U.S. prosecutors last week levied criminal hacking charges against 19-year-old U.K. national Thalha Jubair for allegedly being a core member of Scattered Spider, a prolific cybercrime group blamed for extorting at least $115 million in ransom payments from victims. The charges came as Jubair and an alleged co-conspirator appeared in a London court to face accusations of hacking into and extorting several large U.K. retailers, the London transit system, and healthcare providers in the United States.
At a court hearing last week, U.K. prosecutors laid out a litany of charges against Jubair and 18-year-old Owen Flowers, accusing the teens of involvement in an August 2024 cyberattack that crippled Transport for London, the entity responsible for the public transport network in the Greater London area.

A court artist sketch of Owen Flowers (left) and Thalha Jubair appearing at Westminster Magistrates’ Court last week. Credit: Elizabeth Cook, PA Wire.
On July 10, 2025, KrebsOnSecurity reported that Flowers and Jubair had been arrested in the United Kingdom in connection with recent Scattered Spider ransom attacks against the retailers Marks & Spencer and Harrods, and the British food retailer Co-op Group.
That story cited sources close to the investigation saying Flowers was the Scattered Spider member who anonymously gave interviews to the media in the days after the group’s September 2023 ransomware attacks disrupted operations at Las Vegas casinos operated by MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment.
The story also noted that Jubair’s alleged handles on cybercrime-focused Telegram channels had far lengthier rap sheets involving some of the more consequential and headline-grabbing data breaches over the past four years. What follows is an account of cybercrime activities that prosecutors have attributed to Jubair’s alleged hacker handles, as told by those accounts in posts to public Telegram channels that are closely monitored by multiple cyber intelligence firms.
Jubair is alleged to have been a core member of the LAPSUS$ cybercrime group that broke into dozens of technology companies beginning in late 2021, stealing source code and other internal data from tech giants including Microsoft, Nvidia, Okta, Rockstar Games, Samsung, T-Mobile, and Uber.
That is, according to the former leader of the now-defunct LAPSUS$. In April 2022, KrebsOnSecurity published internal chat records taken from a server that LAPSUS$ used, and those chats indicate Jubair was working with the group using the nicknames Amtrak and Asyntax. In the middle of the gang’s cybercrime spree, Asyntax told the LAPSUS$ leader not to share T-Mobile’s logo in images sent to the group because he’d been previously busted for SIM-swapping and his parents would suspect he was back at it again.
The leader of LAPSUS$ responded by gleefully posting Asyntax’s real name, phone number, and other hacker handles into a public chat room on Telegram:
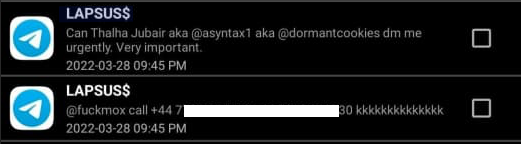
In March 2022, the leader of the LAPSUS$ data extortion group exposed Thalha Jubair’s name and hacker handles in a public chat room on Telegram.
That story about the leaked LAPSUS$ chats also connected Amtrak/Asyntax to several previous hacker identities, including “Everlynn,” who in April 2021 began offering a cybercriminal service that sold fraudulent “emergency data requests” targeting the major social media and email providers.
In these so-called “fake EDR” schemes, the hackers compromise email accounts tied to police departments and government agencies, and then send unauthorized demands for subscriber data (e.g. username, IP/email address), while claiming the information being requested can’t wait for a court order because it relates to an urgent matter of life and death.
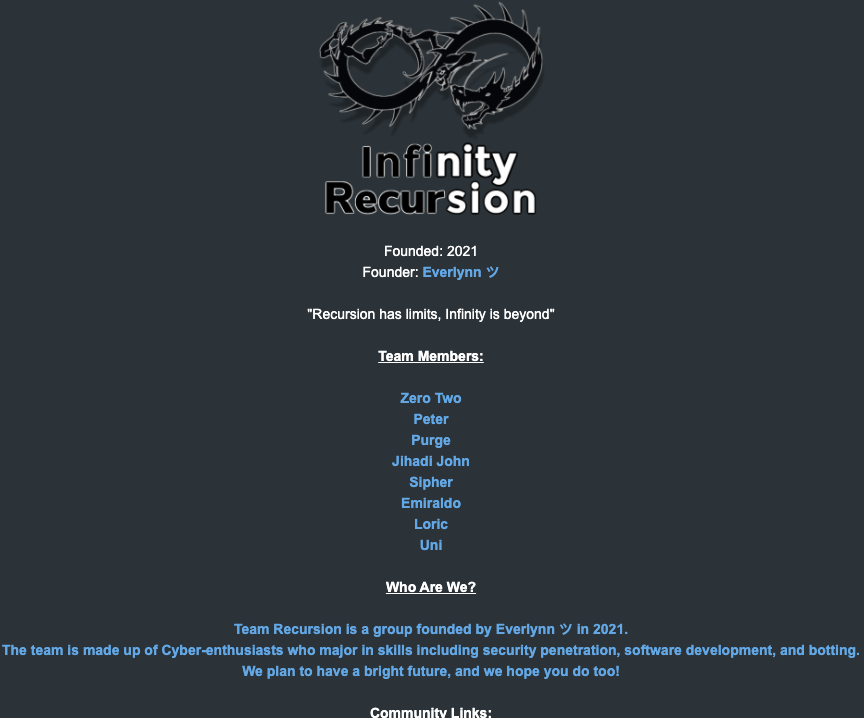
The roster of the now-defunct “Infinity Recursion” hacking team, which sold fake EDRs between 2021 and 2022. The founder “Everlynn” has been tied to Jubair. The member listed as “Peter” became the leader of LAPSUS$ who would later post Jubair’s name, phone number and hacker handles into LAPSUS$’s chat channel.
Prosecutors in New Jersey last week alleged Jubair was part of a threat group variously known as Scattered Spider, 0ktapus, and UNC3944, and that he used the nicknames EarthtoStar, Brad, Austin, and Austistic.
Beginning in 2022, EarthtoStar co-ran a bustling Telegram channel called Star Chat, which was home to a prolific SIM-swapping group that relentlessly used voice- and SMS-based phishing attacks to steal credentials from employees at the major wireless providers in the U.S. and U.K.

Jubair allegedly used the handle “Earth2Star,” a core member of a prolific SIM-swapping group operating in 2022. This ad produced by the group lists various prices for SIM swaps.
The group would then use that access to sell a SIM-swapping service that could redirect a target’s phone number to a device the attackers controlled, allowing them to intercept the victim’s phone calls and text messages (including one-time codes). Members of Star Chat targeted multiple wireless carriers with SIM-swapping attacks, but they focused mainly on phishing T-Mobile employees.
In February 2023, KrebsOnSecurity scrutinized more than seven months of these SIM-swapping solicitations on Star Chat, which almost daily peppered the public channel with “Tmo up!” and “Tmo down!” notices indicating periods wherein the group claimed to have active access to T-Mobile’s network.
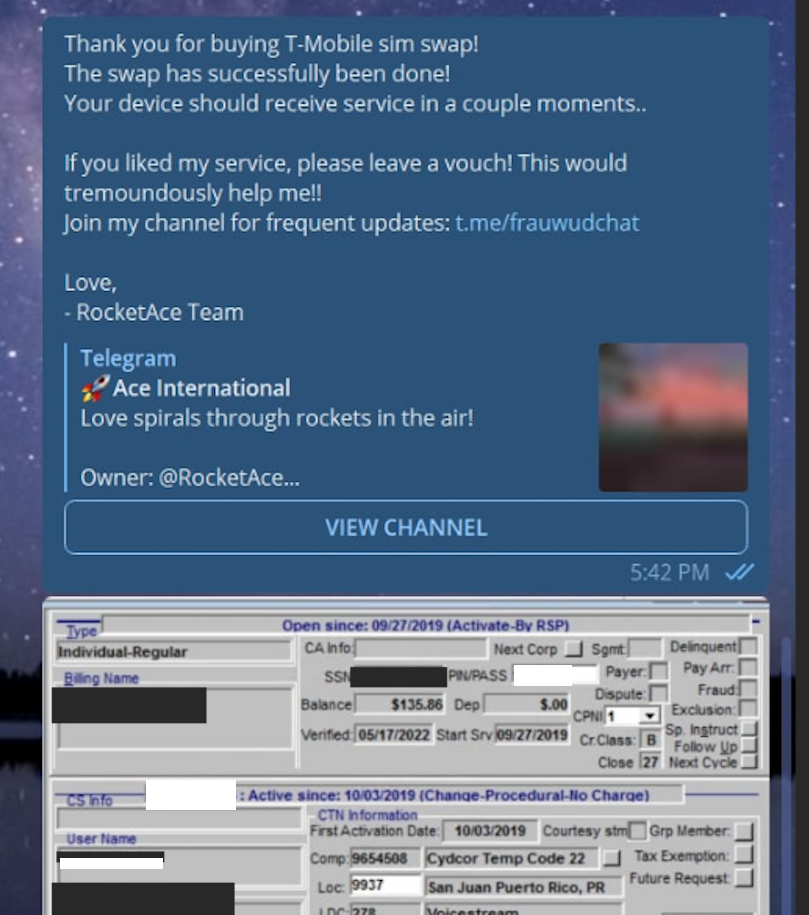
A redacted receipt from Star Chat’s SIM-swapping service targeting a T-Mobile customer after the group gained access to internal T-Mobile employee tools.
