Late last year, security researchers made a startling discovery: Kremlin-backed disinformation campaigns were bypassing moderation on social media platforms by leveraging the same malicious advertising technology that powers a sprawling ecosystem of online hucksters and website hackers. A new report on the fallout from that investigation finds this dark ad tech industry is far more resilient and incestuous than previously known.

Image: Infoblox.
In November 2024, researchers at the security firm Qurium published an investigation into “Doppelganger,” a disinformation network that promotes pro-Russian narratives and infiltrates Europe’s media landscape by pushing fake news through a network of cloned websites.
Doppelganger campaigns use specialized links that bounce the visitor’s browser through a long series of domains before the fake news content is served. Qurium found Doppelganger relies on a sophisticated “domain cloaking” service, a technology that allows websites to present different content to search engines compared to what regular visitors see. The use of cloaking services helps the disinformation sites remain online longer than they otherwise would, while ensuring that only the targeted audience gets to view the intended content.
Qurium discovered that Doppelganger’s cloaking service also promoted online dating sites, and shared much of the same infrastructure with VexTrio, which is thought to be the oldest malicious traffic distribution system (TDS) in existence. While TDSs are commonly used by legitimate advertising networks to manage traffic from disparate sources and to track who or what is behind each click, VexTrio’s TDS largely manages web traffic from victims of phishing, malware, and social engineering scams.
Digging deeper, Qurium noticed Doppelganger’s cloaking service used an Internet provider in Switzerland as the first entry point in a chain of domain redirections. They also noticed the same infrastructure hosted a pair of co-branded affiliate marketing services that were driving traffic to sketchy adult dating sites: LosPollos[.]com and TacoLoco[.]co.
The LosPollos ad network incorporates many elements and references from the hit series “Breaking Bad,” mirroring the fictional “Los Pollos Hermanos” restaurant chain that served as a money laundering operation for a violent methamphetamine cartel.

The LosPollos advertising network invokes characters and themes from the hit show Breaking Bad. The logo for LosPollos (upper left) is the image of Gustavo Fring, the fictional chicken restaurant chain owner in the show.
Affiliates who sign up with LosPollos are given JavaScript-heavy “smartlinks” that drive traffic into the VexTrio TDS, which in turn distributes the traffic among a variety of advertising partners, including dating services, sweepstakes offers, bait-and-switch mobile apps, financial scams and malware download sites.
LosPollos affiliates typically stitch these smart links into WordPress websites that have been hacked via known vulnerabilities, and those affiliates will earn a small commission each time an Internet user referred by any of their hacked sites falls for one of these lures.
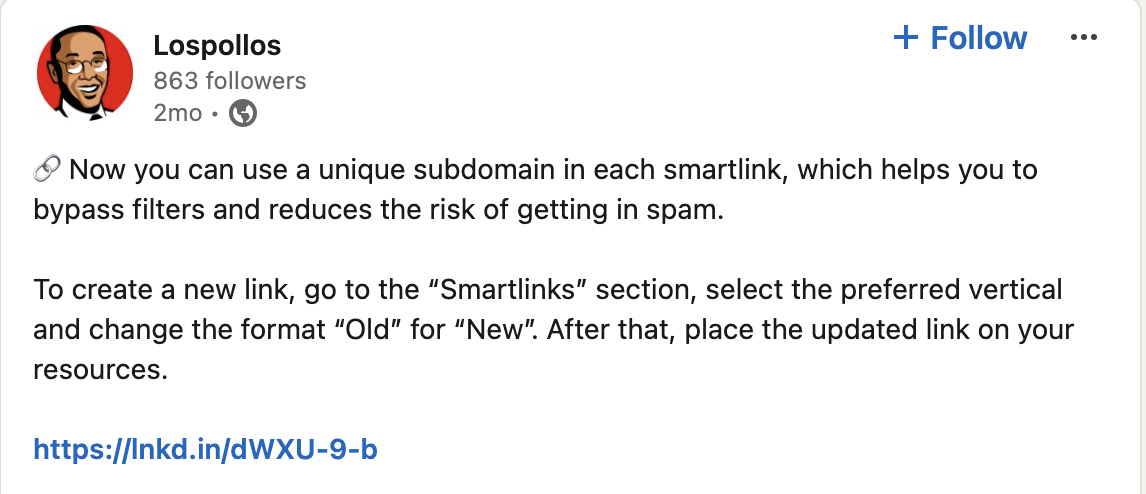
The Los Pollos advertising network promoting itself on LinkedIn.
