The story you are reading is a series of scoops nestled inside a far more urgent Internet-wide security advisory. The vulnerability at issue has been exploited for months already, and it’s time for a broader awareness of the threat. The short version is that everything you thought you knew about the security of the internal network behind your Internet router probably is now dangerously out of date.
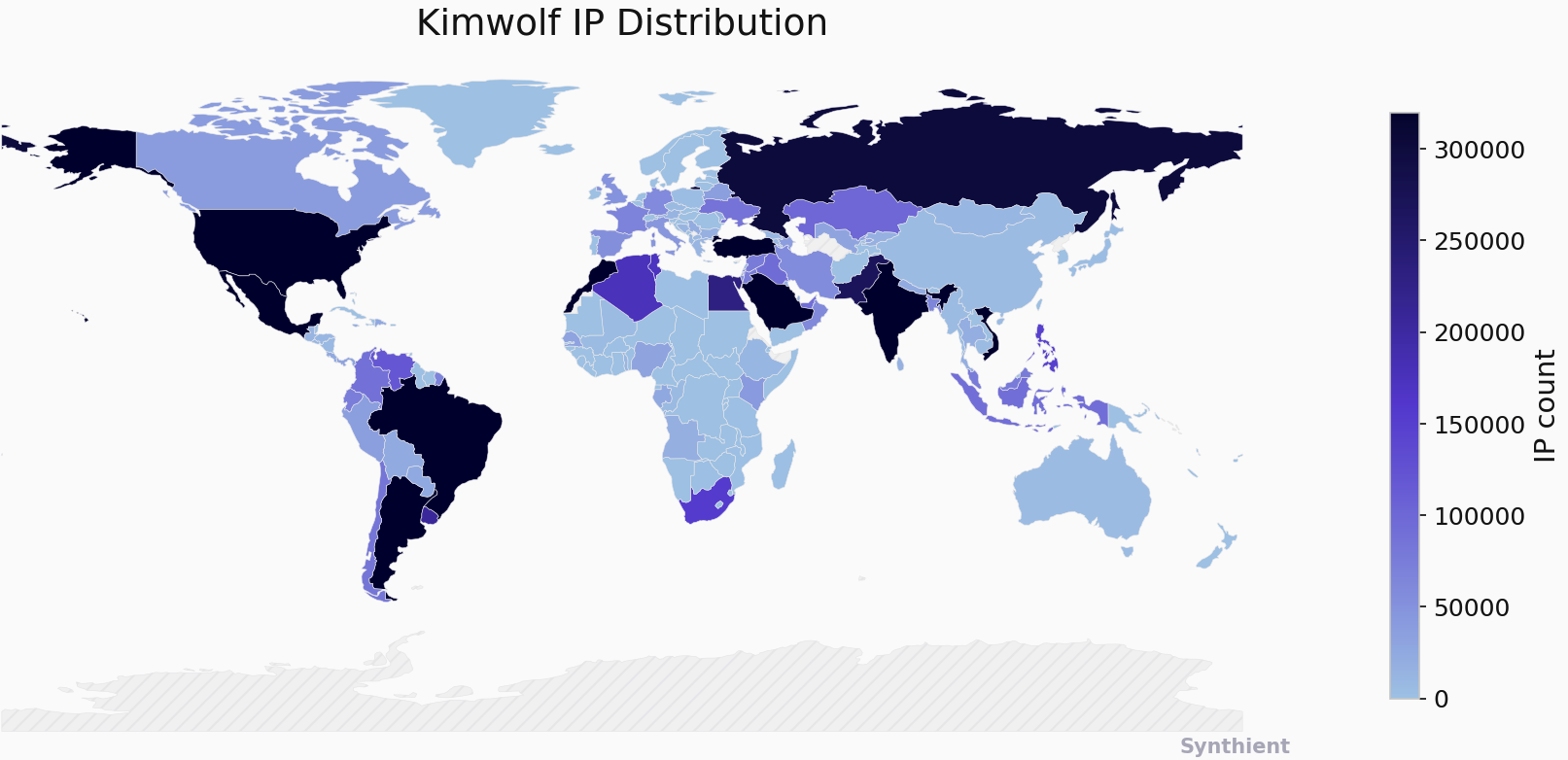
The security company Synthient currently sees more than 2 million infected Kimwolf devices distributed globally but with concentrations in Vietnam, Brazil, India, Saudi Arabia, Russia and the United States. Synthient found that two-thirds of the Kimwolf infections are Android TV boxes with no security or authentication built in.
The past few months have witnessed the explosive growth of a new botnet dubbed Kimwolf, which experts say has infected more than 2 million devices globally. The Kimwolf malware forces compromised systems to relay malicious and abusive Internet traffic — such as ad fraud, account takeover attempts and mass content scraping — and participate in crippling distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks capable of knocking nearly any website offline for days at a time.
More important than Kimwolf’s staggering size, however, is the diabolical method it uses to spread so quickly: By effectively tunneling back through various “residential proxy” networks and into the local networks of the proxy endpoints, and by further infecting devices that are hidden behind the assumed protection of the user’s firewall and Internet router.
Residential proxy networks are sold as a way for customers to anonymize and localize their Web traffic to a specific region, and the biggest of these services allow customers to route their traffic through devices in virtually any country or city around the globe.
The malware that turns an end-user’s Internet connection into a proxy node is often bundled with dodgy mobile apps and games. These residential proxy programs also are commonly installed via unofficial Android TV boxes sold by third-party merchants on popular e-commerce sites like Amazon, BestBuy, Newegg, and Walmart.
These TV boxes range in price from $40 to $400, are marketed under a dizzying range of no-name brands and model numbers, and frequently are advertised as a way to stream certain types of subscription video content for free. But there’s a hidden cost to this transaction: As we’ll explore in a moment, these TV boxes make up a considerable chunk of the estimated two million systems currently infected with Kimwolf.
Some of the unsanctioned Android TV boxes that come with residential proxy malware pre-installed. Image: Synthient.
Kimwolf also is quite good at infecting a range of Internet-connected digital photo frames that likewise are abundant at major e-commerce websites. In November 2025, researchers from Quokka published a report (PDF) detailing serious security issues in Android-based digital picture frames running the Uhale app — including Amazon’s bestselling digital frame as of March 2025.
There are two major security problems with these photo frames and unofficial Android TV boxes. The first is that a considerable percentage of them come with malware pre-installed, or else require the user to download an unofficial Android App Store and malware in order to use the device for its stated purpose (video content piracy). The most typical of these uninvited guests are small programs that turn the device into a residential proxy node that is resold to others.
The second big security nightmare with these photo frames and unsanctioned Android TV boxes is that they rely on a handful of Internet-connected microcomputer boards that have no discernible security or authentication requirements built-in. In other words, if you are on the same network as one or more of these devices, you can likely compromise them simultaneously by issuing a single command across the network.
The combination of these two security realities came to the fore in October 2025, when an undergraduate computer science student at the Rochester Institute of Technology began closely tracking Kimwolf’s growth, and interacting directly with its apparent creators on a daily basis.
Benjamin Brundage is the 22-year-old founder of the security firm Synthient, a startup that helps companies detect proxy networks and learn how those networks are being abused. Conducting much of his research into Kimwolf while studying for final exams, Brundage told KrebsOnSecurity in late October 2025 he suspected Kimwolf was a new Android-based variant of Aisuru, a botnet that was incorrectly blamed for a number of record-smashing DDoS attacks last fall.
