The homepage of Stark Industries Solutions.
Two weeks before Russia invaded Ukraine in February 2022, a large, mysterious new Internet hosting firm called Stark Industries Solutions materialized and quickly became the epicenter of massive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on government and commercial targets in Ukraine and Europe. An investigation into Stark Industries reveals it is being used as a global proxy network that conceals the true source of cyberattacks and disinformation campaigns against enemies of Russia.
At least a dozen patriotic Russian hacking groups have been launching DDoS attacks since the start of the war at a variety of targets seen as opposed to Moscow. But by all accounts, few attacks from those gangs have come close to the amount of firepower wielded by a pro-Russia group calling itself “NoName057(16).”
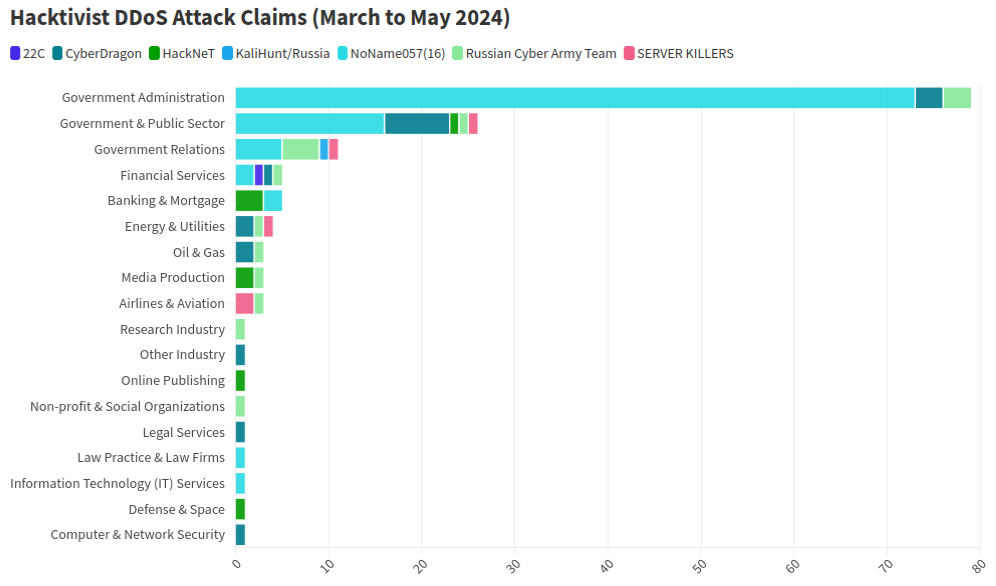
This graphic comes from a recent report from NETSCOUT about DDoS attacks from Russian hacktivist groups.
As detailed by researchers at Radware, NoName has effectively gamified DDoS attacks, recruiting hacktivists via its Telegram channel and offering to pay people who agree to install a piece of software called DDoSia. That program allows NoName to commandeer the host computers and their Internet connections in coordinated DDoS campaigns, and DDoSia users with the most attacks can win cash prizes.
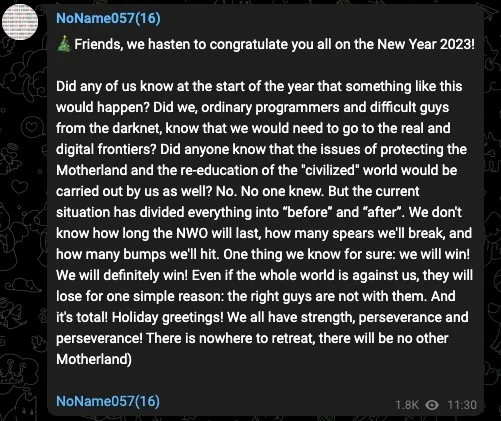
The NoName DDoS group advertising on Telegram. Image: SentinelOne.com.
A report from the security firm Team Cymru found the DDoS attack infrastructure used in NoName campaigns is assigned to two interlinked hosting providers: MIRhosting and Stark Industries. MIRhosting is a hosting provider founded in The Netherlands in 2004. But Stark Industries Solutions Ltd was incorporated on February 10, 2022, just two weeks before the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Security experts say that not long after the war started, Stark began hosting dozens of proxy services and free virtual private networking (VPN) services, which are designed to help users shield their Internet usage and location from prying eyes.
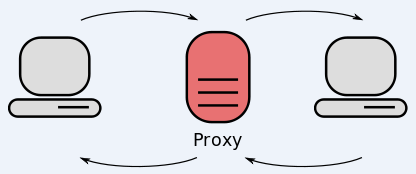
Proxy providers allow users to route their Internet and Web browsing traffic through someone else’s computer. From a website’s perspective, the traffic from a proxy network user appears to originate from the rented IP address, not from the proxy service customer.
These services can be used in a legitimate manner for several business purposes — such as price comparisons or sales intelligence — but they are also massively abused for hiding cybercrime activity because they can make it difficult to trace malicious traffic to its original source.
What’s more, many proxy services do not disclose how they obtain access to the proxies they are renting out, and in many cases the access is obtained through the dissemination of malicious software that turns the infected system into a traffic relay — usually unbeknownst to the legitimate owner of the Internet connection. Other proxy services will allow users to make money by renting out their Internet connection to anyone.
Spur.us is a company that tracks VPNs and proxy services worldwide. Spur finds that Stark Industries (AS44477) currently is home to at least 74 VPN services, and 40 different proxy services. As we’ll see in the final section of this story, just one of those proxy networks has over a million Internet addresses available for rent across the globe.
Raymond Dijkxhoorn operates a hosting firm in The Netherlands called Prolocation. He also co-runs SURBL, an anti-abuse service that flags domains and Internet address ranges that are strongly associated with spam and cybercrime activity, including DDoS.
Dijkxhoorn said last year SURBL heard from multiple people who said they operated VPN services whose web resources were included in SURBL’s block lists.
“We had people doing delistings at SURBL for domain names that were suspended by the registrars,” Dijkhoorn told KrebsOnSecurity. “And at least two of them explained that Stark offered them free VPN services that they were reselling.”
Dijkxhoorn added that Stark Industries also sponsored activist groups from Ukraine.
“How valuable would it be for Russia to know the real IPs from Ukraine’s tech warriors?” he observed.
Richard Hummel is threat intelligence lead at NETSCOUT. Hummel said when he considers the worst of all the hosting providers out there today, Stark Industries is consistently near or at the top of that list.
“The reason is we’ve had at least a dozen service providers come to us saying, ‘There’s this network out there inundating us with traffic,'” Hummel said. “And it wasn’t even DDoS attacks. [The systems] on Stark were just scanning these providers so fast it was crashing some of their services.”
Hummel said NoName will typically launch their attacks using a mix of resources rented from major, legitimate cloud services, and those from so-called “bulletproof” hosting providers like Stark. Bulletproof providers are so named when they earn or cultivate a reputation for ignoring any abuse complaints or police reports about activity on their networks.
Combining bulletproof providers with legitimate cloud hosting, Hummel said, likely makes NoName’s DDoS campaigns more resilient because many network operators will hesitate to be too aggressive in blocking Internet addresses associated with the major cloud services.
“What we typically see here is a distribution of cloud hosting providers and bulletproof hosting providers in DDoS attacks,” he said. “They’re using public cloud hosting providers because a lot of times that’s your first layer of network defense, and because [many companies are wary of] over-blocking access to legitimate cloud resources.”
But even if the cloud provider detects abuse coming from the customer, the provider is probably not going to shut the customer down immediately, Hummel said.
“There is usually a grace period, and even if that’s only an hour or two, you can still launch a large number of attacks in that time,” he said. “And then they just keep coming back and opening new cloud accounts.”
Stark Industries is incorporated at a mail drop address in the United Kingdom. UK business records list an Ivan Vladimirovich Neculiti as the company’s secretary. Mr. Neculiti also is named as the CEO and founder of PQ Hosting Plus S.R.L. (aka Perfect Quality Hosting), a Moldovan company formed in 2019 that lists the same UK mail drop address as Stark Industries.

Ivan Neculiti, as pictured on LinkedIn.
Reached via LinkedIn, Mr. Neculiti said PQ Hosting established Stark Industries as a “white label” of its brand so that “resellers could distribute our services using our IP addresses and their clients would not have any affairs with PQ Hosting.”
“PQ Hosting is a company with over 1,000+ of [our] own physical servers in 38 countries and we have over 100,000 clients,” he said. “Though we are not as large as Hetzner, Amazon and OVH, nevertheless we are a fast growing company that provides services to tens of thousands of private customers and legal entities.”
Asked about the constant stream of DDoS attacks whose origins have traced back to Stark Industries over the past two years, Neculiti maintained Stark hasn’t received any official abuse reports about attacks coming from its networks.
“It was probably some kind of clever attack that we did not see, I do not rule out this fact, because we have a very large number of clients and our Internet channels are quite large,” he said. “But, in this situation, unfortunately, no one contacted us to report that there was an attack from our addresses; if someone had contacted us, we would have definitely blocked the network data.”