According to Qurium, TacoLoco is a traffic monetization network that uses deceptive tactics to trick Internet users into enabling “push notifications,” a cross-platform browser standard that allows websites to show pop-up messages which appear outside of the browser. For example, on Microsoft Windows systems these notifications typically show up in the bottom right corner of the screen — just above the system clock.
In the case of VexTrio and TacoLoco, the notification approval requests themselves are deceptive — disguised as “CAPTCHA” challenges designed to distinguish automated bot traffic from real visitors. For years, VexTrio and its partners have successfully tricked countless users into enabling these site notifications, which are then used to continuously pepper the victim’s device with a variety of phony virus alerts and misleading pop-up messages.
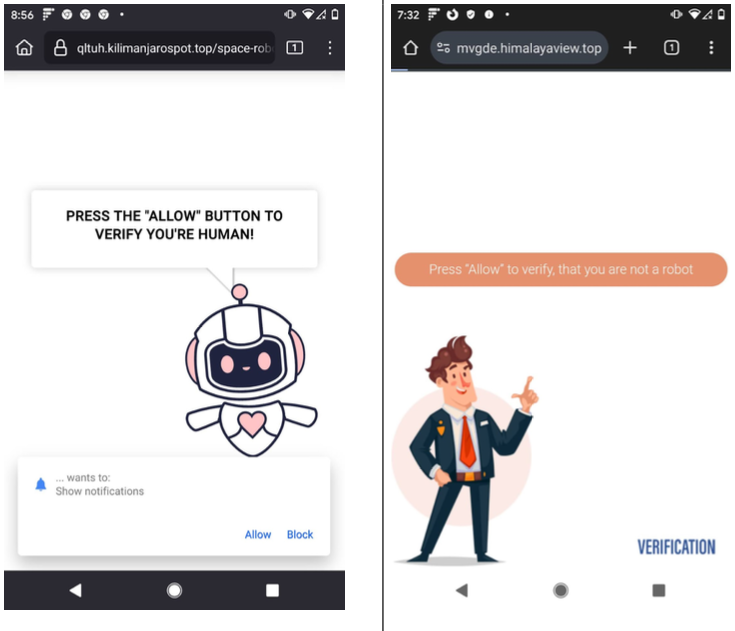
Examples of VexTrio landing pages that lead users to accept push notifications on their device.
According to a December 2024 annual report from GoDaddy, nearly 40 percent of compromised websites in 2024 redirected visitors to VexTrio via LosPollos smartlinks.
On November 14, 2024, Qurium published research to support its findings that LosPollos and TacoLoco were services operated by Adspro Group, a company registered in the Czech Republic and Russia, and that Adspro runs its infrastructure at the Swiss hosting providers C41 and Teknology SA.
Qurium noted the LosPollos and TacoLoco sites state that their content is copyrighted by ByteCore AG and SkyForge Digital AG, both Swiss firms that are run by the owner of Teknology SA, Giulio Vitorrio Leonardo Cerutti. Further investigation revealed LosPollos and TacoLoco were apps developed by a company called Holacode, which lists Cerutti as its CEO.
The apps marketed by Holacode include numerous VPN services, as well as one called Spamshield that claims to stop unwanted push notifications. But in January, Infoblox said they tested the app on their own mobile devices, and found it hides the user’s notifications, and then after 24 hours stops hiding them and demands payment. Spamshield subsequently changed its developer name from Holacode to ApLabz, although Infoblox noted that the Terms of Service for several of the rebranded ApLabz apps still referenced Holacode in their terms of service.
Incredibly, Cerutti threatened to sue me for defamation before I’d even uttered his name or sent him a request for comment (Cerutti sent the unsolicited legal threat back in January after his company and my name were merely tagged in an Infoblox post on LinkedIn about VexTrio).
Asked to comment on the findings by Qurium and Infoblox, Cerutti vehemently denied being associated with VexTrio. Cerutti asserted that his companies all strictly adhere to the regulations of the countries in which they operate, and that they have been completely transparent about all of their operations.
“We are a group operating in the advertising and marketing space, with an affiliate network program,” Cerutti responded. “I am not [going] to say we are perfect, but I strongly declare we have no connection with VexTrio at all.”
