A sprawling academic cheating network turbocharged by Google Ads that has generated nearly $25 million in revenue has curious ties to a Kremlin-connected oligarch whose Russian university builds drones for Russia’s war against Ukraine.
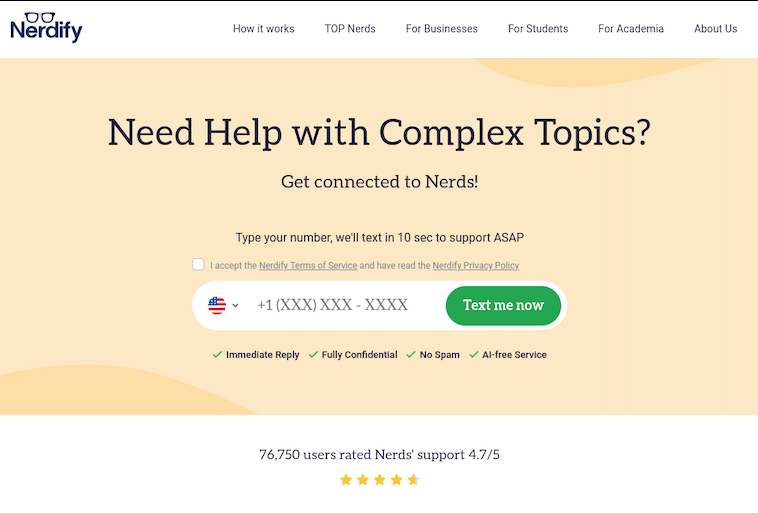
The Nerdify homepage.
The link between essay mills and Russian attack drones might seem improbable, but understanding it begins with a simple question: How does a human-intensive academic cheating service stay relevant in an era when students can simply ask AI to write their term papers? The answer – recasting the business as an AI company – is just the latest chapter in a story of many rebrands that link the operation to Russia’s largest private university.
Search in Google for any terms related to academic cheating services — e.g., “help with exam online” or “term paper online” — and you’re likely to encounter websites with the words “nerd” or “geek” in them, such as thenerdify[.]com and geekly-hub[.]com. With a simple request sent via text message, you can hire their tutors to help with any assignment.
These nerdy and geeky-branded websites frequently cite their “honor code,” which emphasizes they do not condone academic cheating, will not write your term papers for you, and will only offer support and advice for customers. But according to This Isn’t Fine, a Substack blog about contract cheating and essay mills, the Nerdify brand of websites will happily ignore that mantra.
“We tested the quick SMS for a price quote,” wrote This Isn’t Fine author Joseph Thibault. “The honor code references and platitudes apparently stop at the website. Within three minutes, we confirmed that a full three-page, plagiarism- and AI-free MLA formatted Argumentative essay could be ours for the low price of $141.”
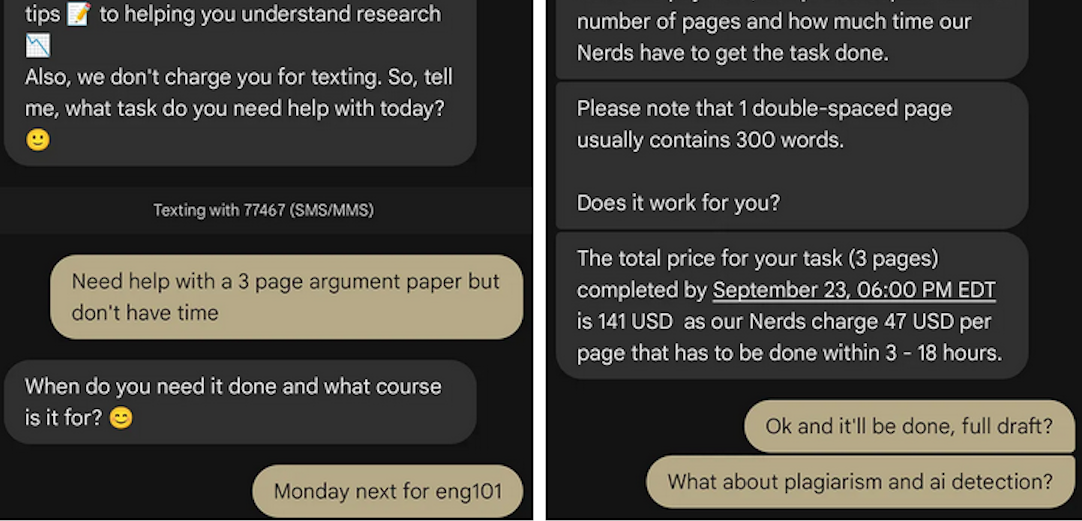
A screenshot from Joseph Thibault’s Substack post shows him purchasing a 3-page paper with the Nerdify service.
Google prohibits ads that “enable dishonest behavior.” Yet, a sprawling global essay and homework cheating network run under the Nerdy brands has quietly bought its way to the top of Google searches – booking revenues of almost $25 million through a maze of companies in Cyprus, Malta and Hong Kong, while pitching “tutoring” that delivers finished work that students can turn in.
When one Nerdy-related Google Ads account got shut down, the group behind the company would form a new entity with a front-person (typically a young Ukrainian woman), start a new ads account along with a new website and domain name (usually with “nerdy” in the brand), and resume running Google ads for the same set of keywords.
UK companies belonging to the group that have been shut down by Google Ads since Jan 2025 include:
–Proglobal Solutions LTD (advertised nerdifyit[.]com);
–AW Tech Limited (advertised thenerdify[.]com);
–Geekly Solutions Ltd (advertised geekly-hub[.]com).
Currently active Google Ads accounts for the Nerdify brands include:
-OK Marketing LTD (advertising geekly-hub[.]net), formed in the name of Olha Karpenko, a young Ukrainian woman;
–Two Sigma Solutions LTD (advertising litero[.]ai), formed in the name of Olekszij (Alexey) Pokatilo.