The data showed that Star Chat — along with two other SIM-swapping groups operating at the same time — collectively broke into T-Mobile over a hundred times in the last seven months of 2022. However, Star Chat was by far the most prolific of the three, responsible for at least 70 of those incidents.
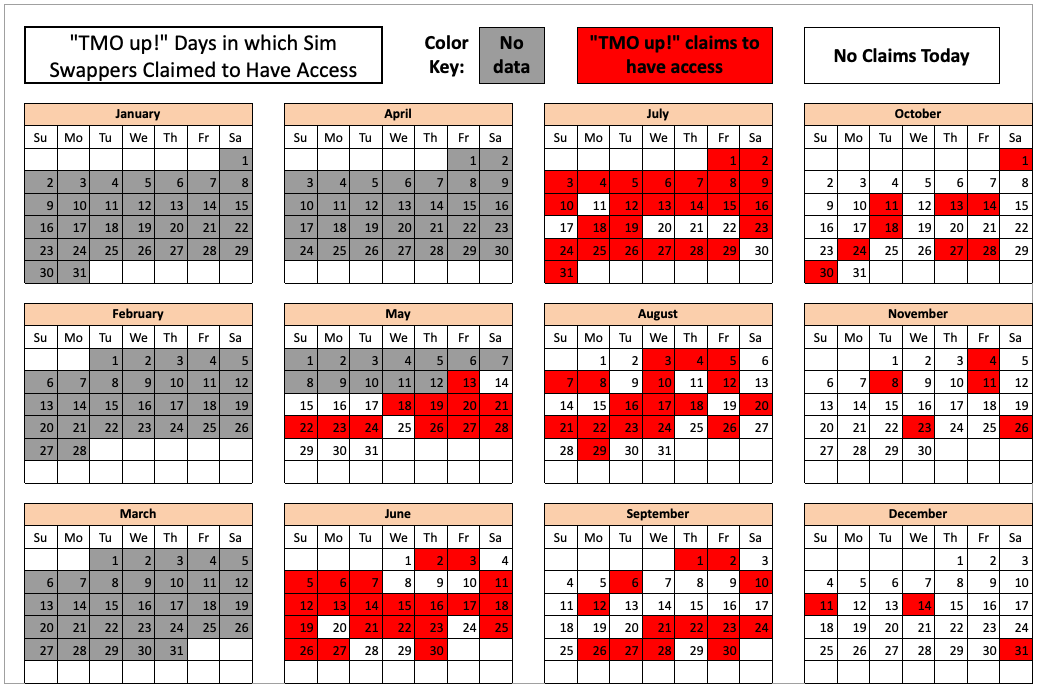
The 104 days in the latter half of 2022 in which different known SIM-swapping groups claimed access to T-Mobile employee tools. Star Chat was responsible for a majority of these incidents. Image: krebsonsecurity.com.
A review of EarthtoStar’s messages on Star Chat as indexed by the threat intelligence firm Flashpoint shows this person also sold “AT&T email resets” and AT&T call forwarding services for up to $1,200 per line. EarthtoStar explained the purpose of this service in post on Telegram:
“Ok people are confused, so you know when u login to chase and it says ‘2fa required’ or whatever the fuck, well it gives you two options, SMS or Call. If you press call, and I forward the line to you then who do you think will get said call?”
New Jersey prosecutors allege Jubair also was involved in a mass SMS phishing campaign during the summer of 2022 that stole single sign-on credentials from employees at hundreds of companies. The text messages asked users to click a link and log in at a phishing page that mimicked their employer’s Okta authentication page, saying recipients needed to review pending changes to their upcoming work schedules.
The phishing websites used a Telegram instant message bot to forward any submitted credentials in real-time, allowing the attackers to use the phished username, password and one-time code to log in as that employee at the real employer website.
That weeks-long SMS phishing campaign led to intrusions and data thefts at more than 130 organizations, including LastPass, DoorDash, Mailchimp, Plex and Signal.
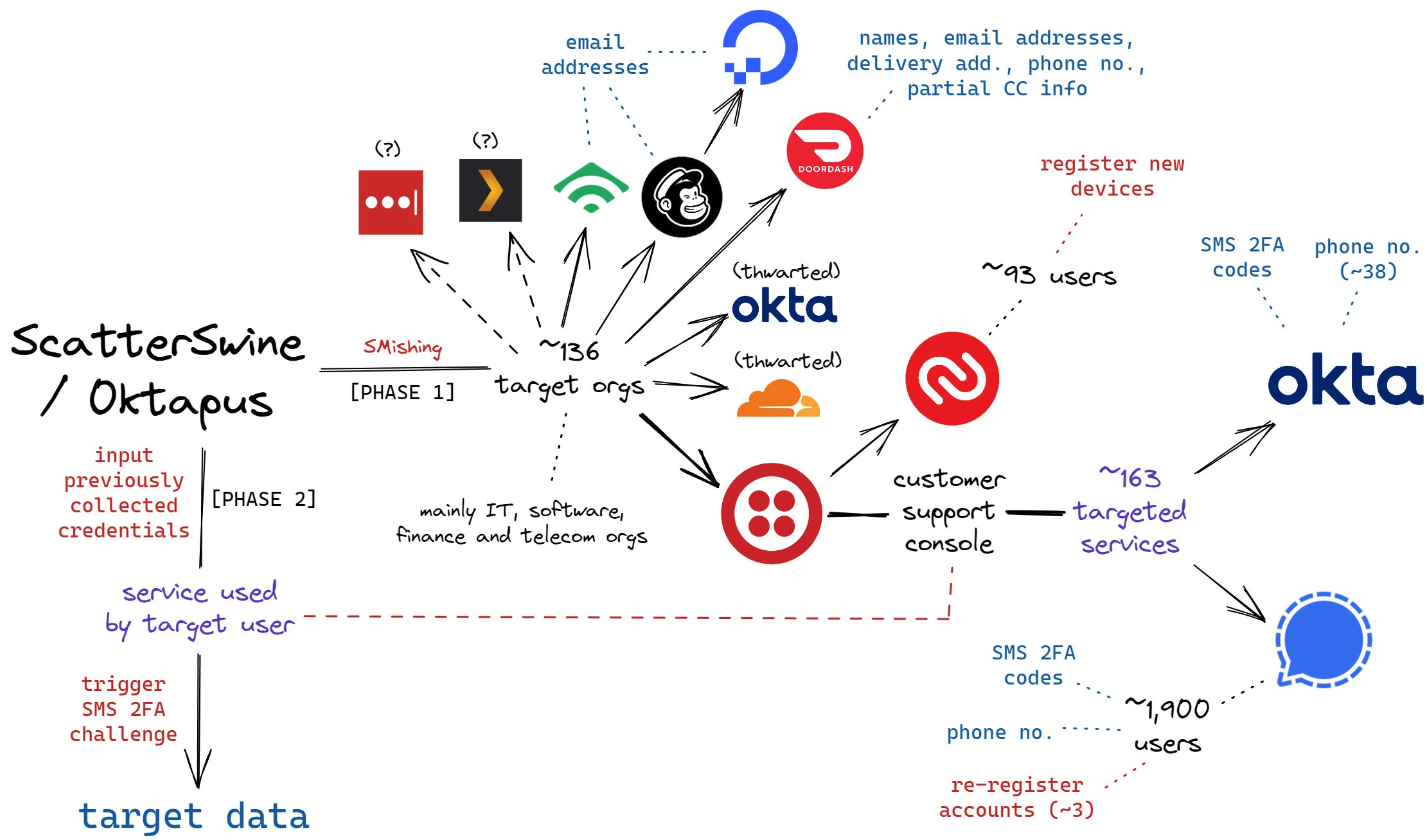
A visual depiction of the attacks by the SMS phishing group known as 0ktapus, ScatterSwine, and Scattered Spider. Image: Amitai Cohen twitter.com/amitaico.