Brundage says Kimwolf grew rapidly by abusing a glaring vulnerability in many of the world’s largest residential proxy services. The crux of the weakness, he explained, was that these proxy services weren’t doing enough to prevent their customers from forwarding requests to internal servers of the individual proxy endpoints.
Most proxy services take basic steps to prevent their paying customers from “going upstream” into the local network of proxy endpoints, by explicitly denying requests for local addresses specified in RFC-1918, including the well-known Network Address Translation (NAT) ranges 10.0.0.0/8, 192.168.0.0/16, and 172.16.0.0/12. These ranges allow multiple devices in a private network to access the Internet using a single public IP address, and if you run any kind of home or office network, your internal address space operates within one or more of these NAT ranges.
However, Brundage discovered that the people operating Kimwolf had figured out how to talk directly to devices on the internal networks of millions of residential proxy endpoints, simply by changing their Domain Name System (DNS) settings to match those in the RFC-1918 address ranges.
“It is possible to circumvent existing domain restrictions by using DNS records that point to 192.168.0.1 or 0.0.0.0,” Brundage wrote in a first-of-its-kind security advisory sent to nearly a dozen residential proxy providers in mid-December 2025. “This grants an attacker the ability to send carefully crafted requests to the current device or a device on the local network. This is actively being exploited, with attackers leveraging this functionality to drop malware.”
As with the digital photo frames mentioned above, many of these residential proxy services run solely on mobile devices that are running some game, VPN or other app with a hidden component that turns the user’s mobile phone into a residential proxy — often without any meaningful consent.
In a report published today, Synthient said key actors involved in Kimwolf were observed monetizing the botnet through app installs, selling residential proxy bandwidth, and selling its DDoS functionality.
“Synthient expects to observe a growing interest among threat actors in gaining unrestricted access to proxy networks to infect devices, obtain network access, or access sensitive information,” the report observed. “Kimwolf highlights the risks posed by unsecured proxy networks and their viability as an attack vector.”
After purchasing a number of unofficial Android TV box models that were most heavily represented in the Kimwolf botnet, Brundage further discovered the proxy service vulnerability was only part of the reason for Kimwolf’s rapid rise: He also found virtually all of the devices he tested were shipped from the factory with a powerful feature called Android Debug Bridge (ADB) mode enabled by default.

Many of the unofficial Android TV boxes infected by Kimwolf include the ominous disclaimer: “Made in China. Overseas use only.” Image: Synthient.
ADB is a diagnostic tool intended for use solely during the manufacturing and testing processes, because it allows the devices to be remotely configured and even updated with new (and potentially malicious) firmware. However, shipping these devices with ADB turned on creates a security nightmare because in this state they constantly listen for and accept unauthenticated connection requests.
For example, opening a command prompt and typing “adb connect” along with a vulnerable device’s (local) IP address followed immediately by “:5555” will very quickly offer unrestricted “super user” administrative access.
Brundage said by early December, he’d identified a one-to-one overlap between new Kimwolf infections and proxy IP addresses offered for rent by China-based IPIDEA, currently the world’s largest residential proxy network by all accounts.
“Kimwolf has almost doubled in size this past week, just by exploiting IPIDEA’s proxy pool,” Brundage told KrebsOnSecurity in early December as he was preparing to notify IPIDEA and 10 other proxy providers about his research.
Brundage said Synthient first confirmed on December 1, 2025 that the Kimwolf botnet operators were tunneling back through IPIDEA’s proxy network and into the local networks of systems running IPIDEA’s proxy software. The attackers dropped the malware payload by directing infected systems to visit a specific Internet address and to call out the pass phrase “krebsfiveheadindustries” in order to unlock the malicious download.
On December 30, Synthient said it was tracking roughly 2 million IPIDEA addresses exploited by Kimwolf in the previous week. Brundage said he has witnessed Kimwolf rebuilding itself after one recent takedown effort targeting its control servers — from almost nothing to two million infected systems just by tunneling through proxy endpoints on IPIDEA for a couple of days.
Brundage said IPIDEA has a seemingly inexhaustible supply of new proxies, advertising access to more than 100 million residential proxy endpoints around the globe in the past week alone. Analyzing the exposed devices that were part of IPIDEA’s proxy pool, Synthient said it found more than two-thirds were Android devices that could be compromised with no authentication needed.
After charting a tight overlap in Kimwolf-infected IP addresses and those sold by IPIDEA, Brundage was eager to make his findings public: The vulnerability had clearly been exploited for several months, although it appeared that only a handful of cybercrime actors were aware of the capability. But he also knew that going public without giving vulnerable proxy providers an opportunity to understand and patch it would only lead to more mass abuse of these services by additional cybercriminal groups.
On December 17, Brundage sent a security notification to all 11 of the apparently affected proxy providers, hoping to give each at least a few weeks to acknowledge and address the core problems identified in his report before he went public. Many proxy providers who received the notification were resellers of IPIDEA that white-labeled the company’s service.
KrebsOnSecurity first sought comment from IPIDEA in October 2025, in reporting on a story about how the proxy network appeared to have benefitted from the rise of the Aisuru botnet, whose administrators appeared to shift from using the botnet primarily for DDoS attacks to simply installing IPIDEA’s proxy program, among others.
On December 25, KrebsOnSecurity received an email from an IPIDEA employee identified only as “Oliver,” who said allegations that IPIDEA had benefitted from Aisuru’s rise were baseless.
“After comprehensively verifying IP traceability records and supplier cooperation agreements, we found no association between any of our IP resources and the Aisuru botnet, nor have we received any notifications from authoritative institutions regarding our IPs being involved in malicious activities,” Oliver wrote. “In addition, for external cooperation, we implement a three-level review mechanism for suppliers, covering qualification verification, resource legality authentication and continuous dynamic monitoring, to ensure no compliance risks throughout the entire cooperation process.”
“IPIDEA firmly opposes all forms of unfair competition and malicious smearing in the industry, always participates in market competition with compliant operation and honest cooperation, and also calls on the entire industry to jointly abandon irregular and unethical behaviors and build a clean and fair market ecosystem,” Oliver continued.
Meanwhile, the same day that Oliver’s email arrived, Brundage shared a response he’d just received from IPIDEA’s security officer, who identified himself only by the first name Byron. The security officer said IPIDEA had made a number of important security changes to its residential proxy service to address the vulnerability identified in Brundage’s report.
“By design, the proxy service does not allow access to any internal or local address space,” Byron explained. “This issue was traced to a legacy module used solely for testing and debugging purposes, which did not fully inherit the internal network access restrictions. Under specific conditions, this module could be abused to reach internal resources. The affected paths have now been fully blocked and the module has been taken offline.”
Byron told Brundage IPIDEA also instituted multiple mitigations for blocking DNS resolution to internal (NAT) IP ranges, and that it was now blocking proxy endpoints from forwarding traffic on “high-risk” ports “to prevent abuse of the service for scanning, lateral movement, or access to internal services.”

An excerpt from an email sent by IPIDEA’s security officer in response to Brundage’s vulnerability notification. Click to enlarge.
Brundage said IPIDEA appears to have successfully patched the vulnerabilities he identified. He also noted he never observed the Kimwolf actors targeting proxy services other than IPIDEA, which has not responded to requests for comment.
Riley Kilmer is founder of Spur.us, a technology firm that helps companies identify and filter out proxy traffic. Kilmer said Spur has tested Brundage’s findings and confirmed that IPIDEA and all of its affiliate resellers indeed allowed full and unfiltered access to the local LAN.
