A 22-year-old Oregon man has been arrested on suspicion of operating “Rapper Bot,” a massive botnet used to power a service for launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against targets — including a March 2025 DDoS that knocked Twitter/X offline. The Justice Department asserts the suspect and an unidentified co-conspirator rented out the botnet to online extortionists, and tried to stay off the radar of law enforcement by ensuring that their botnet was never pointed at KrebsOnSecurity.
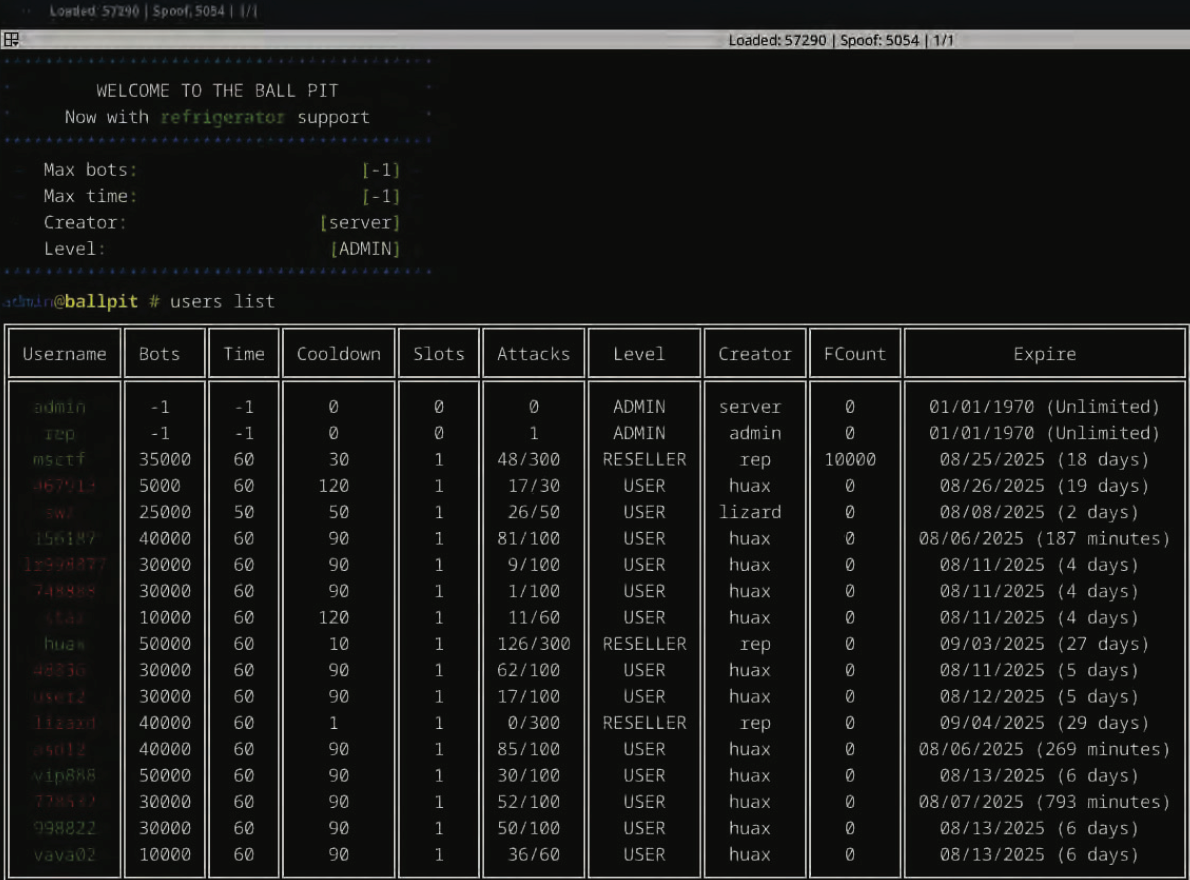
The control panel for the Rapper Bot botnet greets users with the message “Welcome to the Ball Pit, Now with refrigerator support,” an apparent reference to a handful of IoT-enabled refrigerators that were enslaved in their DDoS botnet.
On August 6, 2025, federal agents arrested Ethan J. Foltz of Springfield, Ore. on suspicion of operating Rapper Bot, a globally dispersed collection of tens of thousands of hacked Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
The complaint against Foltz explains the attacks usually clocked in at more than two terabits of junk data per second (a terabit is one trillion bits of data), which is more than enough traffic to cause serious problems for all but the most well-defended targets. The government says Rapper Bot consistently launched attacks that were “hundreds of times larger than the expected capacity of a typical server located in a data center,” and that some of its biggest attacks exceeded six terabits per second.
Indeed, Rapper Bot was reportedly responsible for the March 10, 2025 attack that caused intermittent outages on Twitter/X. The government says Rapper Bot’s most lucrative and frequent customers were involved in extorting online businesses — including numerous gambling operations based in China.
The criminal complaint was written by Elliott Peterson, an investigator with the Defense Criminal Investigative Service (DCIS), the criminal investigative division of the Department of Defense (DoD) Office of Inspector General. The complaint notes the DCIS got involved because several Internet addresses maintained by the DoD were the target of Rapper Bot attacks.
Peterson said he tracked Rapper Bot to Foltz after a subpoena to an ISP in Arizona that was hosting one of the botnet’s control servers showed the account was paid for via PayPal. More legal process to PayPal revealed Foltz’s Gmail account and previously used IP addresses. A subpoena to Google showed the defendant searched security blogs constantly for news about Rapper Bot, and for updates about competing DDoS-for-hire botnets.