EarthtoStar’s group Star Chat specialized in phishing their way into business process outsourcing (BPO) companies that provide customer support for a range of multinational companies, including a number of the world’s largest telecommunications providers. In May 2022, EarthtoStar posted to the Telegram channel “Frauwudchat”:
“Hi, I am looking for partners in order to exfiltrate data from large telecommunications companies/call centers/alike, I have major experience in this field, [including] a massive call center which houses 200,000+ employees where I have dumped all user credentials and gained access to the [domain controller] + obtained global administrator I also have experience with REST API’s and programming. I have extensive experience with VPN, Citrix, cisco anyconnect, social engineering + privilege escalation. If you have any Citrix/Cisco VPN or any other useful things please message me and lets work.”
At around the same time in the Summer of 2022, at least two different accounts tied to Star Chat — “RocketAce” and “Lopiu” — introduced the group’s services to denizens of the Russian-language cybercrime forum Exploit, including:
-SIM-swapping services targeting Verizon and T-Mobile customers;
-Dynamic phishing pages targeting customers of single sign-on providers like Okta;
-Malware development services;
-The sale of extended validation (EV) code signing certificates.
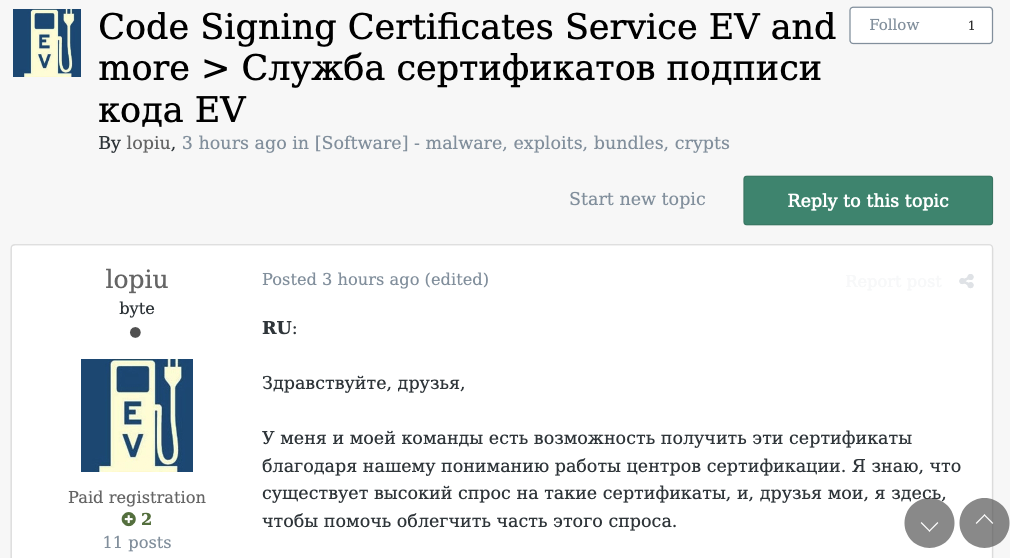
The user “Lopiu” on the Russian cybercrime forum Exploit advertised many of the same unique services offered by EarthtoStar and other Star Chat members. Image source: ke-la.com.
These two accounts on Exploit created multiple sales threads in which they claimed administrative access to U.S. telecommunications providers and asked other Exploit members for help in monetizing that access. In June 2022, RocketAce, which appears to have been just one of EarthtoStar’s many aliases, posted to Exploit:
Hello. I have access to a telecommunications company’s citrix and vpn. I would like someone to help me break out of the system and potentially attack the domain controller so all logins can be extracted we can discuss payment and things leave your telegram in the comments or private message me ! Looking for someone with knowledge in citrix/privilege escalation
On Nov. 15, 2022, EarthtoStar posted to their Star Sanctuary Telegram channel that they were hiring malware developers with a minimum of three years of experience and the ability to develop rootkits, backdoors and malware loaders.
“Optional: Endorsed by advanced APT Groups (e.g. Conti, Ryuk),” the ad concluded, referencing two of Russia’s most rapacious and destructive ransomware affiliate operations. “Part of a nation-state / ex-3l (3 letter-agency).”
The Telegram and Discord chat channels wherein Flowers and Jubair allegedly planned and executed their extortion attacks are part of a loose-knit network known as the Com, an English-speaking cybercrime community consisting mostly of individuals living in the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia.
Many of these Com chat servers have hundreds to thousands of members each, and some of the more interesting solicitations on these communities are job offers for in-person assignments and tasks that can be found if one searches for posts titled, “If you live near,” or “IRL job” — short for “in real life” job.
These “violence-as-a-service” solicitations typically involve “brickings,” where someone is hired to toss a brick through the window at a specified address. Other IRL jobs for hire include tire-stabbings, molotov cocktail hurlings, drive-by shootings, and even home invasions. The people targeted by these services are typically other criminals within the community, but it’s not unusual to see Com members asking others for help in harassing or intimidating security researchers and even the very law enforcement officers who are investigating their alleged crimes.
It remains unclear what precipitated this incident or what followed directly after, but on January 13, 2023, a Star Sanctuary account used by EarthtoStar solicited the home invasion of a sitting U.S. federal prosecutor from New York. That post included a photo of the prosecutor taken from the Justice Department’s website, along with the message:
“Need irl niggas, in home hostage shit no fucking pussies no skinny glock holding 100 pound niggas either”
Throughout late 2022 and early 2023, EarthtoStar’s alias “Brad” (a.k.a. “Brad_banned”) frequently advertised Star Chat’s malware development services, including custom malicious software designed to hide the attacker’s presence on a victim machine:
We can develop KERNEL malware which will achieve persistence for a long time,
bypass firewalls and have reverse shell access.This shit is literally like STAGE 4 CANCER FOR COMPUTERS!!!
Kernel meaning the highest level of authority on a machine.
This can range to simple shells to Bootkits.Bypass all major EDR’s (SentinelOne, CrowdStrike, etc)
Patch EDR’s scanning functionality so it’s rendered useless!Once implanted, extremely difficult to remove (basically impossible to even find)
Development Experience of several years and in multiple APT Groups.Be one step ahead of the game. Prices start from $5,000+. Message @brad_banned to get a quote
In September 2023 , both MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment suffered ransomware attacks at the hands of a Russian ransomware affiliate program known as ALPHV and BlackCat. Caesars reportedly paid a $15 million ransom in that incident.
Within hours of MGM publicly acknowledging the 2023 breach, members of Scattered Spider were claiming credit and telling reporters they’d broken in by social engineering a third-party IT vendor. At a hearing in London last week, U.K. prosecutors told the court Jubair was found in possession of more than $50 million in ill-gotten cryptocurrency, including funds that were linked to the Las Vegas casino hacks.
The Star Chat channel was finally banned by Telegram on March 9, 2025. But U.S. prosecutors say Jubair and fellow Scattered Spider members continued their hacking, phishing and extortion activities up until September 2025.
In April 2025, the Com was buzzing about the publication of “The Com Cast,” a lengthy screed detailing Jubair’s alleged cybercriminal activities and nicknames over the years. This account included photos and voice recordings allegedly of Jubair, and asserted that in his early days on the Com Jubair used the nicknames Clark and Miku (these are both aliases used by Everlynn in connection with their fake EDR services).

Thalha Jubair (right), without his large-rimmed glasses, in an undated photo posted in The Com Cast.
More recently, the anonymous Com Cast author(s) claimed, Jubair had used the nickname “Operator,” which corresponds to a Com member who ran an automated Telegram-based doxing service that pulled consumer records from hacked data broker accounts. That public outing came after Operator allegedly seized control over the Doxbin, a long-running and highly toxic community that is used to “dox” or post deeply personal information on people.
“Operator/Clark/Miku: A key member of the ransomware group Scattered Spider, which consists of a diverse mix of individuals involved in SIM swapping and phishing,” the Com Cast account stated. “The group is an amalgamation of several key organizations, including Infinity Recursion (owned by Operator), True Alcorians (owned by earth2star), and Lapsus, which have come together to form a single collective.”
The New Jersey complaint (PDF) alleges Jubair and other Scattered Spider members committed computer fraud, wire fraud, and money laundering in relation to at least 120 computer network intrusions involving 47 U.S. entities between May 2022 and September 2025. The complaint alleges the group’s victims paid at least $115 million in ransom payments.