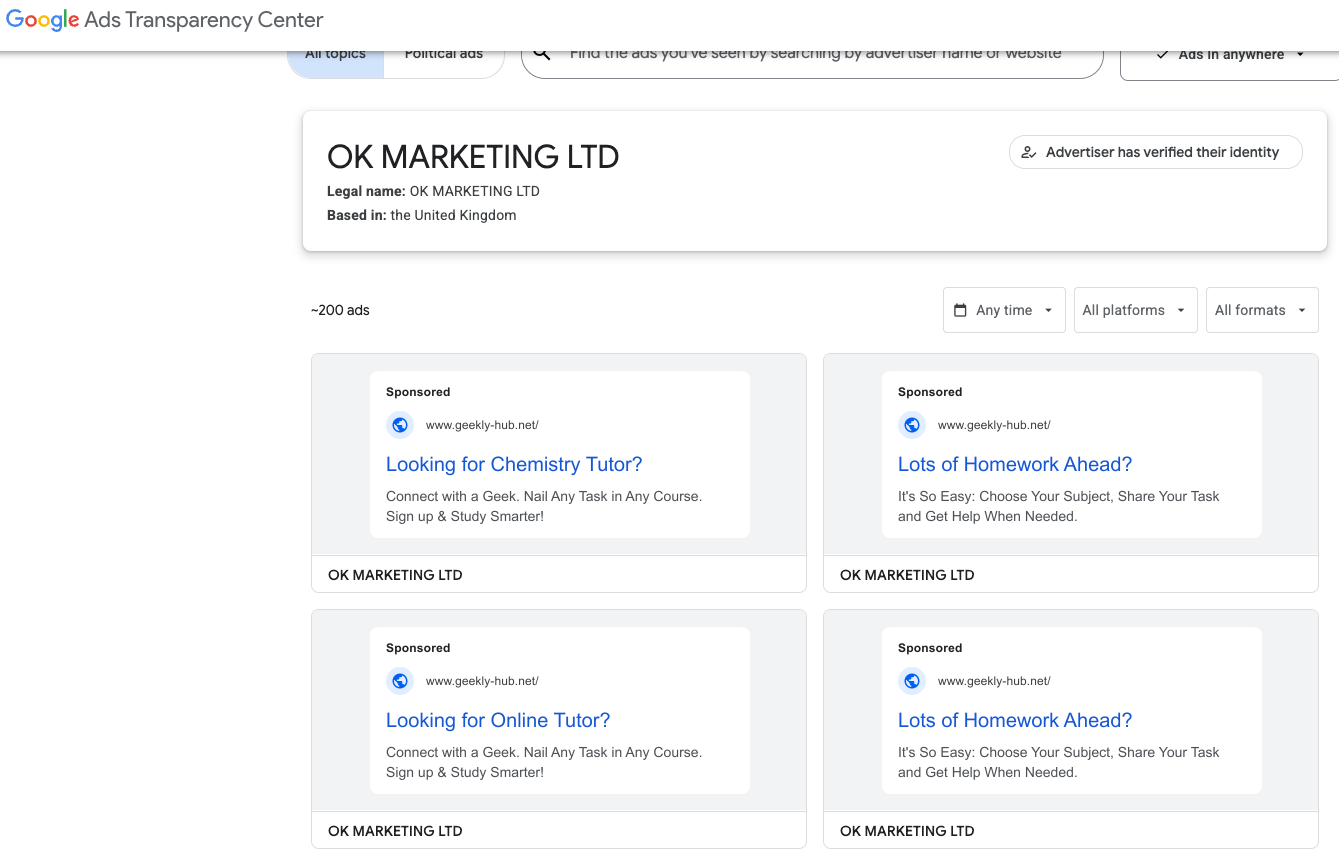
Google’s Ads Transparency page for current Nerdify advertiser OK Marketing LTD.
Mr. Pokatilo has been in the essay-writing business since at least 2009, operating a paper-mill enterprise called Livingston Research alongside Alexander Korsukov, who is listed as an owner. According to a lengthy account from a former employee, Livingston Research mainly farmed its writing tasks out to low-cost workers from Kenya, Philippines, Pakistan, Russia and Ukraine.
Pokatilo moved from Ukraine to the United Kingdom in Sept. 2015 and co-founded a company called Awesome Technologies, which pitched itself as a way for people to outsource tasks by sending a text message to the service’s assistants.
The other co-founder of Awesome Technologies is 36-year-old Filip Perkon, a Swedish man living in London who touts himself as a serial entrepreneur and investor. Years before starting Awesome together, Perkon and Pokatilo co-founded a student group called Russian Business Week while the two were classmates at the London School of Economics. According to the Bulgarian investigative journalist Christo Grozev, Perkon’s birth certificate was issued by the Soviet Embassy in Sweden.

Alexey Pokatilo (left) and Filip Perkon at a Facebook event for startups in San Francisco in mid-2015.
Around the time Perkon and Pokatilo launched Awesome Technologies, Perkon was building a social media propaganda tool called the Russian Diplomatic Online Club, which Perkon said would “turbo-charge” Russian messaging online. The club’s newsletter urged subscribers to install in their Twitter accounts a third-party app called Tweetsquad that would retweet Kremlin messaging on the social media platform.
Perkon was praised by the Russian Embassy in London for his efforts: During the contentious Brexit vote that ultimately led to the United Kingdom leaving the European Union, the Russian embassy in London used this spam tweeting tool to auto-retweet the Russian ambassador’s posts from supporters’ accounts.
Neither Mr. Perkon nor Mr. Pokatilo replied to requests for comment.
A review of corporations tied to Mr. Perkon as indexed by the business research service North Data finds he holds or held director positions in several U.K. subsidiaries of Synergy University, Russia’s largest private education provider. Synergy has more than 35,000 students, and sells T-shirts with patriotic slogans such as “Crimea is Ours,” and “The Russian Empire — Reloaded.”
The president of Synergy University is Vadim Lobov, a Kremlin insider whose headquarters on the outskirts of Moscow reportedly features a wall-sized portrait of Russian President Vladimir Putin in the pop-art style of Andy Warhol. For a number of years, Lobov and Perkon co-produced a cross-cultural event in the U.K. called Russian Film Week.
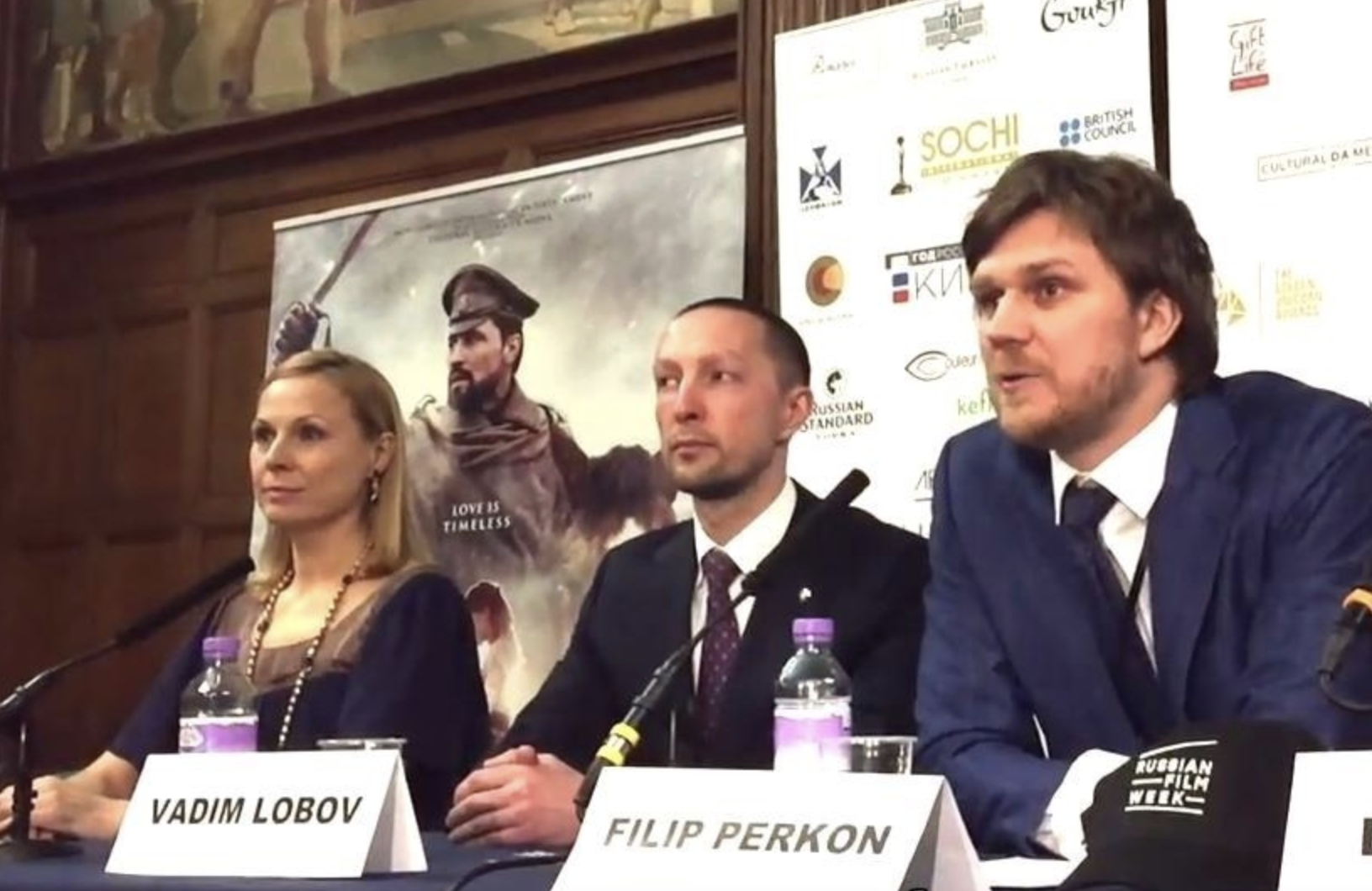

Synergy President Vadim Lobov and Filip Perkon, speaking at a press conference for Russian Film Week, a cross-cultural event in the U.K. co-produced by both men.