DomainTools.com finds Ivan V. Neculiti was the owner of war[.]md, a website launched in 2008 that chronicled the history of a 1990 armed conflict in Moldova known as the Transnistria War and the Moldo-Russian war.

An ad for war.md, circa 2009.
Transnistria is a breakaway pro-Russian region that declared itself a state in 1990, although it is not internationally recognized. The copyright on that website credits the “MercenarieS TeaM,” which was at one time a Moldovan IT firm. Mr. Neculiti confirmed personally registering this domain.
The data breach tracking service Constella Intelligence reports that an Ivan V. Neculiti registered multiple online accounts under the email address dfyz_bk@bk.ru. Cyber intelligence firm Intel 471 shows this email address is tied to the username “dfyz” on more than a half-dozen Russian language cybercrime forums since 2008. The user dfyz on Searchengines[.]ru in 2008 asked other forum members to review war.md, and said they were part of the MercenarieS TeaM.
Back then, dfyz was selling “bulletproof servers for any purpose,” meaning the hosting company would willfully ignore abuse complaints or police inquiries about the activity of its customers.
DomainTools reports there are at least 33 domain names registered to dfyz_bk@bk.ru. Several of these domains have Ivan Neculiti in their registration records, including tracker-free[.]cn, which was registered to an Ivan Neculiti at dfyz_bk@bk.ru and referenced the MercenarieS TeaM in its original registration records.
Dfyz also used the nickname DonChicho, who likewise sold bulletproof hosting services and access to hacked Internet servers. In 2014, a prominent member of the Russian language cybercrime community Antichat filed a complaint against DonChicho, saying this user scammed them and had used the email address dfyz_bk@bk.ru.
The complaint said DonChicho registered on Antichat from the Transnistria Internet address 84.234.55[.]29. Searching this address in Constella reveals it has been used to register just five accounts online that have been created over the years, including one at ask.ru, where the user registered with the email address neculitzy1@yandex.ru. Constella also returns for that email address a user by the name “Ivan” at memoraleak.com and 000webhost.com.
Constella finds that the password most frequently used by the email address dfyz_bk@bk.ru was “filecast,” and that there are more than 90 email addresses associated with this password. Among them are roughly two dozen addresses with the name “Neculiti” in them, as well as the address support@donservers[.]ru.
Intel 471 says DonChicho posted to several Russian cybercrime forums that support@donservers[.]ru was his address, and that he logged into cybercrime forums almost exclusively from Internet addresses in Tiraspol, the capital of Transnistria. A review of DonChicho’s posts shows this person was banned from several forums in 2014 for scamming other users.
Cached copies of DonChicho’s vanity domain (donchicho[.]ru) show that in 2009 he was a spammer who peddled knockoff prescription drugs via Rx-Promotion, once one of the largest pharmacy spam moneymaking programs for Russian-speaking affiliates.
Mr. Neculiti told KrebsOnSecurity he has never used the nickname DonChicho.
“I may assure you that I have no relation to DonChicho nor to his bulletproof servers,” he said.
Below is a mind map that shows the connections between the accounts mentioned above.
Earlier this year, NoName began massively hitting government and industry websites in Moldova. A new report from Arbor Networks says the attacks began around March 6, when NoName alleged the government of Moldova was “craving for Russophobia.”
“Since early March, more than 50 websites have been targeted, according to posted ‘proof’ by the groups involved in attacking the country,” Arbor’s ASERT Team wrote. “While NoName seemingly initiated the ramp of attacks, a host of other DDoS hacktivists have joined the fray in claiming credit for attacks across more than 15 industries.”
The German independent news outlet Correctiv.org last week published a scathing investigative report on Stark Industries and MIRhosting, which notes that Ivan Neculiti operates his hosting companies with the help of his brother, Yuri.
The report points out that Stark Industries continues to host a Russian disinformation news outlet called “Recent Reliable News” (RRN) that was sanctioned by the European Union in 2023 for spreading links to propaganda blogs and fake European media and government websites.
“The website was not running on computers in Moscow or St. Petersburg until recently, but in the middle of the EU, in the Netherlands, on the computers of the Neculiti brothers,” Correctiv reporters wrote.
“After a request from this editorial team, a well-known service was installed that hides the actual web host,” the report continues. “Ivan Neculiti announced that he had blocked the associated access and server following internal investigations. “We very much regret that we are only now finding out that one of our customers is a sanctioned portal,” said the company boss. However, RRN is still accessible via its servers.”
Correctiv also points to a January 2023 report from the Ukrainian government, which found servers from Stark Industries Solutions were used as part of a cyber attack on the Ukrainian news agency “Ukrinform”. Correctiv notes the notorious hacker group Sandworm — an advanced persistent threat (APT) group operated by a cyberwarfare unit of Russia’s military intelligence service — was identified by Ukrainian government authorities as responsible for that attack.
Public records indicate MIRhosting is based in The Netherlands and is operated by 37-year old Andrey Nesterenko, whose personal website says he is an accomplished concert pianist who began performing publicly at a young age.
DomainTools says mirhosting[.]com is registered to Mr. Nesterenko and to Innovation IT Solutions Corp, which lists addresses in London and in Nesterenko’s stated hometown of Nizhny Novgorod, Russia.
This is interesting because according to the book Inside Cyber Warfare by Jeffrey Carr, Innovation IT Solutions Corp. was responsible for hosting StopGeorgia[.]ru, a hacktivist website for organizing cyberattacks against Georgia that appeared at the same time Russian forces invaded the former Soviet nation in 2008. That conflict was thought to be the first war ever fought in which a notable cyberattack and an actual military engagement happened simultaneously.
Responding to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, Mr. Nesterenko said he couldn’t say whether his network had ever hosted the StopGeorgia website back in 2008 because his company didn’t keep records going back that far. But he said Stark Industries Solutions is indeed one of MIRhsoting’s colocation customers.
“Our relationship is purely provider-customer,” Nesterenko said. “They also utilize multiple providers and data centers globally, so connecting them directly to MIRhosting overlooks their broader network.”
“We take any report of malicious activity seriously and are always open to information that can help us identify and prevent misuse of our infrastructure, whether involving Stark Industries or any other customer,” Nesterenko continued. “In cases where our services are exploited for malicious purposes, we collaborate fully with Dutch cyber police and other relevant authorities to investigate and take appropriate measures. However, we have yet to receive any actionable information beyond the article itself, which has not provided us with sufficient detail to identify or block malicious actors.”
In December 2022, security firm Recorded Future profiled the phishing and credential harvesting infrastructure used for Russia-aligned espionage operations by a group dubbed Blue Charlie (aka TAG-53), which has targeted email accounts of nongovernmental organizations and think tanks, journalists, and government and defense officials.
Recorded Future found that virtually all the Blue Charlie domains existed in just ten different ISPs, with a significant concentration located in two networks, one of which was MIRhosting. Both Microsoft and the UK government assess that Blue Charlie is linked to the Russian threat activity groups variously known as Callisto Group, COLDRIVER, and SEABORGIUM.
Mr. Nesterenko took exception to a story on that report from The Record, which is owned by Recorded Future.
“We’ve discussed its contents with our customer, Stark Industries,” he said. “We understand that they have initiated legal proceedings against the website in question, as they firmly believe that the claims made are inaccurate.”
Recorded Future said they updated their story with comments from Mr. Neculiti, but that they stand by their reporting.
Mr. Nesterenko’s LinkedIn profile says he was previously the foreign region sales manager at Serverius-as, a hosting company in The Netherlands that remains in the same data center as MIRhosting.
In February, the Dutch police took 13 servers offline that were used by the infamous LockBit ransomware group, which had originally bragged on its darknet website that its home base was in The Netherlands. Sources tell KrebsOnSecurity the servers seized by the Dutch police were located in Serverius’ data center in Dronten, which is also shared by MIRhosting.
Serverius-as did not respond to requests for comment. Nesterenko said MIRhosting does use one of Serverius’s data centers for its operations in the Netherlands, alongside two other data centers, but that the recent incident involving the seizure of servers has no connection to MIRhosting.
“We are legally prohibited by Dutch law and police regulations from sharing information with third parties regarding any communications we may have had,” he said.
A February 2024 report from security firm ESET found Serverius-as systems were involved in a series of targeted phishing attacks by Russia-aligned groups against Ukrainian entities throughout 2023. ESET observed that after the spearphishing domains were no longer active, they were converted to promoting rogue Internet pharmacy websites.
A review of the Internet address ranges recently added to the network operated by Stark Industries Solutions offers some insight into its customer base, usage, and maybe even true origins. Here is a snapshot (PDF) of all Internet address ranges announced by Stark Industries so far in the month of May 2024 (this information was graciously collated by the network observability platform Kentik.com).
Those records indicate that the largest portion of the IP space used by Stark is in The Netherlands, followed by Germany and the United States. Stark says it is connected to roughly 4,600 Internet addresses that currently list their ownership as Comcast Cable Communications.