U.S. authorities say they traced some of those payments to Scattered Spider to an Internet server controlled by Jubair. The complaint states that a cryptocurrency wallet discovered on that server was used to purchase several gift cards, one of which was used at a food delivery company to send food to his apartment. Another gift card purchased with cryptocurrency from the same server was allegedly used to fund online gaming accounts under Jubair’s name. U.S. prosecutors said that when they seized that server they also seized $36 million in cryptocurrency.
The complaint also charges Jubair with involvement in a hacking incident in January 2025 against the U.S. courts system that targeted a U.S. magistrate judge overseeing a related Scattered Spider investigation. That other investigation appears to have been the prosecution of Noah Michael Urban, a 20-year-old Florida man charged in November 2024 by prosecutors in Los Angeles as one of five alleged Scattered Spider members.
Urban pleaded guilty in April 2025 to wire fraud and conspiracy charges, and in August he was sentenced to 10 years in federal prison. Speaking with KrebsOnSecurity from jail after his sentencing, Urban asserted that the judge gave him more time than prosecutors requested because he was mad that Scattered Spider hacked his email account.
Noah “Kingbob” Urban, posting to Twitter/X around the time of his sentencing on Aug. 20.
A court transcript (PDF) from a status hearing in February 2025 shows Urban was telling the truth about the hacking incident that happened while he was in federal custody. The judge told attorneys for both sides that a co-defendant in the California case was trying to find out about Mr. Urban’s activity in the Florida case, and that the hacker accessed the account by impersonating a judge over the phone and requesting a password reset.
Allison Nixon is chief research officer at the New York based security firm Unit 221B, and easily one of the world’s leading experts on Com-based cybercrime activity. Nixon said the core problem with legally prosecuting well-known cybercriminals from the Com has traditionally been that the top offenders tend to be under the age of 18, and thus difficult to charge under federal hacking statutes.
In the United States, prosecutors typically wait until an underage cybercrime suspect becomes an adult to charge them. But until that day comes, she said, Com actors often feel emboldened to continue committing — and very often bragging about — serious cybercrime offenses.
“Here we have a special category of Com offenders that effectively enjoy legal immunity,” Nixon told KrebsOnSecurity. “Most get recruited to Com groups when they are older, but of those that join very young, such as 12 or 13, they seem to be the most dangerous because at that age they have no grounding in reality and so much longevity before they exit their legal immunity.”
Nixon said U.K. authorities face the same challenge when they briefly detain and search the homes of underage Com suspects: Namely, the teen suspects simply go right back to their respective cliques in the Com and start robbing and hurting people again the minute they’re released.
Indeed, the U.K. court heard from prosecutors last week that both Scattered Spider suspects were detained and/or searched by local law enforcement on multiple occasions, only to return to the Com less than 24 hours after being released each time.
“What we see is these young Com members become vectors for perpetrators to commit enormously harmful acts and even child abuse,” Nixon said. “The members of this special category of people who enjoy legal immunity are meeting up with foreign nationals and conducting these sometimes heinous acts at their behest.”
Nixon said many of these individuals have few friends in real life because they spend virtually all of their waking hours on Com channels, and so their entire sense of identity, community and self-worth gets wrapped up in their involvement with these online gangs. She said if the law was such that prosecutors could treat these people commensurate with the amount of harm they cause society, that would probably clear up a lot of this problem.
“If law enforcement was allowed to keep them in jail, they would quit reoffending,” she said.
The Times of London reports that Flowers is facing three charges under the Computer Misuse Act: two of conspiracy to commit an unauthorized act in relation to a computer causing/creating risk of serious damage to human welfare/national security and one of attempting to commit the same act. Maximum sentences for these offenses can range from 14 years to life in prison, depending on the impact of the crime.
Jubair is reportedly facing two charges in the U.K.: One of conspiracy to commit an unauthorized act in relation to a computer causing/creating risk of serious damage to human welfare/national security and one of failing to comply with a section 49 notice to disclose the key to protected information.
In the United States, Jubair is charged with computer fraud conspiracy, two counts of computer fraud, wire fraud conspiracy, two counts of wire fraud, and money laundering conspiracy. If extradited to the U.S., tried and convicted on all charges, he faces a maximum penalty of 95 years in prison.
In July 2025, the United Kingdom barred victims of hacking from paying ransoms to cybercriminal groups unless approved by officials. U.K. organizations that are considered part of critical infrastructure reportedly will face a complete ban, as will the entire public sector. U.K. victims of a hack are now required to notify officials to better inform policymakers on the scale of Britain’s ransomware problem.
For further reading (bless you), check out Bloomberg’s poignant story last week based on a year’s worth of jailhouse interviews with convicted Scattered Spider member Noah Urban.
Change Healthcare says it has notified approximately 100 million Americans that their personal, financial and healthcare records may have been stolen in a February 2024 ransomware attack that caused the largest ever known data breach of protected health information.

Image: Tamer Tuncay, Shutterstock.com.
A ransomware attack at Change Healthcare in the third week of February quickly spawned disruptions across the U.S. healthcare system that reverberated for months, thanks to the company’s central role in processing payments and prescriptions on behalf of thousands of organizations.
In April, Change estimated the breach would affect a “substantial proportion of people in America.” On Oct 22, the healthcare giant notified the U.S. Department of Health and Human Resources (HHS) that “approximately 100 million notices have been sent regarding this breach.”
A notification letter from Change Healthcare said the breach involved the theft of:
-Health Data: Medical record #s, doctors, diagnoses, medicines, test results, images, care and treatment;
-Billing Records: Records including payment cards, financial and banking records;
-Personal Data: Social Security number; driver’s license or state ID number;
-Insurance Data: Health plans/policies, insurance companies, member/group ID numbers, and Medicaid-Medicare-government payor ID numbers.
The HIPAA Journal reports that in the nine months ending on September 30, 2024, Change’s parent firm United Health Group had incurred $1.521 billion in direct breach response costs, and $2.457 billion in total cyberattack impacts.
Those costs include $22 million the company admitted to paying their extortionists — a ransomware group known as BlackCat and ALPHV — in exchange for a promise to destroy the stolen healthcare data.
That ransom payment went sideways when the affiliate who gave BlackCat access to Change’s network said the crime gang had cheated them out of their share of the ransom. The entire BlackCat ransomware operation shut down after that, absconding with all of the money still owed to affiliates who were hired to install their ransomware.
A few days after BlackCat imploded, the same stolen healthcare data was offered for sale by a competing ransomware affiliate group called RansomHub.
“Affected insurance providers can contact us to prevent leaking of their own data and [remove it] from the sale,” RansomHub’s victim shaming blog announced on April 16. “Change Health and United Health processing of sensitive data for all of these companies is just something unbelievable. For most US individuals out there doubting us, we probably have your personal data.”
It remains unclear if RansomHub ever sold the stolen healthcare data. The chief information security officer for a large academic healthcare system affected by the breach told KrebsOnSecurity they participated in a call with the FBI and were told a third party partner managed to recover at least four terabytes of data that was exfiltrated from Change by the cybercriminal group. The FBI declined to comment.
Change Healthcare’s breach notification letter offers recipients two years of credit monitoring and identity theft protection services from a company called IDX. In the section of the missive titled “Why did this happen?,” Change shared only that “a cybercriminal accessed our computer system without our permission.”
But in June 2024 testimony to the Senate Finance Committee, it emerged that the intruders had stolen or purchased credentials for a Citrix portal used for remote access, and that no multi-factor authentication was required for that account.
Last month, Sens. Mark Warner (D-Va.) and Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) introduced a bill that would require HHS to develop and enforce a set of tough minimum cybersecurity standards for healthcare providers, health plans, clearinghouses and businesses associates. The measure also would remove the existing cap on fines under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, which severely limits the financial penalties HHS can issue against providers.
According to the HIPAA Journal, the biggest penalty imposed to date for a HIPAA violation was the paltry $16 million fine against the insurer Anthem Inc., which suffered a data breach in 2015 affecting 78.8 million individuals. Anthem reported revenues of around $80 billion in 2015.

A post about the Change breach from RansomHub on April 8, 2024. Image: Darkbeast, ke-la.com.
There is little that victims of this breach can do about the compromise of their healthcare records. However, because the data exposed includes more than enough information for identity thieves to do their thing, it would be prudent to place a security freeze on your credit file and on that of your family members if you haven’t already.
The best mechanism for preventing identity thieves from creating new accounts in your name is to freeze your credit file with Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. This process is now free for all Americans, and simply blocks potential creditors from viewing your credit file. Parents and guardians can now also freeze the credit files for their children or dependents.