According to the complaint, after having a search warrant served on his residence the defendant admitted to building and operating Rapper Bot, sharing the profits 50/50 with a person he claimed to know only by the hacker handle “Slaykings.” Foltz also shared with investigators the logs from his Telegram chats, wherein Foltz and Slaykings discussed how best to stay off the radar of law enforcement investigators while their competitors were getting busted.
Specifically, the two hackers chatted about a May 20 attack against KrebsOnSecurity.com that clocked in at more than 6.3 terabits of data per second. The brief attack was notable because at the time it was the largest DDoS that Google had ever mitigated (KrebsOnSecurity sits behind the protection of Project Shield, a free DDoS defense service that Google provides to websites offering news, human rights, and election-related content).
The May 2025 DDoS was launched by an IoT botnet called Aisuru, which I discovered was operated by a 21-year-old man in Brazil named Kaike Southier Leite. This individual was more commonly known online as “Forky,” and Forky told me he wasn’t afraid of me or U.S. federal investigators. Nevertheless, the complaint against Foltz notes that Forky’s botnet seemed to diminish in size and firepower at the same time that Rapper Bot’s infection numbers were on the upswing.
“Both FOLTZ and Slaykings were very dismissive of attention seeking activities, the most extreme of which, in their view, was to launch DDoS attacks against the website of the prominent cyber security journalist Brian Krebs,” Peterson wrote in the criminal complaint.
“You see, they’ll get themselves [expletive],” Slaykings wrote in response to Foltz’s comments about Forky and Aisuru bringing too much heat on themselves.
“Prob cuz [redacted] hit krebs,” Foltz wrote in reply.
“Going against Krebs isn’t a good move,” Slaykings concurred. “It isn’t about being a [expletive] or afraid, you just get a lot of problems for zero money. Childish, but good. Let them die.”
“Ye, it’s good tho, they will die,” Foltz replied.
The government states that just prior to Foltz’s arrest, Rapper Bot had enslaved an estimated 65,000 devices globally. That may sound like a lot, but the complaint notes the defendants weren’t interested in making headlines for building the world’s largest or most powerful botnet.
Quite the contrary: The complaint asserts that the accused took care to maintain their botnet in a “Goldilocks” size — ensuring that “the number of devices afforded powerful attacks while still being manageable to control and, in the hopes of Foltz and his partners, small enough to not be detected.”
The complaint states that several days later, Foltz and Slaykings returned to discussing what that they expected to befall their rival group, with Slaykings stating, “Krebs is very revenge. He won’t stop until they are [expletive] to the bone.”
“Surprised they have any bots left,” Foltz answered.
“Krebs is not the one you want to have on your back. Not because he is scary or something, just because he will not give up UNTIL you are [expletive] [expletive]. Proved it with Mirai and many other cases.”
[Unknown expletives aside, that may well be the highest compliment I’ve ever been paid by a cybercriminal. I might even have part of that quote made into a t-shirt or mug or something. It’s also nice that they didn’t let any of their customers attack my site — if even only out of a paranoid sense of self-preservation.]
Foltz admitted to wiping the user and attack logs for the botnet approximately once a week, so investigators were unable to tally the total number of attacks, customers and targets of this vast crime machine. But the data that was still available showed that from April 2025 to early August, Rapper Bot conducted over 370,000 attacks, targeting 18,000 unique victims across 1,000 networks, with the bulk of victims residing in China, Japan, the United States, Ireland and Hong Kong (in that order).
According to the government, Rapper Bot borrows much of its code from fBot, a DDoS malware strain also known as Satori. In 2020, authorities in Northern Ireland charged a then 20-year-old man named Aaron “Vamp” Sterritt with operating fBot with a co-conspirator. U.S. prosecutors are still seeking Sterritt’s extradition to the United States. fBot is itself a variation of the Mirai IoT botnet that has ravaged the Internet with DDoS attacks since its source code was leaked back in 2016.
The complaint says Foltz and his partner did not allow most customers to launch attacks that were more than 60 seconds in duration — another way they tried to keep public attention to the botnet at a minimum. However, the government says the proprietors also had special arrangements with certain high-paying clients that allowed much larger and longer attacks.

The accused and his alleged partner made light of this blog post about the fallout from one of their botnet attacks.
Most people who have never been on the receiving end of a monster DDoS attack have no idea of the cost and disruption that such sieges can bring. The DCIS’s Peterson wrote that he was able to test the botnet’s capabilities while interviewing Foltz, and that found that “if this had been a server upon which I was running a website, using services such as load balancers, and paying for both outgoing and incoming data, at estimated industry average rates the attack (2+ Terabits per second times 30 seconds) might have cost the victim anywhere from $500 to $10,000.”
“DDoS attacks at this scale often expose victims to devastating financial impact, and a potential alternative, network engineering solutions that mitigate the expected attacks such as overprovisioning, i.e. increasing potential Internet capacity, or DDoS defense technologies, can themselves be prohibitively expensive,” the complaint continues. “This ‘rock and a hard place’ reality for many victims can leave them acutely exposed to extortion demands – ‘pay X dollars and the DDoS attacks stop’.”
The Telegram chat records show that the day before Peterson and other federal agents raided Foltz’s residence, Foltz allegedly told his partner he’d found 32,000 new devices that were vulnerable to a previously unknown exploit.

Foltz and Slaykings discussing the discovery of an IoT vulnerability that will give them 32,000 new devices.
Shortly before the search warrant was served on his residence, Foltz allegedly told his partner that “Once again we have the biggest botnet in the community.” The following day, Foltz told his partner that it was going to be a great day — the biggest so far in terms of income generated by Rapper Bot.
