A Ukrainian man indicted in 2012 for conspiring with a prolific hacking group to steal tens of millions of dollars from U.S. businesses was arrested in Italy and is now in custody in the United States, KrebsOnSecurity has learned.
Sources close to the investigation say Yuriy Igorevich Rybtsov, a 41-year-old from the Russia-controlled city of Donetsk, Ukraine, was previously referenced in U.S. federal charging documents only by his online handle “MrICQ.” According to a 13-year-old indictment (PDF) filed by prosecutors in Nebraska, MrICQ was a developer for a cybercrime group known as “Jabber Zeus.”
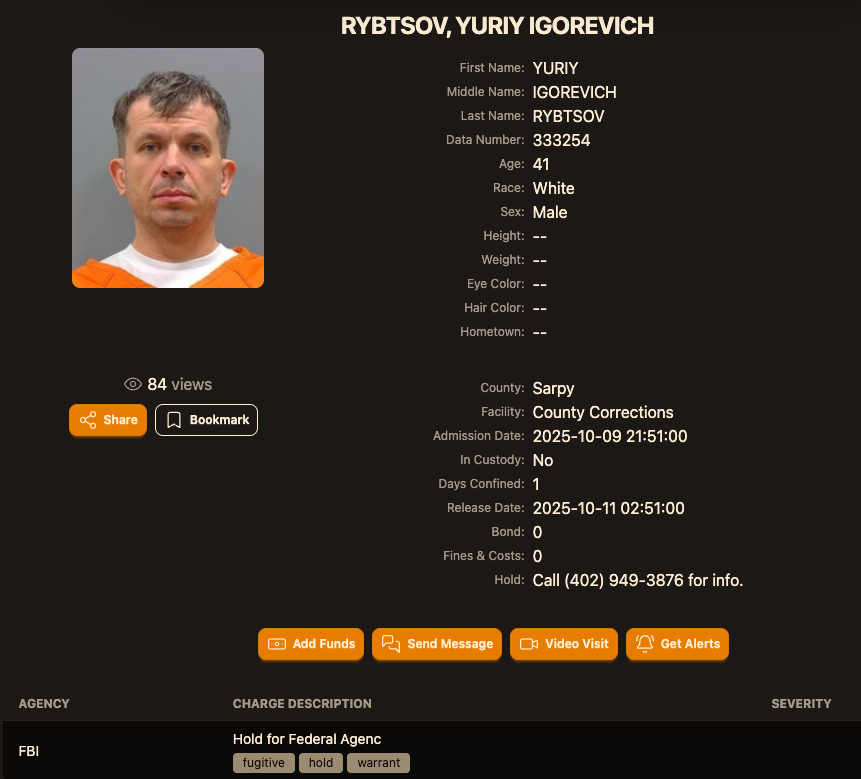
Image: lockedup dot wtf.
The Jabber Zeus name is derived from the malware they used — a custom version of the ZeuS banking trojan — that stole banking login credentials and would send the group a Jabber instant message each time a new victim entered a one-time passcode at a financial institution website. The gang targeted mostly small to mid-sized businesses, and they were an early pioneer of so-called “man-in-the-browser” attacks, malware that can silently intercept any data that victims submit in a web-based form.
Once inside a victim company’s accounts, the Jabber Zeus crew would modify the firm’s payroll to add dozens of “money mules,” people recruited through elaborate work-at-home schemes to handle bank transfers. The mules in turn would forward any stolen payroll deposits — minus their commissions — via wire transfers to other mules in Ukraine and the United Kingdom.
The 2012 indictment targeting the Jabber Zeus crew named MrICQ as “John Doe #3,” and said this person handled incoming notifications of newly compromised victims. The Department of Justice (DOJ) said MrICQ also helped the group launder the proceeds of their heists through electronic currency exchange services.
Two sources familiar with the Jabber Zeus investigation said Rybtsov was arrested in Italy, although the exact date and circumstances of his arrest remain unclear. A summary of recent decisions (PDF) published by the Italian Supreme Court states that in April 2025, Rybtsov lost a final appeal to avoid extradition to the United States.
According to the mugshot website lockedup[.]wtf, Rybtsov arrived in Nebraska on October 9, and was being held under an arrest warrant from the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
The data breach tracking service Constella Intelligence found breached records from the business profiling site bvdinfo[.]com showing that a 41-year-old Yuriy Igorevich Rybtsov worked in a building at 59 Barnaulska St. in Donetsk. Further searching on this address in Constella finds the same apartment building was shared by a business registered to Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, the leader of the Jabber Zeus crew in Ukraine.