“Unfortunately, as a big player in this space we also get to deal with plenty of publisher fraud, sketchy traffic, fake clicks, bots, hacked, listed and resold publisher accounts, etc, etc.,” Cerutti continued. “We bleed lots of money to such malpractices and conduct regular internal screenings and audits in a constant battle to remove bad traffic sources. It is also a highly competitive space, where some upstarts will often play dirty against more established mainstream players like us.”
Working with Qurium, researchers at the security firm Infoblox released details about VexTrio’s infrastructure to their industry partners. Just four days after Qurium published its findings, LosPollos announced it was suspending its push monetization service. Less than a month later, Adspro had rebranded to Aimed Global.
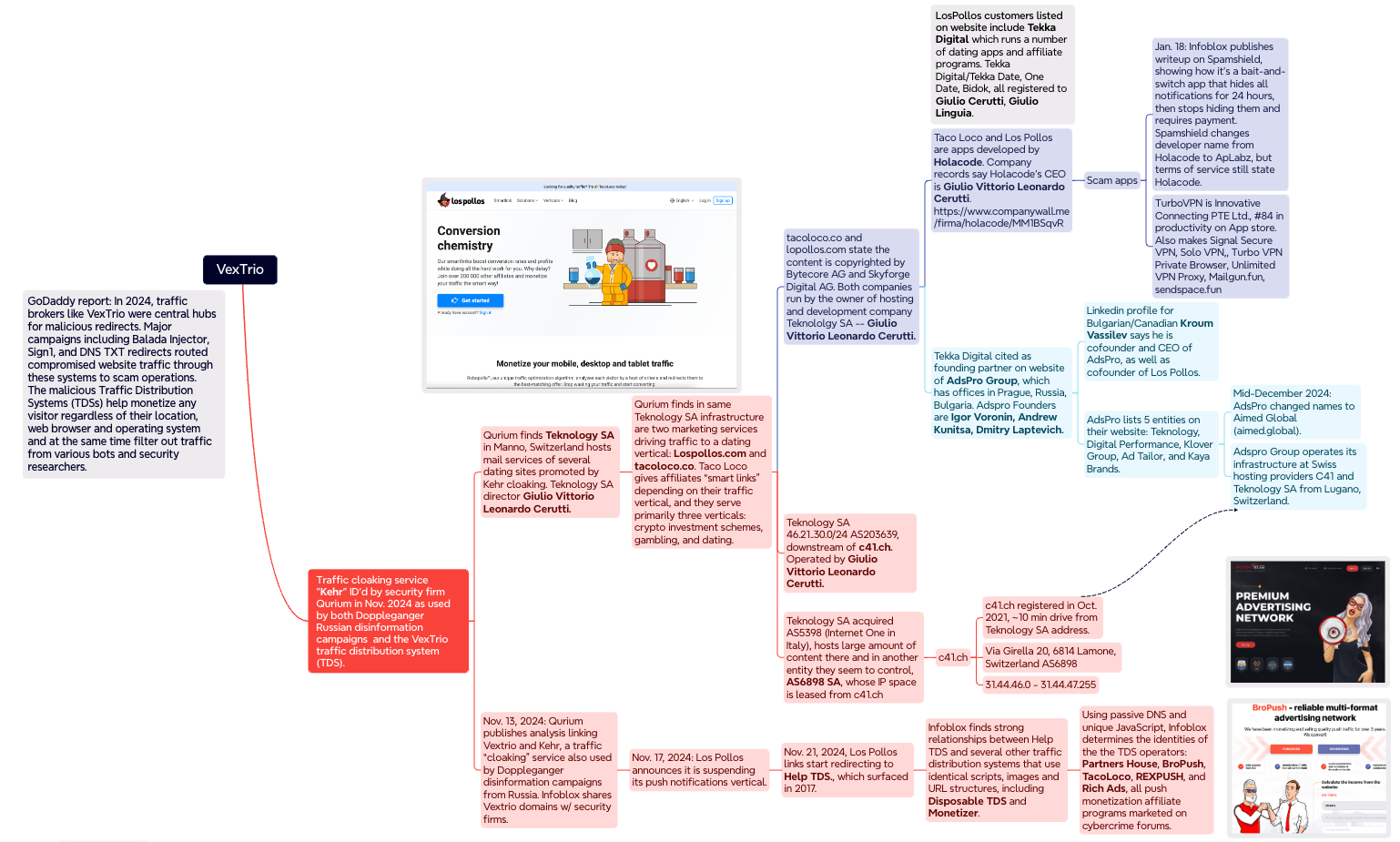
A mind map illustrating some of the key findings and connections in the Infoblox and Qurium investigations. Click to enlarge.