“I sat next to Foltz while the messages poured in — promises of $800, then $1,000, the proceeds ticking up as the day went on,” Peterson wrote. “Noticing a change in Foltz’ behavior and concerned that Foltz was making changes to the botnet configuration in real time, Slaykings asked him ‘What’s up?’ Foltz deftly typed out some quick responses. Reassured by Foltz’ answer, Slaykings responded, ‘Ok, I’m the paranoid one.”
The case is being prosecuted by Assistant U.S. Attorney Adam Alexander in the District of Alaska (at least some of the devices found to be infected with Rapper Bot were located there, and it is where Peterson is stationed). Foltz faces one count of aiding and abetting computer intrusions. If convicted, he faces a maximum penalty of 10 years in prison, although a federal judge is unlikely to award anywhere near that kind of sentence for a first-time conviction.
In May 2025, the U.S. government sanctioned a Chinese national for operating a cloud provider linked to the majority of virtual currency investment scam websites reported to the FBI. But a new report finds the accused continues to operate a slew of established accounts at American tech companies — including Facebook, Github, PayPal and Twitter/X.
On May 29, the U.S. Department of the Treasury announced economic sanctions against Funnull Technology Inc., a Philippines-based company alleged to provide infrastructure for hundreds of thousands of websites involved in virtual currency investment scams known as “pig butchering.” In January 2025, KrebsOnSecurity detailed how Funnull was designed as a content delivery network that catered to foreign cybercriminals seeking to route their traffic through U.S.-based cloud providers.

The Treasury also sanctioned Funnull’s alleged operator, a 40-year-old Chinese national named Liu “Steve” Lizhi. The government says Funnull directly facilitated financial schemes resulting in more than $200 million in financial losses by Americans, and that the company’s operations were linked to the majority of pig butchering scams reported to the FBI.
It is generally illegal for U.S. companies or individuals to transact with people sanctioned by the Treasury. However, as Mr. Lizhi’s case makes clear, just because someone is sanctioned doesn’t necessarily mean big tech companies are going to suspend their online accounts.
The government says Lizhi was born November 13, 1984, and used the nicknames “XXL4” and “Nice Lizhi.” Nevertheless, Steve Liu’s 17-year-old account on LinkedIn (in the name “Liulizhi”) had hundreds of followers (Lizhi’s LinkedIn profile helpfully confirms his birthday) until quite recently: The account was deleted this morning, just hours after KrebsOnSecurity sought comment from LinkedIn.
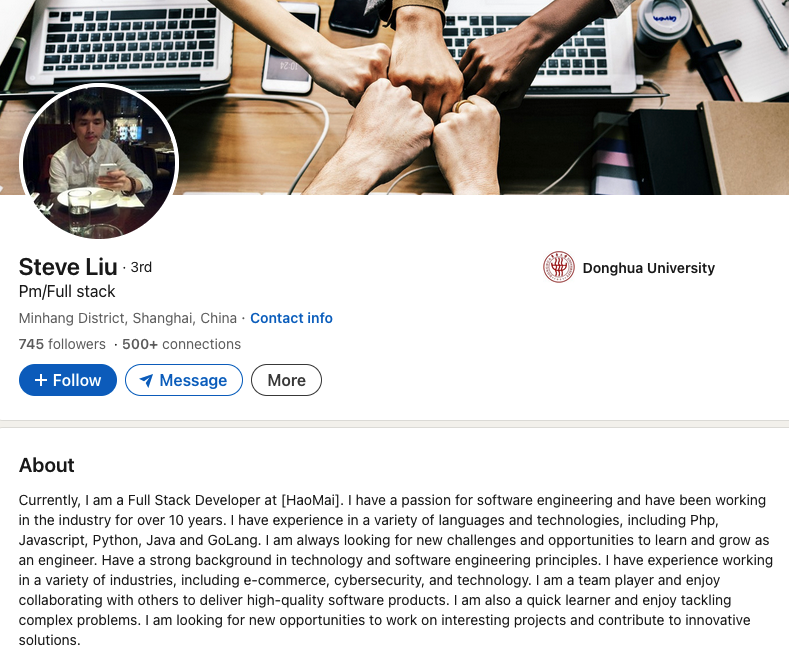
Mr. Lizhi’s LinkedIn account was suspended sometime in the last 24 hours, after KrebsOnSecurity sought comment from LinkedIn.
In an emailed response, a LinkedIn spokesperson said the company’s “Prohibited countries policy” states that LinkedIn “does not sell, license, support or otherwise make available its Premium accounts or other paid products and services to individuals and companies sanctioned by the U.S. government.” LinkedIn declined to say whether the profile in question was a premium or free account.
Mr. Lizhi also maintains a working PayPal account under the name Liu Lizhi and username “@nicelizhi,” another nickname listed in the Treasury sanctions. A 15-year-old Twitter/X account named “Lizhi” that links to Mr. Lizhi’s personal domain remains active, although it has few followers and hasn’t posted in years.
These accounts and many others were flagged by the security firm Silent Push, which has been tracking Funnull’s operations for the past year and calling out U.S. cloud providers like Amazon and Microsoft for failing to more quickly sever ties with the company.