A review of those address ranges at spur.us shows all of them are connected to an entity called Proxyline, which is a sprawling proxy service based in Russia that currently says it has more than 1.6 million proxies globally that are available for rent.

Proxyline dot net.
Reached for comment, Comcast said the Internet address ranges never did belong to Comcast, so it is likely that Stark has been fudging the real location of its routing announcements in some cases.
Stark reports that it has more than 67,000 Internet addresses at Santa Clara, Calif.-based EGIhosting. Spur says the Stark addresses involving EGIhosting all map to Proxyline as well. EGIhosting did not respond to requests for comment.
EGIhosting manages Internet addresses for the Cyprus-based hosting firm ITHOSTLINE LTD (aka HOSTLINE-LTD), which is represented throughout Stark’s announced Internet ranges. Stark says it has more than 21,000 Internet addresses with HOSTLINE. Spur.us finds Proxyline addresses are especially concentrated in the Stark ranges labeled ITHOSTLINE LTD, HOSTLINE-LTD, and Proline IT.
Stark’s network list includes approximately 21,000 Internet addresses at Hockessin, De. based DediPath, which abruptly ceased operations without warning in August 2023. According to a phishing report released last year by Interisle Consulting, DediPath was the fourth most common source of phishing attacks in the year ending Oct. 2022. Spur.us likewise finds that virtually all of the Stark address ranges marked “DediPath LLC” are tied to Proxyline.

Image: Interisle Consulting.
A large number of the Internet address ranges announced by Stark in May originate in India, and the names that are self-assigned to many of these networks indicate they were previously used to send large volumes of spam for herbal medicinal products, with names like HerbalFarm, AdsChrome, Nutravo, Herbzoot and Herbalve.
The anti-spam organization SpamHaus reports that many of the Indian IP address ranges are associated with known “snowshoe spam,” a form of abuse that involves mass email campaigns spread across several domains and IP addresses to weaken reputation metrics and avoid spam filters.
It’s not clear how much of Stark’s network address space traces its origins to Russia, but big chunks of it recently belonged to some of the oldest entities on the Russian Internet (a.k.a. “Runet”).
For example, many Stark address ranges were most recently assigned to a Russian government entity whose full name is the “Federal State Autonomous Educational Establishment of Additional Professional Education Center of Realization of State Educational Policy and Informational Technologies.”
A review of Internet address ranges adjacent to this entity reveals a long list of Russian government organizations that are part of the Federal Guard Service of the Russian Federation. Wikipedia says the Federal Guard Service is a Russian federal government agency concerned with tasks related to protection of several high-ranking state officials, including the President of Russia, as well as certain federal properties. The agency traces its origins to the USSR’s Ninth Directorate of the KGB, and later the presidential security service.
Stark recently announced the address range 213.159.64.0/20 from April 27 to May 1, and this range was previously assigned to an ancient ISP in St. Petersburg, RU called the Computer Technologies Institute Ltd.
According to a post on the Russian language webmaster forum searchengines[.]ru, the domain for Computer Technologies Institute — ctinet[.]ru — is the seventh-oldest domain in the entire history of the Runet.
Curiously, Stark also lists large tracts of Internet addresses (close to 48,000 in total) assigned to a small ISP in Kharkiv, Ukraine called NetAssist. Reached via email, the CEO of NetAssist Max Tulyev confirmed his company provides a number of services to PQ Hosting.
“We colocate their equipment in Warsaw, Madrid, Sofia and Thessaloniki, provide them IP transit and IPv4 addresses,” Tulyev said. “For their size, we receive relatively low number of complains to their networks. I never seen anything about their pro-Russian activity or support of Russian hackers. It is very interesting for me to see proofs of your accusations.”
Spur.us mapped the entire infrastructure of Proxyline, and found more than one million proxies across multiple providers, but by far the biggest concentration was at Stark Industries Solutions. The full list of Proxyline address ranges (.CSV) shows two other ISPs appear repeatedly throughout the list. One is Kharkiv, Ukraine based ITL LLC, also known as Information Technology Laboratories Group, and Integrated Technologies Laboratory.
The second is a related hosting company in Miami, called Green Floid LLC. Green Floid featured in a 2017 scoop by CNN, which profiled the company’s owner and quizzed him about Russian troll farms using proxy networks on Green Floid and its parent firm ITL to mask disinformation efforts tied to the Kremlin’s Internet Research Agency (IRA). At the time, the IRA was using Facebook and other social media networks to spread videos showing police brutality against African Americans in an effort to encourage protests across the United States.

Doug Madory, director of Internet analysis at Kentik, was able to see at a high level the top sources and destinations for traffic traversing Stark’s network.
“Based on our aggregate NetFlow, we see Iran as the top destination (35.1%) for traffic emanating from Stark (AS44477),” Madory said. “Specifically, the top destination is MTN Irancell, while the top source is Facebook. This data supports the theory that AS44477 houses proxy services as Facebook is blocked in Iran.”
On April 30, the security firm Malwarebytes explored an extensive malware operation that targets corporate Internet users with malicious ads. Among the sites used as lures in that campaign were fake Wall Street Journal and CNN websites that told visitors they were required to install a WSJ or CNN-branded browser extension (malware). Malwarebytes found a domain name central to that operation was hosted at Internet addresses owned by Stark Industries.
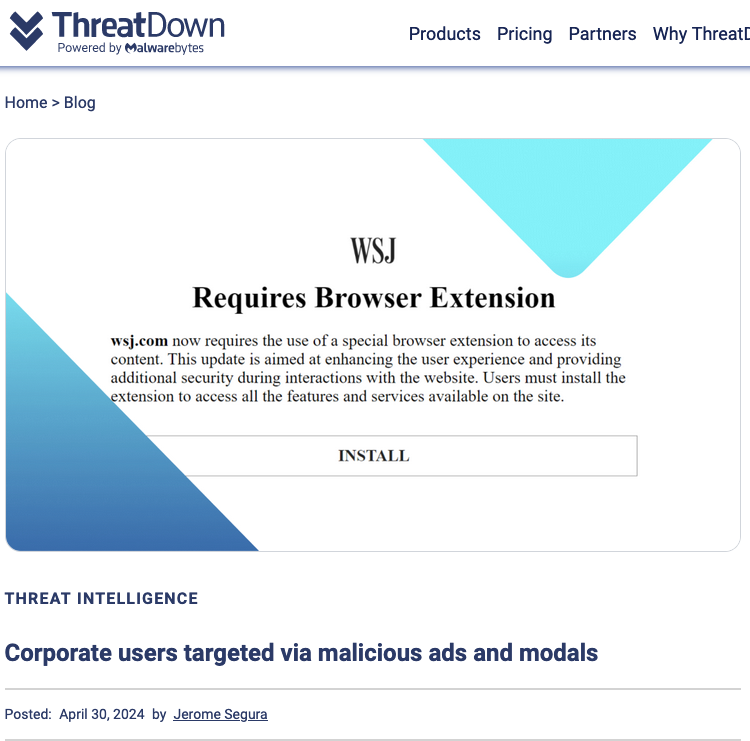
Image: threatdown.com

I think I could count on my hand the people I know who have NOT had their email hacked. Maybe they found a four-leaf clover when they were kids!
Email hacking is one of the very unfortunate downsides of living in our connected, digital world. And it usually occurs as a result of a data breach – a situation that even the savviest tech experts find themselves in.
In simple terms, a data breach happens when personal information is accessed, disclosed without permission, or lost. Companies, organisations, and government departments of any size can be affected. Data stolen can include customer login details (email addresses and passwords), credit card numbers, identifying IDs of customers e.g. driver’s license numbers and/or passport numbers, confidential customer information, company strategy, or even matters of national security.
Data breaches have made headlines, particularly over the last few years. When the Optus and Medibank data breaches hit the news in 2022 affecting almost 10 million Aussies a piece, we were all shaken. But then when Aussie finance company Latitude, was affected in 2023 with a whopping 14 million people from both Australia and New Zealand affected, it almost felt inevitable that by now, most of us would have been impacted.
But these were the data breaches that grabbed our attention. The reality is that data breaches have been happening for years. In fact, the largest data breach in Australian history actually happened in May 2019 to the online design site Canva which affected 137 million users globally including many Aussies.
So, in short – it can happen to anyone, and the chances are you may have already been affected.
The sole objective of a hacker is to get their hands on your data. And any information that you share in your email account can be very valuable to them. But why do they want your data, you ask? It’s simple really – so they can cash in! Some will keep the juicy stuff for themselves – passwords or logins to government departments or large companies they may want to ’target’ with the aim of extracting valuable data and/or funds. But the more sophisticated ones will sell your details including name, telephone, email address, and credit card details, and cash in on the Dark Web. They often do this in batches. Some experts believe they can get as much as AU$250 for a full set of details including credit cards. So, you can see why they’d be interested in you!
The other reason why hackers will be interested in your email address and password is that many of us re-use these login details across our other online accounts too. So, once they’ve got their hands on your email credentials then they may be able to access your online banking and investment accounts – the possibilities are endless if you are using the same login credentials everywhere. So, you can see why I harp on about using a unique password for every online account!