In March 2025, researchers at GoDaddy chronicled how DollyWay — a malware strain that has consistently redirected victims to VexTrio throughout its eight years of activity — suddenly stopped doing that on November 20, 2024. Virtually overnight, DollyWay and several other malware families that had previously used VexTrio began pushing their traffic through another TDS called Help TDS.
Digging further into historical DNS records and the unique code scripts used by the Help TDS, Infoblox determined it has long enjoyed an exclusive relationship with VexTrio (at least until LosPollos ended its push monetization service in November).
In a report released today, Infoblox said an exhaustive analysis of the JavaScript code, website lures, smartlinks and DNS patterns used by VexTrio and Help TDS linked them with at least four other TDS operators (not counting TacoLoco). Those four entities — Partners House, BroPush, RichAds and RexPush — are all Russia-based push monetization programs that pay affiliates to drive signups for a variety of schemes, but mostly online dating services.
“As Los Pollos push monetization ended, we’ve seen an increase in fake CAPTCHAs that drive user acceptance of push notifications, particularly from Partners House,” the Infoblox report reads. “The relationship of these commercial entities remains a mystery; while they are certainly long-time partners redirecting traffic to one another, and they all have a Russian nexus, there is no overt common ownership.”
Renee Burton, vice president of threat intelligence at Infoblox, said the security industry generally treats the deceptive methods used by VexTrio and other malicious TDSs as a kind of legally grey area that is mostly associated with less dangerous security threats, such as adware and scareware.
But Burton argues that this view is myopic, and helps perpetuate a dark adtech industry that also pushes plenty of straight-up malware, noting that hundreds of thousands of compromised websites around the world every year redirect victims to the tangled web of VexTrio and VexTrio-affiliate TDSs.
“These TDSs are a nefarious threat, because they’re the ones you can connect to the delivery of things like information stealers and scams that cost consumers billions of dollars a year,” Burton said. “From a larger strategic perspective, my takeaway is that Russian organized crime has control of malicious adtech, and these are just some of the many groups involved.”
As KrebsOnSecurity warned way back in 2020, it’s a good idea to be very sparing in approving notifications when browsing the Web. In many cases these notifications are benign, but as we’ve seen there are numerous dodgy firms that are paying site owners to install their notification scripts, and then reselling that communications pathway to scammers and online hucksters.
If you’d like to prevent sites from ever presenting notification requests, all of the major browser makers let you do this — either across the board or on a per-website basis. While it is true that blocking notifications entirely can break the functionality of some websites, doing this for any devices you manage on behalf of your less tech-savvy friends or family members might end up saving everyone a lot of headache down the road.