Since very few creditors are willing to grant new lines of credit without being able to determine how risky it is to do so, freezing your credit file with the Big Three is a great way to stymie all sorts of ID theft shenanigans. Having a freeze in place does nothing to prevent you from using existing lines of credit you may already have, such as credit cards, mortgage and bank accounts. When and if you ever do need to allow access to your credit file — such as when applying for a loan or new credit card — you will need to lift or temporarily thaw the freeze in advance with one or more of the bureaus.
All three bureaus allow users to place a freeze electronically after creating an account, but all of them try to steer consumers away from enacting a freeze. Instead, the bureaus are hoping consumers will opt for their confusingly named “credit lock” services, which accomplish the same result but allow the bureaus to continue selling access to your file to select partners.
If you haven’t done so in a while, now would be an excellent time to review your credit file for any mischief or errors. By law, everyone is entitled to one free credit report every 12 months from each of the three credit reporting agencies. But the Federal Trade Commission notes that the big three bureaus have permanently extended a program enacted in 2020 that lets you check your credit report at each of the agencies once a week for free.
A cyberattack that shut down two of the top casinos in Las Vegas last year quickly became one of the most riveting security stories of 2023. It was the first known case of native English-speaking hackers in the United States and Britain teaming up with ransomware gangs based in Russia. But that made-for-Hollywood narrative has eclipsed a far more hideous trend: Many of these young, Western cybercriminals are also members of fast-growing online groups that exist solely to bully, stalk, harass and extort vulnerable teens into physically harming themselves and others.

Image: Shutterstock.
In September 2023, a Russian ransomware group known as ALPHV/Black Cat claimed credit for an intrusion at the MGM Resorts hotel chain that quickly brought MGM’s casinos in Las Vegas to a standstill. While MGM was still trying to evict the intruders from its systems, an individual who claimed to have firsthand knowledge of the hack contacted multiple media outlets to offer interviews about how it all went down.
One account of the hack came from a 17-year-old in the United Kingdom, who told reporters the intrusion began when one of the English-speaking hackers phoned a tech support person at MGM and tricked them into resetting the password for an employee account.
The security firm CrowdStrike dubbed the group “Scattered Spider,” a recognition that the MGM hackers came from different cliques scattered across an ocean of Telegram and Discord servers dedicated to financially-oriented cybercrime.
Collectively, this archipelago of crime-focused chat communities is known as “The Com,” and it functions as a kind of distributed cybercriminal social network that facilitates instant collaboration.
But mostly, The Com is a place where cybercriminals go to boast about their exploits and standing within the community, or to knock others down a peg or two. Top Com members are constantly sniping over who pulled off the most impressive heists, or who has accumulated the biggest pile of stolen virtual currencies.
And as often as they extort victim companies for financial gain, members of The Com are trying to wrest stolen money from their cybercriminal rivals — often in ways that spill over into physical violence in the real world.
CrowdStrike would go on to produce and sell Scattered Spider action figures, and it featured a life-sized Scattered Spider sculpture at this year’s RSA Security Conference in San Francisco.
But marketing security products and services based on specific cybercriminal groups can be tricky, particularly if it turns out that robbing and extorting victims is by no means the most abhorrent activity those groups engage in on a daily basis.
KrebsOnSecurity examined the Telegram user ID number of the account that offered media interviews about the MGM hack — which corresponds to the screen name “@Holy” — and found the same account was used across a number of cybercrime channels that are entirely focused on extorting young people into harming themselves or others, and recording the harm on video.
Holy was known to possess multiple prized Telegram usernames, including @bomb, @halo, and @cute, as well as one of the highest-priced Telegram usernames ever put up for sale: @nazi.
In one post on a Telegram channel dedicated to youth extortion, this same user can be seen asking if anyone knows the current Telegram handles for several core members of 764, an extremist group known for victimizing children through coordinated online campaigns of extortion, doxing, swatting and harassment.
People affiliated with harm groups like 764 will often recruit new members by lurking on gaming platforms, social media sites and mobile applications that are popular with young people, including Discord, Minecraft, Roblox, Steam, Telegram, and Twitch.
“This type of offence usually starts with a direct message through gaming platforms and can move to more private chatrooms on other virtual platforms, typically one with video enabled features, where the conversation quickly becomes sexualized or violent,” warns a recent alert from the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) about the rise of sextortion groups on social media channels.
“One of the tactics being used by these actors is sextortion, however, they are not using it to extract money or for sexual gratification,” the RCMP continued. “Instead they use it to further manipulate and control victims to produce more harmful and violent content as part of their ideological objectives and radicalization pathway.”
The 764 network is among the most populated harm communities, but there are plenty more. Some of the largest such known groups include CVLT, Court, Kaskar, Leak Society, 7997, 8884, 2992, 6996, 555, Slit Town, 545, 404, NMK, 303, and H3ll.
In March, a consortium of reporters from Wired, Der Spiegel, Recorder and The Washington Post examined millions of messages across more than 50 Discord and Telegram chat groups.
“The abuse perpetrated by members of com groups is extreme,” Wired’s Ali Winston wrote. “They have coerced children into sexual abuse or self-harm, causing them to deeply lacerate their bodies to carve ‘cutsigns’ of an abuser’s online alias into their skin.” The story continues:
“Victims have flushed their heads in toilets, attacked their siblings, killed their pets, and in some extreme instances, attempted or died by suicide. Court records from the United States and European nations reveal participants in this network have also been accused of robberies, in-person sexual abuse of minors, kidnapping, weapons violations, swatting, and murder.”
“Some members of the network extort children for sexual pleasure, some for power and control. Some do it merely for the kick that comes from manipulation. Others sell the explicit CSAM content produced by extortion on the dark web.”
KrebsOnSecurity has learned Holy is the 17-year-old who was arrested in July 2024 by the U.K.’s West Midlands Police as part of a joint investigation with the FBI into the MGM hack.
Early in their cybercriminal career (as a 15-year-old), @Holy went by the handle “Vsphere,” and was a proud member of the LAPSUS$ cybercrime group. Throughout 2022, LAPSUS$ would hack and social engineer their way into some of the world’s biggest technology companies, including EA Games, Microsoft, NVIDIA, Okta, Samsung, and T-Mobile.
Another timely example of the overlap between harm communities and top members of The Com can be found in a group of criminals who recently stole obscene amounts of customer records from users of the cloud data provider Snowflake.
At the end of 2023, malicious hackers figured out that many major companies have uploaded massive amounts of valuable and sensitive customer data to Snowflake servers, all the while protecting those Snowflake accounts with little more than a username and password (no multi-factor authentication required). The group then searched darknet markets for stolen Snowflake account credentials, and began raiding the data storage repositories used by some of the world’s largest corporations.
Among those that had data exposed in Snowflake was AT&T, which disclosed in July that cybercriminals had stolen personal information and phone and text message records for roughly 110 million people — nearly all its customers.
A report on the extortion group from the incident response firm Mandiant notes that Snowflake victim companies were privately approached by the hackers, who demanded a ransom in exchange for a promise not to sell or leak the stolen data. All told, more than 160 organizations were extorted, including TicketMaster, Lending Tree, Advance Auto Parts and Neiman Marcus.
On May 2, 2024, a user by the name “Judische” claimed on the fraud-focused Telegram channel Star Chat that they had hacked Santander Bank, one of the first known Snowflake victims. Judische would repeat that claim in Star Chat on May 13 — the day before Santander publicly disclosed a data breach — and would periodically blurt out the names of other Snowflake victims before their data even went up for sale on the cybercrime forums.
A careful review of Judische’s account history and postings on Telegram shows this user is more widely known under the nickname “Waifu,” an early moniker that corresponds to one of the more accomplished SIM-swappers in The Com over the years.
In a SIM-swapping attack, the fraudsters will phish or purchase credentials for mobile phone company employees, and use those credentials to redirect a target’s mobile calls and text messages to a device the attackers control.
Several channels on Telegram maintain a frequently updated leaderboard of the 100 richest SIM-swappers, as well as the hacker handles associated with specific cybercrime groups (Waifu is ranked #24). That leaderboard has long included Waifu on a roster of hackers for a group that called itself “Beige.”
Beige members were implicated in two stories published here in 2020. The first was an August 2020 piece called Voice Phishers Targeting Corporate VPNs, which warned that the COVID-19 epidemic had brought a wave of voice phishing or “vishing” attacks that targeted work-from-home employees via their mobile devices, and tricked many of those people into giving up credentials needed to access their employer’s network remotely.