Kilmer said one model of unsanctioned Android TV boxes that is especially popular — the Superbox, which we profiled in November’s Is Your Android TV Streaming Box Part of a Botnet? — leaves Android Debug Mode running on localhost:5555.
“And since Superbox turns the IP into an IPIDEA proxy, a bad actor just has to use the proxy to localhost on that port and install whatever bad SDKs [software development kits] they want,” Kilmer told KrebsOnSecurity.
Superbox media streaming boxes for sale on Walmart.com.
Both Brundage and Kilmer say IPIDEA appears to be the second or third reincarnation of a residential proxy network formerly known as 911S5 Proxy, a service that operated between 2014 and 2022 and was wildly popular on cybercrime forums. 911S5 Proxy imploded a week after KrebsOnSecurity published a deep dive on the service’s sketchy origins and leadership in China.
In that 2022 profile, we cited work by researchers at the University of Sherbrooke in Canada who were studying the threat 911S5 could pose to internal corporate networks. The researchers noted that “the infection of a node enables the 911S5 user to access shared resources on the network such as local intranet portals or other services.”
“It also enables the end user to probe the LAN network of the infected node,” the researchers explained. “Using the internal router, it would be possible to poison the DNS cache of the LAN router of the infected node, enabling further attacks.”
911S5 initially responded to our reporting in 2022 by claiming it was conducting a top-down security review of the service. But the proxy service abruptly closed up shop just one week later, saying a malicious hacker had destroyed all of the company’s customer and payment records. In July 2024, The U.S. Department of the Treasury sanctioned the alleged creators of 911S5, and the U.S. Department of Justice arrested the Chinese national named in my 2022 profile of the proxy service.
Kilmer said IPIDEA also operates a sister service called 922 Proxy, which the company has pitched from Day One as a seamless alternative to 911S5 Proxy.
“You cannot tell me they don’t want the 911 customers by calling it that,” Kilmer said.
Among the recipients of Synthient’s notification was the proxy giant Oxylabs. Brundage shared an email he received from Oxylabs’ security team on December 31, which acknowledged Oxylabs had started rolling out security modifications to address the vulnerabilities described in Synthient’s report.
Reached for comment, Oxylabs confirmed they “have implemented changes that now eliminate the ability to bypass the blocklist and forward requests to private network addresses using a controlled domain.” But it said there is no evidence that Kimwolf or other other attackers exploited its network.
“In parallel, we reviewed the domains identified in the reported exploitation activity and did not observe traffic associated with them,” the Oxylabs statement continued. “Based on this review, there is no indication that our residential network was impacted by these activities.”
Consider the following scenario, in which the mere act of allowing someone to use your Wi-Fi network could lead to a Kimwolf botnet infection. In this example, a friend or family member comes to stay with you for a few days, and you grant them access to your Wi-Fi without knowing that their mobile phone is infected with an app that turns the device into a residential proxy node. At that point, your home’s public IP address will show up for rent at the website of some residential proxy provider.
Miscreants like those behind Kimwolf then use residential proxy services online to access that proxy node on your IP, tunnel back through it and into your local area network (LAN), and automatically scan the internal network for devices with Android Debug Bridge mode turned on.
By the time your guest has packed up their things, said their goodbyes and disconnected from your Wi-Fi, you now have two devices on your local network — a digital photo frame and an unsanctioned Android TV box — that are infected with Kimwolf. You may have never intended for these devices to be exposed to the larger Internet, and yet there you are.
Here’s another possible nightmare scenario: Attackers use their access to proxy networks to modify your Internet router’s settings so that it relies on malicious DNS servers controlled by the attackers — allowing them to control where your Web browser goes when it requests a website. Think that’s far-fetched? Recall the DNSChanger malware from 2012 that infected more than a half-million routers with search-hijacking malware, and ultimately spawned an entire security industry working group focused on containing and eradicating it.
Much of what is published so far on Kimwolf has come from the Chinese security firm XLab, which was the first to chronicle the rise of the Aisuru botnet in late 2024. In its latest blog post, XLab said it began tracking Kimwolf on October 24, when the botnet’s control servers were swamping Cloudflare’s DNS servers with lookups for the distinctive domain 14emeliaterracewestroxburyma02132[.]su.
This domain and others connected to early Kimwolf variants spent several weeks topping Cloudflare’s chart of the Internet’s most sought-after domains, edging out Google.com and Apple.com of their rightful spots in the top 5 most-requested domains. That’s because during that time Kimwolf was asking its millions of bots to check in frequently using Cloudflare’s DNS servers.

The Chinese security firm XLab found the Kimwolf botnet had enslaved between 1.8 and 2 million devices, with heavy concentrations in Brazil, India, The United States of America and Argentina. Image: blog.xLab.qianxin.com
It is clear from reading the XLab report that KrebsOnSecurity (and security experts) probably erred in misattributing some of Kimwolf’s early activities to the Aisuru botnet, which appears to be operated by a different group entirely. IPDEA may have been truthful when it said it had no affiliation with the Aisuru botnet, but Brundage’s data left no doubt that its proxy service clearly was being massively abused by Aisuru’s Android variant, Kimwolf.
XLab said Kimwolf has infected at least 1.8 million devices, and has shown it is able to rebuild itself quickly from scratch.
“Analysis indicates that Kimwolf’s primary infection targets are TV boxes deployed in residential network environments,” XLab researchers wrote. “Since residential networks usually adopt dynamic IP allocation mechanisms, the public IPs of devices change over time, so the true scale of infected devices cannot be accurately measured solely by the quantity of IPs. In other words, the cumulative observation of 2.7 million IP addresses does not equate to 2.7 million infected devices.”
XLab said measuring Kimwolf’s size also is difficult because infected devices are distributed across multiple global time zones. “Affected by time zone differences and usage habits (e.g., turning off devices at night, not using TV boxes during holidays, etc.), these devices are not online simultaneously, further increasing the difficulty of comprehensive observation through a single time window,” the blog post observed.
XLab noted that the Kimwolf author shows an almost ‘obsessive’ fixation” on Yours Truly, apparently leaving “easter eggs” related to my name in multiple places through the botnet’s code and communications:

Image: XLAB.
One frustrating aspect of threats like Kimwolf is that in most cases it is not easy for the average user to determine if there are any devices on their internal network which may be vulnerable to threats like Kimwolf and/or already infected with residential proxy malware.
Let’s assume that through years of security training or some dark magic you can successfully identify that residential proxy activity on your internal network was linked to a specific mobile device inside your house: From there, you’d still need to isolate and remove the app or unwanted component that is turning the device into a residential proxy.
Also, the tooling and knowledge needed to achieve this kind of visibility just isn’t there from an average consumer standpoint. The work that it takes to configure your network so you can see and interpret logs of all traffic coming in and out is largely beyond the skillset of most Internet users (and, I’d wager, many security experts). But it’s a topic worth exploring in an upcoming story.
Happily, Synthient has erected a page on its website that will state whether a visitor’s public Internet address was seen among those of Kimwolf-infected systems. Brundage also has compiled a list of the unofficial Android TV boxes that are most highly represented in the Kimwolf botnet.
If you own a TV box that matches one of these model names and/or numbers, please just rip it out of your network. If you encounter one of these devices on the network of a family member or friend, send them a link to this story and explain that it’s not worth the potential hassle and harm created by keeping them plugged in.