Mr. Lobov was one of 11 individuals reportedly hand-picked by the convicted Russian spy Marina Butina to attend the 2017 National Prayer Breakfast held in Washington D.C. just two weeks after President Trump’s first inauguration.
While Synergy University promotes itself as Russia’s largest private educational institution, hundreds of international students tell a different story. Online reviews from students paint a picture of unkept promises: Prospective students from Nigeria, Kenya, Ghana, and other nations paying thousands in advance fees for promised study visas to Russia, only to have their applications denied with no refunds offered.
“My experience with Synergy University has been nothing short of heartbreaking,” reads one such account. “When I first discovered the school, their representative was extremely responsive and eager to assist. He communicated frequently and made me believe I was in safe hands. However, after paying my hard-earned tuition fees, my visa was denied. It’s been over 9 months since that denial, and despite their promises, I have received no refund whatsoever. My messages are now ignored, and the same representative who once replied instantly no longer responds at all. Synergy University, how can an institution in Europe feel comfortable exploiting the hopes of Africans who trust you with their life savings? This is not just unethical — it’s predatory.”
This pattern repeats across reviews by multilingual students from Pakistan, Nepal, India, and various African nations — all describing the same scheme: Attractive online marketing, promises of easy visa approval, upfront payment requirements, and then silence after visa denials.
Reddit discussions in r/Moscow and r/AskARussian are filled with warnings. “It’s a scam, a diploma mill,” writes one user. “They literally sell exams. There was an investigation on Rossiya-1 television showing students paying to pass tests.”
The Nerdify website’s “About Us” page says the company was co-founded by Pokatilo and an American named Brian Mellor. The latter identity seems to have been fabricated, or at least there is no evidence that a person with this name ever worked at Nerdify.
Rather, it appears that the SMS assistance company co-founded by Messrs. Pokatilo and Perkon (Awesome Technologies) fizzled out shortly after its creation, and that Nerdify soon adopted the process of accepting assignment requests via text message and routing them to freelance writers.
A closer look at an early “About Us” page for Nerdify in The Wayback Machine suggests that Mr. Perkon was the real co-founder of the company: The photo at the top of the page shows four people wearing Nerdify T-shirts seated around a table on a rooftop deck in San Francisco, and the man facing the camera is Perkon.

Filip Perkon, top right, is pictured wearing a Nerdify T-shirt in an archived copy of the company’s About Us page. Image: archive.org.
Where are they now? Pokatilo is currently running a startup called Litero.Ai, which appears to be an AI-based essay writing service. In July 2025, Mr. Pokatilo received pre-seed funding of $800,000 for Litero from an investment program backed by the venture capital firms AltaIR Capital, Yellow Rocks, Smart Partnership Capital, and I2BF Global Ventures.
Meanwhile, Filip Perkon is busy setting up toy rubber duck stores in Miami and in at least three locations in the United Kingdom. These “Duck World” shops market themselves as “the world’s largest duck store.”
This past week, Mr. Lobov was in India with Putin’s entourage on a charm tour with India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi. Although Synergy is billed as an educational institution, a review of the company’s sprawling corporate footprint (via DNS) shows it also is assisting the Russian government in its war against Ukraine.

Synergy University President Vadim Lobov (right) pictured this week in India next to Natalia Popova, a Russian TV presenter known for her close ties to Putin’s family, particularly Putin’s daughter, who works with Popova at the education and culture-focused Innopraktika Foundation.
The website bpla.synergy[.]bot, for instance, says the company is involved in developing combat drones to aid Russian forces and to evade international sanctions on the supply and re-export of high-tech products.

A screenshot from the website of synergy,bot shows the company is actively engaged in building armed drones for the war in Ukraine.
KrebsOnSecurity would like to thank the anonymous researcher NatInfoSec for their assistance in this investigation.
Update, Dec. 8, 10:06 a.m. ET: Mr. Pokatilo responded to requests for comment after the publication of this story. Pokatilo said he has no relation to Synergy nor to Mr. Lobov, and that his work with Mr. Perkon ended with the dissolution of Awesome Technologies.
“I have had no involvement in any of his projects and business activities mentioned in the article and he has no involvement in Litero.ai,” Pokatilo said of Perkon.
Mr. Pokatilo said his new company Litero “does not provide contract cheating services and is built specifically to improve transparency and academic integrity in the age of universal use of AI by students.”
“I am Ukrainian,” he said in an email. “My close friends, colleagues, and some family members continue to live in Ukraine under the ongoing invasion. Any suggestion that I or my company may be connected in any way to Russia’s war efforts is deeply offensive on a personal level and harmful to the reputation of Litero.ai, a company where many team members are Ukrainian.”
Update, Dec. 11, 12:07 p.m. ET: Mr. Perkon responded to requests for comment after the publication of this story. Perkon said the photo of him in a Nerdify T-shirt (see screenshot above) was taken after a startup event in San Francisco, where he volunteered to act as a photo model to help friends with their project.