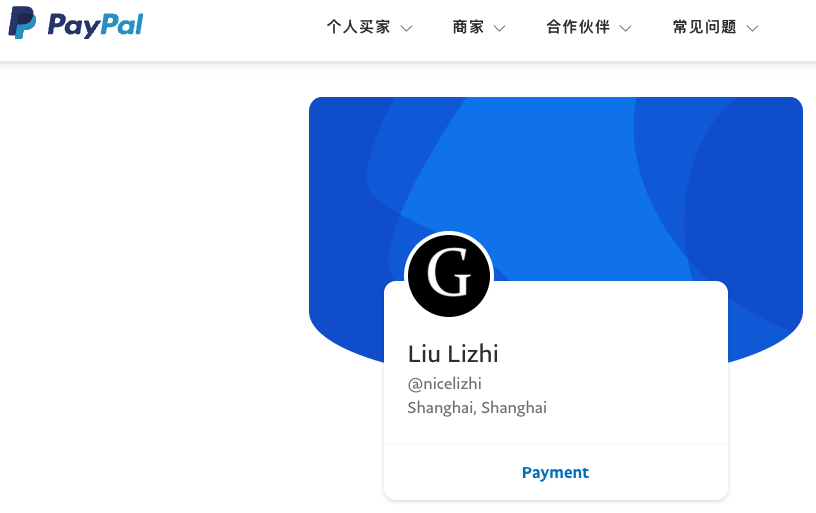
Liu Lizhi’s PayPal account.
In a report released today, Silent Push found Lizhi still operates numerous Facebook accounts and groups, including a private Facebook account under the name Liu Lizhi. Another Facebook account clearly connected to Lizhi is a tourism page for Ganzhou, China called “EnjoyGanzhou” that was named in the Treasury Department sanctions.
“This guy is the technical administrator for the infrastructure that is hosting a majority of scams targeting people in the United States, and hundreds of millions have been lost based on the websites he’s been hosting,” said Zach Edwards, senior threat researcher at Silent Push. “It’s crazy that the vast majority of big tech companies haven’t done anything to cut ties with this guy.”
The FBI says it received nearly 150,000 complaints last year involving digital assets and $9.3 billion in losses — a 66 percent increase from the previous year. Investment scams were the top crypto-related crimes reported, with $5.8 billion in losses.
In a statement, a Meta spokesperson said the company continuously takes steps to meet its legal obligations, but that sanctions laws are complex and varied. They explained that sanctions are often targeted in nature and don’t always prohibit people from having a presence on its platform. Nevertheless, Meta confirmed it had removed the account, unpublished Pages, and removed Groups and events associated with the user for violating its policies.
Attempts to reach Mr. Lizhi via his primary email addresses at Hotmail and Gmail bounced as undeliverable. Likewise, his 14-year-old YouTube channel appears to have been taken down recently.
However, anyone interested in viewing or using Mr. Lizhi’s 146 computer code repositories will have no problem finding GitHub accounts for him, including one registered under the NiceLizhi and XXL4 nicknames mentioned in the Treasury sanctions.
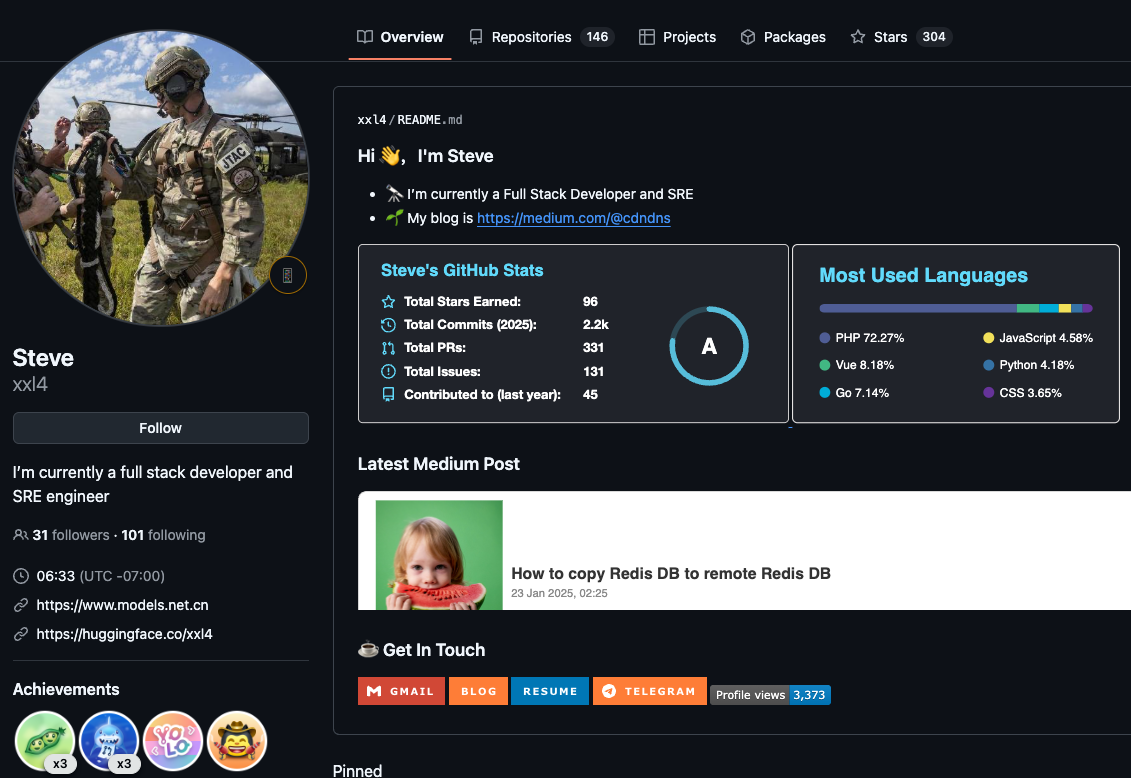
One of multiple GitHub profiles used by Liu “Steve” Lizhi, who uses the nickname XXL4 (a moniker listed in the Treasury sanctions for Mr. Lizhi).