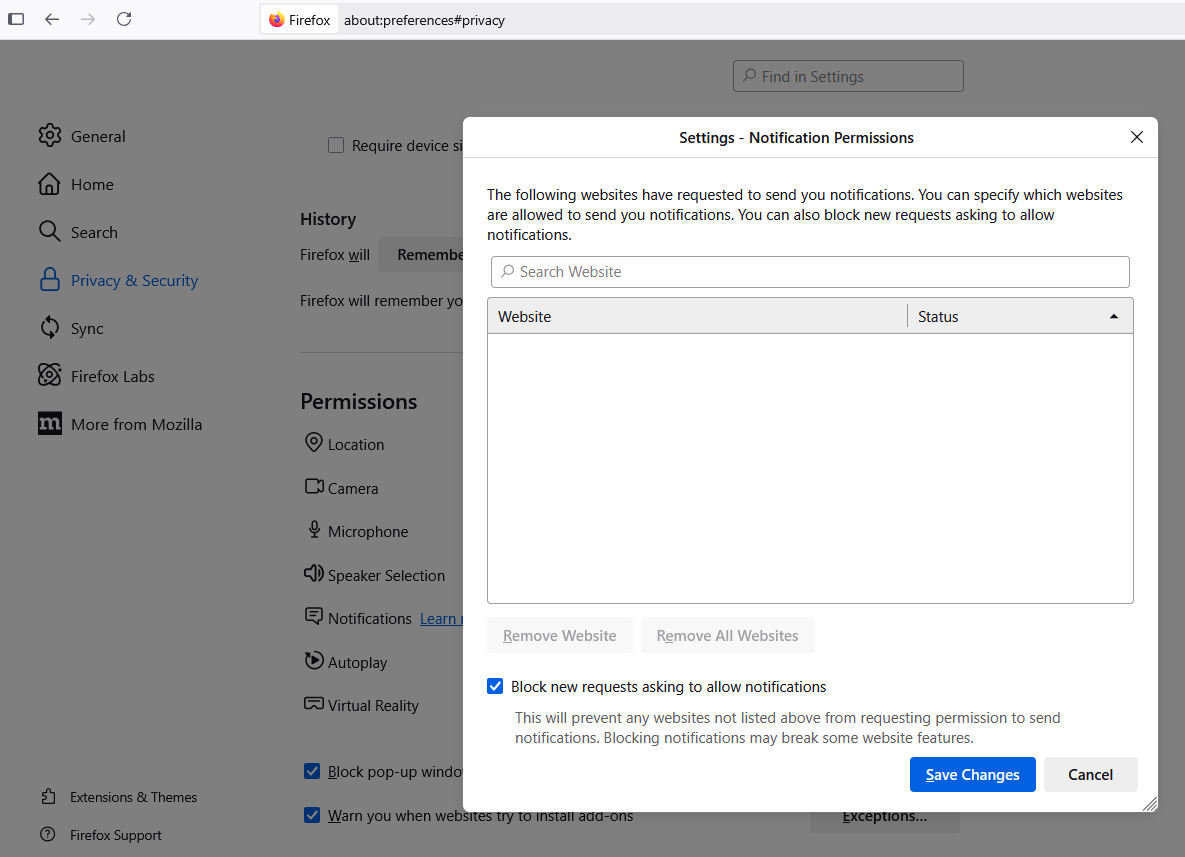
To modify site notification settings in Mozilla Firefox, navigate to Settings, Privacy & Security, Permissions, and click the “Settings” tab next to “Notifications.” That page will display any notifications already permitted and allow you to edit or delete any entries. Tick the box next to “Block new requests asking to allow notifications” to stop them altogether.
In Google Chrome, click the icon with the three dots to the right of the address bar, scroll all the way down to Settings, Privacy and Security, Site Settings, and Notifications. Select the “Don’t allow sites to send notifications” button if you want to banish notification requests forever.
In Apple’s Safari browser, go to Settings, Websites, and click on Notifications in the sidebar. Uncheck the option to “allow websites to ask for permission to send notifications” if you wish to turn off notification requests entirely.
The FBI joined authorities across Europe last week in seizing domain names for Cracked and Nulled, English-language cybercrime forums with millions of users that trafficked in stolen data, hacking tools and malware. An investigation into the history of these communities shows their apparent co-founders quite openly operate an Internet service provider and a pair of e-commerce platforms catering to buyers and sellers on both forums.
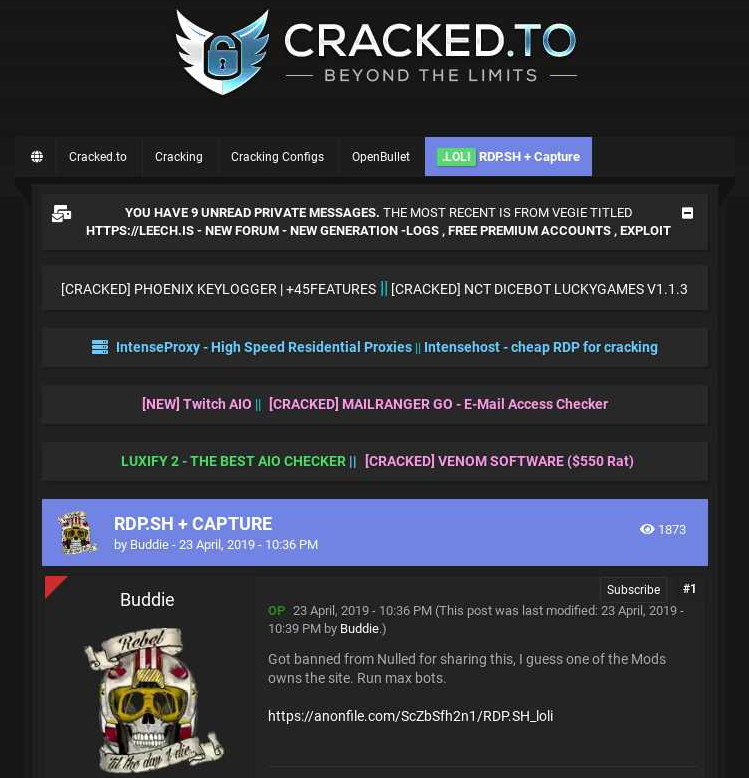
In this 2019 post from Cracked, a forum moderator told the author of the post (Buddie) that the owner of the RDP service was the founder of Nulled, a.k.a. “Finndev.” Image: Ke-la.com.