“I have no business or other relations to Nerdify or any other ventures in that space,” Mr. Perkon said in an email response. “As for Vadim Lobov, I worked for Venture Capital arm at Synergy until 2013 as well as his business school project in the UK, that didn’t get off the ground, so the company related to this was made dormant. Then Synergy kindly provided sponsorship for my Russian Film Week event that I created and ran until 2022 in the U.K., an event that became the biggest independent Russian film festival outside of Russia. Since the start of the Ukraine war in 2022 I closed the festival down.”
“I have had no business with Vadim Lobov since 2021 (the last film festival) and I don’t keep track of his endeavours,” Perkon continued. “As for Alexey Pokatilo, we are university friends. Our business relationship has ended after the concierge service Awesome Technologies didn’t work out, many years ago.”
A Ukrainian man indicted in 2012 for conspiring with a prolific hacking group to steal tens of millions of dollars from U.S. businesses was arrested in Italy and is now in custody in the United States, KrebsOnSecurity has learned.
Sources close to the investigation say Yuriy Igorevich Rybtsov, a 41-year-old from the Russia-controlled city of Donetsk, Ukraine, was previously referenced in U.S. federal charging documents only by his online handle “MrICQ.” According to a 13-year-old indictment (PDF) filed by prosecutors in Nebraska, MrICQ was a developer for a cybercrime group known as “Jabber Zeus.”
Image: lockedup dot wtf.
The Jabber Zeus name is derived from the malware they used — a custom version of the ZeuS banking trojan — that stole banking login credentials and would send the group a Jabber instant message each time a new victim entered a one-time passcode at a financial institution website. The gang targeted mostly small to mid-sized businesses, and they were an early pioneer of so-called “man-in-the-browser” attacks, malware that can silently intercept any data that victims submit in a web-based form.
Once inside a victim company’s accounts, the Jabber Zeus crew would modify the firm’s payroll to add dozens of “money mules,” people recruited through elaborate work-at-home schemes to handle bank transfers. The mules in turn would forward any stolen payroll deposits — minus their commissions — via wire transfers to other mules in Ukraine and the United Kingdom.
The 2012 indictment targeting the Jabber Zeus crew named MrICQ as “John Doe #3,” and said this person handled incoming notifications of newly compromised victims. The Department of Justice (DOJ) said MrICQ also helped the group launder the proceeds of their heists through electronic currency exchange services.
Two sources familiar with the Jabber Zeus investigation said Rybtsov was arrested in Italy, although the exact date and circumstances of his arrest remain unclear. A summary of recent decisions (PDF) published by the Italian Supreme Court states that in April 2025, Rybtsov lost a final appeal to avoid extradition to the United States.
According to the mugshot website lockedup[.]wtf, Rybtsov arrived in Nebraska on October 9, and was being held under an arrest warrant from the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
The data breach tracking service Constella Intelligence found breached records from the business profiling site bvdinfo[.]com showing that a 41-year-old Yuriy Igorevich Rybtsov worked in a building at 59 Barnaulska St. in Donetsk. Further searching on this address in Constella finds the same apartment building was shared by a business registered to Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, the leader of the Jabber Zeus crew in Ukraine.

Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, seen here performing as “DJ Slava Rich” in Ukraine, in an undated photo from social media.
Penchukov was arrested in 2022 while traveling to meet his wife in Switzerland. Last year, a federal court in Nebraska sentenced Penchukov to 18 years in prison and ordered him to pay more than $73 million in restitution.
Lawrence Baldwin is founder of myNetWatchman, a threat intelligence company based in Georgia that began tracking and disrupting the Jabber Zeus gang in 2009. myNetWatchman had secretly gained access to the Jabber chat server used by the Ukrainian hackers, allowing Baldwin to eavesdrop on the daily conversations between MrICQ and other Jabber Zeus members.
Baldwin shared those real-time chat records with multiple state and federal law enforcement agencies, and with this reporter. Between 2010 and 2013, I spent several hours each day alerting small businesses across the country that their payroll accounts were about to be drained by these cybercriminals.
Those notifications, and Baldwin’s tireless efforts, saved countless would-be victims a great deal of money. In most cases, however, we were already too late. Nevertheless, the pilfered Jabber Zeus group chats provided the basis for dozens of stories published here about small businesses fighting their banks in court over six- and seven-figure financial losses.
Baldwin said the Jabber Zeus crew was far ahead of its peers in several respects. For starters, their intercepted chats showed they worked to create a highly customized botnet directly with the author of the original Zeus Trojan — Evgeniy Mikhailovich Bogachev, a Russian man who has long been on the FBI’s “Most Wanted” list. The feds have a standing $3 million reward for information leading to Bogachev’s arrest.

Evgeniy M. Bogachev, in undated photos.
The core innovation of Jabber Zeus was an alert that MrICQ would receive each time a new victim entered a one-time password code into a phishing page mimicking their financial institution. The gang’s internal name for this component was “Leprechaun,” (the video below from myNetWatchman shows it in action). Jabber Zeus would actually re-write the HTML code as displayed in the victim’s browser, allowing them to intercept any passcodes sent by the victim’s bank for multi-factor authentication.
“These guys had compromised such a large number of victims that they were getting buried in a tsunami of stolen banking credentials,” Baldwin told KrebsOnSecurity. “But the whole point of Leprechaun was to isolate the highest-value credentials — the commercial bank accounts with two-factor authentication turned on. They knew these were far juicier targets because they clearly had a lot more money to protect.”
Baldwin said the Jabber Zeus trojan also included a custom “backconnect” component that allowed the hackers to relay their bank account takeovers through the victim’s own infected PC.
“The Jabber Zeus crew were literally connecting to the victim’s bank account from the victim’s IP address, or from the remote control function and by fully emulating the device,” he said. “That trojan was like a hot knife through butter of what everyone thought was state-of-the-art secure online banking at the time.”
Although the Jabber Zeus crew was in direct contact with the Zeus author, the chats intercepted by myNetWatchman show Bogachev frequently ignored the group’s pleas for help. The government says the real leader of the Jabber Zeus crew was Maksim Yakubets, a 38-year Ukrainian man with Russian citizenship who went by the hacker handle “Aqua.”

Alleged Evil Corp leader Maksim “Aqua” Yakubets. Image: FBI
The Jabber chats intercepted by Baldwin show that Aqua interacted almost daily with MrICQ, Tank and other members of the hacking team, often facilitating the group’s money mule and cashout activities remotely from Russia.
The government says Yakubets/Aqua would later emerge as the leader of an elite cybercrime ring of at least 17 hackers that referred to themselves internally as “Evil Corp.” Members of Evil Corp developed and used the Dridex (a.k.a. Bugat) trojan, which helped them siphon more than $100 million from hundreds of victim companies in the United States and Europe.
This 2019 story about the government’s $5 million bounty for information leading to Yakubets’s arrest includes excerpts of conversations between Aqua, Tank, Bogachev and other Jabber Zeus crew members discussing stories I’d written about their victims. Both Baldwin and I were interviewed at length for a new weekly six-part podcast by the BBC that delves deep into the history of Evil Corp. Episode One focuses on the evolution of Zeus, while the second episode centers on an investigation into the group by former FBI agent Jim Craig.