There is a plethora of statistics on just how big this issue is – all of them concerning.
According to the Australian Institute of Criminology, there were over 16,000 reports of identity theft in 2022.
The Department of Home Affairs and Stay Smart Australia reports that cybercrime costs Australian businesses $29 billion a year with the average business spending around $275,000 to remedy a data breach
And although there has been a slight reduction in Aussies falling for phishing scams in recent years (down from 2.7% in 2020/1 to 2.5% in 2022/3), more Australians are falling victim to card fraud scams with a total of $2.2 billion lost in 2023.
But regardless of which statistic you choose to focus on, we have a big issue on our hands!
If you find yourself a victim of email hacking there are a few very important steps you need to take and the key is to take them FAST!!
This is the very first thing you must do to ensure the hacker can’t get back into your account. It is essential that your new password is complex and totally unrelated to previous passwords. Always use at least 8-10 characters with a variety of upper and lower case and throw in some symbols and numbers. I really like the idea of a crazy, nonsensical sentence – easier to remember and harder to crack! But, better still, get yourself a password manager that will create a password that no human would be capable of creating.
If you find the hacker has locked you out of your account by changing your password, you will need to reset the password by clicking on the ‘Forgot My Password’ link.
This is time-consuming but essential. Ensure you change any other accounts that use the same username and password as your compromised email. Hackers love the fact that many people still use the same logins for multiple accounts, so it is guaranteed they will try your info in other email applications and sites such as PayPal, Amazon, Netflix – you name it!
Once the dust has settled, please review your password strategy for all your online accounts. A best practice is to ensure every online account has its own unique and complex password.
A big part of the hacker’s strategy is to ‘get their claws’ into your address book with the aim of hooking others as well. Send a message to all your email contacts as soon as possible so they know to avoid opening any emails (most likely loaded with malware) that have come from you.
Yes, multi-factor authentication (or 2-factor authentication) adds another step to your login but it also adds another layer of protection. Enabling this will mean that in addition to your password, you will need a special one-time use code to log in. This can be sent to your mobile phone or alternatively, it may be generated via an authenticator app. So worthwhile!
It is not uncommon for hackers to modify your email settings so that a copy of every email you receive is automatically forwarded to them. Not only can they monitor your logins for other sites, but they’ll keep a watchful eye over any particularly juicy personal information. So, check your mail forwarding settings to ensure no unexpected email addresses have been added.
Don’t forget to check your email signature to ensure nothing spammy has been added. Also, ensure your ‘reply to’ email address is actually yours! Hackers have been known to create an email address here that looks similar to yours – when someone replies, it goes straight to their account, not yours!
This is essential also. If you find anything, please ensure it is addressed, and then change your email password again. And if you don’t have it – please invest. Comprehensive security software will provide you with a digital shield for your online life. McAfee+ lets you protect all your devices – including your smartphone – from viruses and malware. It also contains a password manager to help you remember and generate unique passwords for all your accounts.
If you have been hacked several times and your email provider isn’t mitigating the amount of spam you are receiving, then consider starting afresh but don’t delete your email address. Many experts warn against deleting email accounts as most email providers will recycle your old email address. This could mean a hacker could spam every site they can find with a ‘forgot my password’ request and try to impersonate you – identity theft!
Your email is an important part of your online identity so being vigilant and addressing any fallout from hacking is essential for your digital reputation. And even though it may feel that ‘getting hacked’ is inevitable, you can definitely reduce your risk by installing some good quality security software on all your devices. Comprehensive security software such as McAfee+ will alert you when visiting risky websites, warn you when a download looks ‘dodgy’, and will block annoying and dangerous emails with anti-spam technology.
It makes sense really – if you don’t receive the ‘dodgy’ phishing email – you can’t click on it! Smart!
And finally, don’t forget that hackers love social media – particularly those of us who overshare on it. So, before you post details of your adorable new kitten, remember it may just provide the perfect clue for a hacker trying to guess your email password!
Till next time
Alex
The post What to Do If Your Email Is Hacked appeared first on McAfee Blog.
Invisible protocol sniffer for finding vulnerabilities in the network. Designed for pentesters and security engineers.
Above: Invisible network protocol sniffer
Designed for pentesters and security engineers
Author: Magama Bazarov, <caster@exploit.org>
Pseudonym: Caster
Version: 2.6
Codename: Introvert
All information contained in this repository is provided for educational and research purposes only. The author is not responsible for any illegal use of this tool.
It is a specialized network security tool that helps both pentesters and security professionals.
Above is a invisible network sniffer for finding vulnerabilities in network equipment. It is based entirely on network traffic analysis, so it does not make any noise on the air. He's invisible. Completely based on the Scapy library.
Above allows pentesters to automate the process of finding vulnerabilities in network hardware. Discovery protocols, dynamic routing, 802.1Q, ICS Protocols, FHRP, STP, LLMNR/NBT-NS, etc.
Detects up to 27 protocols:
MACSec (802.1X AE)
EAPOL (Checking 802.1X versions)
ARP (Passive ARP, Host Discovery)
CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol)
DTP (Dynamic Trunking Protocol)
LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
802.1Q Tags (VLAN)
S7COMM (Siemens)
OMRON
TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus)
ModbusTCP
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol)
HSRP (Host Standby Redundancy Protocol)
GLBP (Gateway Load Balancing Protocol)
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
LLMNR (Link Local Multicast Name Resolution)
NBT-NS (NetBIOS Name Service)
MDNS (Multicast DNS)
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol v6)
ICMPv6 (Internet Control Message Protocol v6)
SSDP (Simple Service Discovery Protocol)
MNDP (MikroTik Neighbor Discovery Protocol)
Above works in two modes:
The tool is very simple in its operation and is driven by arguments:
.pcap as input and looks for protocols in it.pcap file, its name you specify yourselfusage: above.py [-h] [--interface INTERFACE] [--timer TIMER] [--output OUTPUT] [--input INPUT] [--passive-arp]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--interface INTERFACE
Interface for traffic listening
--timer TIMER Time in seconds to capture packets, if not set capture runs indefinitely
--output OUTPUT File name where the traffic will be recorded
--input INPUT File name of the traffic dump
--passive-arp Passive ARP (Host Discovery)
The information obtained will be useful not only to the pentester, but also to the security engineer, he will know what he needs to pay attention to.
When Above detects a protocol, it outputs the necessary information to indicate the attack vector or security issue:
Impact: What kind of attack can be performed on this protocol;
Tools: What tool can be used to launch an attack;
Technical information: Required information for the pentester, sender MAC/IP addresses, FHRP group IDs, OSPF/EIGRP domains, etc.
Mitigation: Recommendations for fixing the security problems
Source/Destination Addresses: For protocols, Above displays information about the source and destination MAC addresses and IP addresses
You can install Above directly from the Kali Linux repositories
caster@kali:~$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install above
Or...
caster@kali:~$ sudo apt-get install python3-scapy python3-colorama python3-setuptools
caster@kali:~$ git clone https://github.com/casterbyte/Above
caster@kali:~$ cd Above/
caster@kali:~/Above$ sudo python3 setup.py install
# Install python3 first
brew install python3
# Then install required dependencies
sudo pip3 install scapy colorama setuptools
# Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/casterbyte/Above
cd Above/
sudo python3 setup.py install
Don't forget to deactivate your firewall on macOS!
Above requires root access for sniffing
Above can be run with or without a timer:
caster@kali:~$ sudo above --interface eth0 --timer 120
To stop traffic sniffing, press CTRL + С
WARNING! Above is not designed to work with tunnel interfaces (L3) due to the use of filters for L2 protocols. Tool on tunneled L3 interfaces may not work properly.
Example:
caster@kali:~$ sudo above --interface eth0 --timer 120
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[+] Start sniffing...
[*] After the protocol is detected - all necessary information about it will be displayed
--------------------------------------------------
[+] Detected SSDP Packet
[*] Attack Impact: Potential for UPnP Device Exploitation
[*] Tools: evil-ssdp
[*] SSDP Source IP: 192.168.0.251
[*] SSDP Source MAC: 02:10:de:64:f2:34
[*] Mitigation: Ensure UPnP is disabled on all devices unless absolutely necessary, monitor UPnP traffic
--------------------------------------------------
[+] Detected MDNS Packet
[*] Attack Impact: MDNS Spoofing, Credentials Interception
[*] Tools: Responder
[*] MDNS Spoofing works specifically against Windows machines
[*] You cannot get NetNTLMv2-SSP from Apple devices
[*] MDNS Speaker IP: fe80::183f:301c:27bd:543
[*] MDNS Speaker MAC: 02:10:de:64:f2:34
[*] Mitigation: Filter MDNS traffic. Be careful with MDNS filtering
--------------------------------------------------
If you need to record the sniffed traffic, use the --output argument
caster@kali:~$ sudo above --interface eth0 --timer 120 --output above.pcap
If you interrupt the tool with CTRL+C, the traffic is still written to the file
If you already have some recorded traffic, you can use the --input argument to look for potential security issues
caster@kali:~$ above --input ospf-md5.cap
Example:
caster@kali:~$ sudo above --input ospf-md5.cap
[+] Analyzing pcap file...