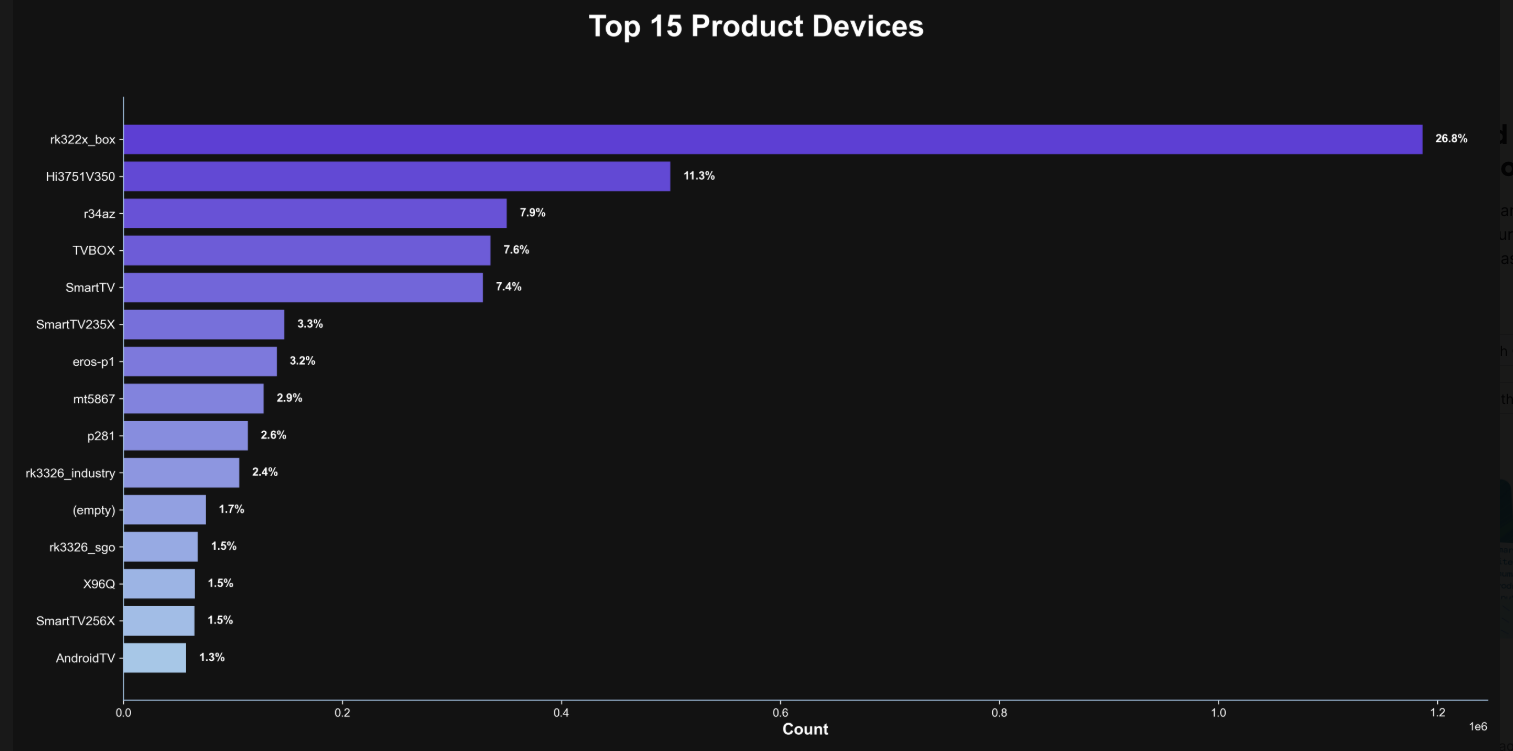
The top 15 product devices represented in the Kimwolf botnet, according to Synthient.
Chad Seaman is a principal security researcher with Akamai Technologies. Seaman said he wants more consumers to be wary of these pseudo Android TV boxes to the point where they avoid them altogether.
“I want the consumer to be paranoid of these crappy devices and of these residential proxy schemes,” he said. “We need to highlight why they’re dangerous to everyone and to the individual. The whole security model where people think their LAN (Local Internal Network) is safe, that there aren’t any bad guys on the LAN so it can’t be that dangerous is just really outdated now.”
“The idea that an app can enable this type of abuse on my network and other networks, that should really give you pause,” about which devices to allow onto your local network, Seaman said. “And it’s not just Android devices here. Some of these proxy services have SDKs for Mac and Windows, and the iPhone. It could be running something that inadvertently cracks open your network and lets countless random people inside.”
In July 2025, Google filed a “John Doe” lawsuit (PDF) against 25 unidentified defendants collectively dubbed the “BadBox 2.0 Enterprise,” which Google described as a botnet of over ten million unsanctioned Android streaming devices engaged in advertising fraud. Google said the BADBOX 2.0 botnet, in addition to compromising multiple types of devices prior to purchase, also can infect devices by requiring the download of malicious apps from unofficial marketplaces.
Google’s lawsuit came on the heels of a June 2025 advisory from the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which warned that cyber criminals were gaining unauthorized access to home networks by either configuring the products with malware prior to the user’s purchase, or infecting the device as it downloads required applications that contain backdoors — usually during the set-up process.
The FBI said BADBOX 2.0 was discovered after the original BADBOX campaign was disrupted in 2024. The original BADBOX was identified in 2023, and primarily consisted of Android operating system devices that were compromised with backdoor malware prior to purchase.
Lindsay Kaye is vice president of threat intelligence at HUMAN Security, a company that worked closely on the BADBOX investigations. Kaye said the BADBOX botnets and the residential proxy networks that rode on top of compromised devices were detected because they enabled a ridiculous amount of advertising fraud, as well as ticket scalping, retail fraud, account takeovers and content scraping.
Kaye said consumers should stick to known brands when it comes to purchasing things that require a wired or wireless connection.
“If people are asking what they can do to avoid being victimized by proxies, it’s safest to stick with name brands,” Kaye said. “Anything promising something for free or low-cost, or giving you something for nothing just isn’t worth it. And be careful about what apps you allow on your phone.”
Many wireless routers these days make it relatively easy to deploy a “Guest” wireless network on-the-fly. Doing so allows your guests to browse the Internet just fine but it blocks their device from being able to talk to other devices on the local network — such as shared folders, printers and drives. If someone — a friend, family member, or contractor — requests access to your network, give them the guest Wi-Fi network credentials if you have that option.
There is a small but vocal pro-piracy camp that is almost condescendingly dismissive of the security threats posed by these unsanctioned Android TV boxes. These tech purists positively chafe at the idea of people wholesale discarding one of these TV boxes. A common refrain from this camp is that Internet-connected devices are not inherently bad or good, and that even factory-infected boxes can be flashed with new firmware or custom ROMs that contain no known dodgy software.
However, it’s important to point out that the majority of people buying these devices are not security or hardware experts; the devices are sought out because they dangle something of value for “free.” Most buyers have no idea of the bargain they’re making when plugging one of these dodgy TV boxes into their network.
It is somewhat remarkable that we haven’t yet seen the entertainment industry applying more visible pressure on the major e-commerce vendors to stop peddling this insecure and actively malicious hardware that is largely made and marketed for video piracy. These TV boxes are a public nuisance for bundling malicious software while having no apparent security or authentication built-in, and these two qualities make them an attractive nuisance for cybercriminals.
Stay tuned for Part II in this series, which will poke through clues left behind by the people who appear to have built Kimwolf and benefited from it the most.
Microsoft today released updates to fix more than 100 security flaws in its Windows operating systems and other software. At least 13 of the bugs received Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating, meaning they could be abused by malware or malcontents to gain remote access to a Windows system with little or no help from users.