Beige group members also have claimed credit for a breach at the domain registrar GoDaddy. In November 2020, intruders thought to be associated with the Beige Group tricked a GoDaddy employee into installing malicious software, and with that access they were able to redirect the web and email traffic for multiple cryptocurrency trading platforms.
The Telegram channels that Judische and his related accounts frequented over the years show this user divides their time between posting in SIM-swapping and cybercrime cashout channels, and harassing and stalking others in harm communities like Leak Society and Court.
Mandiant has attributed the Snowflake compromises to a group it calls “UNC5537,” with members based in North America and Turkey. KrebsOnSecurity has learned Judische is a 26-year-old software engineer in Ontario, Canada.
Sources close to the investigation into the Snowflake incident tell KrebsOnSecurity the UNC5537 member in Turkey is John Erin Binns, an elusive American man indicted by the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) for a 2021 breach at T-Mobile that exposed the personal information of at least 76.6 million customers.
Binns is currently in custody in a Turkish prison and fighting his extradition. Meanwhile, he has been suing almost every federal agency and agent that contributed investigative resources to his case.
In June 2024, a Mandiant employee told Bloomberg that UNC5537 members have made death threats against cybersecurity experts investigating the hackers, and that in one case the group used artificial intelligence to create fake nude photos of a researcher to harass them.
In June 2024, two American men pleaded guilty to hacking into a U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) online portal that tapped into 16 different federal law enforcement databases. Sagar “Weep” Singh, a 20-year-old from Rhode Island, and Nicholas “Convict” Ceraolo, 25, of Queens, NY, were both active in SIM-swapping communities.
Singh and Ceraolo hacked into a number of foreign police department email accounts, and used them to make phony “emergency data requests” to social media platforms seeking account information about specific users they were stalking. According to the government, in each case the men impersonating the foreign police departments told those platforms the request was urgent because the account holders had been trading in child pornography or engaging in child extortion.
Eventually, the two men formed part of a group of cybercriminals known to its members as “ViLE,” who specialize in obtaining personal information about third-party victims, which they then used to harass, threaten or extort the victims, a practice known as “doxing.”
The U.S. government says Singh and Ceraolo worked closely with a third man — referenced in the indictment as co-conspirator #1 or “CC-1” — to administer a doxing forum where victims could pay to have their personal information removed.
The government doesn’t name CC-1 or the doxing forum, but CC-1’s hacker handle is “Kayte” (a.k.a. “KT“) which corresponds to the nickname of a 23-year-old man who lives with his parents in Coffs Harbor, Australia. For several years (with a brief interruption), KT has been the administrator of a truly vile doxing community known as the Doxbin.

A screenshot of the website for the cybercriminal group “ViLE.” Image: USDOJ.
People whose names and personal information appear on the Doxbin can quickly find themselves the target of extended harassment campaigns, account hacking, SIM-swapping and even swatting — which involves falsely reporting a violent incident at a target’s address to trick local police into responding with potentially deadly force.
A handful of Com members targeted by federal authorities have gone so far as to perpetrate swatting, doxing, and other harassment against the same federal agents who are trying to unravel their alleged crimes. This has led some investigators working cases involving the Com to begin redacting their names from affidavits and indictments filed in federal court.
In January 2024, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that prosecutors in Florida had charged a 19-year-old alleged Scattered Spider member named Noah Michael Urban with wire fraud and identity theft. That story recounted how Urban’s alleged hacker identities “King Bob” and “Sosa” inhabited a world in which rival cryptocurrency theft rings frequently settled disputes through so-called “violence-as-a-service” offerings — hiring strangers online to perpetrate firebombings, beatings and kidnappings against their rivals.
Urban’s indictment shows the name of the federal agent who testified to it has been blacked out:

The final page of Noah Michael Urban’s indictment shows the investigating agent redacted their name from charging documents.
In June 2022, this blog told the story of two men charged with hacking into the Ring home security cameras of a dozen random people and then methodically swatting each of them. Adding insult to injury, the men used the compromised security cameras to record live footage of local police swarming those homes.

McCarty, in a mugshot.
James Thomas Andrew McCarty, Charlotte, N.C., and Kya “Chumlul” Nelson, of Racine, Wisc., conspired to hack into Yahoo email accounts belonging to victims in the United States. The two would check how many of those Yahoo accounts were associated with Ring accounts, and then target people who used the same password for both accounts.
The Telegram and Discord aliases allegedly used by McCarty — “Aspertaine” and “Couch,” among others — correspond to an identity that was active in certain channels dedicated to SIM-swapping.
What KrebsOnSecurity didn’t report at the time is that both ChumLul and Aspertaine were active members of CVLT, wherein those identities clearly participated in harassing and exploiting young teens online.
In June 2024, McCarty was sentenced to seven years in prison after pleading guilty to making hoax calls that elicited police SWAT responses. Nelson also pleaded guilty and received a seven-year prison sentence.
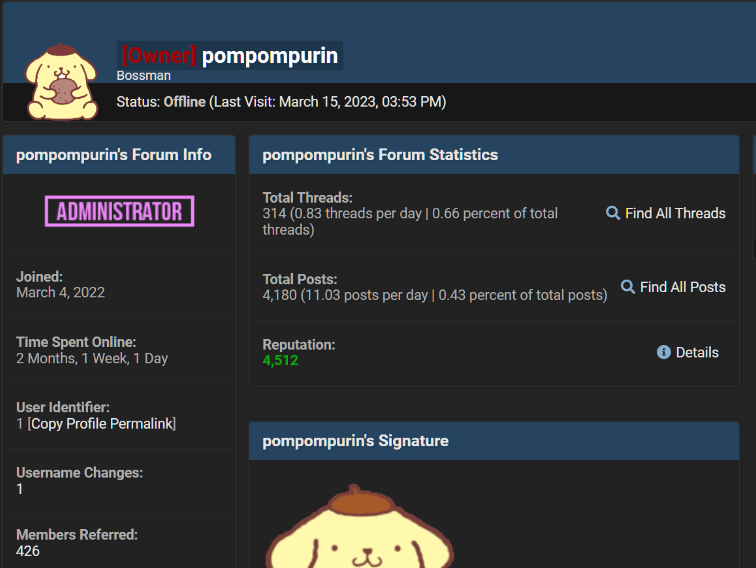
In March 2023, U.S. federal agents in New York announced they’d arrested “Pompompurin,” the alleged administrator of Breachforums, an English-language cybercrime forum where hacked corporate databases frequently appear for sale. In cases where the victim organization isn’t extorted in advance by hackers, being listed on Breachforums has often been the way many victims first learned of an intrusion.
Pompompurin had been a nemesis to the FBI for several years. In November 2021, KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that thousands of fake emails about a cybercrime investigation were blasted out from the FBI’s email systems and Internet addresses.
Pompompurin took credit for that stunt, and said he was able to send the FBI email blast by exploiting a flaw in an FBI portal designed to share information with state and local law enforcement authorities. The FBI later acknowledged that a software misconfiguration allowed someone to send the fake emails.
In December, 2022, KrebsOnSecurity detailed how hackers active on BreachForums had infiltrated the FBI’s InfraGard program, a vetted network designed to build cyber and physical threat information sharing partnerships with experts in the private sector. The hackers impersonated the CEO of a major financial company, applied for InfraGard membership in the CEO’s name, and were granted admission to the community.
The feds named Pompompurin as 21-year-old Peekskill resident Conor Brian Fitzpatrick, who was originally charged with one count of conspiracy to solicit individuals to sell unauthorized access devices (stolen usernames and passwords). But after FBI agents raided and searched the home where Fitzpatrick lived with his parents, prosecutors tacked on charges for possession of child pornography.
Recent actions by the DOJ indicate the government is well aware of the significant overlap between leading members of The Com and harm communities. But the government also is growing more sensitive to the criticism that it can often take months or years to gather enough evidence to criminally charge some of these suspects, during which time the perpetrators can abuse and recruit countless new victims.
Late last year, however, the DOJ signaled a new tactic in pursuing leaders of harm communities like 764: Charging them with domestic terrorism.
In December 2023, the government charged (PDF) a Hawaiian man with possessing and sharing sexually explicit videos and images of prepubescent children being abused. Prosecutors allege Kalana Limkin, 18, of Hilo, Hawaii, admitted he was an associate of CVLT and 764, and that he was the founder of a splinter harm group called Cultist. Limkin’s Telegram profile shows he also was active on the harm community Slit Town.