On Jan. 30, the U.S. Department of Justice said it seized eight domain names that were used to operate Cracked, a cybercrime forum that sprang up in 2018 and attracted more than four million users. The DOJ said the law enforcement action, dubbed Operation Talent, also seized domains tied to Sellix, Cracked’s payment processor.
In addition, the government seized the domain names for two popular anonymity services that were heavily advertised on Cracked and Nulled and allowed customers to rent virtual servers: StarkRDP[.]io, and rdp[.]sh.
Those archived webpages show both RDP services were owned by an entity called 1337 Services Gmbh. According to corporate records compiled by Northdata.com, 1337 Services GmbH is also known as AS210558 and is incorporated in Hamburg, Germany.
The Cracked forum administrator went by the nicknames “FlorainN” and “StarkRDP” on multiple cybercrime forums. Meanwhile, a LinkedIn profile for a Florian M. from Germany refers to this person as the co-founder of Sellix and founder of 1337 Services GmbH.
Northdata’s business profile for 1337 Services GmbH shows the company is controlled by two individuals: 32-year-old Florian Marzahl and Finn Alexander Grimpe, 28.
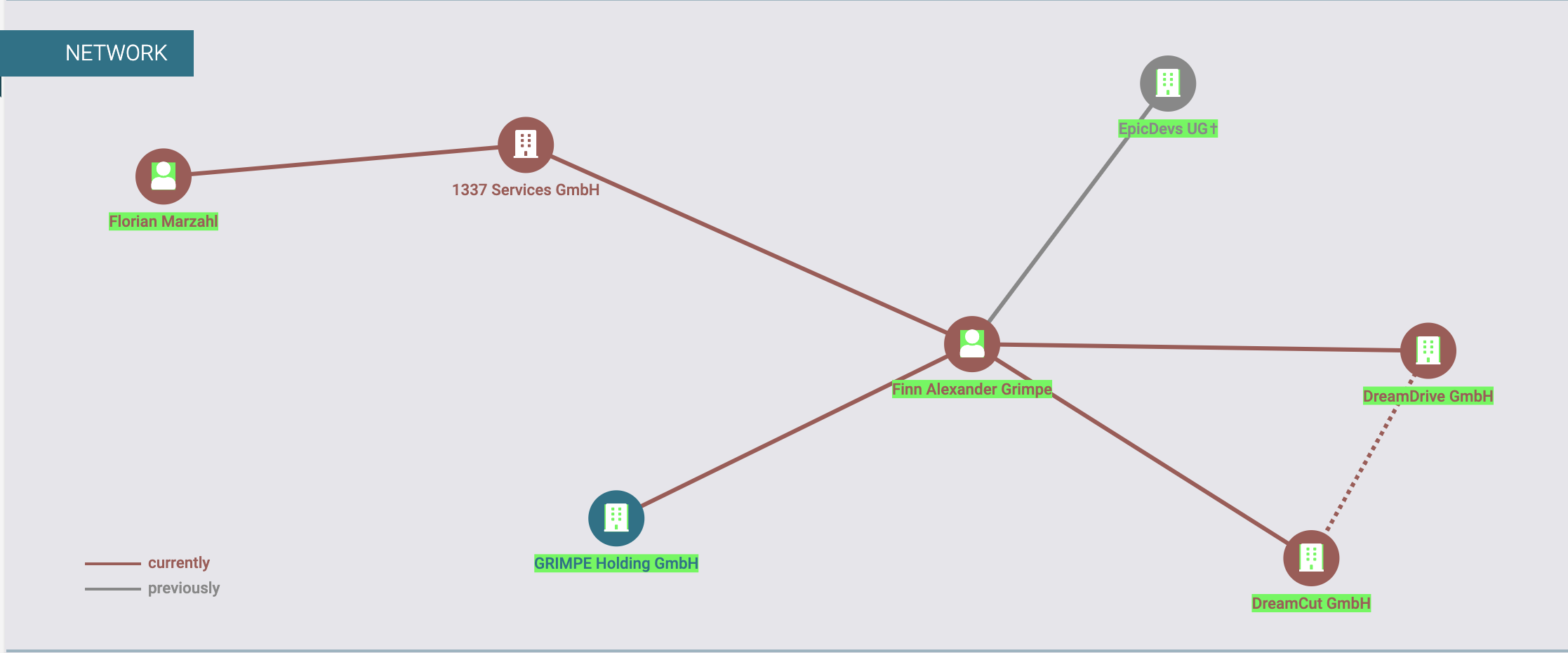
An organization chart showing the owners of 1337 Services GmbH as Florian Marzahl and Finn Grimpe. Image: Northdata.com.