--------------------------------------------------
[+] Detected OSPF Packet
[+] Attack Impact: Subnets Discovery, Blackhole, Evil Twin
[*] Tools: Loki, Scapy, FRRouting
[*] OSPF Area ID: 0.0.0.0
[*] OSPF Neighbor IP: 10.0.0.1
[*] OSPF Neighbor MAC: 00:0c:29:dd:4c:54
[!] Authentication: MD5
[*] Tools for bruteforce: Ettercap, John the Ripper
[*] OSPF Key ID: 1
[*] Mitigation: Enable passive interfaces, use authentication
--------------------------------------------------
[+] Detected OSPF Packet
[+] Attack Impact: Subnets Discovery, Blackhole, Evil Twin
[*] Tools: Loki, Scapy, FRRouting
[*] OSPF Area ID: 0.0.0.0
[*] OSPF Neighbor IP: 192.168.0.2
[*] OSPF Neighbor MAC: 00:0c:29:43:7b:fb
[!] Authentication: MD5
[*] Tools for bruteforce: Ettercap, John the Ripper
[*] OSPF Key ID: 1
[*] Mitigation: Enable passive interfaces, use authentication
The tool can detect hosts without noise in the air by processing ARP frames in passive mode
caster@kali:~$ sudo above --interface eth0 --passive-arp --timer 10
[+] Host discovery using Passive ARP
--------------------------------------------------
[+] Detected ARP Reply
[*] ARP Reply for IP: 192.168.1.88
[*] MAC Address: 00:00:0c:07:ac:c8
--------------------------------------------------
[+] Detected ARP Reply
[*] ARP Reply for IP: 192.168.1.40
[*] MAC Address: 00:0c:29:c5:82:81
--------------------------------------------------
I wrote this tool because of the track "A View From Above (Remix)" by KOAN Sound. This track was everything to me when I was working on this sniffer.

Image: Shutterstock.
Apple and the satellite-based broadband service Starlink each recently took steps to address new research into the potential security and privacy implications of how their services geo-locate devices. Researchers from the University of Maryland say they relied on publicly available data from Apple to track the location of billions of devices globally — including non-Apple devices like Starlink systems — and found they could use this data to monitor the destruction of Gaza, as well as the movements and in many cases identities of Russian and Ukrainian troops.
At issue is the way that Apple collects and publicly shares information about the precise location of all Wi-Fi access points seen by its devices. Apple collects this location data to give Apple devices a crowdsourced, low-power alternative to constantly requesting global positioning system (GPS) coordinates.
Both Apple and Google operate their own Wi-Fi-based Positioning Systems (WPS) that obtain certain hardware identifiers from all wireless access points that come within range of their mobile devices. Both record the Media Access Control (MAC) address that a Wi-FI access point uses, known as a Basic Service Set Identifier or BSSID.
Periodically, Apple and Google mobile devices will forward their locations — by querying GPS and/or by using cellular towers as landmarks — along with any nearby BSSIDs. This combination of data allows Apple and Google devices to figure out where they are within a few feet or meters, and it’s what allows your mobile phone to continue displaying your planned route even when the device can’t get a fix on GPS.
With Google’s WPS, a wireless device submits a list of nearby Wi-Fi access point BSSIDs and their signal strengths — via an application programming interface (API) request to Google — whose WPS responds with the device’s computed position. Google’s WPS requires at least two BSSIDs to calculate a device’s approximate position.
Apple’s WPS also accepts a list of nearby BSSIDs, but instead of computing the device’s location based off the set of observed access points and their received signal strengths and then reporting that result to the user, Apple’s API will return the geolocations of up to 400 hundred more BSSIDs that are nearby the one requested. It then uses approximately eight of those BSSIDs to work out the user’s location based on known landmarks.
In essence, Google’s WPS computes the user’s location and shares it with the device. Apple’s WPS gives its devices a large enough amount of data about the location of known access points in the area that the devices can do that estimation on their own.
That’s according to two researchers at the University of Maryland, who theorized they could use the verbosity of Apple’s API to map the movement of individual devices into and out of virtually any defined area of the world. The UMD pair said they spent a month early in their research continuously querying the API, asking it for the location of more than a billion BSSIDs generated at random.
They learned that while only about three million of those randomly generated BSSIDs were known to Apple’s Wi-Fi geolocation API, Apple also returned an additional 488 million BSSID locations already stored in its WPS from other lookups.
UMD Associate Professor David Levin and Ph.D student Erik Rye found they could mostly avoid requesting unallocated BSSIDs by consulting the list of BSSID ranges assigned to specific device manufacturers. That list is maintained by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which is also sponsoring the privacy and security conference where Rye is slated to present the UMD research later today.
Plotting the locations returned by Apple’s WPS between November 2022 and November 2023, Levin and Rye saw they had a near global view of the locations tied to more than two billion Wi-Fi access points. The map showed geolocated access points in nearly every corner of the globe, apart from almost the entirety of China, vast stretches of desert wilderness in central Australia and Africa, and deep in the rainforests of South America.
The researchers said that by zeroing in on or “geofencing” other smaller regions indexed by Apple’s location API, they could monitor how Wi-Fi access points moved over time. Why might that be a big deal? They found that by geofencing active conflict zones in Ukraine, they were able to determine the location and movement of Starlink devices used by both Ukrainian and Russian forces.
The reason they were able to do that is that each Starlink terminal — the dish and associated hardware that allows a Starlink customer to receive Internet service from a constellation of orbiting Starlink satellites — includes its own Wi-Fi access point, whose location is going to be automatically indexed by any nearby Apple devices that have location services enabled.
The University of Maryland team geo-fenced various conflict zones in Ukraine, and identified at least 3,722 Starlink terminals geolocated in Ukraine.
“We find what appear to be personal devices being brought by military personnel into war zones, exposing pre-deployment sites and military positions,” the researchers wrote. “Our results also show individuals who have left Ukraine to a wide range of countries, validating public reports of where Ukrainian refugees have resettled.”
In an interview with KrebsOnSecurity, the UMD team said they found that in addition to exposing Russian troop pre-deployment sites, the location data made it easy to see where devices in contested regions originated from.
“This includes residential addresses throughout the world,” Levin said. “We even believe we can identify people who have joined the Ukraine Foreign Legion.”
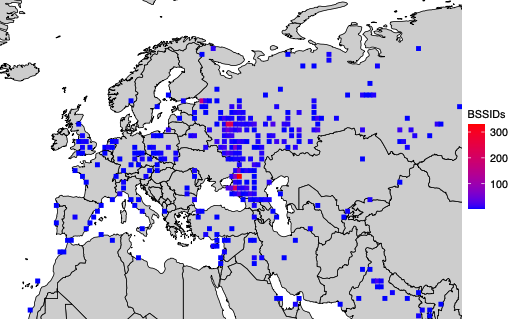
A simplified map of where BSSIDs that enter the Donbas and Crimea regions of Ukraine originate. Image: UMD.
Levin and Rye said they shared their findings with Starlink in March 2024, and that Starlink told them the company began shipping software updates in 2023 that force Starlink access points to randomize their BSSIDs.
Starlink’s parent SpaceX did not respond to requests for comment. But the researchers shared a graphic they said was created from their Starlink BSSID monitoring data, which shows that just in the past month there was a substantial drop in the number of Starlink devices that were geo-locatable using Apple’s API.
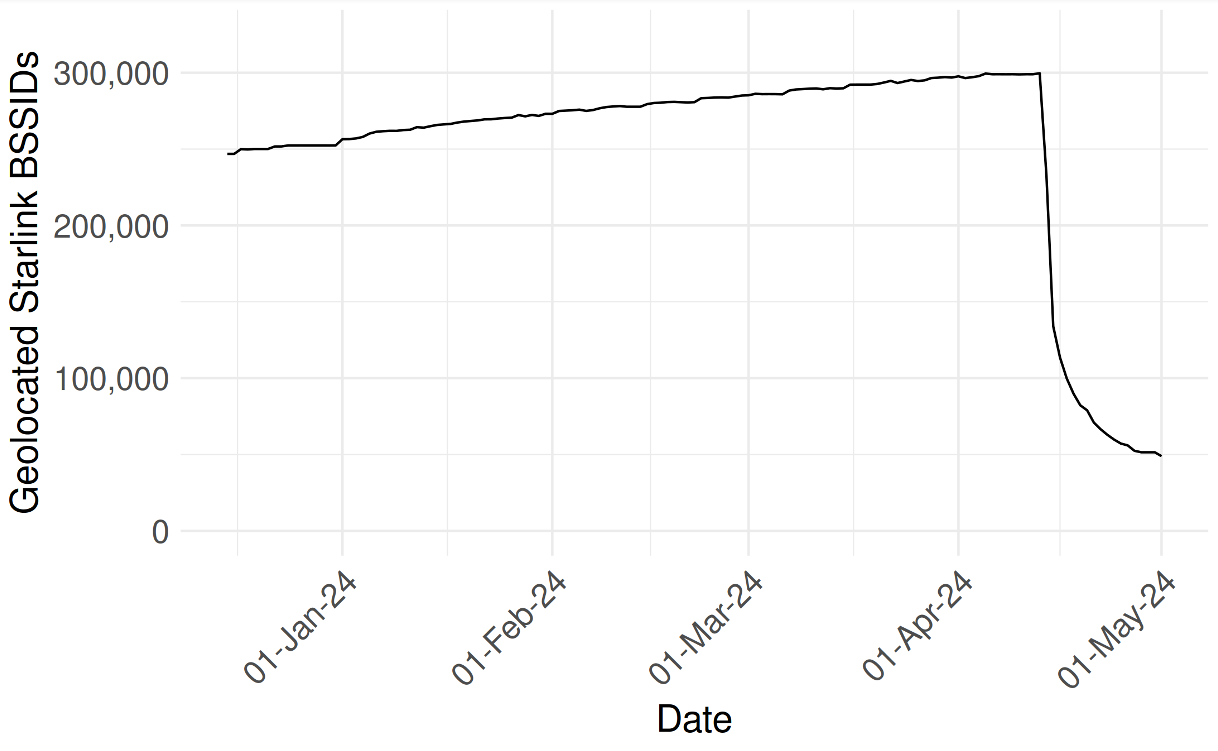
UMD researchers shared this graphic, which shows their ability to monitor the location and movement of Starlink devices by BSSID dropped precipitously in the past month.