Mr. Lizhi also operates a GitHub page for an open source e-commerce platform called NexaMerchant, which advertises itself as a payment gateway working with numerous American financial institutions. Interestingly, this profile’s “followers” page shows several other accounts that appear to be Mr. Lizhi’s. All of the account’s followers are tagged as “suspended,” even though that suspended message does not display when one visits those individual profiles.
In response to questions, GitHub said it has a process in place to identify when users and customers are Specially Designated Nationals or other denied or blocked parties, but that it locks those accounts instead of removing them. According to its policy, GitHub takes care that users and customers aren’t impacted beyond what is required by law.
All of the follower accounts for the XXL4 GitHub account appear to be Mr. Lizhi’s, and have been suspended by GitHub, but their code is still accessible.
“This includes keeping public repositories, including those for open source projects, available and accessible to support personal communications involving developers in sanctioned regions,” the policy states. “This also means GitHub will advocate for developers in sanctioned regions to enjoy greater access to the platform and full access to the global open source community.”
Edwards said it’s great that GitHub has a process for handling sanctioned accounts, but that the process doesn’t seem to communicate risk in a transparent way, noting that the only indicator on the locked accounts is the message, “This repository has been archived by the owner. It is not read-only.”
“It’s an odd message that doesn’t communicate, ‘This is a sanctioned entity, don’t fork this code or use it in a production environment’,” Edwards said.
Mark Rasch is a former federal cybercrime prosecutor who now serves as counsel for the New York City based security consulting firm Unit 221B. Rasch said when Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) sanctions a person or entity, it then becomes illegal for businesses or organizations to transact with the sanctioned party.
Rasch said financial institutions have very mature systems for severing accounts tied to people who become subject to OFAC sanctions, but that tech companies may be far less proactive — particularly with free accounts.
“Banks have established ways of checking [U.S. government sanctions lists] for sanctioned entities, but tech companies don’t necessarily do a good job with that, especially for services that you can just click and sign up for,” Rasch said. “It’s potentially a risk and liability for the tech companies involved, but only to the extent OFAC is willing to enforce it.”
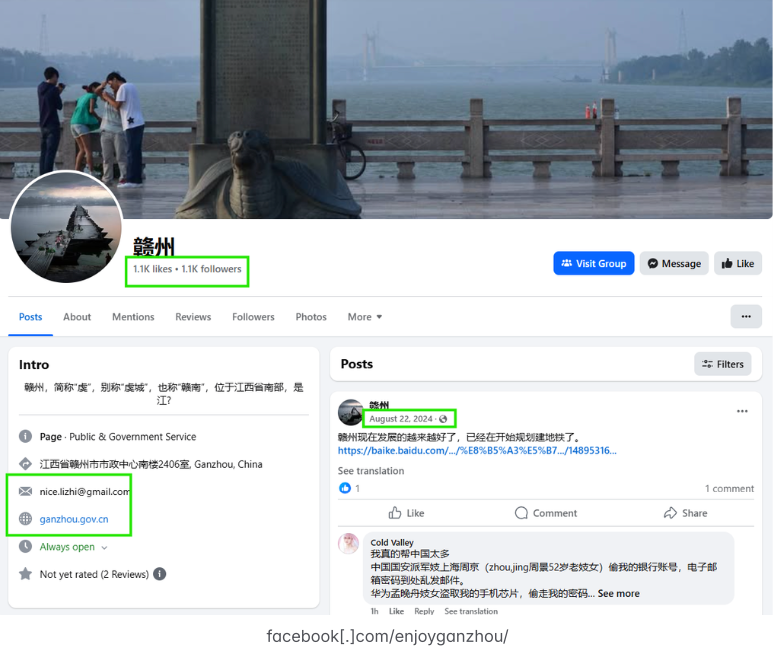
Liu Lizhi operates numerous Facebook accounts and groups, including this one for an entity specified in the OFAC sanctions: The “Enjoy Ganzhou” tourism page for Ganzhou, China. Image: Silent Push.
In July 2024, Funnull purchased the domain polyfill[.]io, the longtime home of a legitimate open source project that allowed websites to ensure that devices using legacy browsers could still render content in newer formats. After the Polyfill domain changed hands, at least 384,000 websites were caught in a supply-chain attack that redirected visitors to malicious sites. According to the Treasury, Funnull used the code to redirect people to scam websites and online gambling sites, some of which were linked to Chinese criminal money laundering operations.
The U.S. government says Funnull provides domain names for websites on its purchased IP addresses, using domain generation algorithms (DGAs) — programs that generate large numbers of similar but unique names for websites — and that it sells web design templates to cybercriminals.
“These services not only make it easier for cybercriminals to impersonate trusted brands when creating scam websites, but also allow them to quickly change to different domain names and IP addresses when legitimate providers attempt to take the websites down,” reads a Treasury statement.
Meanwhile, Funnull appears to be morphing nearly all aspects of its business in the wake of the sanctions, Edwards said.
“Whereas before they might have used 60 DGA domains to hide and bounce their traffic, we’re seeing far more now,” he said. “They’re trying to make their infrastructure harder to track and more complicated, so for now they’re not going away but more just changing what they’re doing. And a lot more organizations should be holding their feet to the fire.”
Update, 2:48 PM ET: Added response from Meta, which confirmed it has closed the accounts and groups connected to Mr. Lizhi.
Update, July 7, 6:56 p.m. ET: In a written statement, PayPal said it continually works to combat and prevent the illicit use of its services.