Neither Marzahl nor Grimpe responded to requests for comment. But Grimpe’s first name is interesting because it corresponds to the nickname chosen by the founder of Nulled, who goes by the monikers “Finn” and “Finndev.” NorthData reveals that Grimpe was the founder of a German entity called DreamDrive GmbH, which rented out high-end sports cars and motorcycles.
According to the cyber intelligence firm Intel 471, a user named Finndev registered on multiple cybercrime forums, including Raidforums [seized by the FBI in 2022], Void[.]to, and vDOS, a DDoS-for-hire service that was shut down in 2016 after its founders were arrested.
The email address used for those accounts was f.grimpe@gmail.com. DomainTools.com reports f.grimpe@gmail.com was used to register at least nine domain names, including nulled[.]lol and nulled[.]it. Neither of these domains were among those seized in Operation Talent.
Intel471 finds the user FlorainN registered across multiple cybercrime forums using the email address olivia.messla@outlook.de. The breach tracking service Constella Intelligence says this email address used the same password (and slight variations of it) across many accounts online — including at hacker forums — and that the same password was used in connection with dozens of other email addresses, such as florianmarzahl@hotmail.de, and fmarzahl137@gmail.com.
The Justice Department said the Nulled marketplace had more than five million members, and has been selling stolen login credentials, stolen identification documents and hacking services, as well as tools for carrying out cybercrime and fraud, since 2016.
Perhaps fittingly, both Cracked and Nulled have been hacked over the years, exposing countless private messages between forum users. A review of those messages archived by Intel 471 showed that dozens of early forum members referred privately to Finndev as the owner of shoppy[.]gg, an e-commerce platform that caters to the same clientele as Sellix.
Shoppy was not targeted as part of Operation Talent, and its website remains online. Northdata reports that Shoppy’s business name — Shoppy Ecommerce Ltd. — is registered at an address in Gan-Ner, Israel, but there is no ownership information about this entity. Shoppy did not respond to requests for comment.
Constella found that a user named Shoppy registered on Cracked in 2019 using the email address finn@shoppy[.]gg. Constella says that email address is tied to a Twitter/X account for Shoppy Ecommerce in Israel.
The DOJ said one of the alleged administrators of Nulled, a 29-year-old Argentinian national named Lucas Sohn, was arrested in Spain. The government has not announced any other arrests or charges associated with Operation Talent.
Indeed, both StarkRDP and FloraiN have posted to their accounts on Telegram that there were no charges levied against the proprietors of 1337 Services GmbH. FlorainN told former customers they were in the process of moving to a new name and domain for StarkRDP, where existing accounts and balances would be transferred.
“StarkRDP has always been operating by the law and is not involved in any of these alleged crimes and the legal process will confirm this,” the StarkRDP Telegram account wrote on January 30. “All of your servers are safe and they have not been collected in this operation. The only things that were seized is the website server and our domain. Unfortunately, no one can tell who took it and with whom we can talk about it. Therefore, we will restart operation soon, under a different name, to close the chapter [of] ‘StarkRDP.'”