They also shared a written statement they received from Starlink, which acknowledged that Starlink User Terminal routers originally used a static BSSID/MAC:
“In early 2023 a software update was released that randomized the main router BSSID. Subsequent software releases have included randomization of the BSSID of WiFi repeaters associated with the main router. Software updates that include the repeater randomization functionality are currently being deployed fleet-wide on a region-by-region basis. We believe the data outlined in your paper is based on Starlink main routers and or repeaters that were queried prior to receiving these randomization updates.”
The researchers also focused their geofencing on the Israel-Hamas war in Gaza, and were able to track the migration and disappearance of devices throughout the Gaza Strip as Israeli forces cut power to the country and bombing campaigns knocked out key infrastructure.
“As time progressed, the number of Gazan BSSIDs that are geolocatable continued to decline,” they wrote. “By the end of the month, only 28% of the original BSSIDs were still found in the Apple WPS.”
In late March 2024, Apple quietly updated its website to note that anyone can opt out of having the location of their wireless access points collected and shared by Apple — by appending “_nomap” to the end of the Wi-Fi access point’s name (SSID). Adding “_nomap” to your Wi-Fi network name also blocks Google from indexing its location.
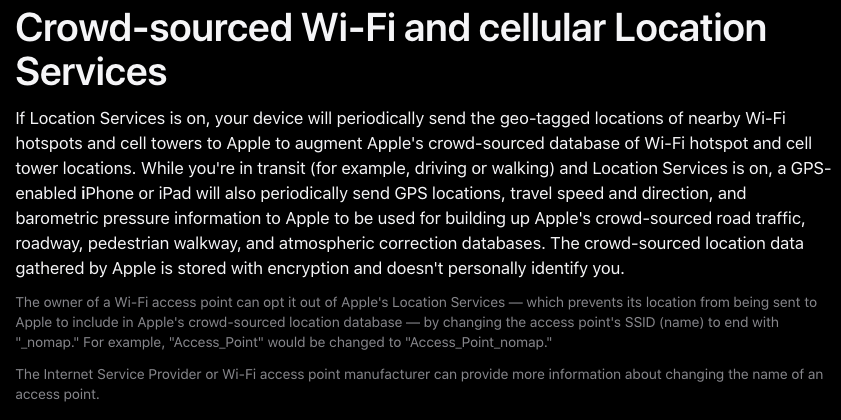
Apple updated its privacy and location services policy in March 2024 to allow people to opt out of having their Wi-Fi access point indexed by its service, by appending “_nomap” to the network’s name.
Asked about the changes, Apple said they have respected the “_nomap” flag on SSIDs for some time, but that this was only called out in a support article earlier this year.
Rye said Apple’s response addressed the most depressing aspect of their research: That there was previously no way for anyone to opt out of this data collection.
“You may not have Apple products, but if you have an access point and someone near you owns an Apple device, your BSSID will be in [Apple’s] database,” he said. “What’s important to note here is that every access point is being tracked, without opting in, whether they run an Apple device or not. Only after we disclosed this to Apple have they added the ability for people to opt out.”
The researchers said they hope Apple will consider additional safeguards, such as proactive ways to limit abuses of its location API.
“It’s a good first step,” Levin said of Apple’s privacy update in March. “But this data represents a really serious privacy vulnerability. I would hope Apple would put further restrictions on the use of its API, like rate-limiting these queries to keep people from accumulating massive amounts of data like we did.”
The UMD researchers said they omitted certain details from their study to protect the users they were able to track, noting that the methods they used could present risks for those fleeing abusive relationships or stalkers.
“We observe routers move between cities and countries, potentially representing their owner’s relocation or a business transaction between an old and new owner,” they wrote. “While there is not necessarily a 1-to-1 relationship between Wi-Fi routers and users, home routers typically only have several. If these users are vulnerable populations, such as those fleeing intimate partner violence or a stalker, their router simply being online can disclose their new location.”
The researchers said Wi-Fi access points that can be created using a mobile device’s built-in cellular modem do not create a location privacy risk for their users because mobile phone hotspots will choose a random BSSID when activated.
“Modern Android and iOS devices will choose a random BSSID when you go into hotspot mode,” he said. “Hotspots are already implementing the strongest recommendations for privacy protections. It’s other types of devices that don’t do that.”
For example, they discovered that certain commonly used travel routers compound the potential privacy risks.
“Because travel routers are frequently used on campers or boats, we see a significant number of them move between campgrounds, RV parks, and marinas,” the UMD duo wrote. “They are used by vacationers who move between residential dwellings and hotels. We have evidence of their use by military members as they deploy from their homes and bases to war zones.”
A copy of the UMD research is available here (PDF).
Update, May 22, 4:54 p.m. ET: Added response from Apple.

At the beginning of the year, the Associated Press described artificial intelligence (AI) as “easily the biggest buzzword for world leaders and corporate bosses.” You’ve likely heard talk about AI everywhere from the news to social media to around the dinner table. Amid this chatter, it’s easy to wonder: what exactly is AI, and why is it of such importance?
Artificial intelligence is defined as “a machine’s ability to perform the cognitive functions we associate with human minds, such as perceiving, reasoning, learning, interacting with the environment, problem-solving, and even exercising creativity.” AI is a branch of computer science with subfields, including machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics.
AI traces its roots to the mid-20th century, with pioneers like Alan Turing and John McCarthy laying the groundwork for its development. In 1956, the Dartmouth Conference marked a significant milestone, officially inaugurating AI as a distinct field of study.
Since then, AI has evolved rapidly, with researchers and innovators continuously pushing boundaries to create intelligent machines capable of emulating human cognitive abilities. AI’s potential impact on technology, society, and various industries continues to expand, shaping the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
Most people interact with AI every day, often without even realizing it. AI has become integrated into daily life, simplifying tasks, delivering personalized content, and enhancing convenience for consumers across various digital platforms. From using voice assistants like Siri or Alexa to receiving personalized recommendations on streaming platforms like Netflix or Spotify, AI plays a significant role in enhancing user experiences.
Social media platforms utilize AI algorithms to curate news feeds and suggest content tailored to individual preferences. AI-powered product recommendations and chatbots that assist with customer inquiries enrich online shopping experiences. Ride-sharing services employ AI to match drivers with passengers efficiently, enhancing accessibility and reducing wait times.
AI chatbots like ChatGPT assist people daily by providing instant access to information and guidance. Whether troubleshooting technical issues, offering advice, or providing recommendations, AI chatbots serve as efficient virtual assistants that enable users to quickly find solutions to their questions.
AI has the potential to revolutionize industries, address societal challenges, and transform everyday life through increased efficiency and innovation. For example, in healthcare, new hope for a cancer cure has emerged as a personalized cancer vaccine is being developed using AI and DNA sequencing. AI-powered systems are also assisting doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately and quickly, leading to better patient outcomes.
This kind of progress is incredible, but AI also presents challenges and risks.
One notably concerning aspect is the rise of deepfake technology, which enables the creation of highly realistic but fake videos or audio recordings. These deepfakes can be used for everything from voice cloning attacks to creating a fake Taylor Swift advertisement. Deepfakes have the potential to deceive and manipulate individuals, spread misinformation, and undermine trust in visual and audio media.
In an election year, AI-driven manipulation is especially dangerous. From automated disinformation campaigns to targeted voter suppression tactics, AI algorithms can be deployed to sway public opinion, amplify divisive rhetoric, and undermine the integrity of the electoral process. Deepfake videos could be used to fabricate scandalous incidents or speeches, leading to widespread confusion and mistrust among voters. That’s why we joined other leading tech companies in a commitment to combat the deceptive use of AI in the 2024 elections.
