked device.
In other words, the flaw could apparently be exploited only if the attacker had physical access to the targeted vulnerable device. And as the old infosec industry adage goes, if an adversary has physical access to your device, it’s most likely not your device anymore.
I can’t speak to Google’s Advanced Protection Mode personally, because I don’t use Google or Android devices. But I have had Apple’s Lockdown Mode enabled on all of my Apple devices since it was first made available in September 2022. I can only think of a single occasion when one of my apps failed to work properly with Lockdown Mode turned on, and in that case I was able to add a temporary exception for that app in Lockdown Mode’s settings.
My main gripe with Lockdown Mode was captured in a March 2025 column by TechCrunch’s Lorenzo Francheschi-Bicchierai, who wrote about its penchant for periodically sending mystifying notifications that someone has been blocked from contacting you, even though nothing then prevents you from contacting that person directly. This has happened to me at least twice, and in both cases the person in question was already an approved contact, and said they had not attempted to reach out.
Although it would be nice if Apple’s Lockdown Mode sent fewer, less alarming and more informative alerts, the occasional baffling warning message is hardly enough to make me turn it off.
Malicious hackers are exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in Versa Director, a software product used by many Internet and IT service providers. Researchers believe the activity is linked to Volt Typhoon, a Chinese cyber espionage group focused on infiltrating critical U.S. networks and laying the groundwork for the ability to disrupt communications between the United States and Asia during any future armed conflict with China.
Image: Shutterstock.com
Versa Director systems are primarily used by Internet service providers (ISPs), as well as managed service providers (MSPs) that cater to the IT needs of many small to mid-sized businesses simultaneously. In a security advisory published Aug. 26, Versa urged customers to deploy a patch for the vulnerability (CVE-2024-39717), which the company said is fixed in Versa Director 22.1.4 or later.
Versa said the weakness allows attackers to upload a file of their choosing to vulnerable systems. The advisory placed much of the blame on Versa customers who “failed to implement system hardening and firewall guidelines…leaving a management port exposed on the internet that provided the threat actors with initial access.”
Versa’s advisory doesn’t say how it learned of the zero-day flaw, but its vulnerability listing at mitre.org acknowledges “there are reports of others based on backbone telemetry observations of a 3rd party provider, however these are unconfirmed to date.”
Those third-party reports came in late June 2024 from Michael Horka, senior lead information security engineer at Black Lotus Labs, the security research arm of Lumen Technologies, which operates one of the global Internet’s largest backbones.
In an interview with KrebsOnSecurity, Horka said Black Lotus Labs identified a web-based backdoor on Versa Director systems belonging to four U.S. victims and one non-U.S. victim in the ISP and MSP sectors, with the earliest known exploit activity occurring at a U.S. ISP on June 12, 2024.
“This makes Versa Director a lucrative target for advanced persistent threat (APT) actors who would want to view or control network infrastructure at scale, or pivot into additional (or downstream) networks of interest,” Horka wrote in a blog post published today.
Black Lotus Labs said it assessed with “medium” confidence that Volt Typhoon was responsible for the compromises, noting the intrusions bear the hallmarks of the Chinese state-sponsored espionage group — including zero-day attacks targeting IT infrastructure providers, and Java-based backdoors that run in memory only.
In May 2023, the National Security Agency (NSA), the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), and the Cybersecurity Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued a joint warning (PDF) about Volt Typhoon, also known as “Bronze Silhouette” and “Insidious Taurus,” which described how the group uses small office/home office (SOHO) network devices to hide their activity.
In early December 2023, Black Lotus Labs published its findings on “KV-botnet,” thousands of compromised SOHO routers that were chained together to form a covert data transfer network supporting various Chinese state-sponsored hacking groups, including Volt Typhoon.
In January 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice disclosed the FBI had executed a court-authorized takedown of the KV-botnet shortly before Black Lotus Labs released its December report.
In February 2024, CISA again joined the FBI and NSA in warning Volt Typhoon had compromised the IT environments of multiple critical infrastructure organizations — primarily in communications, energy, transportation systems, and water and wastewater sectors — in the continental and non-continental United States and its territories, including Guam.
“Volt Typhoon’s choice of targets and pattern of behavior is not consistent with traditional cyber espionage or intelligence gathering operations, and the U.S. authoring agencies assess with high confidence that Volt Typhoon actors are pre-positioning themselves on IT networks to enable lateral movement to OT [operational technology] assets to disrupt functions,” that alert warned.
In a speech at Vanderbilt University in April, FBI Director Christopher Wray said China is developing the “ability to physically wreak havoc on our critical infrastructure at a time of its choosing,” and that China’s plan is to “land blows against civilian infrastructure to try to induce panic.”
Ryan English, an information security engineer at Lumen, said it’s disappointing his employer didn’t at least garner an honorable mention in Versa’s security advisory. But he said he’s glad there are now a lot fewer Versa systems exposed to this attack.
“Lumen has for the last nine weeks been very intimate with their leadership with the goal in mind of helping them mitigate this,” English said. “We’ve given them everything we could along the way, so it kind of sucks being referenced just as a third party.”