Image: https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/w3ct89y8
A cybercriminal group that used voice phishing attacks to siphon more than a billion records from Salesforce customers earlier this year has launched a website that threatens to publish data stolen from dozens of Fortune 500 firms if they refuse to pay a ransom. The group also claimed responsibility for a recent breach involving Discord user data, and for stealing terabytes of sensitive files from thousands of customers of the enterprise software maker Red Hat.
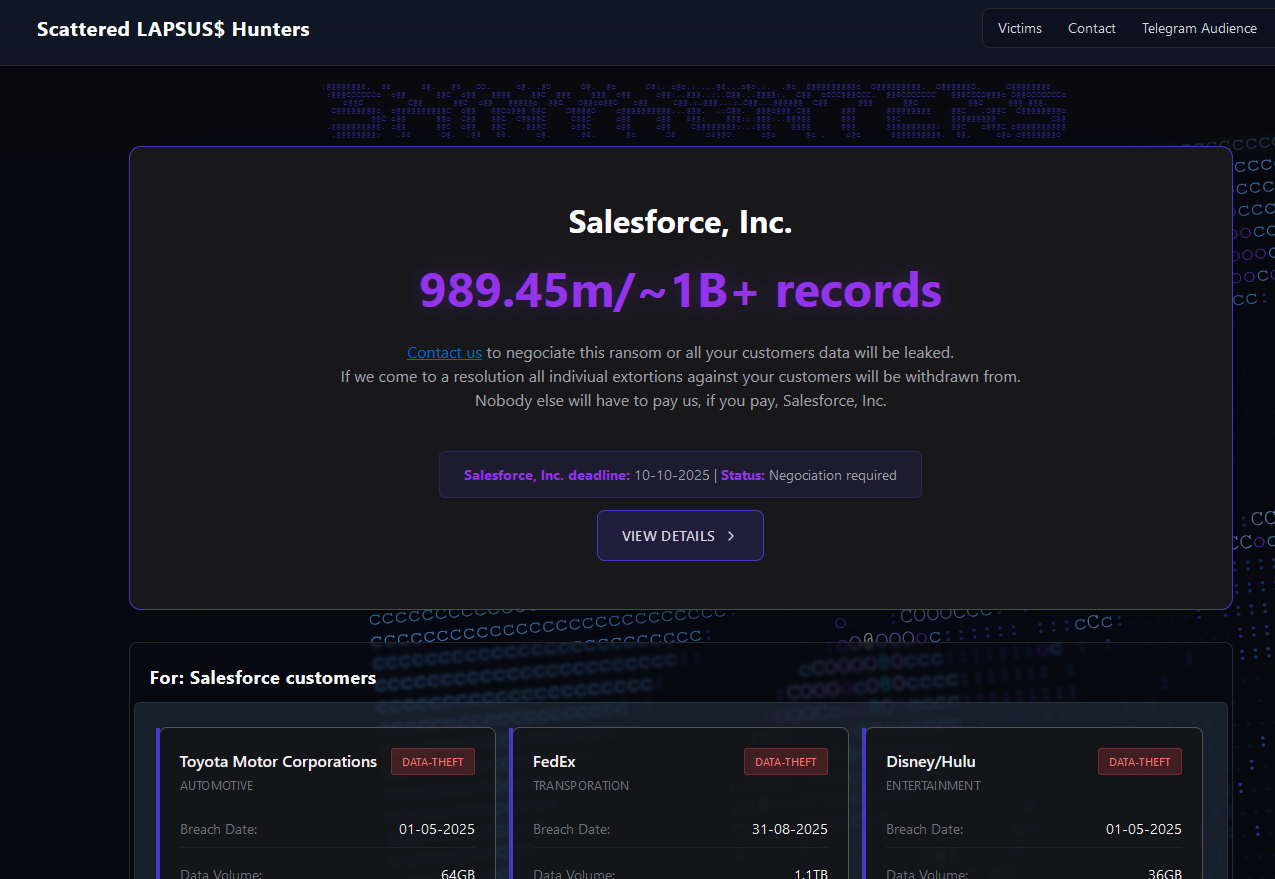
The new extortion website tied to ShinyHunters (UNC6040), which threatens to publish stolen data unless Salesforce or individual victim companies agree to pay a ransom.
In May 2025, a prolific and amorphous English-speaking cybercrime group known as ShinyHunters launched a social engineering campaign that used voice phishing to trick targets into connecting a malicious app to their organization’s Salesforce portal.
The first real details about the incident came in early June, when the Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) warned that ShinyHunters — tracked by Google as UNC6040 — was extorting victims over their stolen Salesforce data, and that the group was poised to launch a data leak site to publicly shame victim companies into paying a ransom to keep their records private. A month later, Google acknowledged that one of its own corporate Salesforce instances was impacted in the voice phishing campaign.
Last week, a new victim shaming blog dubbed “Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters” began publishing the names of companies that had customer Salesforce data stolen as a result of the May voice phishing campaign.
“Contact us to negotiate this ransom or all your customers data will be leaked,” the website stated in a message to Salesforce. “If we come to a resolution all individual extortions against your customers will be withdrawn from. Nobody else will have to pay us, if you pay, Salesforce, Inc.”
Below that message were more than three dozen entries for companies that allegedly had Salesforce data stolen, including Toyota, FedEx, Disney/Hulu, and UPS. The entries for each company specified the volume of stolen data available, as well as the date that the information was retrieved (the stated breach dates range between May and September 2025).
Image: Mandiant.
On October 5, the Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters victim shaming and extortion blog announced that the group was responsible for a breach in September involving a GitLab server used by Red Hat that contained more than 28,000 Git code repositories, including more than 5,000 Customer Engagement Reports (CERs).
“Alot of folders have their client’s secrets such as artifactory access tokens, git tokens, azure, docker (redhat docker, azure containers, dockerhub), their client’s infrastructure details in the CERs like the audits that were done for them, and a whole LOT more, etc.,” the hackers claimed.
Their claims came several days after a previously unknown hacker group calling itself the Crimson Collective took credit for the Red Hat intrusion on Telegram.
Red Hat disclosed on October 2 that attackers had compromised a company GitLab server, and said it was in the process of notifying affected customers.
“The compromised GitLab instance housed consulting engagement data, which may include, for example, Red Hat’s project specifications, example code snippets, internal communications about consulting services, and limited forms of business contact information,” Red Hat wrote.
Separately, Discord has started emailing users affected by another breach claimed by ShinyHunters. Discord said an incident on September 20 at a “third-party customer service provider” impacted a “limited number of users” who communicated with Discord customer support or Trust & Safety teams. The information included Discord usernames, emails, IP address, the last four digits of any stored payment cards, and government ID images submitted during age verification appeals.
The Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters claim they will publish data stolen from Salesforce and its customers if ransom demands aren’t paid by October 10. The group also claims it will soon begin extorting hundreds more organizations that lost data in August after a cybercrime group stole vast amounts of authentication tokens from Salesloft, whose AI chatbot is used by many corporate websites to convert customer interaction into Salesforce leads.