“We devote significant resources globally to financial crime compliance, and we proactively refer cases to and assist law enforcement officials around the world in their efforts to identify, investigate and stop illegal activity,” the statement reads.
The U.S. government today unsealed criminal charges against 16 individuals accused of operating and selling DanaBot, a prolific strain of information-stealing malware that has been sold on Russian cybercrime forums since 2018. The FBI says a newer version of DanaBot was used for espionage, and that many of the defendants exposed their real-life identities after accidentally infecting their own systems with the malware.

DanaBot’s features, as promoted on its support site. Image: welivesecurity.com.
Initially spotted in May 2018 by researchers at the email security firm Proofpoint, DanaBot is a malware-as-a-service platform that specializes in credential theft and banking fraud.
Today, the U.S. Department of Justice unsealed a criminal complaint and indictment from 2022, which said the FBI identified at least 40 affiliates who were paying between $3,000 and $4,000 a month for access to the information stealer platform.
The government says the malware infected more than 300,000 systems globally, causing estimated losses of more than $50 million. The ringleaders of the DanaBot conspiracy are named as Aleksandr Stepanov, 39, a.k.a. “JimmBee,” and Artem Aleksandrovich Kalinkin, 34, a.k.a. “Onix”, both of Novosibirsk, Russia. Kalinkin is an IT engineer for the Russian state-owned energy giant Gazprom. His Facebook profile name is “Maffiozi.”
According to the FBI, there were at least two major versions of DanaBot; the first was sold between 2018 and June 2020, when the malware stopped being offered on Russian cybercrime forums. The government alleges that the second version of DanaBot — emerging in January 2021 — was provided to co-conspirators for use in targeting military, diplomatic and non-governmental organization computers in several countries, including the United States, Belarus, the United Kingdom, Germany, and Russia.
“Unindicted co-conspirators would use the Espionage Variant to compromise computers around the world and steal sensitive diplomatic communications, credentials, and other data from these targeted victims,” reads a grand jury indictment dated Sept. 20, 2022. “This stolen data included financial transactions by diplomatic staff, correspondence concerning day-to-day diplomatic activity, as well as summaries of a particular country’s interactions with the United States.”
The indictment says the FBI in 2022 seized servers used by the DanaBot authors to control their malware, as well as the servers that stored stolen victim data. The government said the server data also show numerous instances in which the DanaBot defendants infected their own PCs, resulting in their credential data being uploaded to stolen data repositories that were seized by the feds.
“In some cases, such self-infections appeared to be deliberately done in order to test, analyze, or improve the malware,” the criminal complaint reads. “In other cases, the infections seemed to be inadvertent – one of the hazards of committing cybercrime is that criminals will sometimes infect themselves with their own malware by mistake.”
Image: welivesecurity.com
A statement from the DOJ says that as part of today’s operation, agents with the Defense Criminal Investigative Service (DCIS) seized the DanaBot control servers, including dozens of virtual servers hosted in the United States. The government says it is now working with industry partners to notify DanaBot victims and help remediate infections. The statement credits a number of security firms with providing assistance to the government, including ESET, Flashpoint, Google, Intel 471, Lumen, PayPal, Proofpoint, Team CYMRU, and ZScaler.
It’s not unheard of for financially-oriented malicious software to be repurposed for espionage. A variant of the ZeuS Trojan, which was used in countless online banking attacks against companies in the United States and Europe between 2007 and at least 2015, was for a time diverted to espionage tasks by its author.
As detailed in this 2015 story, the author of the ZeuS trojan created a custom version of the malware to serve purely as a spying machine, which scoured infected systems in Ukraine for specific keywords in emails and documents that would likely only be found in classified documents.
The public charging of the 16 DanaBot defendants comes a day after Microsoft joined a slew of tech companies in disrupting the IT infrastructure for another malware-as-a-service offering — Lumma Stealer, which is likewise offered to affiliates under tiered subscription prices ranging from $250 to $1,000 per month. Separately, Microsoft filed a civil lawsuit to seize control over 2,300 domain names used by Lumma Stealer and its affiliates.
Further reading:
Danabot: Analyzing a Fallen Empire
ZScaler blog: DanaBot Launches DDoS Attack Against the Ukrainian Ministry of Defense
Flashpoint: Operation Endgame DanaBot Malware
Team CYMRU: Inside DanaBot’s Infrastructure: In Support of Operation Endgame II
March 2022 criminal complaint v. Artem Aleksandrovich Kalinkin
September 2022 grand jury indictment naming the 16 defendants
China-based purveyors of SMS phishing kits are enjoying remarkable success converting phished payment card data into mobile wallets from Apple and Google. Until recently, the so-called “Smishing Triad” mainly impersonated toll road operators and shipping companies. But experts say these groups are now directly targeting customers of international financial institutions, while dramatically expanding their cybercrime infrastructure and support staff.

An image of an iPhone device farm shared on Telegram by one of the Smishing Triad members. Image: Prodaft.
If you own a mobile device, the chances are excellent that at some point in the past two years you’ve received at least one instant message that warns of a delinquent toll road fee, or a wayward package from the U.S. Postal Service (USPS). Those who click the promoted link are brought to a website that spoofs the USPS or a local toll road operator and asks for payment card information.
The site will then complain that the visitor’s bank needs to “verify” the transaction by sending a one-time code via SMS. In reality, the bank is sending that code to the mobile number on file for their customer because the fraudsters have just attempted to enroll that victim’s card details into a mobile wallet.