August’s patch batch from Redmond includes an update for CVE-2025-53786, a vulnerability that allows an attacker to pivot from a compromised Microsoft Exchange Server directly into an organization’s cloud environment, potentially gaining control over Exchange Online and other connected Microsoft Office 365 services. Microsoft first warned about this bug on Aug. 6, saying it affects Exchange Server 2016 and Exchange Server 2019, as well as its flagship Exchange Server Subscription Edition.
Ben McCarthy, lead cyber security engineer at Immersive, said a rough search reveals approximately 29,000 Exchange servers publicly facing on the internet that are vulnerable to this issue, with many of them likely to have even older vulnerabilities.
McCarthy said the fix for CVE-2025-53786 requires more than just installing a patch, such as following Microsoft’s manual instructions for creating a dedicated service to oversee and lock down the hybrid connection.
“In effect, this vulnerability turns a significant on-premise Exchange breach into a full-blown, difficult-to-detect cloud compromise with effectively living off the land techniques which are always harder to detect for defensive teams,” McCarthy said.
CVE-2025-53779 is a weakness in the Windows Kerberos authentication system that allows an unauthenticated attacker to gain domain administrator privileges. Microsoft credits the discovery of the flaw to Akamai researcher Yuval Gordon, who dubbed it “BadSuccessor” in a May 2025 blog post. The attack exploits a weakness in “delegated Managed Service Account” or dMSA — a feature that was introduced in Windows Server 2025.
Some of the critical flaws addressed this month with the highest severity (between 9.0 and 9.9 CVSS scores) include a remote code execution bug in the Windows GDI+ component that handles graphics rendering (CVE-2025-53766) and CVE-2025-50165, another graphics rendering weakness. Another critical patch involves CVE-2025-53733, a vulnerability in Microsoft Word that can be exploited without user interaction and triggered through the Preview Pane.
One final critical bug tackled this month deserves attention: CVE-2025-53778, a bug in Windows NTLM, a core function of how Windows systems handle network authentication. According to Microsoft, the flaw could allow an attacker with low-level network access and basic user privileges to exploit NTLM and elevate to SYSTEM-level access — the highest level of privilege in Windows. Microsoft rates the exploitation of this bug as “more likely,” although there is no evidence the vulnerability is being exploited at the moment.
Feel free to holler in the comments if you experience problems installing any of these updates. As ever, the SANS Internet Storm Center has its useful breakdown of the Microsoft patches indexed by severity and CVSS score, and AskWoody.com is keeping an eye out for Windows patches that may cause problems for enterprises and end users.
Windows 10 users out there likely have noticed by now that Microsoft really wants you to upgrade to Windows 11. The reason is that after the Patch Tuesday on October 14, 2025, Microsoft will stop shipping free security updates for Windows 10 computers. The trouble is, many PCs running Windows 10 do not meet the hardware specifications required to install Windows 11 (or they do, but just barely).
If the experience with Windows XP is any indicator, many of these older computers will wind up in landfills or else will be left running in an unpatched state. But if your Windows 10 PC doesn’t have the hardware chops to run Windows 11 and you’d still like to get some use out of it safely, consider installing a newbie-friendly version of Linux, like Linux Mint.
Like most modern Linux versions, Mint will run on anything with a 64-bit CPU that has at least 2GB of memory, although 4GB is recommended. In other words, it will run on almost any computer produced in the last decade.
There are many versions of Linux available, but Linux Mint is likely to be the most intuitive interface for regular Windows users, and it is largely configurable without any fuss at the text-only command-line prompt. Mint and other flavors of Linux come with LibreOffice, which is an open source suite of tools that includes applications similar to Microsoft Office, and it can open, edit and save documents as Microsoft Office files.
If you’d prefer to give Linux a test drive before installing it on a Windows PC, you can always just download it to a removable USB drive. From there, reboot the computer (with the removable drive plugged in) and select the option at startup to run the operating system from the external USB drive. If you don’t see an option for that after restarting, try restarting again and hitting the F8 button, which should open a list of bootable drives. Here’s a fairly thorough tutorial that walks through exactly how to do all this.
And if this is your first time trying out Linux, relax and have fun: The nice thing about a “live” version of Linux (as it’s called when the operating system is run from a removable drive such as a CD or a USB stick) is that none of your changes persist after a reboot. Even if you somehow manage to break something, a restart will return the system back to its original state.
Microsoft today released security updates to fix at least 67 vulnerabilities in its Windows operating systems and software. Redmond warns that one of the flaws is already under active attack, and that software blueprints showing how to exploit a pervasive Windows bug patched this month are now public.

The sole zero-day flaw this month is CVE-2025-33053, a remote code execution flaw in the Windows implementation of WebDAV — an HTTP extension that lets users remotely manage files and directories on a server. While WebDAV isn’t enabled by default in Windows, its presence in legacy or specialized systems still makes it a relevant target, said Seth Hoyt, senior security engineer at Automox.
Adam Barnett, lead software engineer at Rapid7, said Microsoft’s advisory for CVE-2025-33053 does not mention that the Windows implementation of WebDAV is listed as deprecated since November 2023, which in practical terms means that the WebClient service no longer starts by default.
“The advisory also has attack complexity as low, which means that exploitation does not require preparation of the target environment in any way that is beyond the attacker’s control,” Barnett said. “Exploitation relies on the user clicking a malicious link. It’s not clear how an asset would be immediately vulnerable if the service isn’t running, but all versions of Windows receive a patch, including those released since the deprecation of WebClient, like Server 2025 and Windows 11 24H2.”
Microsoft warns that an “elevation of privilege” vulnerability in the Windows Server Message Block (SMB) client (CVE-2025-33073) is likely to be exploited, given that proof-of-concept code for this bug is now public. CVE-2025-33073 has a CVSS risk score of 8.8 (out of 10), and exploitation of the flaw leads to the attacker gaining “SYSTEM” level control over a vulnerable PC.
“What makes this especially dangerous is that no further user interaction is required after the initial connection—something attackers can often trigger without the user realizing it,” said Alex Vovk, co-founder and CEO of Action1. “Given the high privilege level and ease of exploitation, this flaw poses a significant risk to Windows environments. The scope of affected systems is extensive, as SMB is a core Windows protocol used for file and printer sharing and inter-process communication.”
Beyond these highlights, 10 of the vulnerabilities fixed this month were rated “critical” by Microsoft, including eight remote code execution flaws.
Notably absent from this month’s patch batch is a fix for a newly discovered weakness in Windows Server 2025 that allows attackers to act with the privileges of any user in Active Directory. The bug, dubbed “BadSuccessor,” was publicly disclosed by researchers at Akamai on May 21, and several public proof-of-concepts are now available. Tenable’s Satnam Narang said organizations that have at least one Windows Server 2025 domain controller should review permissions for principals and limit those permissions as much as possible.
Adobe has released updates for Acrobat Reader and six other products addressing at least 259 vulnerabilities, most of them in an update for Experience Manager. Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome both recently released security updates that require a restart of the browser to take effect. The latest Chrome update fixes two zero-day exploits in the browser (CVE-2025-5419 and CVE-2025-4664).
For a detailed breakdown on the individual security updates released by Microsoft today, check out the Patch Tuesday roundup from the SANS Internet Storm Center. Action 1 has a breakdown of patches from Microsoft and a raft of other software vendors releasing fixes this month. As always, please back up your system and/or data before patching, and feel free to drop a note in the comments if you run into any problems applying these updates.