In addition to deepfake technology, AI is being increasingly utilized for nefarious purposes such as phishing attacks. By leveraging AI algorithms, hackers can craft highly convincing emails or messages impersonating trusted individuals or organizations. These AI-driven phishing attempts can manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
Consequently, there is a pressing need to develop safeguards to mitigate AI’s negative impact while harnessing its positive potential for the benefit of society. Individuals can utilize identity theft protection software powered by AI to stay vigilant against such threats, receiving real-time alerts about suspicious activities and potential breaches to safeguard their personal information.
AI represents the frontier where technology converges with the complexities of human intelligence, propelling innovation towards unprecedented realms of possibility. It holds immense significance in today’s world because it offers unprecedented opportunities for innovation and progress.
The post What is Artificial Intelligence? appeared first on McAfee Blog.
V'ger is an interactive command-line application for post-exploitation of authenticated Jupyter instances with a focus on AI/ML security operations.
pip install vgervger --helpCurrently, vger interactive has maximum functionality, maintaining state for discovered artifacts and recurring jobs. However, most functionality is also available by-name in non-interactive format with vger <module>. List available modules with vger --help.
Once a connection is established, users drop into a nested set of menus.
The top level menu is: - Reset: Configure a different host. - Enumerate: Utilities to learn more about the host. - Exploit: Utilities to perform direct action and manipulation of the host and artifacts. - Persist: Utilities to establish persistence mechanisms. - Export: Save output to a text file. - Quit: No one likes quitters.
These menus contain the following functionality: - List modules: Identify imported modules in target notebooks to determine what libraries are available for injected code. - Inject: Execute code in the context of the selected notebook. Code can be provided in a text editor or by specifying a local .py file. Either input is processed as a string and executed in runtime of the notebook. - Backdoor: Launch a new JupyterLab instance open to 0.0.0.0, with allow-root on a user-specified port with a user-specified password. - Check History: See ipython commands recently run in the target notebook. - Run shell command: Spawn a terminal, run the command, return the output, and delete the terminal. - List dir or get file: List directories relative to the Jupyter directory. If you don't know, start with /. - Upload file: Upload file from localhost to the target. Specify paths in the same format as List dir (relative to the Jupyter directory). Provide a full path including filename and extension. - Delete file: Delete a file. Specify paths in the same format as List dir (relative to the Jupyter directory). - Find models: Find models based on common file formats. - Download models: Download discovered models. - Snoop: Monitor notebook execution and results until timeout. - Recurring jobs: Launch/Kill recurring snippets of code silently run in the target environment.
With pip install vger[ai] you'll get LLM generated summaries of notebooks in the target environment. These are meant to be rough translation for non-DS/AI folks to do quick triage of if (or which) notebooks are worth investigating further.
There was an inherent tradeoff on model size vs. ability and that's something I'll continue to tinker with, but hopefully this is helpful for some more traditional security users. I'd love to see folks start prompt injecting their notebooks ("these are not the droids you're looking for").

According to Pew, three-in-ten U.S. adults say they have used a dating site or app. That number climbs to 53% for people under the age of 30. More and more people are turning to digital platforms to find love and companionship or simply to expand their social circles. However, as the popularity of online dating grows, so do the potential risks associated with it. From privacy concerns to identity theft, the digital dating world can be fraught with peril if you’re not careful. But fear not, by following a few simple guidelines, you can navigate the online dating scene safely and securely.
This article is for you or anyone you know who may be hopping onto an online dating app like Match, Bumble, Plenty of Fish, eHarmony, Tinder, or OkCupid. Think of it as an advice column of a different sort, where we talk about dating in light of your online privacy and safety.
For starters, we have a couple of previous blogs that offer sound advice about online dating. The first covers ways you can protect your privacy when you’re using online dating apps, which starts with picking a dating app that has a good reputation. The second rounds out the topic with further online dating advice for adults and teens alike. Give them a look!
It starts with basic hygiene. Digital hygiene, that is. Before you dive into a dating app, ensure that your device (and all your connected devices while you’re at it) has a comprehensive security solution in place. As you surf, chat, and meet up online, you’ll want to know that you’re protected against malware, viruses, phishing attacks, sketchy links, and so forth. Other features will come in handy (and be necessary as well), like ones that help you manage your passwords, protect your identity, safeguard your privacy, and more—all of which we’ll talk about in a bit.
Picking the right app is like picking the right date. From a security standpoint, these apps are the keepers of highly personal information about you, so you’ll want to know how they handle data, what privacy protections are in place, what information they gather when you first sign up, and what they continue to gather as you use the app. Do your research. Read up on their privacy policies. See what other people have to say about their experiences. And get a sense of what the app is all about. What’s its approach to dating? What kind of relationships are they focusing on? Make sure all of it feels right to you.
Only give the app the information that’s absolutely necessary to sign up. Dating apps ask questions so that they can help you find an ideal match, yet only share what you feel comfortable sharing. This is true from a personal standpoint, but it’s true from a security standpoint too. Anything you share along those lines could be at risk of a hack or a breach, the likes of which were reported by Wired and Forbes last year. If your info is compromised, it could lead to anywhere from identity theft to harassment, so when you use a dating app, keep the sharing to a minimum—and keep your eyes peeled for any suspicious activity across your social media, online accounts, and even your finances.
Another password to remember! That’s just what you need, right? Right! It absolutely is, and a strong one is vital. You can create one and manage all of your passwords with McAfee+’s password manager. It’ll encrypt your passwords and use multi-factor authentication, which offers even further protection from hacks and attacks on your account.
You can help keep your chats more private, and just about anything else you’re doing online, by using a VPN (virtual private network). For example, our VPN uses bank-level encryption to keep your personal data and activities private from hackers. And it’ll hide other information associated with your dating account while you’re online, like personal details, credit card numbers, and so forth. Given the security risks we’ve talked about so far, you’ll want to look into a VPN.
If you’re not using a VPN on your device, don’t use your dating app on public Wi-Fi. The issue is this: plenty of public Wi-Fi hotspots aren’t secure. Someone else on the network could easily intercept the information you send over it, including your passwords, any photos you share, and any chats you have. In other words, using public Wi-Fi without protection is like opening a door that leads right to you and your most personal data. This applies to everything on public Wi-Fi, not just dating apps. If you use public Wi-Fi at all, you really should use a VPN.
In the ever-evolving landscape of online dating, safeguarding your privacy and security is paramount. By implementing strategies such as using strong passwords, employing a reliable VPN, and exercising caution on public Wi-Fi, you can navigate the digital dating sphere with confidence. Remember, your safety and privacy are non-negotiable priorities in the pursuit of love and companionship online.
The post How to Safely Date Online appeared first on McAfee Blog.
An open-source, prototype implementation of property graphs for JavaScript based on the esprima parser, and the EsTree SpiderMonkey Spec. JAW can be used for analyzing the client-side of web applications and JavaScript-based programs.
This project is licensed under GNU AFFERO GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE V3.0. See here for more information.
JAW has a Github pages website available at https://soheilkhodayari.github.io/JAW/.
Release Notes:
JAW-V2 branch.JAW-V1 branch.The architecture of the JAW is shown below.
JAW can be used in two distinct ways:
Arbitrary JavaScript Analysis: Utilize JAW for modeling and analyzing any JavaScript program by specifying the program's file system path.
Web Application Analysis: Analyze a web application by providing a single seed URL.
Use the collected web resources to create a Hybrid Program Graph (HPG), which will be imported into a Neo4j database.
Optionally, supply the HPG construction module with a mapping of semantic types to custom JavaScript language tokens, facilitating the categorization of JavaScript functions based on their purpose (e.g., HTTP request functions).
Query the constructed Neo4j graph database for various analyses. JAW offers utility traversals for data flow analysis, control flow analysis, reachability analysis, and pattern matching. These traversals can be used to develop custom security analyses.
JAW also includes built-in traversals for detecting client-side CSRF, DOM Clobbering and request hijacking vulnerabilities.
The outputs will be stored in the same folder as that of input.
The installation script relies on the following prerequisites: - Latest version of npm package manager (node js) - Any stable version of python 3.x - Python pip package manager
Afterwards, install the necessary dependencies via:
$ ./install.sh
For detailed installation instructions, please see here.
You can run an instance of the pipeline in a background screen via:
$ python3 -m run_pipeline --conf=config.yaml
The CLI provides the following options:
$ python3 -m run_pipeline -h
usage: run_pipeline.py [-h] [--conf FILE] [--site SITE] [--list LIST] [--from FROM] [--to TO]
This script runs the tool pipeline.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--conf FILE, -C FILE pipeline configuration file. (default: config.yaml)
--site SITE, -S SITE website to test; overrides config file (default: None)
--list LIST, -L LIST site list to test; overrides config file (default: None)
--from FROM, -F FROM the first entry to consider when a site list is provided; overrides config file (default: -1)
--to TO, -T TO the last entry to consider when a site list is provided; overrides config file (default: -1)
Input Config: JAW expects a .yaml config file as input. See config.yaml for an example.