If the visitor supplies that one-time code, their payment card is then added to a new mobile wallet on an Apple or Google device that is physically controlled by the phishers. The phishing gangs typically load multiple stolen cards to digital wallets on a single Apple or Android device, and then sell those phones in bulk to scammers who use them for fraudulent e-commerce and tap-to-pay transactions.
A screenshot of the administrative panel for a smishing kit. On the left is the (test) data entered at the phishing site. On the right we can see the phishing kit has superimposed the supplied card number onto an image of a payment card. When the phishing kit scans that created card image into Apple or Google Pay, it triggers the victim’s bank to send a one-time code. Image: Ford Merrill.
The moniker “Smishing Triad” comes from Resecurity, which was among the first to report in August 2023 on the emergence of three distinct mobile phishing groups based in China that appeared to share some infrastructure and innovative phishing techniques. But it is a bit of a misnomer because the phishing lures blasted out by these groups are not SMS or text messages in the conventional sense.
Rather, they are sent via iMessage to Apple device users, and via RCS on Google Android devices. Thus, the missives bypass the mobile phone networks entirely and enjoy near 100 percent delivery rate (at least until Apple and Google suspend the spammy accounts).
In a report published on March 24, the Swiss threat intelligence firm Prodaft detailed the rapid pace of innovation coming from the Smishing Triad, which it characterizes as a loosely federated group of Chinese phishing-as-a-service operators with names like Darcula, Lighthouse, and the Xinxin Group.
Prodaft said they’re seeing a significant shift in the underground economy, particularly among Chinese-speaking threat actors who have historically operated in the shadows compared to their Russian-speaking counterparts.
“Chinese-speaking actors are introducing innovative and cost-effective systems, enabling them to target larger user bases with sophisticated services,” Prodaft wrote. “Their approach marks a new era in underground business practices, emphasizing scalability and efficiency in cybercriminal operations.”
A new report from researchers at the security firm SilentPush finds the Smishing Triad members have expanded into selling mobile phishing kits targeting customers of global financial institutions like CitiGroup, MasterCard, PayPal, Stripe, and Visa, as well as banks in Canada, Latin America, Australia and the broader Asia-Pacific region.

Phishing lures from the Smishing Triad spoofing PayPal. Image: SilentPush.
SilentPush found the Smishing Triad now spoofs recognizable brands in a variety of industry verticals across at least 121 countries and a vast number of industries, including the postal, logistics, telecommunications, transportation, finance, retail and public sectors.
According to SilentPush, the domains used by the Smishing Triad are rotated frequently, with approximately 25,000 phishing domains active during any 8-day period and a majority of them sitting at two Chinese hosting companies: Tencent (AS132203) and Alibaba (AS45102).
“With nearly two-thirds of all countries in the world targeted by [the] Smishing Triad, it’s safe to say they are essentially targeting every country with modern infrastructure outside of Iran, North Korea, and Russia,” SilentPush wrote. “Our team has observed some potential targeting in Russia (such as domains that mentioned their country codes), but nothing definitive enough to indicate Russia is a persistent target. Interestingly, even though these are Chinese threat actors, we have seen instances of targeting aimed at Macau and Hong Kong, both special administrative regions of China.”
SilentPush’s Zach Edwards said his team found a vulnerability that exposed data from one of the Smishing Triad’s phishing pages, which revealed the number of visits each site received each day across thousands of phishing domains that were active at the time. Based on that data, SilentPush estimates those phishing pages received well more than a million visits within a 20-day time span.
The report notes the Smishing Triad boasts it has “300+ front desk staff worldwide” involved in one of their more popular phishing kits — Lighthouse — staff that is mainly used to support various aspects of the group’s fraud and cash-out schemes.
The Smishing Triad members maintain their own Chinese-language sales channels on Telegram, which frequently offer videos and photos of their staff hard at work. Some of those images include massive walls of phones used to send phishing messages, with human operators seated directly in front of them ready to receive any time-sensitive one-time codes.
As noted in February’s story How Phished Data Turns Into Apple and Google Wallets, one of those cash-out schemes involves an Android app called Z-NFC, which can relay a valid NFC transaction from one of these compromised digital wallets to anywhere in the world. For a $500 month subscription, the customer can wave their phone at any payment terminal that accepts Apple or Google pay, and the app will relay an NFC transaction over the Internet from a stolen wallet on a phone in China.
Chinese nationals were recently busted trying to use these NFC apps to buy high-end electronics in Singapore. And in the United States, authorities in California and Tennessee arrested Chinese nationals accused of using NFC apps to fraudulently purchase gift cards from retailers.
The Prodaft researchers said they were able to find a previously undocumented backend management panel for Lucid, a smishing-as-a-service operation tied to the XinXin Group. The panel included victim figures that suggest the smishing campaigns maintain an average success rate of approximately five percent, with some domains receiving over 500 visits per week.
“In one observed instance, a single phishing website captured 30 credit card records from 550 victim interactions over a 7-day period,” Prodaft wrote.
Prodaft’s report details how the Smishing Triad has achieved such success in sending their spam messages. For example, one phishing vendor appears to send out messages using dozens of Android device emulators running in parallel on a single machine.