Vyacheslav “Tank” Penchukov, seen here performing as “DJ Slava Rich” in Ukraine, in an undated photo from social media.
Penchukov was arrested in 2022 while traveling to meet his wife in Switzerland. Last year, a federal court in Nebraska sentenced Penchukov to 18 years in prison and ordered him to pay more than $73 million in restitution.
Lawrence Baldwin is founder of myNetWatchman, a threat intelligence company based in Georgia that began tracking and disrupting the Jabber Zeus gang in 2009. myNetWatchman had secretly gained access to the Jabber chat server used by the Ukrainian hackers, allowing Baldwin to eavesdrop on the daily conversations between MrICQ and other Jabber Zeus members.
Baldwin shared those real-time chat records with multiple state and federal law enforcement agencies, and with this reporter. Between 2010 and 2013, I spent several hours each day alerting small businesses across the country that their payroll accounts were about to be drained by these cybercriminals.
Those notifications, and Baldwin’s tireless efforts, saved countless would-be victims a great deal of money. In most cases, however, we were already too late. Nevertheless, the pilfered Jabber Zeus group chats provided the basis for dozens of stories published here about small businesses fighting their banks in court over six- and seven-figure financial losses.
Baldwin said the Jabber Zeus crew was far ahead of its peers in several respects. For starters, their intercepted chats showed they worked to create a highly customized botnet directly with the author of the original Zeus Trojan — Evgeniy Mikhailovich Bogachev, a Russian man who has long been on the FBI’s “Most Wanted” list. The feds have a standing $3 million reward for information leading to Bogachev’s arrest.

Evgeniy M. Bogachev, in undated photos.
The core innovation of Jabber Zeus was an alert that MrICQ would receive each time a new victim entered a one-time password code into a phishing page mimicking their financial institution. The gang’s internal name for this component was “Leprechaun,” (the video below from myNetWatchman shows it in action). Jabber Zeus would actually re-write the HTML code as displayed in the victim’s browser, allowing them to intercept any passcodes sent by the victim’s bank for multi-factor authentication.
“These guys had compromised such a large number of victims that they were getting buried in a tsunami of stolen banking credentials,” Baldwin told KrebsOnSecurity. “But the whole point of Leprechaun was to isolate the highest-value credentials — the commercial bank accounts with two-factor authentication turned on. They knew these were far juicier targets because they clearly had a lot more money to protect.”
Baldwin said the Jabber Zeus trojan also included a custom “backconnect” component that allowed the hackers to relay their bank account takeovers through the victim’s own infected PC.
“The Jabber Zeus crew were literally connecting to the victim’s bank account from the victim’s IP address, or from the remote control function and by fully emulating the device,” he said. “That trojan was like a hot knife through butter of what everyone thought was state-of-the-art secure online banking at the time.”
Although the Jabber Zeus crew was in direct contact with the Zeus author, the chats intercepted by myNetWatchman show Bogachev frequently ignored the group’s pleas for help. The government says the real leader of the Jabber Zeus crew was Maksim Yakubets, a 38-year Ukrainian man with Russian citizenship who went by the hacker handle “Aqua.”

Alleged Evil Corp leader Maksim “Aqua” Yakubets. Image: FBI
The Jabber chats intercepted by Baldwin show that Aqua interacted almost daily with MrICQ, Tank and other members of the hacking team, often facilitating the group’s money mule and cashout activities remotely from Russia.
The government says Yakubets/Aqua would later emerge as the leader of an elite cybercrime ring of at least 17 hackers that referred to themselves internally as “Evil Corp.” Members of Evil Corp developed and used the Dridex (a.k.a. Bugat) trojan, which helped them siphon more than $100 million from hundreds of victim companies in the United States and Europe.
This 2019 story about the government’s $5 million bounty for information leading to Yakubets’s arrest includes excerpts of conversations between Aqua, Tank, Bogachev and other Jabber Zeus crew members discussing stories I’d written about their victims. Both Baldwin and I were interviewed at length for a new weekly six-part podcast by the BBC that delves deep into the history of Evil Corp. Episode One focuses on the evolution of Zeus, while the second episode centers on an investigation into the group by former FBI agent Jim Craig.