In a communication sent to customers today, Salesforce emphasized that the theft of any third-party Salesloft data allegedly stolen by ShinyHunters did not originate from a vulnerability within the core Salesforce platform. The company also stressed that it has no plans to meet any extortion demands.
“Salesforce will not engage, negotiate with, or pay any extortion demand,” the message to customers read. “Our focus is, and remains, on defending our environment, conducting thorough forensic analysis, supporting our customers, and working with law enforcement and regulatory authorities.”
The GTIG tracked the group behind the Salesloft data thefts as UNC6395, and says the group has been observed harvesting the data for authentication tokens tied to a range of cloud services like Snowflake and Amazon’s AWS.
Google catalogs Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters by so many UNC names (throw in UNC6240 for good measure) because it is thought to be an amalgamation of three hacking groups — Scattered Spider, Lapsus$ and ShinyHunters. The members of these groups hail from many of the same chat channels on the Com, a mostly English-language cybercriminal community that operates across an ocean of Telegram and Discord servers.
The Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters darknet blog is currently offline. The outage appears to have coincided with the disappearance of the group’s new clearnet blog — breachforums[.]hn — which vanished after shifting its Domain Name Service (DNS) servers from DDoS-Guard to Cloudflare.
But before it died, the websites disclosed that hackers were exploiting a critical zero-day vulnerability in Oracle’s E-Business Suite software. Oracle has since confirmed that a security flaw tracked as CVE-2025-61882 allows attackers to perform unauthenticated remote code execution, and is urging customers to apply an emergency update to address the weakness.
Mandiant’s Charles Carmakal shared on LinkedIn that CVE-2025-61882 was initially exploited in August 2025 by the Clop ransomware gang to steal data from Oracle E-Business Suite servers. Bleeping Computer writes that news of the Oracle zero-day first surfaced on the Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters blog, which published a pair of scripts that were used to exploit vulnerable Oracle E-Business Suite instances.
On Monday evening, KrebsOnSecurity received a malware-laced message from a reader that threatened physical violence unless their unstated demands were met. The missive, titled “Shiny hunters,” contained the hashtag $LAPSU$$SCATEREDHUNTER, and urged me to visit a page on limewire[.]com to view their demands.
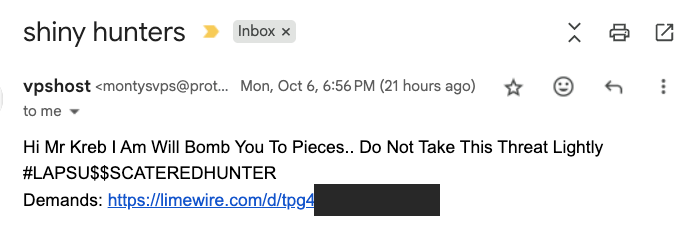
A screenshot of the phishing message linking to a malicious trojan disguised as a Windows screensaver file.
KrebsOnSecurity did not visit this link, but instead forwarded it to Mandiant, which confirmed that similar menacing missives were sent to employees at Mandiant and other security firms around the same time.
The link in the message fetches a malicious trojan disguised as a Windows screensaver file (Virustotal’s analysis on this malware is here). Simply viewing the booby-trapped screensaver on a Windows PC is enough to cause the bundled trojan to launch in the background.
Mandiant’s Austin Larsen said the trojan is a commercially available backdoor known as ASYNCRAT, a .NET-based backdoor that communicates using a custom binary protocol over TCP, and can execute shell commands and download plugins to extend its features.
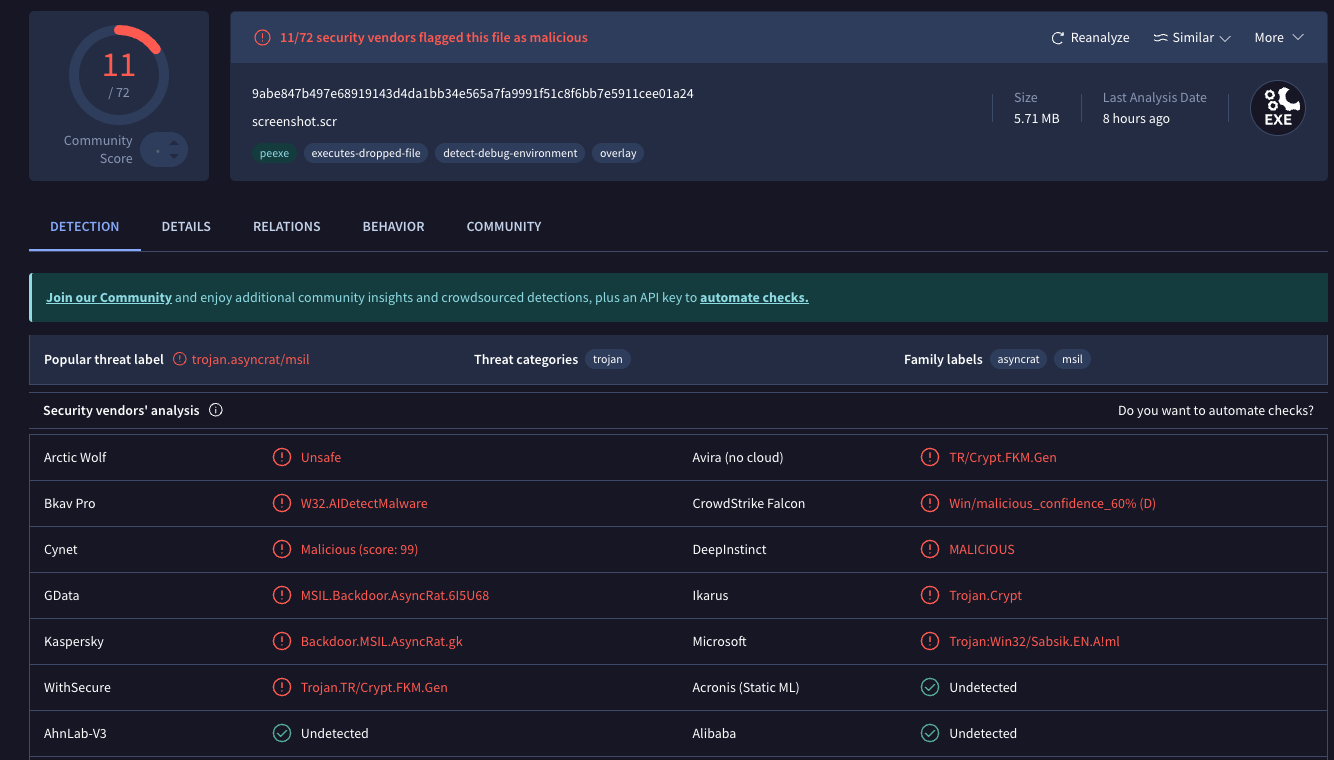
A scan of the malicious screensaver file at Virustotal.com shows it is detected as bad by nearly a dozen security and antivirus tools.