The relevant citation from Limkin’s complaint reads:
“Members of the group ‘764’ have conspired and continue to conspire in both online and in-person venues to engage in violent actions in furtherance of a Racially Motivated Violent Extremist ideology, wholly or in part through activities that violate federal criminal law meeting the statutory definition of Domestic Terrorism, defined in Title 18, United States Code, § 2331.”
Experts say charging harm groups under anti-terrorism statutes potentially gives the government access to more expedient investigative powers than it would normally have in a run-of-the-mill criminal hacking case.
“What it ultimately gets you is additional tools you can use in the investigation, possibly warrants and things like that,” said Mark Rasch, a former U.S. federal cybercrime prosecutor and now general counsel for the New York-based cybersecurity firm Unit 221B. “It can also get you additional remedies at the end of the case, like greater sanctions, more jail time, fines and forfeiture.”
But Rasch said this tactic can backfire on prosecutors who overplay their hand and go after someone who ends up challenging the charges in court.
“If you’re going to charge a hacker or pedophile with a crime like terrorism, that’s going to make it harder to get a conviction,” Rasch said. “It adds to the prosecutorial burden and increases the likelihood of getting an acquittal.”
Rasch said it’s unclear where it is appropriate to draw the line in the use of terrorism statutes to disrupt harm groups online, noting that there certainly are circumstances where individuals can commit violations of domestic anti-terrorism statutes through their Internet activity alone.
“The Internet is a platform like any other, where virtually any kind of crime that can be committed in the real world can also be committed online,” he said. “That doesn’t mean all misuse of computers fits within the statutory definition of terrorism.”
The RCMP’s advisory on sexual extortion of minors over the Internet lists a number of potential warning signs that teens may exhibit if they become entangled in these harm groups. The FBI urges anyone who believes their child or someone they know is being exploited to contact their local FBI field office, call 1-800-CALL-FBI, or report it online at tips.fbi.gov.
There are indications that U.S. healthcare giant Change Healthcare has made a $22 million extortion payment to the infamous BlackCat ransomware group (a.k.a. “ALPHV“) as the company struggles to bring services back online amid a cyberattack that has disrupted prescription drug services nationwide for weeks. However, the cybercriminal who claims to have given BlackCat access to Change’s network says the crime gang cheated them out of their share of the ransom, and that they still have the sensitive data Change reportedly paid the group to destroy. Meanwhile, the affiliate’s disclosure appears to have prompted BlackCat to cease operations entirely.

Image: Varonis.
In the third week of February, a cyber intrusion at Change Healthcare began shutting down important healthcare services as company systems were taken offline. It soon emerged that BlackCat was behind the attack, which has disrupted the delivery of prescription drugs for hospitals and pharmacies nationwide for nearly two weeks.
On March 1, a cryptocurrency address that security researchers had already mapped to BlackCat received a single transaction worth approximately $22 million. On March 3, a BlackCat affiliate posted a complaint to the exclusive Russian-language ransomware forum Ramp saying that Change Healthcare had paid a $22 million ransom for a decryption key, and to prevent four terabytes of stolen data from being published online.
The affiliate claimed BlackCat/ALPHV took the $22 million payment but never paid him his percentage of the ransom. BlackCat is known as a “ransomware-as-service” collective, meaning they rely on freelancers or affiliates to infect new networks with their ransomware. And those affiliates in turn earn commissions ranging from 60 to 90 percent of any ransom amount paid.
“But after receiving the payment ALPHV team decide to suspend our account and keep lying and delaying when we contacted ALPHV admin,” the affiliate “Notchy” wrote. “Sadly for Change Healthcare, their data [is] still with us.”
Change Healthcare has neither confirmed nor denied paying, and has responded to multiple media outlets with a similar non-denial statement — that the company is focused on its investigation and on restoring services.
Assuming Change Healthcare did pay to keep their data from being published, that strategy seems to have gone awry: Notchy said the list of affected Change Healthcare partners they’d stolen sensitive data from included Medicare and a host of other major insurance and pharmacy networks.
On the bright side, Notchy’s complaint seems to have been the final nail in the coffin for the BlackCat ransomware group, which was infiltrated by the FBI and foreign law enforcement partners in late December 2023. As part of that action, the government seized the BlackCat website and released a decryption tool to help victims recover their systems.
BlackCat responded by re-forming, and increasing affiliate commissions to as much as 90 percent. The ransomware group also declared it was formally removing any restrictions or discouragement against targeting hospitals and healthcare providers.
However, instead of responding that they would compensate and placate Notchy, a representative for BlackCat said today the group was shutting down and that it had already found a buyer for its ransomware source code.

The seizure notice now displayed on the BlackCat darknet website.
“There’s no sense in making excuses,” wrote the RAMP member “Ransom.” “Yes, we knew about the problem, and we were trying to solve it. We told the affiliate to wait. We could send you our private chat logs where we are shocked by everything that’s happening and are trying to solve the issue with the transactions by using a higher fee, but there’s no sense in doing that because we decided to fully close the project. We can officially state that we got screwed by the feds.”
BlackCat’s website now features a seizure notice from the FBI, but several researchers noted that this image seems to have been merely cut and pasted from the notice the FBI left in its December raid of BlackCat’s network. The FBI has not responded to requests for comment.
Fabian Wosar, head of ransomware research at the security firm Emsisoft, said it appears BlackCat leaders are trying to pull an “exit scam” on affiliates by withholding many ransomware payment commissions at once and shutting down the service.
“ALPHV/BlackCat did not get seized,” Wosar wrote on Twitter/X today. “They are exit scamming their affiliates. It is blatantly obvious when you check the source code of their new takedown notice.”
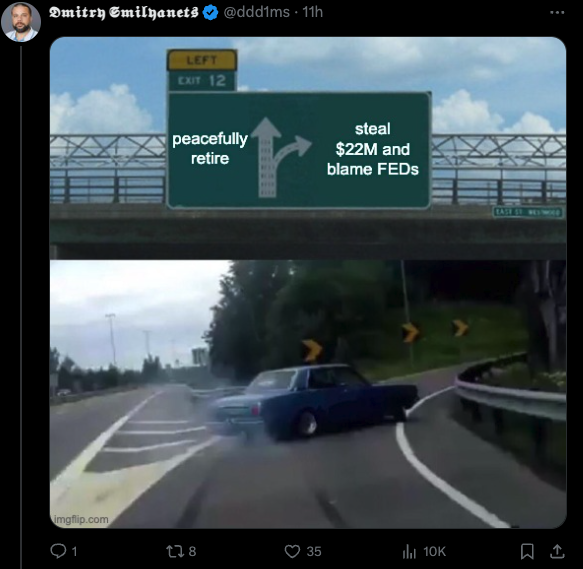
Dmitry Smilyanets, a researcher for the security firm Recorded Future, said BlackCat’s exit scam was especially dangerous because the affiliate still has all the stolen data, and could still demand additional payment or leak the information on his own.
“The affiliates still have this data, and they’re mad they didn’t receive this money, Smilyanets told Wired.com. “It’s a good lesson for everyone. You cannot trust criminals; their word is worth nothing.”
BlackCat’s apparent demise comes closely on the heels of the implosion of another major ransomware group — LockBit, a ransomware gang estimated to have extorted over $120 million in payments from more than 2,000 victims worldwide. On Feb. 20, LockBit’s website was seized by the FBI and the U.K.’s National Crime Agency (NCA) following a months-long infiltration of the group.
LockBit also tried to restore its reputation on the cybercrime forums by resurrecting itself at a new darknet website, and by threatening to release data from a number of major companies that were hacked by the group in the weeks and days prior to the FBI takedown.
But LockBit appears to have since lost any credibility the group may have once had. After a much-promoted attack on the government of Fulton County, Ga., for example, LockBit threatened to release Fulton County’s data unless paid a ransom by Feb. 29. But when Feb. 29 rolled around, LockBit simply deleted the entry for Fulton County from its site, along with those of several financial organizations that had previously been extorted by the group.
Fulton County held a press conference to say that it had not paid a ransom to LockBit, nor had anyone done so on their behalf, and that they were just as mystified as everyone else as to why LockBit never followed through on its threat to publish the county’s data. Experts told KrebsOnSecurity LockBit likely balked because it was bluffing, and that the FBI likely relieved them of that data in their raid.
Smilyanets’ comments are driven home in revelations first published last month by Recorded Future, which quoted an NCA official as saying LockBit never deleted the data after being paid a ransom, even though that is the only reason many of its victims paid.
“If we do not give you decrypters, or we do not delete your data after payment, then nobody will pay us in the future,” LockBit’s extortion notes typically read.