Image: https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/w3ct89y8

How do hackers hack phones? In several ways. But also, there are several ways you can prevent it from happening to you. The thing is that our phones are like little treasure chests. They’re loaded with plenty of personal data, and we use them to shop, bank, and take care of other personal and financial matters—all of which are of high value to identity thieves. However, you can protect yourself and your phone by knowing what to look out for and by taking a few simple steps. Let’s break it down by first understanding what phone hacking is, taking a look at some common attacks, and learning how you can prevent it.
Phone hacking refers to any method where an unauthorized third party gains access to your smartphone and its data. This isn’t just one single technique; it covers a wide range of cybercrimes. A phone hack can happen through software vulnerabilities, like the spyware campaigns throughout the years that could monitor calls and messages. It can also occur over unsecured networks, such as a hacker intercepting your data on public Wi-Fi. Sometimes, it’s as simple as physical access, where someone installs tracking software on an unattended device.
Hackers have multiple avenues of attacking your phone. Among these common methods are using malicious apps disguised as legitimate software, exploiting the vulnerabilities of unsecure public Wi-Fi networks, or deploying sophisticated zero-click exploits that require no interaction from you at all. The most common method, however, remains social engineering, where they trick you into giving them access. Let’s further explore these common hacking techniques below.
Whether hackers sneak it onto your phone by physically accessing your phone or by tricking you into installing it via a phony app, a sketchy website, or a phishing attack, hacking software can create problems for you in a couple of ways:
Some possible signs of hacking software on your phone include:
In all, hacking software can eat up system resources, create conflicts with other apps, and use your data or internet connection to pass your personal information into the hands of hackers.
This classic form of attack has been leveled at our computers for years. Phishing is where hackers impersonate a company or trusted individual to get access to your accounts or personal info or both. These attacks take many forms such as emails, texts, instant messages, and so forth, some of which can look really legitimate. Common to them are links to bogus sites that attempt to trick you into handing over personal info or that install malware to wreak havoc on your device or likewise steal information. Learning to spot a phishing attack is one way to keep yourself from falling victim to one.
Professional hackers can use dedicated technologies that search for vulnerable mobile devices with an open Bluetooth connection. Hackers can pull off these attacks when they are within range of your phone, up to 30 feet away, usually in a populated area. When hackers make a Bluetooth connection to your phone, they might access your data and info, yet that data and info must be downloaded while the phone is within range. This is a more sophisticated attack given the effort and technology involved.
In August of 2019, then CEO of Twitter had his phone hacked by SIM card swapping scam. In this type of scam, a hacker contacts your phone provider, pretends to be you, then asks for a replacement SIM card. Once the provider sends the new SIM to the hacker, the old SIM card is deactivated, and your phone number will be effectively stolen. This enables the hacker to take control of your phone calls, messages, among others. The task of impersonating someone else seems difficult, yet it happened to the CEO of a major tech company, underscoring the importance of protecting your personal info and identity online to prevent hackers from pulling off this and other crimes.
While a phone call itself cannot typically install malware on your device, it is a primary tool for social engineering, known as vishing or voice phishing. A hacker might call, impersonating your bank or tech support company, and trick you into revealing sensitive information like passwords or financial details. They might also try to convince you to install a malicious app. Another common tactic is the “one-ring” scam, where they hang up hoping you’ll call back a premium-rate number. To stay safe, be wary of unsolicited calls, never provide personal data, block suspicious numbers, and check that your call forwarding isn’t enabled.
Generally, a phone that is powered off is a difficult target for remote hackers. However, modern smartphones aren’t always truly off. Features like Apple’s Find My network can operate in a low-power mode, keeping certain radios active. Furthermore, if a device has been previously compromised with sophisticated firmware-level malware, it could activate upon startup. The more common risk involves data that was already stolen before the phone was turned off or if the device is physically stolen. While it’s an uncommon scenario, the only sure way to take a device offline and completely sever all power is by removing the battery, where possible.
Hacking a phone’s camera is referred to as camfecting, usually done through malware or spyware hidden within a rogue application. Once installed, these apps can gain unauthorized permission to access your camera and record video or capture images without your knowledge. Occasionally, vulnerabilities in a phone’s operating system (OS) have been discovered that could allow for this, though these are rare and usually patched quickly. Protect yourself by regularly reviewing app permissions in your phone’s settings—for both iOS and Android—and revoking camera access for any app that doesn’t absolutely need it. Always keep your OS and apps updated to the latest versions.
This is a long-standing debate with no simple answer. iPhones are generally considered more secure due to Apple’s walled garden approach: a closed ecosystem, a strict vetting process for the App Store, and timely security updates for all supported devices. Android’s open-source nature offers more flexibility but also creates a more fragmented ecosystem, where security updates can be delayed depending on the device manufacturer. However, both platforms use powerful security features like application sandboxing.
The most important factor is not the brand but your behavior. A user who practices good digital hygiene—using strong passwords, avoiding suspicious links, and vetting apps—is well-protected on any platform.
Detecting a phone hack early can save you from significant trouble. Watch for key red flags: your battery draining much faster than usual, unexpected spikes in your mobile data usage, a persistently hot device even when idle, or a sudden barrage of pop-up ads. You might also notice apps you don’t remember installing or find that your phone is running unusually slow. To check, go into your settings to review your battery and data usage reports for any strange activity. The most effective step you can take is to install a comprehensive security app, like McAfee® Mobile Security, to run an immediate scan and detect any threats.
Discovering that your phone has been hacked can be alarming, but acting quickly can help you regain control and protect your personal information. Here are the urgent steps to take so you can remove the hacker, secure your accounts, and prevent future intrusions.
While there are several ways a hacker can get into your phone and steal personal and critical information, here are a few tips to keep that from happening:
Your smartphone is central to your life, so protecting it is essential. Ultimately, your proactive security habits are your strongest defense against mobile hacking. Make a habit of keeping your operating system and apps updated, be cautious about the links you click and the networks you join, and use a comprehensive security solution like McAfee® Mobile Security.
By staying vigilant and informed, you can enjoy all the benefits of your mobile device with confidence and peace of mind. Stay tuned to McAfee for the latest on how to protect your digital world from emerging threats.
The post How Do Hackers Hack Phones and How Can I Prevent It? appeared first on McAfee Blog.