Hint. The config file specifies different passes (e.g., crawling, static analysis, etc) which can be enabled or disabled for each vulnerability class. This allows running the tool building blocks individually, or in a different order (e.g., crawl all webapps first, then conduct security analysis).
For running a quick example demonstrating how to build a property graph and run Cypher queries over it, do:
$ python3 -m analyses.example.example_analysis --input=$(pwd)/data/test_program/test.js
This module collects the data (i.e., JavaScript code and state values of web pages) needed for testing. If you want to test a specific JavaScipt file that you already have on your file system, you can skip this step.
JAW has crawlers based on Selenium (JAW-v1), Puppeteer (JAW-v2, v3) and Playwright (JAW-v3). For most up-to-date features, it is recommended to use the Puppeteer- or Playwright-based versions.
This web crawler employs foxhound, an instrumented version of Firefox, to perform dynamic taint tracking as it navigates through webpages. To start the crawler, do:
$ cd crawler
$ node crawler-taint.js --seedurl=https://google.com --maxurls=100 --headless=true --foxhoundpath=<optional-foxhound-executable-path>
The foxhoundpath is by default set to the following directory: crawler/foxhound/firefox which contains a binary named firefox.
Note: you need a build of foxhound to use this version. An ubuntu build is included in the JAW-v3 release.
To start the crawler, do:
$ cd crawler
$ node crawler.js --seedurl=https://google.com --maxurls=100 --browser=chrome --headless=true
See here for more information.
To start the crawler, do:
$ cd crawler/hpg_crawler
$ vim docker-compose.yaml # set the websites you want to crawl here and save
$ docker-compose build
$ docker-compose up -d
Please refer to the documentation of the hpg_crawler here for more information.
To generate an HPG for a given (set of) JavaScript file(s), do:
$ node engine/cli.js --lang=js --graphid=graph1 --input=/in/file1.js --input=/in/file2.js --output=$(pwd)/data/out/ --mode=csv
optional arguments:
--lang: language of the input program
--graphid: an identifier for the generated HPG
--input: path of the input program(s)
--output: path of the output HPG, must be i
--mode: determines the output format (csv or graphML)
To import an HPG inside a neo4j graph database (docker instance), do:
$ python3 -m hpg_neo4j.hpg_import --rpath=<path-to-the-folder-of-the-csv-files> --id=<xyz> --nodes=<nodes.csv> --edges=<rels.csv>
$ python3 -m hpg_neo4j.hpg_import -h
usage: hpg_import.py [-h] [--rpath P] [--id I] [--nodes N] [--edges E]
This script imports a CSV of a property graph into a neo4j docker database.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--rpath P relative path to the folder containing the graph CSV files inside the `data` directory
--id I an identifier for the graph or docker container
--nodes N the name of the nodes csv file (default: nodes.csv)
--edges E the name of the relations csv file (default: rels.csv)
In order to create a hybrid property graph for the output of the hpg_crawler and import it inside a local neo4j instance, you can also do:
$ python3 -m engine.api <path> --js=<program.js> --import=<bool> --hybrid=<bool> --reqs=<requests.out> --evts=<events.out> --cookies=<cookies.pkl> --html=<html_snapshot.html>
Specification of Parameters:
<path>: absolute path to the folder containing the program files for analysis (must be under the engine/outputs folder).--js=<program.js>: name of the JavaScript program for analysis (default: js_program.js).--import=<bool>: whether the constructed property graph should be imported to an active neo4j database (default: true).--hybrid=bool: whether the hybrid mode is enabled (default: false). This implies that the tester wants to enrich the property graph by inputing files for any of the HTML snapshot, fired events, HTTP requests and cookies, as collected by the JAW crawler.--reqs=<requests.out>: for hybrid mode only, name of the file containing the sequence of obsevered network requests, pass the string false to exclude (default: request_logs_short.out).--evts=<events.out>: for hybrid mode only, name of the file containing the sequence of fired events, pass the string false to exclude (default: events.out).--cookies=<cookies.pkl>: for hybrid mode only, name of the file containing the cookies, pass the string false to exclude (default: cookies.pkl).--html=<html_snapshot.html>: for hybrid mode only, name of the file containing the DOM tree snapshot, pass the string false to exclude (default: html_rendered.html).For more information, you can use the help CLI provided with the graph construction API:
$ python3 -m engine.api -h
The constructed HPG can then be queried using Cypher or the NeoModel ORM.
You should place and run your queries in analyses/<ANALYSIS_NAME>.
You can use the NeoModel ORM to query the HPG. To write a query:
example_query_orm.py in the analyses/example folder.$ python3 -m analyses.example.example_query_orm
For more information, please see here.
You can use Cypher to write custom queries. For this:
example_query_cypher.py in the analyses/example folder.$ python3 -m analyses.example.example_query_cypher
For more information, please see here.
This section describes how to configure and use JAW for vulnerability detection, and how to interpret the output. JAW contains, among others, self-contained queries for detecting client-side CSRF and DOM Clobbering
Step 1. enable the analysis component for the vulnerability class in the input config.yaml file:
request_hijacking:
enabled: true
# [...]
#
domclobbering:
enabled: false
# [...]
cs_csrf:
enabled: false
# [...]
Step 2. Run an instance of the pipeline with:
$ python3 -m run_pipeline --conf=config.yaml
Hint. You can run multiple instances of the pipeline under different screens:
$ screen -dmS s1 bash -c 'python3 -m run_pipeline --conf=conf1.yaml; exec sh'
$ screen -dmS s2 bash -c 'python3 -m run_pipeline --conf=conf2.yaml; exec sh'
$ # [...]
To generate parallel configuration files automatically, you may use the generate_config.py script.
The outputs will be stored in a file called sink.flows.out in the same folder as that of the input. For Client-side CSRF, for example, for each HTTP request detected, JAW outputs an entry marking the set of semantic types (a.k.a, semantic tags or labels) associated with the elements constructing the request (i.e., the program slices). For example, an HTTP request marked with the semantic type ['WIN.LOC'] is forgeable through the window.location injection point. However, a request marked with ['NON-REACH'] is not forgeable.
An example output entry is shown below:
[*] Tags: ['WIN.LOC']
[*] NodeId: {'TopExpression': '86', 'CallExpression': '87', 'Argument': '94'}
[*] Location: 29
[*] Function: ajax
[*] Template: ajaxloc + "/bearer1234/"
[*] Top Expression: $.ajax({ xhrFields: { withCredentials: "true" }, url: ajaxloc + "/bearer1234/" })
1:['WIN.LOC'] variable=ajaxloc
0 (loc:6)- var ajaxloc = window.location.href
This entry shows that on line 29, there is a $.ajax call expression, and this call expression triggers an ajax request with the url template value of ajaxloc + "/bearer1234/, where the parameter ajaxloc is a program slice reading its value at line 6 from window.location.href, thus forgeable through ['WIN.LOC'].
In order to streamline the testing process for JAW and ensure that your setup is accurate, we provide a simple node.js web application which you can test JAW with.
First, install the dependencies via:
$ cd tests/test-webapp
$ npm install
Then, run the application in a new screen:
$ screen -dmS jawwebapp bash -c 'PORT=6789 npm run devstart; exec sh'
For more information, visit our wiki page here. Below is a table of contents for quick access.
Pull requests are always welcomed. This project is intended to be a safe, welcoming space, and contributors are expected to adhere to the contributor code of conduct.
If you use the JAW for academic research, we encourage you to cite the following paper:
@inproceedings{JAW,
title = {JAW: Studying Client-side CSRF with Hybrid Property Graphs and Declarative Traversals},
author= {Soheil Khodayari and Giancarlo Pellegrino},
booktitle = {30th {USENIX} Security Symposium ({USENIX} Security 21)},
year = {2021},
address = {Vancouver, B.C.},
publisher = {{USENIX} Association},
}
JAW has come a long way and we want to give our contributors a well-deserved shoutout here!
@tmbrbr, @c01gide, @jndre, and Sepehr Mirzaei.

There are now over 5 billion active social media users worldwide, representing 62.3% of the global population. While social networks serve as valuable tools for staying connected with loved ones and documenting life events, the ease of sharing information raises concerns. With a mere few clicks, posts and messages can inadvertently divulge significant personal details, potentially compromising privacy and leaving individuals vulnerable to identity theft. That’s why it’s crucial to make sure you’ve got the know-how to keep your privacy protected while using these platforms.
To empower you in this digital age, we’ve compiled a comprehensive guide featuring ten essential tips to fortify your online security and preserve your privacy on social networks:
Whether you’re a seasoned social media user or just dipping your toes into the digital waters, these strategies will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to safeguard your online identity effectively. With the added support of McAfee+, you can ensure an extra layer of security to keep your online presence more secure and private through advanced privacy features, 24/7 identity monitoring and alerts, and real-time protection against viruses, hackers, and risky links.
The post How to Protect Yourself on Social Networks appeared first on McAfee Blog.