“Downloaded plugins may be executed directly in memory or stored in the registry,” Larsen wrote in an analysis shared via email. “Capabilities added via plugins include screenshot capture, file transfer, keylogging, video capture, and cryptocurrency mining. ASYNCRAT also supports a plugin that targets credentials stored by Firefox and Chromium-based web browsers.”
Malware-laced targeted emails are not out of character for certain members of the Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters, who have previously harassed and threatened security researchers and even law enforcement officials who are investigating and warning about the extent of their attacks.
With so many big data breaches and ransom attacks now coming from cybercrime groups operating on the Com, law enforcement agencies on both sides of the pond are under increasing pressure to apprehend the criminal hackers involved. In late September, prosecutors in the U.K. charged two alleged Scattered Spider members aged 18 and 19 with extorting at least $115 million in ransom payments from companies victimized by data theft.
U.S. prosecutors heaped their own charges on the 19 year-old in that duo — U.K. resident Thalha Jubair — who is alleged to have been involved in data ransom attacks against Marks & Spencer and Harrods, the British food retailer Co-op Group, and the 2023 intrusions at MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment. Jubair also was allegedly a key member of LAPSUS$, a cybercrime group that broke into dozens of technology companies beginning in late 2021.
A Mastodon post by Kevin Beaumont, lamenting the prevalence of major companies paying millions to extortionist teen hackers, refers derisively to Thalha Jubair as a part of an APT threat known as “Advanced Persistent Teenagers.”
In August, convicted Scattered Spider member and 20-year-old Florida man Noah Michael Urban was sentenced to 10 years in federal prison and ordered to pay roughly $13 million in restitution to victims.
In April 2025, a 23-year-old Scottish man thought to be an early Scattered Spider member was extradited from Spain to the U.S., where he is facing charges of wire fraud, conspiracy and identity theft. U.S. prosecutors allege Tyler Robert Buchanan and co-conspirators hacked into dozens of companies in the United States and abroad, and that he personally controlled more than $26 million stolen from victims.
Update, Oct. 8, 8:59 a.m. ET: A previous version of this story incorrectly referred to the malware sent by the reader as a Windows screenshot file. Rather, it is a Windows screensaver file.
KrebsOnSecurity recently heard from a reader whose boss’s email account got phished and was used to trick one of the company’s customers into sending a large payment to scammers. An investigation into the attacker’s infrastructure points to a long-running Nigerian cybercrime ring that is actively targeting established companies in the transportation and aviation industries.

Image: Shutterstock, Mr. Teerapon Tiuekhom.
A reader who works in the transportation industry sent a tip about a recent successful phishing campaign that tricked an executive at the company into entering their credentials at a fake Microsoft 365 login page. From there, the attackers quickly mined the executive’s inbox for past communications about invoices, copying and modifying some of those messages with new invoice demands that were sent to some of the company’s customers and partners.
Speaking on condition of anonymity, the reader said the resulting phishing emails to customers came from a newly registered domain name that was remarkably similar to their employer’s domain, and that at least one of their customers fell for the ruse and paid a phony invoice. They said the attackers had spun up a look-alike domain just a few hours after the executive’s inbox credentials were phished, and that the scam resulted in a customer suffering a six-figure financial loss.
The reader also shared that the email addresses in the registration records for the imposter domain — roomservice801@gmail.com — is tied to many such phishing domains. Indeed, a search on this email address at DomainTools.com finds it is associated with at least 240 domains registered in 2024 or 2025. Virtually all of them mimic legitimate domains for companies in the aerospace and transportation industries worldwide.
An Internet search for this email address reveals a humorous blog post from 2020 on the Russian forum hackware[.]ru, which found roomservice801@gmail.com was tied to a phishing attack that used the lure of phony invoices to trick the recipient into logging in at a fake Microsoft login page. We’ll come back to this research in a moment.
DomainTools shows that some of the early domains registered to roomservice801@gmail.com in 2016 include other useful information. For example, the WHOIS records for alhhomaidhicentre[.]biz reference the technical contact of “Justy John” and the email address justyjohn50@yahoo.com.
A search at DomainTools found justyjohn50@yahoo.com has been registering one-off phishing domains since at least 2012. At this point, I was convinced that some security company surely had already published an analysis of this particular threat group, but I didn’t yet have enough information to draw any solid conclusions.
DomainTools says the Justy John email address is tied to more than two dozen domains registered since 2012, but we can find hundreds more phishing domains and related email addresses simply by pivoting on details in the registration records for these Justy John domains. For example, the street address used by the Justy John domain axisupdate[.]net — 7902 Pelleaux Road in Knoxville, TN — also appears in the registration records for accountauthenticate[.]com, acctlogin[.]biz, and loginaccount[.]biz, all of which at one point included the email address rsmith60646@gmail.com.
That Rsmith Gmail address is connected to the 2012 phishing domain alibala[.]biz (one character off of the Chinese e-commerce giant alibaba.com, with a different top-level domain of .biz). A search in DomainTools on the phone number in those domain records — 1.7736491613 — reveals even more phishing domains as well as the Nigerian phone number “2348062918302” and the email address michsmith59@gmail.com.
DomainTools shows michsmith59@gmail.com appears in the registration records for the domain seltrock[.]com, which was used in the phishing attack documented in the 2020 Russian blog post mentioned earlier. At this point, we are just two steps away from identifying the threat actor group.
The same Nigerian phone number shows up in dozens of domain registrations that reference the email address sebastinekelly69@gmail.com, including 26i3[.]net, costamere[.]com, danagruop[.]us, and dividrilling[.]com. A Web search on any of those domains finds they were indexed in an “indicator of compromise” list on GitHub maintained by Palo Alto Networks‘ Unit 42 research team.
According to Unit 42, the domains are the handiwork of a vast cybercrime group based in Nigeria that it dubbed “SilverTerrier” back in 2014. In an October 2021 report, Palo Alto said SilverTerrier excels at so-called “business e-mail compromise” or BEC scams, which target legitimate business email accounts through social engineering or computer intrusion activities. BEC criminals use that access to initiate or redirect the transfer of business funds for personal gain.
Palo Alto says SilverTerrier encompasses hundreds of BEC fraudsters, some of whom have been arrested in various international law enforcement operations by Interpol. In 2022, Interpol and the Nigeria Police Force arrested 11 alleged SilverTerrier members, including a prominent SilverTerrier leader who’d been flaunting his wealth on social media for years. Unfortunately, the lure of easy money, endemic poverty and corruption, and low barriers to entry for cybercrime in Nigeria conspire to provide a constant stream of new recruits.
BEC scams were the 7th most reported crime tracked by the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) in 2024, generating more than 21,000 complaints. However, BEC scams were the second most costly form of cybercrime reported to the feds last year, with nearly $2.8 billion in claimed losses. In its 2025 Fraud and Control Survey Report, the Association for Financial Professionals found 63 percent of organizations experienced a BEC last year.
Poking at some of the email addresses that spool out from this research reveals a number of Facebook accounts for people residing in Nigeria or in the United Arab Emirates, many of whom do not appear to have tried to mask their real-life identities. Palo Alto’s Unit 42 researchers reached a similar conclusion, noting that although a small subset of these crooks went to great lengths to conceal their identities, it was usually simple to learn their identities on social media accounts and the major messaging services.