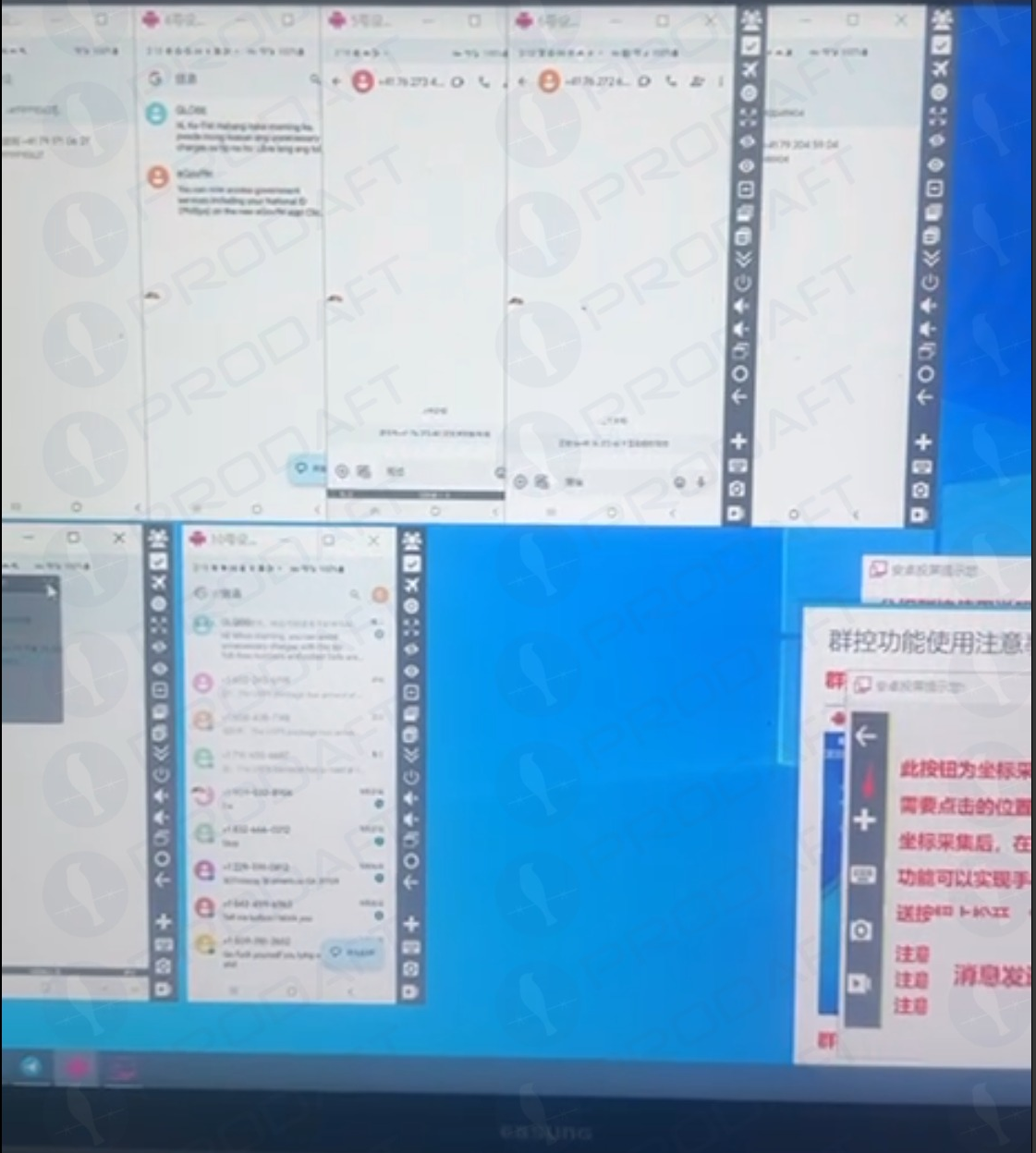
Phishers using multiple virtualized Android devices to orchestrate and distribute RCS-based scam campaigns. Image: Prodaft.
According to Prodaft, the threat actors first acquire phone numbers through various means including data breaches, open-source intelligence, or purchased lists from underground markets. They then exploit technical gaps in sender ID validation within both messaging platforms.
“For iMessage, this involves creating temporary Apple IDs with impersonated display names, while RCS exploitation leverages carrier implementation inconsistencies in sender verification,” Prodaft wrote. “Message delivery occurs through automated platforms using VoIP numbers or compromised credentials, often deployed in precisely timed multi-wave campaigns to maximize effectiveness.
In addition, the phishing links embedded in these messages use time-limited single-use URLs that expire or redirect based on device fingerprinting to evade security analysis, they found.
“The economics strongly favor the attackers, as neither RCS nor iMessage messages incur per-message costs like traditional SMS, enabling high-volume campaigns at minimal operational expense,” Prodaft continued. “The overlap in templates, target pools, and tactics among these platforms underscores a unified threat landscape, with Chinese-speaking actors driving innovation in the underground economy. Their ability to scale operations globally and evasion techniques pose significant challenges to cybersecurity defenses.”
Ford Merrill works in security research at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group company. Merrill said he’s observed at least one video of a Windows binary that wraps a Chrome executable and can be used to load in target phone numbers and blast messages via RCS, iMessage, Amazon, Instagram, Facebook, and WhatsApp.
“The evidence we’ve observed suggests the ability for a single device to send approximately 100 messages per second,” Merrill said. “We also believe that there is capability to source country specific SIM cards in volume that allow them to register different online accounts that require validation with specific country codes, and even make those SIM cards available to the physical devices long-term so that services that rely on checks of the validity of the phone number or SIM card presence on a mobile network are thwarted.”
Experts say this fast-growing wave of card fraud persists because far too many financial institutions still default to sending one-time codes via SMS for validating card enrollment in mobile wallets from Apple or Google. KrebsOnSecurity interviewed multiple security executives at non-U.S. financial institutions who spoke on condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak to the press. Those banks have since done away with SMS-based one-time codes and are now requiring customers to log in to the bank’s mobile app before they can link their card to a digital wallet.