KrebsOnSecurity last week was hit by a near record distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack that clocked in at more than 6.3 terabits of data per second (a terabit is one trillion bits of data). The brief attack appears to have been a test run for a massive new Internet of Things (IoT) botnet capable of launching crippling digital assaults that few web destinations can withstand. Read on for more about the botnet, the attack, and the apparent creator of this global menace.

For reference, the 6.3 Tbps attack last week was ten times the size of the assault launched against this site in 2016 by the Mirai IoT botnet, which held KrebsOnSecurity offline for nearly four days. The 2016 assault was so large that Akamai – which was providing pro-bono DDoS protection for KrebsOnSecurity at the time — asked me to leave their service because the attack was causing problems for their paying customers.
Since the Mirai attack, KrebsOnSecurity.com has been behind the protection of Project Shield, a free DDoS defense service that Google provides to websites offering news, human rights, and election-related content. Google Security Engineer Damian Menscher told KrebsOnSecurity the May 12 attack was the largest Google has ever handled. In terms of sheer size, it is second only to a very similar attack that Cloudflare mitigated and wrote about in April.
After comparing notes with Cloudflare, Menscher said the botnet that launched both attacks bears the fingerprints of Aisuru, a digital siege machine that first surfaced less than a year ago. Menscher said the attack on KrebsOnSecurity lasted less than a minute, hurling large UDP data packets at random ports at a rate of approximately 585 million data packets per second.
“It was the type of attack normally designed to overwhelm network links,” Menscher said, referring to the throughput connections between and among various Internet service providers (ISPs). “For most companies, this size of attack would kill them.”
The Aisuru botnet comprises a globally-dispersed collection of hacked IoT devices, including routers, digital video recorders and other systems that are commandeered via default passwords or software vulnerabilities. As documented by researchers at QiAnXin XLab, the botnet was first identified in an August 2024 attack on a large gaming platform.
Aisuru reportedly went quiet after that exposure, only to reappear in November with even more firepower and software exploits. In a January 2025 report, XLab found the new and improved Aisuru (a.k.a. “Airashi“) had incorporated a previously unknown zero-day vulnerability in Cambium Networks cnPilot routers.
The people behind the Aisuru botnet have been peddling access to their DDoS machine in public Telegram chat channels that are closely monitored by multiple security firms. In August 2024, the botnet was rented out in subscription tiers ranging from $150 per day to $600 per week, offering attacks of up to two terabits per second.
“You may not attack any measurement walls, healthcare facilities, schools or government sites,” read a notice posted on Telegram by the Aisuru botnet owners in August 2024.
Interested parties were told to contact the Telegram handle “@yfork” to purchase a subscription. The account @yfork previously used the nickname “Forky,” an identity that has been posting to public DDoS-focused Telegram channels since 2021.
According to the FBI, Forky’s DDoS-for-hire domains have been seized in multiple law enforcement operations over the years. Last year, Forky said on Telegram he was selling the domain stresser[.]best, which saw its servers seized by the FBI in 2022 as part of an ongoing international law enforcement effort aimed at diminishing the supply of and demand for DDoS-for-hire services.
“The operator of this service, who calls himself ‘Forky,’ operates a Telegram channel to advertise features and communicate with current and prospective DDoS customers,” reads an FBI seizure warrant (PDF) issued for stresser[.]best. The FBI warrant stated that on the same day the seizures were announced, Forky posted a link to a story on this blog that detailed the domain seizure operation, adding the comment, “We are buying our new domains right now.”
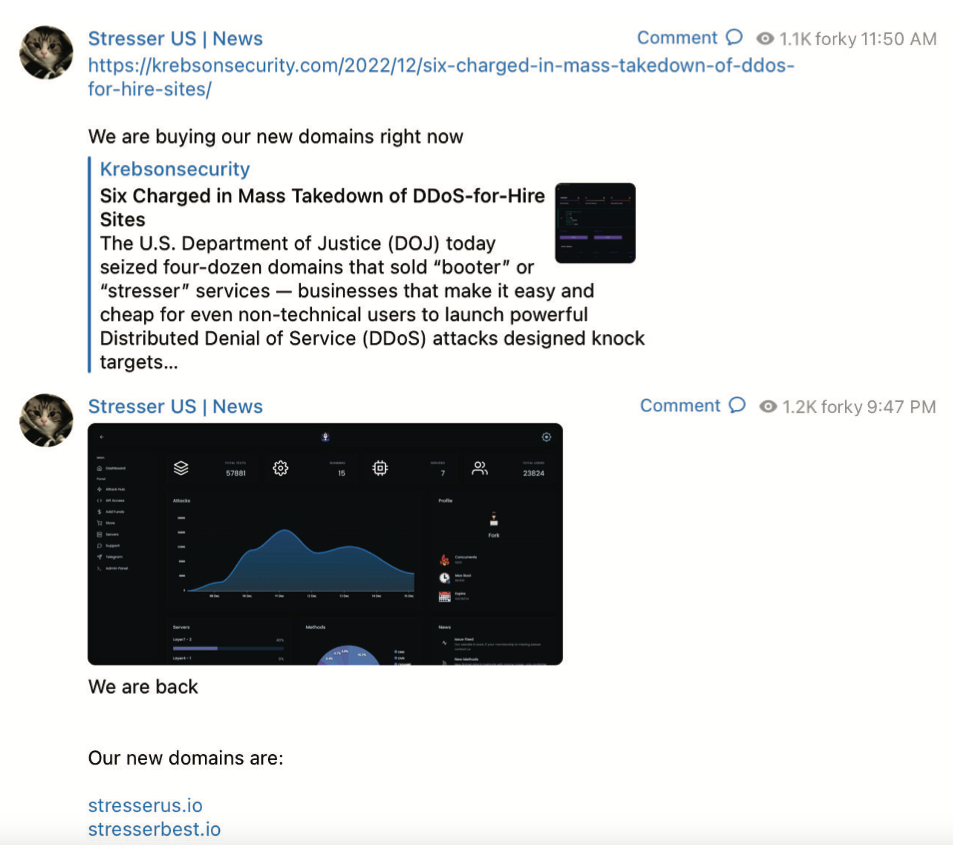
A screenshot from the FBI’s seizure warrant for Forky’s DDoS-for-hire domains shows Forky announcing the resurrection of their service at new domains.
Approximately ten hours later, Forky posted again, including a screenshot of the stresser[.]best user dashboard, instructing customers to use their saved passwords for the old website on the new one.
A review of Forky’s posts to public Telegram channels — as indexed by the cyber intelligence firms Unit 221B and Flashpoint — reveals a 21-year-old individual who claims to reside in Brazil [full disclosure: Flashpoint is currently an advertiser on this blog].
Since late 2022, Forky’s posts have frequently promoted a DDoS mitigation company and ISP that he operates called botshield[.]io. The Botshield website is connected to a business entity registered in the United Kingdom called Botshield LTD, which lists a 21-year-old woman from Sao Paulo, Brazil as the director. Internet routing records indicate Botshield (AS213613) currently controls several hundred Internet addresses that were allocated to the company earlier this year.
Domaintools.com reports that botshield[.]io was registered in July 2022 to a Kaike Southier Leite in Sao Paulo. A LinkedIn profile by the same name says this individual is a network specialist from Brazil who works in “the planning and implementation of robust network infrastructures, with a focus on security, DDoS mitigation, colocation and cloud server services.”