Palo Alto said BEC actors have become far more organized over time, and that while it remains easy to find actors working as a group, the practice of using one phone number, email address or alias to register malicious infrastructure in support of multiple actors has made it far more time consuming (but not impossible) for cybersecurity and law enforcement organizations to sort out which actors committed specific crimes.
“We continue to find that SilverTerrier actors, regardless of geographical location, are often connected through only a few degrees of separation on social media platforms,” the researchers wrote.
Palo Alto has published a useful list of recommendations that organizations can adopt to minimize the incidence and impact of BEC attacks. Many of those tips are prophylactic, such as conducting regular employee security training and reviewing network security policies.
But one recommendation — getting familiar with a process known as the “financial fraud kill chain” or FFKC — bears specific mention because it offers the single best hope for BEC victims who are seeking to claw back payments made to fraudsters, and yet far too many victims don’t know it exists until it is too late.
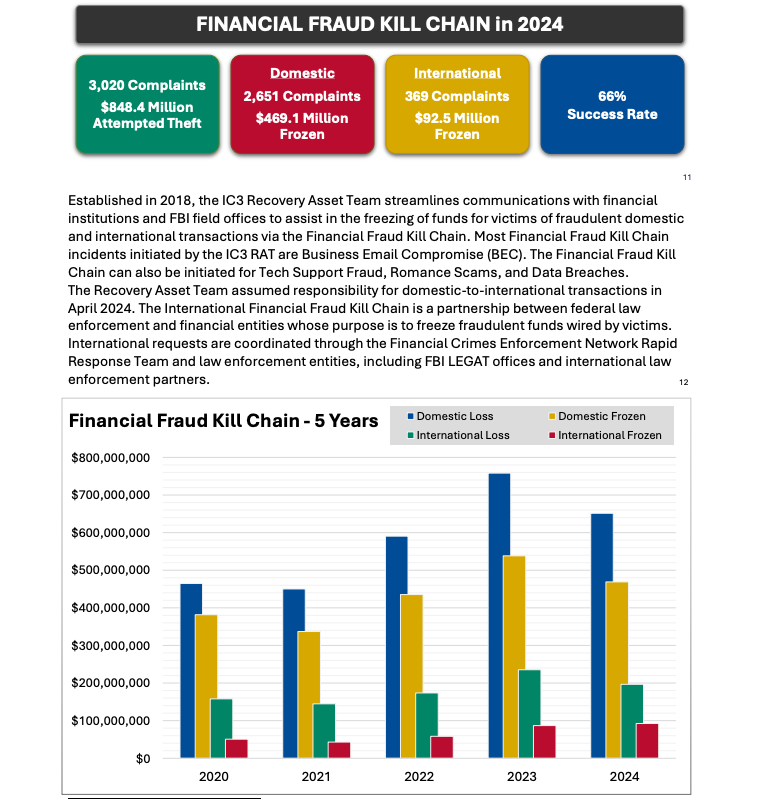
Image: ic3.gov.
As explained in this FBI primer, the International Financial Fraud Kill Chain is a partnership between federal law enforcement and financial entities whose purpose is to freeze fraudulent funds wired by victims. According to the FBI, viable victim complaints filed with ic3.gov promptly after a fraudulent transfer (generally less than 72 hours) will be automatically triaged by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
The FBI noted in its IC3 annual report (PDF) that the FFKC had a 66 percent success rate in 2024. Viable ic3.gov complaints involve losses of at least $50,000, and include all records from the victim or victim bank, as well as a completed FFKC form (provided by FinCEN) containing victim information, recipient information, bank names, account numbers, location, SWIFT, and any additional information.
Marko Elez, a 25-year-old employee at Elon Musk’s Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), has been granted access to sensitive databases at the U.S. Social Security Administration, the Treasury and Justice departments, and the Department of Homeland Security. So it should fill all Americans with a deep sense of confidence to learn that Mr. Elez over the weekend inadvertently published a private key that allowed anyone to interact directly with more than four dozen large language models (LLMs) developed by Musk’s artificial intelligence company xAI.

Image: Shutterstock, @sdx15.
On July 13, Mr. Elez committed a code script to GitHub called “agent.py” that included a private application programming interface (API) key for xAI. The inclusion of the private key was first flagged by GitGuardian, a company that specializes in detecting and remediating exposed secrets in public and proprietary environments. GitGuardian’s systems constantly scan GitHub and other code repositories for exposed API keys, and fire off automated alerts to affected users.
Philippe Caturegli, “chief hacking officer” at the security consultancy Seralys, said the exposed API key allowed access to at least 52 different LLMs used by xAI. The most recent LLM in the list was called “grok-4-0709” and was created on July 9, 2025.
Grok, the generative AI chatbot developed by xAI and integrated into Twitter/X, relies on these and other LLMs (a query to Grok before publication shows Grok currently uses Grok-3, which was launched in Feburary 2025). Earlier today, xAI announced that the Department of Defense will begin using Grok as part of a contract worth up to $200 million. The contract award came less than a week after Grok began spewing antisemitic rants and invoking Adolf Hitler.
Mr. Elez did not respond to a request for comment. The code repository containing the private xAI key was removed shortly after Caturegli notified Elez via email. However, Caturegli said the exposed API key still works and has not yet been revoked.
“If a developer can’t keep an API key private, it raises questions about how they’re handling far more sensitive government information behind closed doors,” Caturegli told KrebsOnSecurity.
Prior to joining DOGE, Marko Elez worked for a number of Musk’s companies. His DOGE career began at the Department of the Treasury, and a legal battle over DOGE’s access to Treasury databases showed Elez was sending unencrypted personal information in violation of the agency’s policies.
While still at Treasury, Elez resigned after The Wall Street Journal linked him to social media posts that advocated racism and eugenics. When Vice President J.D. Vance lobbied for Elez to be rehired, President Trump agreed and Musk reinstated him.
Since his re-hiring as a DOGE employee, Elez has been granted access to databases at one federal agency after another. TechCrunch reported in February 2025 that he was working at the Social Security Administration. In March, Business Insider found Elez was part of a DOGE detachment assigned to the Department of Labor.

Marko Elez, in a photo from a social media profile.
In April, The New York Times reported that Elez held positions at the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) bureaus, as well as the Department of Homeland Security. The Washington Post later reported that Elez, while serving as a DOGE advisor at the Department of Justice, had gained access to the Executive Office for Immigration Review’s Courts and Appeals System (EACS).
Elez is not the first DOGE worker to publish internal API keys for xAI: In May, KrebsOnSecurity detailed how another DOGE employee leaked a private xAI key on GitHub for two months, exposing LLMs that were custom made for working with internal data from Musk’s companies, including SpaceX, Tesla and Twitter/X.
Caturegli said it’s difficult to trust someone with access to confidential government systems when they can’t even manage the basics of operational security.
“One leak is a mistake,” he said. “But when the same type of sensitive key gets exposed again and again, it’s not just bad luck, it’s a sign of deeper negligence and a broken security culture.”