Hopefully, more companies are starting to get the memo that paying cybercrooks to delete stolen data is a losing proposition all around.
Three Americans were charged this week with stealing more than $400 million in a November 2022 SIM-swapping attack. The U.S. government did not name the victim organization, but there is every indication that the money was stolen from the now-defunct cryptocurrency exchange FTX, which had just filed for bankruptcy on that same day.
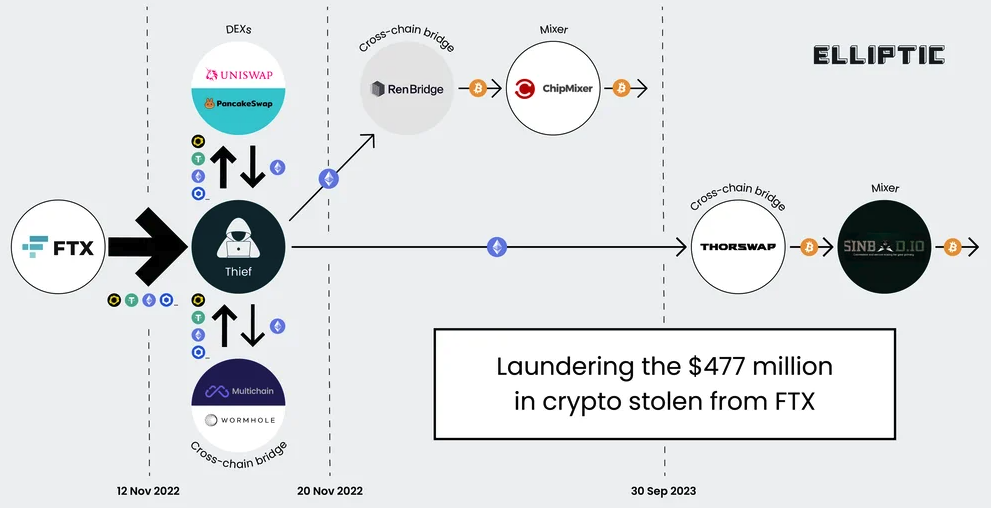
A graphic illustrating the flow of more than $400 million in cryptocurrencies stolen from FTX on Nov. 11-12, 2022. Image: Elliptic.co.
An indictment unsealed this week and first reported on by Ars Technica alleges that Chicago man Robert Powell, a.k.a. “R,” “R$” and “ElSwapo1,” was the ringleader of a SIM-swapping group called the “Powell SIM Swapping Crew.” Colorado resident Emily “Em” Hernandez allegedly helped the group gain access to victim devices in service of SIM-swapping attacks between March 2021 and April 2023. Indiana resident Carter Rohn, a.k.a. “Carti,” and “Punslayer,” allegedly assisted in compromising devices.
In a SIM-swapping attack, the crooks transfer the target’s phone number to a device they control, allowing them to intercept any text messages or phone calls sent to the victim, including one-time passcodes for authentication or password reset links sent via SMS.
The indictment states that the perpetrators in this heist stole the $400 million in cryptocurrencies on Nov. 11, 2022 after they SIM-swapped an AT&T customer by impersonating them at a retail store using a fake ID. However, the document refers to the victim in this case only by the name “Victim 1.”
Wired’s Andy Greenberg recently wrote about FTX’s all-night race to stop a $1 billion crypto heist that occurred on the evening of November 11:
“FTX’s staff had already endured one of the worst days in the company’s short life. What had recently been one of the world’s top cryptocurrency exchanges, valued at $32 billion only 10 months earlier, had just declared bankruptcy. Executives had, after an extended struggle, persuaded the company’s CEO, Sam Bankman-Fried, to hand over the reins to John Ray III, a new chief executive now tasked with shepherding the company through a nightmarish thicket of debts, many of which it seemed to have no means to pay.”
“FTX had, it seemed, hit rock bottom. Until someone—a thief or thieves who have yet to be identified—chose that particular moment to make things far worse. That Friday evening, exhausted FTX staffers began to see mysterious outflows of the company’s cryptocurrency, publicly captured on the Etherscan website that tracks the Ethereum blockchain, representing hundreds of millions of dollars worth of crypto being stolen in real time.”
The indictment says the $400 million was stolen over several hours between November 11 and 12, 2022. Tom Robinson, co-founder of the blockchain intelligence firm Elliptic, said the attackers in the FTX heist began to drain FTX wallets on the evening of Nov. 11, 2022 local time, and continuing until the 12th of November.
Robinson said Elliptic is not aware of any other crypto heists of that magnitude occurring on that date.
“We put the value of the cryptoassets stolen at $477 million,” Robinson said. “The FTX administrators have reported overall losses due to “unauthorized third-party transfers” of $413 million – the discrepancy is likely due to subsequent seizure and return of some of the stolen assets. Either way, it’s certainly over $400 million, and we are not aware of any other thefts from crypto exchanges on this scale, on this date.”
The SIM-swappers allegedly responsible for the $400 million crypto theft are all U.S. residents. But there are some indications they had help from organized cybercriminals based in Russia. In October 2023, Elliptic released a report that found the money stolen from FTX had been laundered through exchanges with ties to criminal groups based in Russia.
“A Russia-linked actor seems a stronger possibility,” Elliptic wrote. “Of the stolen assets that can be traced through ChipMixer, significant amounts are combined with funds from Russia-linked criminal groups, including ransomware gangs and darknet markets, before being sent to exchanges. This points to the involvement of a broker or other intermediary with a nexus in Russia.”
Nick Bax, director of analytics at the cryptocurrency wallet recovery firm Unciphered, said the flow of stolen FTX funds looks more like what his team has seen from groups based in Eastern Europe and Russian than anything they’ve witnessed from US-based SIM-swappers.
“I was a bit surprised by this development but it seems to be consistent with reports from CISA [the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency] and others that “Scattered Spider” has worked with [ransomware] groups like ALPHV/BlackCat,” Bax said.
CISA’s alert on Scattered Spider says they are a cybercriminal group that targets large companies and their contracted information technology (IT) help desks.
“Scattered Spider threat actors, per trusted third parties, have typically engaged in data theft for extortion and have also been known to utilize BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware alongside their usual TTPs,” CISA said, referring to the group’s signature “Tactics, Techniques an Procedures.”
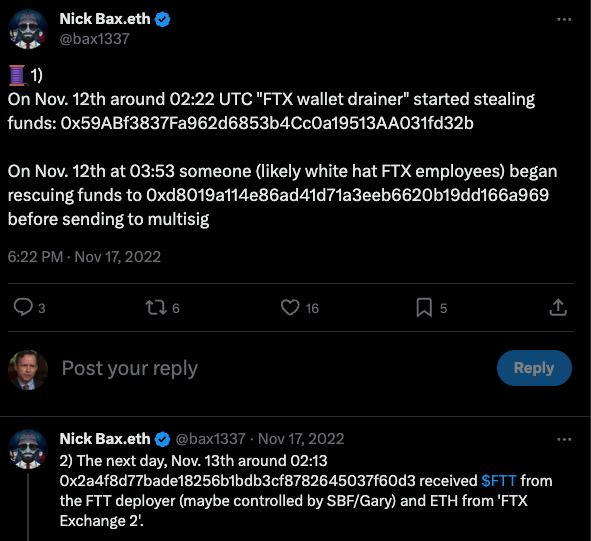
Nick Bax, posting on Twitter/X in Nov 2022 about his research on the $400 million FTX heist.
Earlier this week, KrebsOnSecurity published a story noting that a Florida man recently charged with being part of a SIM-swapping conspiracy is thought to be a key member of Scattered Spider, a hacking group also known as 0ktapus. That group has been blamed for a string of cyber intrusions at major U.S. technology companies during the summer of 2022.
Financial claims involving FTX’s bankruptcy proceedings are being handled by the financial and risk consulting giant Kroll. In August 2023, Kroll suffered its own breach after a Kroll employee was SIM-swapped. According to Kroll, the thieves stole user information for multiple cryptocurrency platforms that rely on Kroll services to handle bankruptcy proceedings.
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment for this story from Kroll, the FBI, the prosecuting attorneys, and Sullivan & Cromwell, the law firm handling the FTX bankruptcy. This story will be updated in the event any of them respond.
Attorneys for Mr. Powell said they do not know who Victim 1 is in the indictment, as the government hasn’t shared that information yet. Powell’s next court date is a detention hearing on Feb. 2, 2024.
Update, Feb. 3, 12:19 p.m. ET: The FBI declined a request to comment.