Image: Jaclyn Vernace / Shutterstock.com.
In his posts to public Telegram chat channels, Forky has hardly attempted to conceal his whereabouts or identity. In countless chat conversations indexed by Unit 221B, Forky could be seen talking about everyday life in Brazil, often remarking on the extremely low or high prices in Brazil for a range of goods, from computer and networking gear to narcotics and food.
Reached via Telegram, Forky claimed he was “not involved in this type of illegal actions for years now,” and that the project had been taken over by other unspecified developers. Forky initially told KrebsOnSecurity he had been out of the botnet scene for years, only to concede this wasn’t true when presented with public posts on Telegram from late last year that clearly showed otherwise.
Forky denied being involved in the attack on KrebsOnSecurity, but acknowledged that he helped to develop and market the Aisuru botnet. Forky claims he is now merely a staff member for the Aisuru botnet team, and that he stopped running the botnet roughly two months ago after starting a family. Forky also said the woman named as director of Botshield is related to him.
Forky offered equivocal, evasive responses to a number of questions about the Aisuru botnet and his business endeavors. But on one point he was crystal clear:
“I have zero fear about you, the FBI, or Interpol,” Forky said, asserting that he is now almost entirely focused on their hosting business — Botshield.
Forky declined to discuss the makeup of his ISP’s clientele, or to clarify whether Botshield was more of a hosting provider or a DDoS mitigation firm. However, Forky has posted on Telegram about Botshield successfully mitigating large DDoS attacks launched against other DDoS-for-hire services.
DomainTools finds the same Sao Paulo street address in the registration records for botshield[.]io was used to register several other domains, including cant-mitigate[.]us. The email address in the WHOIS records for that domain is forkcontato@gmail.com, which DomainTools says was used to register the domain for the now-defunct DDoS-for-hire service stresser[.]us, one of the domains seized in the FBI’s 2023 crackdown.
On May 8, 2023, the U.S. Department of Justice announced the seizure of stresser[.]us, along with a dozen other domains offering DDoS services. The DOJ said ten of the 13 domains were reincarnations of services that were seized during a prior sweep in December, which targeted 48 top stresser services (also known as “booters”).
Forky claimed he could find out who attacked my site with Aisuru. But when pressed a day later on the question, Forky said he’d come up empty-handed.
“I tried to ask around, all the big guys are not retarded enough to attack you,” Forky explained in an interview on Telegram. “I didn’t have anything to do with it. But you are welcome to write the story and try to put the blame on me.”
The 6.3 Tbps attack last week caused no visible disruption to this site, in part because it was so brief — lasting approximately 45 seconds. DDoS attacks of such magnitude and brevity typically are produced when botnet operators wish to test or demonstrate their firepower for the benefit of potential buyers. Indeed, Google’s Menscher said it is likely that both the May 12 attack and the slightly larger 6.5 Tbps attack against Cloudflare last month were simply tests of the same botnet’s capabilities.
In many ways, the threat posed by the Aisuru/Airashi botnet is reminiscent of Mirai, an innovative IoT malware strain that emerged in the summer of 2016 and successfully out-competed virtually all other IoT malware strains in existence at the time.
As first revealed by KrebsOnSecurity in January 2017, the Mirai authors were two U.S. men who co-ran a DDoS mitigation service — even as they were selling far more lucrative DDoS-for-hire services using the most powerful botnet on the planet.
Less than a week after the Mirai botnet was used in a days-long DDoS against KrebsOnSecurity, the Mirai authors published the source code to their botnet so that they would not be the only ones in possession of it in the event of their arrest by federal investigators.
Ironically, the leaking of the Mirai source is precisely what led to the eventual unmasking and arrest of the Mirai authors, who went on to serve probation sentences that required them to consult with FBI investigators on DDoS investigations. But that leak also rapidly led to the creation of dozens of Mirai botnet clones, many of which were harnessed to fuel their own powerful DDoS-for-hire services.
Menscher told KrebsOnSecurity that as counterintuitive as it may sound, the Internet as a whole would probably be better off if the source code for Aisuru became public knowledge. After all, he said, the people behind Aisuru are in constant competition with other IoT botnet operators who are all striving to commandeer a finite number of vulnerable IoT devices globally.
Such a development would almost certainly cause a proliferation of Aisuru botnet clones, he said, but at least then the overall firepower from each individual botnet would be greatly diminished — or at least within range of the mitigation capabilities of most DDoS protection providers.
Barring a source code leak, Menscher said, it would be nice if someone published the full list of software exploits being used by the Aisuru operators to grow their botnet so quickly.
“Part of the reason Mirai was so dangerous was that it effectively took out competing botnets,” he said. “This attack somehow managed to compromise all these boxes that nobody else knows about. Ideally, we’d want to see that fragmented out, so that no [individual botnet operator] controls too much.”
The payment card giant MasterCard just fixed a glaring error in its domain name server settings that could have allowed anyone to intercept or divert Internet traffic for the company by registering an unused domain name. The misconfiguration persisted for nearly five years until a security researcher spent $300 to register the domain and prevent it from being grabbed by cybercriminals.
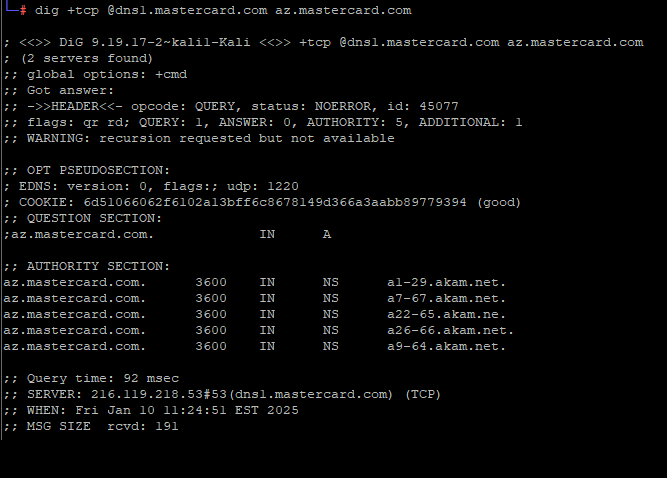
A DNS lookup on the domain az.mastercard.com on Jan. 14, 2025 shows the mistyped domain name a22-65.akam.ne.
From June 30, 2020 until January 14, 2025, one of the core Internet servers that MasterCard uses to direct traffic for portions of the mastercard.com network was misnamed. MasterCard.com relies on five shared Domain Name System (DNS) servers at the Internet infrastructure provider Akamai [DNS acts as a kind of Internet phone book, by translating website names to numeric Internet addresses that are easier for computers to manage].
All of the Akamai DNS server names that MasterCard uses are supposed to end in “akam.net” but one of them was misconfigured to rely on the domain “akam.ne.”
This tiny but potentially critical typo was discovered recently by Philippe Caturegli, founder of the security consultancy Seralys. Caturegli said he guessed that nobody had yet registered the domain akam.ne, which is under the purview of the top-level domain authority for the West Africa nation of Niger.
Caturegli said it took $300 and nearly three months of waiting to secure the domain with the registry in Niger. After enabling a DNS server on akam.ne, he noticed hundreds of thousands of DNS requests hitting his server each day from locations around the globe. Apparently, MasterCard wasn’t the only organization that had fat-fingered a DNS entry to include “akam.ne,” but they were by far the largest.
Had he enabled an email server on his new domain akam.ne, Caturegli likely would have received wayward emails directed toward mastercard.com or other affected domains. If he’d abused his access, he probably could have obtained website encryption certificates (SSL/TLS certs) that were authorized to accept and relay web traffic for affected websites. He may even have been able to passively receive Microsoft Windows authentication credentials from employee computers at affected companies.
But the researcher said he didn’t attempt to do any of that. Instead, he alerted MasterCard that the domain was theirs if they wanted it, copying this author on his notifications. A few hours later, MasterCard acknowledged the mistake, but said there was never any real threat to the security of its operations.
“We have looked into the matter and there was not a risk to our systems,” a MasterCard spokesperson wrote. “This typo has now been corrected.”
Meanwhile, Caturegli received a request submitted through Bugcrowd, a program that offers financial rewards and recognition to security researchers who find flaws and work privately with the affected vendor to fix them. The message suggested his public disclosure of the MasterCard DNS error via a post on LinkedIn (after he’d secured the akam.ne domain) was not aligned with ethical security practices, and passed on a request from MasterCard to have the post removed.
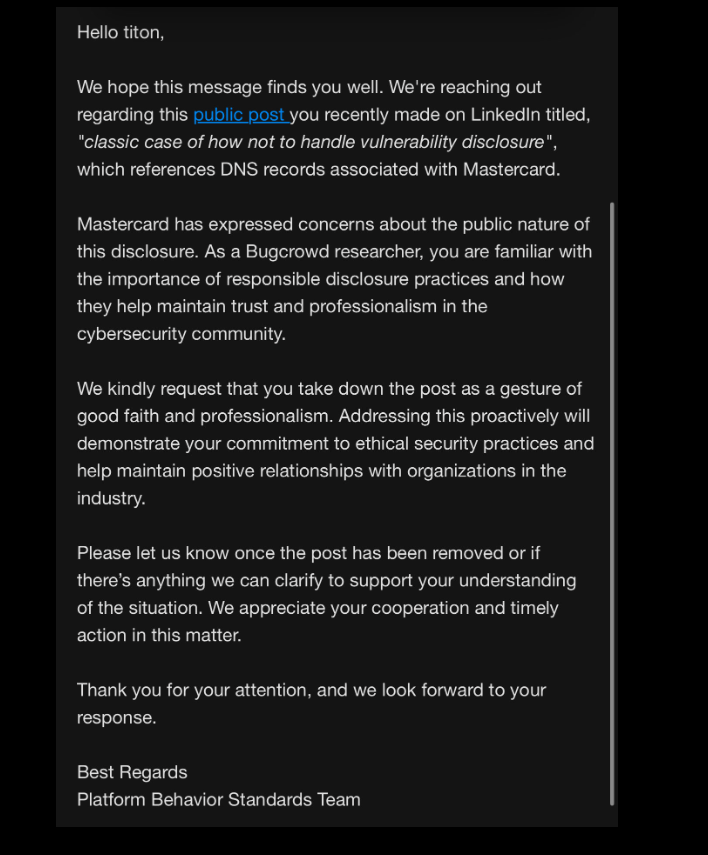
MasterCard’s request to Caturegli, a.k.a. “Titon” on infosec.exchange.
Caturegli said while he does have an account on Bugcrowd, he has never submitted anything through the Bugcrowd program, and that he reported this issue directly to MasterCard.
“I did not disclose this issue through Bugcrowd,” Caturegli wrote in reply. “Before making any public disclosure, I ensured that the affected domain was registered to prevent exploitation, mitigating any risk to MasterCard or its customers. This action, which we took at our own expense, demonstrates our commitment to ethical security practices and responsible disclosure.”
Most organizations have at least two authoritative domain name servers, but some handle so many DNS requests that they need to spread the load over additional DNS server domains. In MasterCard’s case, that number is five, so it stands to reason that if an attacker managed to seize control over just one of those domains they would only be able to see about one-fifth of the overall DNS requests coming in.
But Caturegli said the reality is that many Internet users are relying at least to some degree on public traffic forwarders or DNS resolvers like Cloudflare and Google.
“So all we need is for one of these resolvers to query our name server and cache the result,” Caturegli said. By setting their DNS server records with a long TTL or “Time To Live” — a setting that can adjust the lifespan of data packets on a network — an attacker’s poisoned instructions for the target domain can be propagated by large cloud providers.
“With a long TTL, we may reroute a LOT more than just 1/5 of the traffic,” he said.
The researcher said he’d hoped that the credit card giant might thank him, or at least offer to cover the cost of buying the domain.
“We obviously disagree with this assessment,” Caturegli wrote in a follow-up post on LinkedIn regarding MasterCard’s public statement. “But we’ll let you judge— here are some of the DNS lookups we recorded before reporting the issue.”
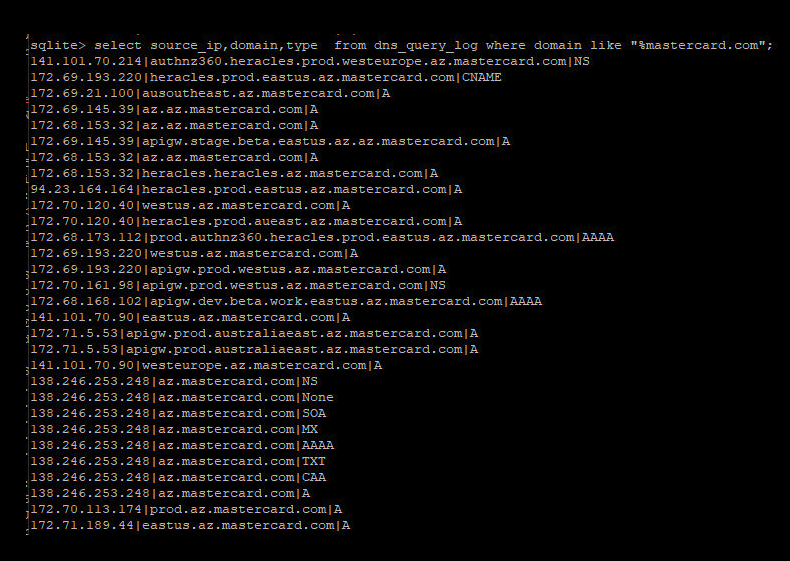
Caturegli posted this screenshot of MasterCard domains that were potentially at risk from the misconfigured domain.
As the screenshot above shows, the misconfigured DNS server Caturegli found involved the MasterCard subdomain az.mastercard.com. It is not clear exactly how this subdomain is used by MasterCard, however their naming conventions suggest the domains correspond to production servers at Microsoft’s Azure cloud service. Caturegli said the domains all resolve to Internet addresses at Microsoft.
“Don’t be like Mastercard,” Caturegli concluded in his LinkedIn post. “Don’t dismiss risk, and don’t let your marketing team handle security disclosures.”
One final note: The domain akam.ne has been registered previously — in December 2016 by someone using the email address um-i-delo@yandex.ru. The Russian search giant Yandex reports this user account belongs to an “Ivan I.” from Moscow. Passive DNS records from DomainTools.com show that between 2016 and 2018 the domain was connected to an Internet server in Germany, and that the domain was left to expire in 2018.
This is interesting given a comment on Caturegli’s LinkedIn post from an ex-Cloudflare employee who linked to a report he co-authored on a similar typo domain apparently registered in 2017 for organizations that may have mistyped their AWS DNS server as “awsdns-06.ne” instead of “awsdns-06.net.” DomainTools reports that this typo domain also was registered to a Yandex user (playlotto@yandex.ru), and was hosted at the same German ISP — Team Internet (AS61969).